Deck 7: Costs in the Long Run
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/125
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Costs in the Long Run
1
Below is short-run cost data for four different plant sizes. Plant 2 has exactly twice as many inputs as does Plant 1. Plant 3 has exactly three times as many inputs as does Plant 1 and Plant 4 has exactly four times as many inputs as does Plant 1.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is economic capacity in Plant 2?
A) 20.
B) 30.
C) 40.
D) 50.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is economic capacity in Plant 2?
A) 20.
B) 30.
C) 40.
D) 50.
20.
2
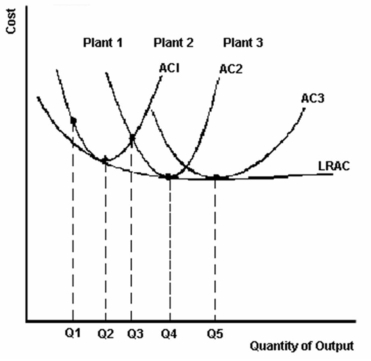
-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. All of the following statements except one are correct. Which is the exception?
A) Plant 1 has excess capacity at output level Q1.
B) Output level Q3 is economic capacity for plant size 1.
C) Output level Q3 can be produced for the same cost in plant 1 and in plant 2.
D) Plant 2 achieves minimum efficient scale.
E) Increasing returns to scale are experienced when output is increased from Q1 to Q4.
Output level Q3 is economic capacity for plant size 1.
3
Below is short-run cost data for four different plant sizes. Plant 2 has exactly twice as many inputs as does Plant 1. Plant 3 has exactly three times as many inputs as does Plant 1 and Plant 4 has exactly four times as many inputs as does Plant 1.
-Which of the following statements is correct if a firm's capacity output increases from 300 to 600 and its total costs rise from $40,000 to $78,000?
A) The firm is experiencing constant returns to scale.
B) The firm is experiencing decreasing returns to scale.
C) The firm is experiencing increasing returns to scale.
D) The firm's long-run average cost must have decreased but its short-run average cost could have either decreased or increased.
-Which of the following statements is correct if a firm's capacity output increases from 300 to 600 and its total costs rise from $40,000 to $78,000?
A) The firm is experiencing constant returns to scale.
B) The firm is experiencing decreasing returns to scale.
C) The firm is experiencing increasing returns to scale.
D) The firm's long-run average cost must have decreased but its short-run average cost could have either decreased or increased.
The firm is experiencing increasing returns to scale.
4
What is meant by the term economic capacity?
A) An output level where the firm is physically unable to increase output.
B) The output level where average variable cost is at a minimum.
C) The output level where average total cost is at a minimum.
D) Total fixed costs are at a minimum.
A) An output level where the firm is physically unable to increase output.
B) The output level where average variable cost is at a minimum.
C) The output level where average total cost is at a minimum.
D) Total fixed costs are at a minimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Below is short-run cost data for four different plant sizes. Plant 2 has exactly twice as many inputs as does Plant 1. Plant 3 has exactly three times as many inputs as does Plant 1 and Plant 4 has exactly four times as many inputs as does Plant 1.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the best plant to use for an output of 25?
A) Plant 1.
B) Plant 2.
C) Plant 3.
D) Plant 4.
E) Any of the four plants would be fine.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the best plant to use for an output of 25?
A) Plant 1.
B) Plant 2.
C) Plant 3.
D) Plant 4.
E) Any of the four plants would be fine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Below are some cost data pertaining to Plant 1, which has total fixed costs of $1,000. Suppose that Plant 2 is exactly twice the size of Plant 1 while using (at economic capacity) twice the amount of labour and materials, and that it produces exactly twice the output. Further, assume that the prices of these inputs do not change.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the output produced if the total cost in Plant 2 is $14,000?
A) 10.
B) 20.
C) 30.
D) 40.
E) 80.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the output produced if the total cost in Plant 2 is $14,000?
A) 10.
B) 20.
C) 30.
D) 40.
E) 80.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
All of the following statements except one are correct. Which is the exception?
A) Firms always operate in the short run.
B) The law of diminishing returns applies in both the short run and the long run.
C) All inputs are variable in the long run.
D) As output increases, long run average cost could decline, remain constant or increase.
E) The long run can be described as a planning horizon.
A) Firms always operate in the short run.
B) The law of diminishing returns applies in both the short run and the long run.
C) All inputs are variable in the long run.
D) As output increases, long run average cost could decline, remain constant or increase.
E) The long run can be described as a planning horizon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Between what output levels do increasing returns to scale exist?
A) Q1 and Q2 only.
B) Q1 and Q3 only.
C) Q1 and Q4.
D) Q1 and Q5.
E) Q4 and Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Below is short-run cost data for four different plant sizes. Plant 2 has exactly twice as many inputs as does Plant 1. Plant 3 has exactly three times as many inputs as does Plant 1 and Plant 4 has exactly four times as many inputs as does Plant 1.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Given the cost data above, which of the following statements is correct?
A) This firm experiences constant returns to scale.
B) This firm experiences increasing returns to scale.
C) This firm experiences decreasing returns to scale.
D) This firm experiences constant, increasing and decreasing returns to scale.
E) No comment about returns to scale can be made.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Given the cost data above, which of the following statements is correct?
A) This firm experiences constant returns to scale.
B) This firm experiences increasing returns to scale.
C) This firm experiences decreasing returns to scale.
D) This firm experiences constant, increasing and decreasing returns to scale.
E) No comment about returns to scale can be made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Below are some cost data pertaining to Plant 1, which has total fixed costs of $1,000. Suppose that Plant 2 is exactly twice the size of Plant 1 while using (at economic capacity) twice the amount of labour and materials, and that it produces exactly twice the output. Further, assume that the prices of these inputs do not change.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is capacity output in Plant 1?
A) 10.
B) 30.
C) 60.
D) 70.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is capacity output in Plant 1?
A) 10.
B) 30.
C) 60.
D) 70.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Below is short-run cost data for four different plant sizes. Plant 2 has exactly twice as many inputs as does Plant 1. Plant 3 has exactly three times as many inputs as does Plant 1 and Plant 4 has exactly four times as many inputs as does Plant 1.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Which of the following statements about the shape of the LRAC curve is correct?
A) It is U shaped.
B) It has an inverse U shape.
C) It declines until an output of 40 is reached and is horizontal there after.
D) It declines continuously.
E) It is horizontal.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Which of the following statements about the shape of the LRAC curve is correct?
A) It is U shaped.
B) It has an inverse U shape.
C) It declines until an output of 40 is reached and is horizontal there after.
D) It declines continuously.
E) It is horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Below are some cost data pertaining to Plant 1, which has total fixed costs of $1,000. Suppose that Plant 2 is exactly twice the size of Plant 1 while using (at economic capacity) twice the amount of labour and materials, and that it produces exactly twice the output. Further, assume that the prices of these inputs do not change.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the total cost of producing an output of 60 in Plant 2?
A) $7,000.
B) $9,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $24,500.
E) $30,000.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What is the total cost of producing an output of 60 in Plant 2?
A) $7,000.
B) $9,000.
C) $15,000.
D) $24,500.
E) $30,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is correct in reference to the long run?
A) All costs are explicit costs.
B) Both fixed and variable costs exist.
C) All inputs are variable.
D) Only one input is variable while all others are fixed.
A) All costs are explicit costs.
B) Both fixed and variable costs exist.
C) All inputs are variable.
D) Only one input is variable while all others are fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Below is short-run cost data for four different plant sizes. Plant 2 has exactly twice as many inputs as does Plant 1. Plant 3 has exactly three times as many inputs as does Plant 1 and Plant 4 has exactly four times as many inputs as does Plant 1.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. If the firm is currently producing an output of 20 using Plant 1 and it decides to build Plant 2, what will happen to its short-run average cost if its output remains unchanged?
A) It will remain unchanged.
B) It will rise by $3.
C) It will fall by $3.
D) It will fall by $11.
E) It will rise by $11.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. If the firm is currently producing an output of 20 using Plant 1 and it decides to build Plant 2, what will happen to its short-run average cost if its output remains unchanged?
A) It will remain unchanged.
B) It will rise by $3.
C) It will fall by $3.
D) It will fall by $11.
E) It will rise by $11.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Below are some cost data pertaining to Plant 1, which has total fixed costs of $1,000. Suppose that Plant 2 is exactly twice the size of Plant 1 while using (at economic capacity) twice the amount of labour and materials, and that it produces exactly twice the output. Further, assume that the prices of these inputs do not change.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. How much is total fixed cost in Plant 2?
A) $2,000.
B) $4,500.
C) $9,000.
D) $15,000.
E) $24,500.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. How much is total fixed cost in Plant 2?
A) $2,000.
B) $4,500.
C) $9,000.
D) $15,000.
E) $24,500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Below is short-run cost data for four different plant sizes. Plant 2 has exactly twice as many inputs as does Plant 1. Plant 3 has exactly three times as many inputs as does Plant 1 and Plant 4 has exactly four times as many inputs as does Plant 1.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Which of the following should the firm consider doing if it is currently producing an output of 40 using Plant 2?
A) Build Plant 3 only.
B) Build Plant 4 only.
C) Build Plant 3 or 4.
D) Scale down its plant size.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. Which of the following should the firm consider doing if it is currently producing an output of 40 using Plant 2?
A) Build Plant 3 only.
B) Build Plant 4 only.
C) Build Plant 3 or 4.
D) Scale down its plant size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. All of the following statements except one are correct. Which is the exception?
A) AC1, AC2 and AC3 are long-run average cost curves.
B) The long-run average cost curve illustrates both increasing and constant returns to scale.
C) Constant returns to scale exist between outputs Q4 and Q5.
D) An increase in output from Q1 to Q3 could occur in plant 1.
E) Both the short-run and the long run-costs are illustrated in this graph.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the long-run average cost curve?
A) A graphical representation of the total variable cost.
B) A measurement of the percentage of an industry's total sales which is controlled by the four largest firms.
C) A graphical representation of those costs that do not vary with the level of output.
D) A graphical representation of the average costs of production in the long run.
E) A portion of the short-run average total cost curve.
A) A graphical representation of the total variable cost.
B) A measurement of the percentage of an industry's total sales which is controlled by the four largest firms.
C) A graphical representation of those costs that do not vary with the level of output.
D) A graphical representation of the average costs of production in the long run.
E) A portion of the short-run average total cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Below are some cost data pertaining to Plant 1, which has total fixed costs of $1,000. Suppose that Plant 2 is exactly twice the size of Plant 1 while using (at economic capacity) twice the amount of labour and materials, and that it produces exactly twice the output. Further, assume that the prices of these inputs do not change.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What comment can be made in reference to returns to scale between Plants 1 and 2?
A) Constant returns to scale are present.
B) Increasing returns to scale are present.
C) Decreasing returns to scale are present.
D) Diminishing marginal returns are present.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. What comment can be made in reference to returns to scale between Plants 1 and 2?
A) Constant returns to scale are present.
B) Increasing returns to scale are present.
C) Decreasing returns to scale are present.
D) Diminishing marginal returns are present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) A firm can operate in either the short run or the long run.
B) While a firm's plant size could be too small in the long run, its size cannot be too small in the short run.
C) A firm can enjoy economies of scale in either the short run or the long run.
D) While a firm can plan as if it is in the long run, it can operate only in the short run.
A) A firm can operate in either the short run or the long run.
B) While a firm's plant size could be too small in the long run, its size cannot be too small in the short run.
C) A firm can enjoy economies of scale in either the short run or the long run.
D) While a firm can plan as if it is in the long run, it can operate only in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following is the most likely cause of diseconomies of scale?
A) Increasing returns to scale.
B) A small scale of operations and output.
C) Low productivity.
D) Complex interpersonal communication structures.
A) Increasing returns to scale.
B) A small scale of operations and output.
C) Low productivity.
D) Complex interpersonal communication structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Between what output levels do constant returns to scale exist?
A) Q1 and Q2.
B) Q1 and Q3.
C) Q1 and Q4.
D) Q1 and Q5.
E) Q4 and Q5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose that a firm, operating efficiently, doubles the size of its operations and discovers that, as a result, its average cost of production has fallen. What does this imply?
A) Decreasing returns to scale are present.
B) Increasing returns to scale are present.
C) Constant returns to scale are present.
D) No conclusion about returns to scale can be made.
A) Decreasing returns to scale are present.
B) Increasing returns to scale are present.
C) Constant returns to scale are present.
D) No conclusion about returns to scale can be made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is true regarding economies of scale?
A) It is another term for constant returns to scale.
B) They are present only in pecuniary forms.
C) They exist in both the short run and the long run.
D) They are cost advantages that are achieved as a result of large-scale operations.
A) It is another term for constant returns to scale.
B) They are present only in pecuniary forms.
C) They exist in both the short run and the long run.
D) They are cost advantages that are achieved as a result of large-scale operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose that a firm, operating efficiently, doubles the size of its operations and discovers that, as a result, its average cost of production has increased. What does this imply?
A) Decreasing returns to scale are present.
B) Increasing returns to scale are present.
C) Constant returns to scale are present.
D) No conclusion about returns to scale can be made.
A) Decreasing returns to scale are present.
B) Increasing returns to scale are present.
C) Constant returns to scale are present.
D) No conclusion about returns to scale can be made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What is the shape of the long-run average cost curve under conditions of economies of scale?
A) It is horizontal.
B) It initially falls and then rises.
C) It continuously rises.
D) It continuously falls.
A) It is horizontal.
B) It initially falls and then rises.
C) It continuously rises.
D) It continuously falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All of the following except one are examples of pecuniary economies of scale. Which is the exception?
A) Bulk buying and selling.
B) Management and machine specialization.
C) Lower costs of borrowing.
D) Lower costs of advertising.
A) Bulk buying and selling.
B) Management and machine specialization.
C) Lower costs of borrowing.
D) Lower costs of advertising.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What is true if decreasing returns to scale are present?
A) Average fixed cost will rise.
B) Total variable cost will fall.
C) Economies of scale are also present.
D) Diseconomies of scale are present.
A) Average fixed cost will rise.
B) Total variable cost will fall.
C) Economies of scale are also present.
D) Diseconomies of scale are present.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What is the effect of diseconomies of scale?
A) The short-run average cost curve falls.
B) The short-run average cost curve rises.
C) The long-run average cost curve falls.
D) The long-run average cost curve rises.
A) The short-run average cost curve falls.
B) The short-run average cost curve rises.
C) The long-run average cost curve falls.
D) The long-run average cost curve rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What are diseconomies of scale?
A) The situation where a firm's output decreases in proportion to the decrease in its inputs.
B) The situation where a firm is able to obtain lower prices for the inputs it buys because of bulk buying.
C) Bureaucratic inefficiencies in management that result in decreasing returns to scale.
D) The smallest level of output at which a firm is able to minimize long-run average cost.
A) The situation where a firm's output decreases in proportion to the decrease in its inputs.
B) The situation where a firm is able to obtain lower prices for the inputs it buys because of bulk buying.
C) Bureaucratic inefficiencies in management that result in decreasing returns to scale.
D) The smallest level of output at which a firm is able to minimize long-run average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following would illustrate diseconomies of scale?
A) The rising segment of the SRAC curve.
B) The rising segment of the LRAC curve
C) A growing margin between short-run and long-run average cost as output increased.
D) Marginal cost below short-run average cost.
E) Marginal cost above short-run average cost.
A) The rising segment of the SRAC curve.
B) The rising segment of the LRAC curve
C) A growing margin between short-run and long-run average cost as output increased.
D) Marginal cost below short-run average cost.
E) Marginal cost above short-run average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Technical economies of scale are closely related to which of the following?
A) The law of diminishing returns.
B) Decreasing returns to scale.
C) Rising short-run average total cost.
D) Falling short-run marginal cost.
E) Increasing returns to scale.
A) The law of diminishing returns.
B) Decreasing returns to scale.
C) Rising short-run average total cost.
D) Falling short-run marginal cost.
E) Increasing returns to scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following statements about diseconomies of scale is correct?
A) They pertain to the short run only.
B) They pertain to the long run only.
C) They pertain to both the short run and the long run.
D) They are synonymous with increasing returns to scale.
A) They pertain to the short run only.
B) They pertain to the long run only.
C) They pertain to both the short run and the long run.
D) They are synonymous with increasing returns to scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
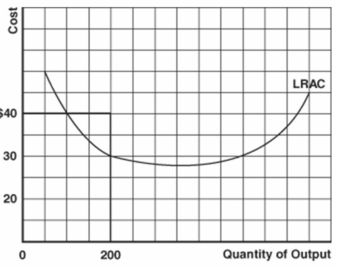
-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Can this firm produce an output of 200 at an average total cost of $40?
A) Yes, and that output would be economic capacity.
B) Yes, but production would be inefficient.
C) No, this combination is unobtainable given present resource prices and the current state of technology.
D) No, this combination would be unobtainable because production is inefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Could this firm produce an output of 200 at an average total cost of $20?
A) Yes, and that output is economic capacity.
B) Yes, but production would be inefficient.
C) No, this combination would be unobtainable given present resource prices and the current state of technology.
D) No, this combination is unobtainable because production would be inefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Could this firm produce an output of 200 at an average total cost of $30?
A) Yes, and that output would be economic capacity.
B) Yes, but production would be inefficient.
C) No, this combination is unobtainable given present resource prices and the current state of technology.
D) No, this combination is unobtainable because production would be inefficient.
E) Yes, and the firm is experiencing economies of scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If we know that a firm is experiencing diseconomies of scale, which of the following statements is true?
A) The firm is operating on the upward-sloping segment of its LRAC curve.
B) The firm is experiencing increasing returns to scale.
C) Both pecuniary and technical economies of scale must be present.
D) If all inputs were increased by 10% then output would rise by more than 10%.
E) The firm is also experiencing diminishing marginal returns.
A) The firm is operating on the upward-sloping segment of its LRAC curve.
B) The firm is experiencing increasing returns to scale.
C) Both pecuniary and technical economies of scale must be present.
D) If all inputs were increased by 10% then output would rise by more than 10%.
E) The firm is also experiencing diminishing marginal returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
All of the following, except one, are reasons for economies of scale to be present in production. Which is the exception?
A) Advantages of the division of labour.
B) Management and machine specialization.
C) Lower costs of borrowing.
D) Lower costs of advertising.
E) The law of diminishing returns.
A) Advantages of the division of labour.
B) Management and machine specialization.
C) Lower costs of borrowing.
D) Lower costs of advertising.
E) The law of diminishing returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following statements is correct if a firm builds a large plant and, at economic capacity output, its short-run average cost increases?
A) Decreasing returns to scale must be present.
B) Increasing returns to scale must be present.
C) Constant returns to scale must be present.
D) Decreasing, increasing and constant returns to scale are all possible.
A) Decreasing returns to scale must be present.
B) Increasing returns to scale must be present.
C) Constant returns to scale must be present.
D) Decreasing, increasing and constant returns to scale are all possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
If a firm builds a larger plant and diseconomies of scale apply, which of the following statements is correct?
A) The economic capacity output of the larger plant has a lower average cost.
B) The economic capacity output of the larger plant has the same average cost.
C) The economic capacity output of the larger plant has higher average cost.
D) The LRAC cost curve will decrease as output increases.
A) The economic capacity output of the larger plant has a lower average cost.
B) The economic capacity output of the larger plant has the same average cost.
C) The economic capacity output of the larger plant has higher average cost.
D) The LRAC cost curve will decrease as output increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Suppose that the firm is producing an output between Q1 and Q2. All of the following statements, except one, are correct. Which is the exception?
A) The firm is neither too large nor too small.
B) The firm is certainly achieving economic capacity.
C) The firm might or might not benefit by increasing or decreasing its output.
D) The firm could not benefit by increasing or decreasing its scale of plant.
A) The firm is neither too large nor too small.
B) The firm is certainly achieving economic capacity.
C) The firm might or might not benefit by increasing or decreasing its output.
D) The firm could not benefit by increasing or decreasing its scale of plant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Refer to the graph above to answer this question. All of the following statements, except one, are correct. Which is the exception?
A) Firms that produce an output less than Q1 are too small.
B) Firms that produce an output which greater than Q2 are too large.
C) Firms that produce output Q2 are achieving MES.
D) Firms that produce an output which is between Q1 and Q2 are neither too large nor too small.
E) Firms that produce an output which is less than Q1 cannot be achieving economic capacity.
A) Firms that produce an output less than Q1 are too small.
B) Firms that produce an output which greater than Q2 are too large.
C) Firms that produce output Q2 are achieving MES.
D) Firms that produce an output which is between Q1 and Q2 are neither too large nor too small.
E) Firms that produce an output which is less than Q1 cannot be achieving economic capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is the graphical effect of a decrease in the prices of factor inputs such as labour and materials?
A) The SRAC curve would shift down and the LRAC curve would shift up.
B) The SRAC curve would shift up and the LRAC curve would shift down.
C) Both the SRAC curve and the LRAC curve would shift up.
D) Both the SRAC curve and the LRAC curve would shift down.
A) The SRAC curve would shift down and the LRAC curve would shift up.
B) The SRAC curve would shift up and the LRAC curve would shift down.
C) Both the SRAC curve and the LRAC curve would shift up.
D) Both the SRAC curve and the LRAC curve would shift down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Assume that a firm's total cost of producing an output of 2,000 units is currently $20,000. If output increases to 2,500 units, total cost increases to $50,000 and the price of inputs and technology remain unchanged. What will be the effect on average total cost?
A) Increase of $20
B) Decrease of $10
C) Increase of $10
D) No change
A) Increase of $20
B) Decrease of $10
C) Increase of $10
D) No change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What does the term minimum efficient scale mean?
A) The largest-size plant capable of achieving minimum long-run average cost.
B) The lowest average cost of production for a particular size of plant.
C) The smallest size of plant capable of producing a particular output.
D) The lowest level of efficiency which a firm is capable of producing.
E) The smallest-size plant capable of achieving minimum long-run average cost.
A) The largest-size plant capable of achieving minimum long-run average cost.
B) The lowest average cost of production for a particular size of plant.
C) The smallest size of plant capable of producing a particular output.
D) The lowest level of efficiency which a firm is capable of producing.
E) The smallest-size plant capable of achieving minimum long-run average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What does the term "decreasing returns to scale" mean?
A) The situation where a doubling of inputs results in output increasing by less than double.
B) The situation where a firm's output decreases in proportion to the decrease in its inputs.
C) It means that the firm is operating on the falling portion of its long run average cost curve.
D) It means that the firm is operating on the horizontal portion of its long run average cost curve.
A) The situation where a doubling of inputs results in output increasing by less than double.
B) The situation where a firm's output decreases in proportion to the decrease in its inputs.
C) It means that the firm is operating on the falling portion of its long run average cost curve.
D) It means that the firm is operating on the horizontal portion of its long run average cost curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
In the graph below six short-run average cost curves labeled a through f are illustrated.
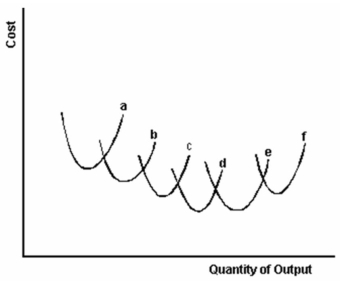
-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Which set of short-run average cost curves illustrates constant returns to scale?
A) a and b only.
B) a, b and c only.
C) a, b, c, and d.
D) d and e only.
E) e and f only.

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Which set of short-run average cost curves illustrates constant returns to scale?
A) a and b only.
B) a, b and c only.
C) a, b, c, and d.
D) d and e only.
E) e and f only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Q1 must be the best output for a firm to produce.
B) Q2 must be the best output for a firm to produce.
C) While it is possible for a firm to be too small, it could not be too large.
D) While it is possible for a firm to be too large, it could not be too small.
E) Firms that produce an output which is less than Q1 cannot be achieving minimum efficient scale.
A) Q1 must be the best output for a firm to produce.
B) Q2 must be the best output for a firm to produce.
C) While it is possible for a firm to be too small, it could not be too large.
D) While it is possible for a firm to be too large, it could not be too small.
E) Firms that produce an output which is less than Q1 cannot be achieving minimum efficient scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Assume that a firm's total cost of producing an output of 1,000 units is currently $20,000. If output increases to 2,000 units, total cost increases to $40,000 and the price of inputs and technology remain unchanged, calculate the change in average total cost.
A) Increase of $20
B) Decrease of $20
C) Increase of $40
D) No change
A) Increase of $20
B) Decrease of $20
C) Increase of $40
D) No change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
All of the following, except one, would result in lower average cost. Which is the exception?
A) An increase in output if the firm was operating below its capacity output.
B) Building a larger plant if the firm was experiencing increasing returns to scale.
C) Down-sizing the scale of operations if the firm was experiencing diseconomies of scale.
D) Down-sizing the scale of operations if the firm was experiencing constant returns to scale.
A) An increase in output if the firm was operating below its capacity output.
B) Building a larger plant if the firm was experiencing increasing returns to scale.
C) Down-sizing the scale of operations if the firm was experiencing diseconomies of scale.
D) Down-sizing the scale of operations if the firm was experiencing constant returns to scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Assume that a firm's total cost of producing an output of 300 units is currently $30,000. If output increases to 600 units, total cost increases to $60,000 and the price of inputs and technology remain unchanged, state whether constant returns to scale, economies of scale or diseconomies of scale exist in this case.
A) Economies of scale
B) Diseconomies of scale
C) Constant returns to scale
D) Increasing returns to scale
A) Economies of scale
B) Diseconomies of scale
C) Constant returns to scale
D) Increasing returns to scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Suppose that a firm's output increases from 500 to 600 units and its total cost increases from $50,000 to $72,000, and if the price of inputs and technology remain unchanged, calculate the change in average total cost and state whether constant returns to scale, economies of scale or diseconomies of scale exist in this case.
A) Increase of $20 and economies of scale
B) Increase of $20 and diseconomies of scale
C) Increase of $20 and constant returns to scale
D) No change and constant returns to scale
A) Increase of $20 and economies of scale
B) Increase of $20 and diseconomies of scale
C) Increase of $20 and constant returns to scale
D) No change and constant returns to scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Refer to the graph above to answer this question. All of the following statements except one is correct. Which is the exception?
A) The LRAC curve illustrates both the advantages of the division of labour and the law of diminishing returns.
B) Economies, diseconomies and constant returns to scale are illustrated in the LRAC curve.
C) Given the LRAC curve illustrated, a firm could be too small or too large.
D) Diseconomies of scale exist at output levels above Q2.
Sayre - Chapter 07 #59
A) The LRAC curve illustrates both the advantages of the division of labour and the law of diminishing returns.
B) Economies, diseconomies and constant returns to scale are illustrated in the LRAC curve.
C) Given the LRAC curve illustrated, a firm could be too small or too large.
D) Diseconomies of scale exist at output levels above Q2.
Sayre - Chapter 07 #59


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Under what circumstances does an increase in inputs by x percent result in an increase in output of less than x percent?
A) Diseconomies of scale.
B) Constant returns to scale.
C) Economies of scale.
D) Minimum efficient scale.
A) Diseconomies of scale.
B) Constant returns to scale.
C) Economies of scale.
D) Minimum efficient scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose that a firm's output increases from 500 to 1,000 units and its total cost increases from $50,000 to $100,000, and if the price of inputs and technology remain unchanged, calculate the change in average total cost and state whether constant returns to scale, economies of scale or diseconomies of scale exist in this case.
A) Increase of $100 and economies of scale
B) Increase of $100 and diseconomies of scale
C) Increase of $100 and constant returns to scale
D) No change and constant returns to scale
A) Increase of $100 and economies of scale
B) Increase of $100 and diseconomies of scale
C) Increase of $100 and constant returns to scale
D) No change and constant returns to scale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which of the following statements is correct if the appropriately sized firm is one with a large output?
A) Constant returns to scale must begin at low levels of output.
B) Economies of scale must prevail until high levels of output are reached.
C) Diseconomies of scale must begin at low levels of output.
D) Constant returns to scale must be absent.
A) Constant returns to scale must begin at low levels of output.
B) Economies of scale must prevail until high levels of output are reached.
C) Diseconomies of scale must begin at low levels of output.
D) Constant returns to scale must be absent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the graphical effect of technological change?
A) The SRAC curves would shift down and the LRAC curve would shift up.
B) The SRAC curves would shift up and the LRAC curve would shift down.
C) The SRAC curves and the LRAC curve would shift up.
D) The SRAC curves and the LRAC curve would shift down.
A) The SRAC curves would shift down and the LRAC curve would shift up.
B) The SRAC curves would shift up and the LRAC curve would shift down.
C) The SRAC curves and the LRAC curve would shift up.
D) The SRAC curves and the LRAC curve would shift down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In the graph below six short-run average cost curves labeled a through f are illustrated.

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Which set of short-run average cost curves illustrates economies of scale?
A) a and b only.
B) a, b and c only.
C) a, b, c, and d.
D) d and e only.
E) e and f only.

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Which set of short-run average cost curves illustrates economies of scale?
A) a and b only.
B) a, b and c only.
C) a, b, c, and d.
D) d and e only.
E) e and f only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In the graph below six short-run average cost curves labeled a through f are illustrated.

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Which set of short-run average cost curves illustrates diseconomies of scale?
A) a and b only.
B) a, b and c only.
C) a, b, c, and d.
D) d and e only.
E) e and f only.

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Which set of short-run average cost curves illustrates diseconomies of scale?
A) a and b only.
B) a, b and c only.
C) a, b, c, and d.
D) d and e only.
E) e and f only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The existence of both economies of scale and diseconomies of scale would have what effect on the LRAC curve?
A) It would make it upward-sloping.
B) It would make it downward-sloping.
C) It would give it an inverse U shape.
D) It would give it a U shape.
E) It would make it horizontal.
A) It would make it upward-sloping.
B) It would make it downward-sloping.
C) It would give it an inverse U shape.
D) It would give it a U shape.
E) It would make it horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If a firm builds a larger plant and constant returns to scale apply, which of the following statements is correct?
A) The capacity output of the larger plant has a lower average cost.
B) The capacity output of the larger plant has the same average cost.
C) Economies of scale are present.
D) LRAC will decrease as output increases.
A) The capacity output of the larger plant has a lower average cost.
B) The capacity output of the larger plant has the same average cost.
C) Economies of scale are present.
D) LRAC will decrease as output increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Economies of scale:
A) Is another term for constant returns to scale.
B) Are cost advantages achieved as a result of large-scale operations.
C) Only come in pecuniary forms.
D) Are the same as decreasing returns to scale.
A) Is another term for constant returns to scale.
B) Are cost advantages achieved as a result of large-scale operations.
C) Only come in pecuniary forms.
D) Are the same as decreasing returns to scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is correct in reference to the long run?
A) All inputs are variable.
B) Only one input is variable, and all others are fixed.
C) Only one input is fixed and all others are variable.
D) All inputs are fixed.
A) All inputs are variable.
B) Only one input is variable, and all others are fixed.
C) Only one input is fixed and all others are variable.
D) All inputs are fixed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Suppose that a firm's total cost of producing an output of 400 units a day is currently $2,000. If technology and the price of inputs remain unchanged, what level of output would be produced if total cost rises to $4,000 and decreasing returns to scale exist?
A) 5 units.
B) More than 400 but less than 800 units.
C) 800 units.
D) More than 800 units.
A) 5 units.
B) More than 400 but less than 800 units.
C) 800 units.
D) More than 800 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What is meant by the term "economic capacity"?
A) The output level at which the firm is physically unable to increase output.
B) The output level at which average variable cost is at a minimum.
C) The output level at which average total cost is at a minimum.
D) The output level at which marginal cost is at a minimum.
A) The output level at which the firm is physically unable to increase output.
B) The output level at which average variable cost is at a minimum.
C) The output level at which average total cost is at a minimum.
D) The output level at which marginal cost is at a minimum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose a firm builds a larger plant and increases its output. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Its MES output must increase.
B) Its MES output will decrease.
C) It will be able to achieve its MES output only if it also achieves economic capacity.
D) Its short-run average cost curve for the original plant will have shifted down.
E) Its long-run average costs must have increased.
A) Its MES output must increase.
B) Its MES output will decrease.
C) It will be able to achieve its MES output only if it also achieves economic capacity.
D) Its short-run average cost curve for the original plant will have shifted down.
E) Its long-run average costs must have increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
All of the following, except one, are examples of pecuniary economies of scale. Which is the exception?
A) A lower interest rate paid on money borrowed.
B) The ability to sell the by-products of production.
C) The ability to use specialized inputs such as a robotics assembly line.
D) The ability to obtain lower prices by buying in bulk.
A) A lower interest rate paid on money borrowed.
B) The ability to sell the by-products of production.
C) The ability to use specialized inputs such as a robotics assembly line.
D) The ability to obtain lower prices by buying in bulk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The graph below includes two plant sizes as illustrated by AC1 and AC2.
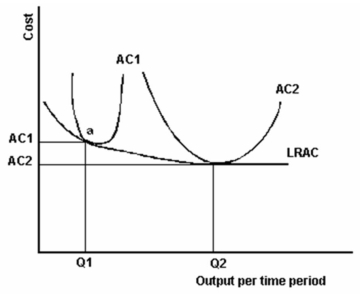
Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Which of the following statements is correct if a firm is operating at point a on AC1?
A) The firm has achieved capacity output.
B) The firm is achieving MES.
C) An increase in the output would not lower costs.
D) Building a larger plant would result in lower long-run average cost.
E) Building a larger plant would not result in lower long-run average cost.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Which of the following statements is correct if a firm is operating at point a on AC1?
A) The firm has achieved capacity output.
B) The firm is achieving MES.
C) An increase in the output would not lower costs.
D) Building a larger plant would result in lower long-run average cost.
E) Building a larger plant would not result in lower long-run average cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The ability of a person to supervise 12 workers just as well as 8 is an example of:
A) The division of labour.
B) Labour specialization.
C) Management specialization.
D) Decreasing returns to scale.
A) The division of labour.
B) Labour specialization.
C) Management specialization.
D) Decreasing returns to scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Suppose that a firm's total cost of producing an output of 400 units a day is currently $2,000. If technology and the price of inputs remain unchanged, what level of output would be produced if total cost rises to $4,000 and increasing returns to scale exist?
A) 5 units.
B) More than 400 but less than 800 units.
C) 800 units.
D) More than 800 units.
A) 5 units.
B) More than 400 but less than 800 units.
C) 800 units.
D) More than 800 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The graph below includes two plant sizes as illustrated by AC1 and AC2.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. All of the following statements except one are correct if a small market limits a firm's output to Q1. Which is the exception?
A) The firm is not achieving capacity output in plant 1.
B) The firm is not achieving minimum efficient scale.
C) The firm is experiencing excess capacity.
D) The firm would benefit from a larger market.
E) Building a larger plant would lower the firm's average cost of producing Q1.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. All of the following statements except one are correct if a small market limits a firm's output to Q1. Which is the exception?
A) The firm is not achieving capacity output in plant 1.
B) The firm is not achieving minimum efficient scale.
C) The firm is experiencing excess capacity.
D) The firm would benefit from a larger market.
E) Building a larger plant would lower the firm's average cost of producing Q1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following statements is correct if a firm builds a larger plant and, at any particular output, its short-run average cost increases?
A) Diseconomies of scale must be present.
B) Economies of scale must be present.
C) Constant returns to scale must be present.
D) Economies, diseconomies, and constant returns to scale are all possible.
A) Diseconomies of scale must be present.
B) Economies of scale must be present.
C) Constant returns to scale must be present.
D) Economies, diseconomies, and constant returns to scale are all possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which of the following is the most likely cause of diseconomies of scale?
A) Increasing returns to scale.
B) A small scale of operations and output.
C) Low productivity.
D) Bureaucracy.
A) Increasing returns to scale.
B) A small scale of operations and output.
C) Low productivity.
D) Bureaucracy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The graph below includes two plant sizes as illustrated by AC1 and AC2.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. If the firm is producing in a plant with AC1 as its short run average cost curve, and a small market is limiting the firm's output to Q1, which of the following statements is true?
A) Building a larger plant would lower the firm's average cost of producing Q10.
B) Increasing the output in the current plant size would not lower the short-run average cost.
C) The firm would benefit from a larger market because it could build a larger plant, capture economies of scale and achieve economic capacity.
D) The firm would benefit from a larger market because it could build a larger plant and capture economies of scale, but it still would not be able to achieve economic capacity.

Refer to the graph above to answer this question. If the firm is producing in a plant with AC1 as its short run average cost curve, and a small market is limiting the firm's output to Q1, which of the following statements is true?
A) Building a larger plant would lower the firm's average cost of producing Q10.
B) Increasing the output in the current plant size would not lower the short-run average cost.
C) The firm would benefit from a larger market because it could build a larger plant, capture economies of scale and achieve economic capacity.
D) The firm would benefit from a larger market because it could build a larger plant and capture economies of scale, but it still would not be able to achieve economic capacity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following statements is correct if constant returns to scale are present?
A) A doubling of inputs will lead to output more than doubling.
B) A doubling of inputs will lead to output also doubling.
C) A doubling of output will lead to inputs more than doubling.
D) Output remains constant irrespective of inputs.
A) A doubling of inputs will lead to output more than doubling.
B) A doubling of inputs will lead to output also doubling.
C) A doubling of output will lead to inputs more than doubling.
D) Output remains constant irrespective of inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If economies of scale are present, then:
A) Average variable costs are falling but average fixed costs are constant.
B) Average costs are constant.
C) Average costs are decreasing.
D) Average costs are increasing.
A) Average variable costs are falling but average fixed costs are constant.
B) Average costs are constant.
C) Average costs are decreasing.
D) Average costs are increasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Which of the following statements is correct?
A) A firm can operate in either the short run or the long run.
B) While a firm can plan as if it is in the long run, it can operate only in the short run.
C) The short run is a period of time of less than six months.
D) The short run is a period of time of less than one year.
A) A firm can operate in either the short run or the long run.
B) While a firm can plan as if it is in the long run, it can operate only in the short run.
C) The short run is a period of time of less than six months.
D) The short run is a period of time of less than one year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Which of the following statements is correct if a firm's capacity output increases from 400 to 800 and its total costs rise from $60,000 to $110,000?
A) The firm is experiencing constant returns to scale.
B) The firm is experiencing diseconomies of scale.
C) The firm is experiencing economies of scale.
D) The firm's long-run average cost must have decreased, but its short-run average cost could have either decreased or increased.
A) The firm is experiencing constant returns to scale.
B) The firm is experiencing diseconomies of scale.
C) The firm is experiencing economies of scale.
D) The firm's long-run average cost must have decreased, but its short-run average cost could have either decreased or increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What does the term "minimum efficient scale" mean?
A) The smallest size a firm can be in order to minimize both short-run and long-run average costs.
B) The smallest size a firm can be in order to minimize short-run marginal cost.
C) The smallest size a firm can be in order to minimize short-run average cost.
D) The smallest size a firm can be in order to minimize long-run marginal cost.
E) The smallest size a firm can be in order to minimize both short-run and long-run marginal cost.
A) The smallest size a firm can be in order to minimize both short-run and long-run average costs.
B) The smallest size a firm can be in order to minimize short-run marginal cost.
C) The smallest size a firm can be in order to minimize short-run average cost.
D) The smallest size a firm can be in order to minimize long-run marginal cost.
E) The smallest size a firm can be in order to minimize both short-run and long-run marginal cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The fact that a one-minute television commercial costs a large firm no more than a small firm is an example of which of the following?
A) Increasing returns to scale.
B) Pecuniary economies of scale.
C) Technical economies of scale.
D) Management specialization.
A) Increasing returns to scale.
B) Pecuniary economies of scale.
C) Technical economies of scale.
D) Management specialization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



