Deck 2: Demand and Supply: an Introduction
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/198
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Demand and Supply: an Introduction
1
What is meant by the term change in the quantity demanded?
A) The change in the quantity which results from a price change and implies a movement along the demand curve.
B) The change in the quantity which results from a change in any factor other than the price and implies a movement along the demand curve.
C) The change in the quantity which results from a price change and implies a shift in the demand curve.
D) The change in the quantity which results from a change in any factor other than the price and implies a shift in the demand curve.
A) The change in the quantity which results from a price change and implies a movement along the demand curve.
B) The change in the quantity which results from a change in any factor other than the price and implies a movement along the demand curve.
C) The change in the quantity which results from a price change and implies a shift in the demand curve.
D) The change in the quantity which results from a change in any factor other than the price and implies a shift in the demand curve.
A
2
What is the term for the quantities which consumers are willing and able to buy per period of time at various prices?
A) Desire.
B) Supply.
C) Demand.
D) Market.
E) Human wants.
A) Desire.
B) Supply.
C) Demand.
D) Market.
E) Human wants.
C
3
What is the term for the effect which a price change has on real income and therefore on the quantity demanded of a product?
A) Income effect.
B) Substitution effect.
C) Market demand.
D) Change in the quantity demanded.
E) Opportunity cost.
A) Income effect.
B) Substitution effect.
C) Market demand.
D) Change in the quantity demanded.
E) Opportunity cost.
A
4
What is meant by the term ceteris paribus?
A) A downward-sloping demand curve.
B) Other things being equal.
C) All things vary.
D) Prices remain constant.
A) A downward-sloping demand curve.
B) Other things being equal.
C) All things vary.
D) Prices remain constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What is the term for the total demand for a product by all consumers?
A) Schedule of wants.
B) Market Supply.
C) Product market.
D) Quota.
E) Market Demand.
A) Schedule of wants.
B) Market Supply.
C) Product market.
D) Quota.
E) Market Demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the effect of a decrease in the price of a product?
A) It will decrease the demand.
B) It will increase the demand.
C) It will decrease the quantity demanded.
D) It will increase the quantity demanded.
A) It will decrease the demand.
B) It will increase the demand.
C) It will decrease the quantity demanded.
D) It will increase the quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is the term for a table that shows the various quantities demanded per period of time at different prices?
A) Production possibilities table.
B) Demand schedule.
C) Supply schedule.
D) Market schedule.
E) Schedule of equilibrium points.
A) Production possibilities table.
B) Demand schedule.
C) Supply schedule.
D) Market schedule.
E) Schedule of equilibrium points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
All of the following, except one, is demand. Which is the exception?
A) The quantities which consumers are willing and able to buy per period of time at various prices.
B) The relationship between various prices and quantities demanded for a product.
C) A hypothetical construct which expresses the desire and ability to purchase, not at a single price, but over a range of prices.
D) The quantities which consumers want to buy.
A) The quantities which consumers are willing and able to buy per period of time at various prices.
B) The relationship between various prices and quantities demanded for a product.
C) A hypothetical construct which expresses the desire and ability to purchase, not at a single price, but over a range of prices.
D) The quantities which consumers want to buy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What is supply?
A) The quantities which producers are both willing and able to sell per period of time at various prices.
B) The total demand for a product by all consumers.
C) The quantity which prevails at the equilibrium price.
D) The quantity sold at a certain price.
A) The quantities which producers are both willing and able to sell per period of time at various prices.
B) The total demand for a product by all consumers.
C) The quantity which prevails at the equilibrium price.
D) The quantity sold at a certain price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What is the income effect?
A) The effect of a change in income on the demand for a product.
B) The effect of a change in income on the demand for a substitute product.
C) The effect of a price change on real income and therefore on the quantity demanded of a product.
D) The effect of a change in income on the demand for an inferior product.
A) The effect of a change in income on the demand for a product.
B) The effect of a change in income on the demand for a substitute product.
C) The effect of a price change on real income and therefore on the quantity demanded of a product.
D) The effect of a change in income on the demand for an inferior product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the term for a table showing the various quantities supplied per period of time at different prices?
A) Demand schedule.
B) Price schedule.
C) Supply schedule.
D) Market supply.
A) Demand schedule.
B) Price schedule.
C) Supply schedule.
D) Market supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What is the term for a change in the amounts that a producer is willing and able to make available as a result of a price change?
A) Change in the quantity supplied.
B) Change in the individual supply.
C) Change in the market supply.
D) Change in the market demand.
A) Change in the quantity supplied.
B) Change in the individual supply.
C) Change in the market supply.
D) Change in the market demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is explained by the combination of the substitution effect and the income effect?
A) The direct relationship between price and quantity demanded.
B) The inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
C) Market demand.
D) Equilibrium price.
A) The direct relationship between price and quantity demanded.
B) The inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
C) Market demand.
D) Equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is market demand?
A) The substitution of one product for another as a result of a change in their relative prices.
B) The total demand for a product by all consumers.
C) An increase or decrease in prices based on the quantity demanded of a product.
D) The desire to purchase cheaper competing products rather than relatively more expensive products.
A) The substitution of one product for another as a result of a change in their relative prices.
B) The total demand for a product by all consumers.
C) An increase or decrease in prices based on the quantity demanded of a product.
D) The desire to purchase cheaper competing products rather than relatively more expensive products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is explained by the combination of the substitution effect and the income effect?
A) Ceteris paribus.
B) Downward sloping demand curves.
C) Market demand.
D) Equilibrium price.
A) Ceteris paribus.
B) Downward sloping demand curves.
C) Market demand.
D) Equilibrium price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is the substitution effect?
A) The effect that a change in income has on the demand for a substitute product.
B) The sacrifice which has to be made when an additional quantity of one product is purchased.
C) The substitution of one product for another as a result of a change in their relative prices.
D) The substitution of a normal product for an inferior product as the result of an increase in income.
A) The effect that a change in income has on the demand for a substitute product.
B) The sacrifice which has to be made when an additional quantity of one product is purchased.
C) The substitution of one product for another as a result of a change in their relative prices.
D) The substitution of a normal product for an inferior product as the result of an increase in income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the term for income measured by the amount of goods and services which it will buy?
A) Income effect.
B) Net income.
C) Real income.
D) Nominal income.
E) Actual income.
A) Income effect.
B) Net income.
C) Real income.
D) Nominal income.
E) Actual income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What is the term for the substitution of one product for another as a result of a change in their relative prices?
A) Income effect.
B) Substitution effect.
C) Market effect.
D) Law of demand.
A) Income effect.
B) Substitution effect.
C) Market effect.
D) Law of demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the most likely reason that your instructor does not have a demand for a top-of-the-line BMW?
A) He or she does not wish to own such an expensive car.
B) He or she does not want to own a German-made car.
C) He or she would prefer to own no car at all.
D) He or she cannot afford to own such an expensive car.
A) He or she does not wish to own such an expensive car.
B) He or she does not want to own a German-made car.
C) He or she would prefer to own no car at all.
D) He or she cannot afford to own such an expensive car.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the correct way to label the axis on a graph which illustrates a demand curve?
A) Income on the horizontal axis and price on the vertical axis.
B) Price on the horizontal axis and income on the vertical axis.
C) Quantity on horizontal axis and price on the vertical axis.
D) Price on horizontal axis and quantity on the vertical axis.
A) Income on the horizontal axis and price on the vertical axis.
B) Price on the horizontal axis and income on the vertical axis.
C) Quantity on horizontal axis and price on the vertical axis.
D) Price on horizontal axis and quantity on the vertical axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
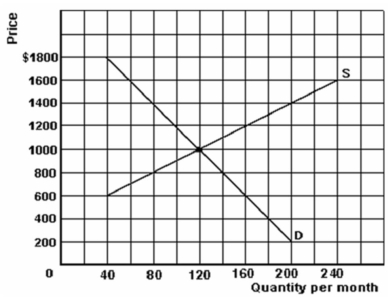
-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What would be the new equilibrium price and quantity if demand decreased by 60?
A) $1,000 and 80.
B) $800 and 80.
C) $1,400 and 80.
D) $1,400 and 60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is not a result of the greater availability of electronic communication?
A) Buyers have access to more information.
B) The sellers markets are expanding.
C) Supply chain bottlenecks are increasing.
D) The need to stockpile inventory is diminishing.
A) Buyers have access to more information.
B) The sellers markets are expanding.
C) Supply chain bottlenecks are increasing.
D) The need to stockpile inventory is diminishing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What is the term for the total supply of a product offered by all producers?
A) Equilibrium quantity.
B) Market Supply.
C) Saturation point.
D) Aggregate supply.
A) Equilibrium quantity.
B) Market Supply.
C) Saturation point.
D) Aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is a result of the greater availability of electronic communication?
A) There is more emphasis on personal service in the market.
B) Markets are becoming smaller.
C) Markets are becoming inefficient.
D) Markets are becoming more efficient.
A) There is more emphasis on personal service in the market.
B) Markets are becoming smaller.
C) Markets are becoming inefficient.
D) Markets are becoming more efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What is supply?
A) The total quantity of goods produced but not sold.
B) The maximum possible quantity that producers could make available.
C) The quantity made available by a typical producer.
D) The quantities that producers are willing and able to sell per period of time at various prices.
A) The total quantity of goods produced but not sold.
B) The maximum possible quantity that producers could make available.
C) The quantity made available by a typical producer.
D) The quantities that producers are willing and able to sell per period of time at various prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What is the effect if the price is $1,000.
A) There is neither a shortage nor a surplus.
B) Price will rise.
C) Price will fall.
D) The quantity traded is 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the price of a product does not change immediately, which of the following will cause an initial shortage of a product?
A) An increase in the demand or an increase in the supply.
B) A decrease in the demand or a decrease in the supply.
C) An increase in the demand or a decrease in the supply.
D) A decrease in the demand or an increase in the supply.
E) A change in the quantity supplied.
A) An increase in the demand or an increase in the supply.
B) A decrease in the demand or a decrease in the supply.
C) An increase in the demand or a decrease in the supply.
D) A decrease in the demand or an increase in the supply.
E) A change in the quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Graphically, what is the effect of a decrease in the price of a product?
A) A leftward movement on the supply curve.
B) A rightward movement on the supply curve.
C) A leftward shift in the supply curve.
D) A rightward shift in the supply curve.
A) A leftward movement on the supply curve.
B) A rightward movement on the supply curve.
C) A leftward shift in the supply curve.
D) A rightward shift in the supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What is the effect if the price is $1,200.
A) The quantity demanded is 120.
B) Price will rise.
C) The quantity supplied is 160.
D) The quantity traded is 120.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If the price of a product does not change immediately, which of the following will cause an initial surplus of a product?
A) An increase in the demand or an increase in the supply.
B) A decrease in the demand or a decrease in the supply.
C) An increase in the demand or a decrease in the supply.
D) A decrease in the demand or an increase in the supply.
E) A change in the quantity demanded.
A) An increase in the demand or an increase in the supply.
B) A decrease in the demand or a decrease in the supply.
C) An increase in the demand or a decrease in the supply.
D) A decrease in the demand or an increase in the supply.
E) A change in the quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What is market supply?
A) The total supply of a product demanded by all consumers.
B) The total quantity sold in a market.
C) The total supply of a product offered by all producers.
D) The surplus over and above the market demand.
A) The total supply of a product demanded by all consumers.
B) The total quantity sold in a market.
C) The total supply of a product offered by all producers.
D) The surplus over and above the market demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What is the effect of an increase in the price of a product?
A) An increase in supply.
B) A decrease in supply.
C) An increase in the quantity supplied.
D) A decrease in the quantity supplied.
A) An increase in supply.
B) A decrease in supply.
C) An increase in the quantity supplied.
D) A decrease in the quantity supplied.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What would be the new equilibrium price and quantity if supply increased by 120?
A) $1,000 and 240.
B) $600 and 240.
C) $600 and 160.
D) $800 and 140.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What is the equilibrium price?
A) The price at which there is no surplus, but there may be a shortage.
B) The price at which there is no shortage, but there may be a surplus.
C) The price at which everyone is able to buy the quantities they desire.
D) The price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied.
E) The price that both buyers and sellers agree is fair.
A) The price at which there is no surplus, but there may be a shortage.
B) The price at which there is no shortage, but there may be a surplus.
C) The price at which everyone is able to buy the quantities they desire.
D) The price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied.
E) The price that both buyers and sellers agree is fair.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What is the term for the mechanism which brings buyers and sellers together to assist them in negotiation the exchange of products?
A) Production possibilities.
B) Laissez-faire.
C) Opportunity cost.
D) The market.
E) Supply and demand.
A) Production possibilities.
B) Laissez-faire.
C) Opportunity cost.
D) The market.
E) Supply and demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What would be the new equilibrium price and quantity if demand increased by 60?
A) $1,600 and 120.
B) $1,400 and 140.
C) $1,200 and 160.
D) $1,000 and 140.
E) $1,000 and 180.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What is the effect if the price is $600.
A) The quantity demanded is 120.
B) Price will fall.
C) The quantity supplied is 120.
D) The quantity traded is 40.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is the term for the quantities which producers are willing and able to sell per period of time at various prices?
A) Quantity supplied.
B) Quantity demanded.
C) Surplus.
D) Supply.
E) Product availability.
A) Quantity supplied.
B) Quantity demanded.
C) Surplus.
D) Supply.
E) Product availability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What would be the new equilibrium price and quantity if supply decreased by 120?
A) Supply would be zero.
B) $1,400 and 80.
C) $1,000 and 40.
D) $800 and 80.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What is the effect if the price is $800?
A) There is a surplus of 30.
B) There is a shortage of 30.
C) 160 will be purchased.
D) There is a shortage of 60.
E) The price will increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What is the term for those products which consumers see as interchangeable (one for the other)?
A) Normal products.
B) Complementary products.
C) Substitute products.
D) Inferior products.
A) Normal products.
B) Complementary products.
C) Substitute products.
D) Inferior products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
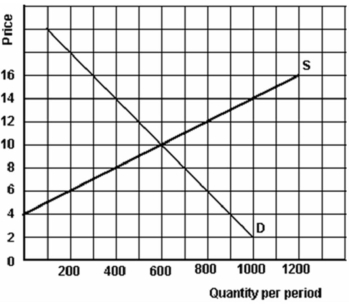
-Refer to the above graph to answer this question. What are the implications if the price of this product is $8?
A) The price would be above equilibrium.
B) There would be a shortage of 300 units.
C) There would be a shortage of 600 units.
D) There would be a surplus of 300 units.
E) There would be a surplus of 600 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43

-Refer to the above graph to answer this question. If the price of the product is $14, how many units would be sold?
A) 400 units.
B) 600 units.
C) 800 units.
D) 1,000 units.
E) Cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What is the relationship between pizzas and hamburgers?
A) They are complementary products.
B) They are substitute products.
C) They are customary products.
D) They are cooperative products.
E) They are unrelated products.
A) They are complementary products.
B) They are substitute products.
C) They are customary products.
D) They are cooperative products.
E) They are unrelated products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the term for those products whose demand will decrease as a result of an increase in income and will increase as a result of a decrease in income?
A) Normal products.
B) Complementary products.
C) Substitute products.
D) Inferior products.
E) Related products.
A) Normal products.
B) Complementary products.
C) Substitute products.
D) Inferior products.
E) Related products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46

-Refer to the above graph to answer this question. What are the implications if the price of this product is $14?
A) The price would be below equilibrium.
B) There would be a shortage of 600 units.
C) There would be a shortage of 1,200 units.
D) There would be a surplus of 600 units.
E) There would be a surplus of 1,200 units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following pairs of products are complements?
A) Automobiles and steel.
B) Steel and oil.
C) Bread and flour.
D) Cameras and films.
E) Flour and wheat.
A) Automobiles and steel.
B) Steel and oil.
C) Bread and flour.
D) Cameras and films.
E) Flour and wheat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is an inferior product?
A) It is a product which consumers buy more of as their incomes increase.
B) It is a product which consumers buy less of as their incomes increase.
C) It is a product which consumers buy less of as their incomes decrease.
D) It is a low-quality luxury product.
A) It is a product which consumers buy more of as their incomes increase.
B) It is a product which consumers buy less of as their incomes increase.
C) It is a product which consumers buy less of as their incomes decrease.
D) It is a low-quality luxury product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following pairs of products are substitutes?
A) Grapes and wine.
B) Grapes and beer.
C) Grapefruit juice and beer.
D) Grapefruits and wine.
E) Grapes and grapefruits.
A) Grapes and wine.
B) Grapes and beer.
C) Grapefruit juice and beer.
D) Grapefruits and wine.
E) Grapes and grapefruits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the relationship between computers and printers?
A) They are complementary products.
B) They are competitive products.
C) They are substitute products.
D) They are cooperative products.
E) They are rival products.
A) They are complementary products.
B) They are competitive products.
C) They are substitute products.
D) They are cooperative products.
E) They are rival products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51

-Refer to the above graph to answer this question. What is the minimum price the quantity sold at a price of $14 could have been sold for?
A) $6.
B) $8.
C) $10.
D) $12.
E) Cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What is the term for those products which tend to be purchased jointly and whose demands therefore are related?
A) Normal products.
B) Complementary products.
C) Substitute products.
D) Inferior products.
A) Normal products.
B) Complementary products.
C) Substitute products.
D) Inferior products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What is true of complementary products?
A) When the price of one increases, the quantity purchased of the other decreases.
B) When the price of one increases, the quantity purchased of the other increases.
C) When the price of one decreases, the quantity purchased of the other decreases.
D) They are products which compete with one another.
A) When the price of one increases, the quantity purchased of the other decreases.
B) When the price of one increases, the quantity purchased of the other increases.
C) When the price of one decreases, the quantity purchased of the other decreases.
D) They are products which compete with one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is true of substitute products?
A) When the price of one increases, the quantity purchased of the other decreases.
B) When the price of one increases, the quantity purchased of the other increases.
C) When the price of one decreases, the quantity purchased of the other increases.
D) They are products which are always purchased together.
A) When the price of one increases, the quantity purchased of the other decreases.
B) When the price of one increases, the quantity purchased of the other increases.
C) When the price of one decreases, the quantity purchased of the other increases.
D) They are products which are always purchased together.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What is the name of those products whose demand will increase as a result of an increase in income?
A) Normal products.
B) Complementary products.
C) Substitute products.
D) Inferior products.
A) Normal products.
B) Complementary products.
C) Substitute products.
D) Inferior products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56

-Refer to the above graph to answer this question. What is the maximum price the quantity sold at a price of $8 could have been sold for?
A) $8.
B) $10.
C) $12.
D) $14.
E) Cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What will cause the demand for a normal product to increase?
A) The expectation by consumers that future prices will be higher.
B) A decrease in the price of a substitute product.
C) An increase in the price of a complementary product.
D) A decrease in income levels.
E) A decrease in the size of the population.
A) The expectation by consumers that future prices will be higher.
B) A decrease in the price of a substitute product.
C) An increase in the price of a complementary product.
D) A decrease in income levels.
E) A decrease in the size of the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What is a normal product?
A) It is a product which consumers buy regularly.
B) It is a product which consumers buy more of as their incomes increase.
C) It is a product which consumers buy less of as their incomes increase.
D) It is a product which consumers buy more of as their incomes decrease.
A) It is a product which consumers buy regularly.
B) It is a product which consumers buy more of as their incomes increase.
C) It is a product which consumers buy less of as their incomes increase.
D) It is a product which consumers buy more of as their incomes decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59

-Refer to the above graph to answer this question. If the price of the product is $8, how many units would be sold?
A) 400 units.
B) 500 units.
C) 600 units.
D) 800 units.
E) Cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What will cause the demand for a normal product to decrease?
A) The expectation by consumers that future prices will be higher.
B) An increase in the price of a substitute product.
C) An increase in the price of a complementary product.
D) An increase in income levels.
E) An increase in the size of the population.
A) The expectation by consumers that future prices will be higher.
B) An increase in the price of a substitute product.
C) An increase in the price of a complementary product.
D) An increase in income levels.
E) An increase in the size of the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What is the effect of consumers' expecting that the future price of a product will increase?
A) It will cause an increase in the quantity demanded.
B) It will cause an increase in demand.
C) It will cause a decrease in demand.
D) It will cause a decrease in the quantity demanded.
E) It will cause a decrease in supply.
A) It will cause an increase in the quantity demanded.
B) It will cause an increase in demand.
C) It will cause a decrease in demand.
D) It will cause a decrease in the quantity demanded.
E) It will cause a decrease in supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The following table shows the initial weekly demand (D1) and the new demand (D2) for packets of pretzels (a bar snack):
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. In order to produce the change in demand from D1 to D2, what might have happened to the price of a substitute product like a packet of nuts?
A) It has not changed, but people must be buying less.
B) It has not changed, but people must be buying more.
C) It has decreased.
D) It has increased.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. In order to produce the change in demand from D1 to D2, what might have happened to the price of a substitute product like a packet of nuts?
A) It has not changed, but people must be buying less.
B) It has not changed, but people must be buying more.
C) It has decreased.
D) It has increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
All of the following except one will cause the supply of a product to decrease. Which is the exception?
A) A decrease in the price of a substitute in production.
B) An increase in business taxes.
C) The expectation of suppliers that the future price of the product will be higher.
D) An increase in the price of resources.
E) A decrease in the number of suppliers.
A) A decrease in the price of a substitute in production.
B) An increase in business taxes.
C) The expectation of suppliers that the future price of the product will be higher.
D) An increase in the price of resources.
E) A decrease in the number of suppliers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the effect on product A of an increase in the price of substitute product B?
A) It will cause an increase in the quantity demanded.
B) It will cause an increase in demand.
C) It will cause a decrease in demand.
D) It will cause an increase in supply.
E) It will cause a decrease in supply.
A) It will cause an increase in the quantity demanded.
B) It will cause an increase in demand.
C) It will cause a decrease in demand.
D) It will cause an increase in supply.
E) It will cause a decrease in supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The product is a normal product.
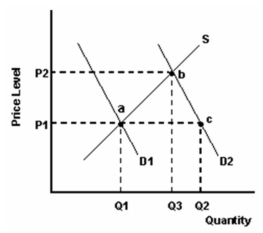
-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Both ab and ac represent an increase in the quantity demanded.
B) Both ab and ac represent an increase in demand.
C) While ab represents an increase in demand, ac represents an increase in supply.
D) While ac represents an increase in demand, ab represents an increase in the quantity supplied.
E) Both ab and cb represent an increase in demand.

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. Which of the following statements is correct?
A) Both ab and ac represent an increase in the quantity demanded.
B) Both ab and ac represent an increase in demand.
C) While ab represents an increase in demand, ac represents an increase in supply.
D) While ac represents an increase in demand, ab represents an increase in the quantity supplied.
E) Both ab and cb represent an increase in demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The product is a normal product.

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What does the distance Q1 - Q2 represent?
A) An increase in the quantity demanded.
B) A surplus at price P1.
C) A shortage at price P1.
D) The result of a decrease in income.

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What does the distance Q1 - Q2 represent?
A) An increase in the quantity demanded.
B) A surplus at price P1.
C) A shortage at price P1.
D) The result of a decrease in income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The product is a normal product.

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What does the distance Q1 to Q3 represent?
A) The increase in equilibrium quantity traded resulting from an increase in demand.
B) The decrease in equilibrium quantity traded resulting from an increase in demand.
C) The increase in equilibrium quantity traded resulting from an increase in quantity demanded.
D) The increase in equilibrium quantity traded resulting from an increase in quantity supplied.
E) A shortage at price P2.

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What does the distance Q1 to Q3 represent?
A) The increase in equilibrium quantity traded resulting from an increase in demand.
B) The decrease in equilibrium quantity traded resulting from an increase in demand.
C) The increase in equilibrium quantity traded resulting from an increase in quantity demanded.
D) The increase in equilibrium quantity traded resulting from an increase in quantity supplied.
E) A shortage at price P2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
All of the following except one will cause the supply of a product to increase. Which is the exception?
A) A decrease in the price of a substitute in production.
B) An increase in business taxes.
C) The expectation of suppliers that the future price of the product will be lower.
D) A decrease in the price of resources.
E) An improvement in technology.
A) A decrease in the price of a substitute in production.
B) An increase in business taxes.
C) The expectation of suppliers that the future price of the product will be lower.
D) A decrease in the price of resources.
E) An improvement in technology.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What will cause the supply of a product to decrease?
A) A decrease in the price of resources.
B) An increase in the number of suppliers.
C) The expectation of producers that the future price will be lower.
D) An improvement in the technology of producing the product.
E) An increase in the price of a substitute in production.
A) A decrease in the price of resources.
B) An increase in the number of suppliers.
C) The expectation of producers that the future price will be lower.
D) An improvement in the technology of producing the product.
E) An increase in the price of a substitute in production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The following table shows the initial weekly demand (D1) and the new demand (D2) for packets of pretzels (a bar snack):
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. In order to have produced the change in demand from D1 to D2, what might have happened to the price of a complementary product like beer?
A) It has not changed, but people must be buying less.
B) It has not changed, but people must be buying more.
C) It has decreased.
D) It has increased.
-Refer to the information above to answer this question. In order to have produced the change in demand from D1 to D2, what might have happened to the price of a complementary product like beer?
A) It has not changed, but people must be buying less.
B) It has not changed, but people must be buying more.
C) It has decreased.
D) It has increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
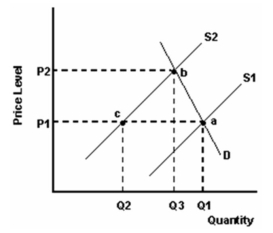
-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. What does the distance Q1 - Q2 represent?
A) A decrease in the quantity supplied.
B) A shortage at price P1.
C) A surplus at price P1.
D) The result of a decrease in the sales tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What is the effect on a normal product if income increases?
A) It will cause an increase in the quantity demanded.
B) It will cause an increase in demand.
C) It will cause a decrease in demand.
D) It will cause an increase in supply.
E) It will cause a decrease in supply.
A) It will cause an increase in the quantity demanded.
B) It will cause an increase in demand.
C) It will cause a decrease in demand.
D) It will cause an increase in supply.
E) It will cause a decrease in supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. All of the following except one could have caused the shift from S1 to S2. Which is the exception?
A) A decrease in income.
B) An increase in the sales tax.
C) An increase in the price of a substitute in production.
D) A decrease in the number of suppliers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What will cause the supply of a product to increase?
A) An increase in the price of resources.
B) A decrease in the number of suppliers.
C) The expectation of producers that the future price will be higher.
D) An improvement in the technology of producing the product.
E) An increase in the price of a productively related product.
A) An increase in the price of resources.
B) A decrease in the number of suppliers.
C) The expectation of producers that the future price will be higher.
D) An improvement in the technology of producing the product.
E) An increase in the price of a productively related product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
All of the following except one will cause the demand for a normal product to increase. Which is the exception?
A) The expectation by consumers that the future price will be higher.
B) The fear of consumers of a future strike in the industry.
C) An increase in the price of a complementary product.
D) An increase in the price of a substitute product.
E) An increase in consumer incomes.
A) The expectation by consumers that the future price will be higher.
B) The fear of consumers of a future strike in the industry.
C) An increase in the price of a complementary product.
D) An increase in the price of a substitute product.
E) An increase in consumer incomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
What is the effect of a decrease in the supply of a product?
A) It will cause an increase in both the price and in the quantity traded.
B) It will cause an increase in the price but a decrease in the quantity traded.
C) It will cause a decrease in both the price and in the quantity traded.
D) It will cause a decrease in the price but an increase in the quantity traded.
A) It will cause an increase in both the price and in the quantity traded.
B) It will cause an increase in the price but a decrease in the quantity traded.
C) It will cause a decrease in both the price and in the quantity traded.
D) It will cause a decrease in the price but an increase in the quantity traded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The product is a normal product.

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. All of the following except one could have caused the shift from D1 to D2. Which is the exception?
A) An increase in income.
B) An increase in the price of a substitute good.
C) An increase in the price of a complement good.
D) Growth in the size of the market.

-Refer to the graph above to answer this question. All of the following except one could have caused the shift from D1 to D2. Which is the exception?
A) An increase in income.
B) An increase in the price of a substitute good.
C) An increase in the price of a complement good.
D) Growth in the size of the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
All of the following except one will cause the demand for a normal product to decrease. Which is the exception?
A) The expectation by consumers that the future price will be higher.
B) The fear of consumers of a future recession.
C) An increase in the price of a complementary product.
D) A decrease in the price of a substitute product.
E) A decrease in consumer incomes.
A) The expectation by consumers that the future price will be higher.
B) The fear of consumers of a future recession.
C) An increase in the price of a complementary product.
D) A decrease in the price of a substitute product.
E) A decrease in consumer incomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the effect on an inferior product if income increases?
A) It will cause an increase in the quantity demanded.
B) It will cause an increase in demand.
C) It will cause a decrease in demand.
D) It will cause an increase in supply.
E) It will cause a decrease in supply.
A) It will cause an increase in the quantity demanded.
B) It will cause an increase in demand.
C) It will cause a decrease in demand.
D) It will cause an increase in supply.
E) It will cause a decrease in supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What is the effect on product A of an increase in the price of complementary product B?
A) It will cause an increase in the quantity demanded.
B) It will cause an increase in demand.
C) It will cause a decrease in demand.
D) It will cause an increase in supply.
E) It will cause a decrease in supply.
A) It will cause an increase in the quantity demanded.
B) It will cause an increase in demand.
C) It will cause a decrease in demand.
D) It will cause an increase in supply.
E) It will cause a decrease in supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 198 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



