Deck 23: The Exchange Rate and the Balance of Payments
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/154
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: The Exchange Rate and the Balance of Payments
1
When the exchange rate falls, in the foreign exchange market the
A)quantity demanded of the currency increases.
B)demand for the currency increases.
C)demand for the currency decreases.
D)quantity demanded of the currency decreases.
A)quantity demanded of the currency increases.
B)demand for the currency increases.
C)demand for the currency decreases.
D)quantity demanded of the currency decreases.
A
2
When a good is imported into Australia, there is created a
A)supply of foreign currency with no effect on the market for the Australian dollar.
B)demand for foreign currencies and a supply of Australian dollars.
C)supply of foreign currencies and a demand for Australian dollars.
D)demand for Australian dollars with no effect on the markets for foreign currencies.
A)supply of foreign currency with no effect on the market for the Australian dollar.
B)demand for foreign currencies and a supply of Australian dollars.
C)supply of foreign currencies and a demand for Australian dollars.
D)demand for Australian dollars with no effect on the markets for foreign currencies.
B
3
If the Australian dollar's value changes from 100 yen per dollar to 95 yen per dollar, the Australian dollar has
A)devalued.
B)appreciated.
C)depreciated.
D)demanded.
A)devalued.
B)appreciated.
C)depreciated.
D)demanded.
C
4
China has used a fixed yuan exchange rate and a crawling peg exchange rate. In both cases, China pegs its currency to the
A)Japanese yen.
B)U.S. dollar.
C)Australian dollar.
D)euro.
A)Japanese yen.
B)U.S. dollar.
C)Australian dollar.
D)euro.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a country is currently lending more to the rest of the world than it is borrowing from the rest of the world, the country is a
A)net borrower.
B)net lender.
C)creditor nation.
D)debtor nation.
A)net borrower.
B)net lender.
C)creditor nation.
D)debtor nation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The government sector balance is equal to .
A)tariffs minus imports
B)net taxes minus government purchases of goods and services
C)saving minus investment
D)exports minus imports
A)tariffs minus imports
B)net taxes minus government purchases of goods and services
C)saving minus investment
D)exports minus imports

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following statements is true?
A)If private investment is greater than private saving, then either the government or the net export sector must have a surplus.
B)If private investment is greater than private saving, then the private sector has a deficit.
C)If private saving is greater than private investment, then the private sector has a surplus.
D)All of the above answers are correct.
A)If private investment is greater than private saving, then either the government or the net export sector must have a surplus.
B)If private investment is greater than private saving, then the private sector has a deficit.
C)If private saving is greater than private investment, then the private sector has a surplus.
D)All of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Important factors that change the demand for dollars and shift the demand curve for dollars include which of the following?
I. Interest rates around the world
II. The current exchange rate
III. The expected future exchange rate
A)I and II
B)II
C)I and III
D)I, II and III
I. Interest rates around the world
II. The current exchange rate
III. The expected future exchange rate
A)I and II
B)II
C)I and III
D)I, II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the figure above, the shift in the demand curve for Australian dollars from D0 to D1 could occur when
A)foreign interest rates drop.
B)the expected future exchange rate falls.
C)people expect that the dollar will depreciate.
D)the Australian interest rate drops.
A)foreign interest rates drop.
B)the expected future exchange rate falls.
C)people expect that the dollar will depreciate.
D)the Australian interest rate drops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Suppose a Japanese bank offers a 4 per cent interest rate and Australian banks offer a 2 per cent interest rate. People must expect the yen to
A)depreciate by 2 per cent.
B)appreciate by 2 per cent.
C)appreciate by 6 per cent.
D)depreciate by 6 per cent.
A)depreciate by 2 per cent.
B)appreciate by 2 per cent.
C)appreciate by 6 per cent.
D)depreciate by 6 per cent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the interest rate on Japanese yen assets falls, the
A)quantity of dollars demanded will decrease.
B)quantity of dollars demanded will increase.
C)demand for dollars will increase.
D)demand for dollars will decrease.
A)quantity of dollars demanded will decrease.
B)quantity of dollars demanded will increase.
C)demand for dollars will increase.
D)demand for dollars will decrease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Interest rates in Australia rise relative to interest rates in other countries. As a result, in the foreign exchange market
A)there is an upward movement along the supply curve of Australian dollars.
B)the demand curve for Australian dollars shifts leftward.
C)the supply curve of Australian dollars shifts rightward.
D)the supply curve of Australian dollars shifts leftward.
A)there is an upward movement along the supply curve of Australian dollars.
B)the demand curve for Australian dollars shifts leftward.
C)the supply curve of Australian dollars shifts rightward.
D)the supply curve of Australian dollars shifts leftward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If the Reserve Bank raises Australian interest rates, the demand for dollars and the exchange rate .
A)decreases; falls
B)decreases; rises
C)increases; falls
D)increases; rises
A)decreases; falls
B)decreases; rises
C)increases; falls
D)increases; rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The balance of payments account which records foreign investment in Australia and Australian investments abroad is the
A)official settlements account.
B)current account.
C)capital and financial account.
D)None of the above because foreign investment in Australia is included in one account and Australian investment abroad is included in another account.
A)official settlements account.
B)current account.
C)capital and financial account.
D)None of the above because foreign investment in Australia is included in one account and Australian investment abroad is included in another account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Suppose the exchange rate of Australian dollar was 80 Japanese yen per Australian dollar on Thursday, and on Friday the exchange rate was 90 Japanese yen per Australian dollar. Which of the following BEST explains what has happened between Thursday and Friday?
A)The Australian dollar appreciated against the Japanese yen.
B)The Japanese yen appreciated against the Australian dollar.
C)The Japanese yen depreciated against the Australian dollar.
D)Both answers A and C are correct.
A)The Australian dollar appreciated against the Japanese yen.
B)The Japanese yen appreciated against the Australian dollar.
C)The Japanese yen depreciated against the Australian dollar.
D)Both answers A and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The demand curve for Australian dollars slopes downward because as the Australian dollar
Australian goods become expensive to foreign residents, so they purchase fewer Australian goods, and the quantity of Australian dollars demanded decreases.
A)depreciates; more
B)appreciates; less
C)appreciates; more
D)depreciates; less
Australian goods become expensive to foreign residents, so they purchase fewer Australian goods, and the quantity of Australian dollars demanded decreases.
A)depreciates; more
B)appreciates; less
C)appreciates; more
D)depreciates; less

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When Australia exports goods to foreign countries, we
A)decrease our inflation rate.
B)receive payments from the rest of the world.
C)make payments to the rest of the world.
D)increase our inflation rate.
A)decrease our inflation rate.
B)receive payments from the rest of the world.
C)make payments to the rest of the world.
D)increase our inflation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In 2010/11, the Australian capital and financial account had a
A)deficit of $33 billion.
B)surplus of $33 billion.
C)surplus of $36 billion.
D)deficit of $36 billion.
A)deficit of $33 billion.
B)surplus of $33 billion.
C)surplus of $36 billion.
D)deficit of $36 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Today, the dollar is worth 1.15 euros. Due to changes in economic conditions, people come to expect the dollar will be worth 1.20 euros in one month. This belief
A)increases the demand for dollars.
B)increases the value of exports to Europe.
C)decreases the demand for dollars.
D)increases the demand for euros.
A)increases the demand for dollars.
B)increases the value of exports to Europe.
C)decreases the demand for dollars.
D)increases the demand for euros.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
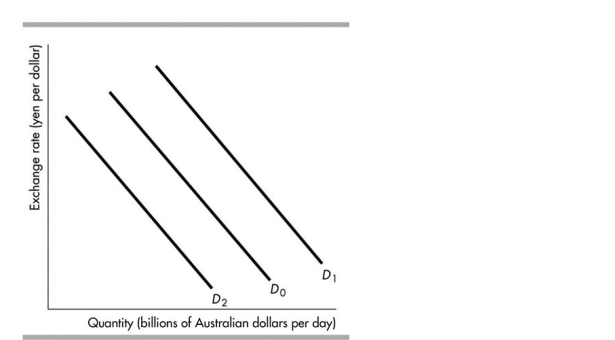
In the figure above, the shift in the demand curve for Australian dollars from D0 to D2 could occur when
A)people expect that the dollar will appreciate.
B)foreign interest rates fall.
C)the Australian interest rate rises.
D)the Australian interest rate falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A German publishing company buys an Australian publishing company based in Perth. In Australia's balance of payments accounts, this transaction directly appears in
A)the capital and financial account.
B)the official settlements account.
C)the imports part of the current account.
D)the net transfers part of the current account.
A)the capital and financial account.
B)the official settlements account.
C)the imports part of the current account.
D)the net transfers part of the current account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following occurrences would NOT shift the demand curve for Australian dollars in the foreign exchange market?
A)An increase in Australian interest rates
B)An increase in the expected future Australian exchange rate
C)An increase in foreign interest rates
D)An increase in the Australian exchange rate
A)An increase in Australian interest rates
B)An increase in the expected future Australian exchange rate
C)An increase in foreign interest rates
D)An increase in the Australian exchange rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
To pay for a current account deficit, a country can
A)lend money abroad.
B)transfer money from the capital account to the reserve assets account.
C)increase official reserves to cover the shortfall.
D)borrow money from abroad.
A)lend money abroad.
B)transfer money from the capital account to the reserve assets account.
C)increase official reserves to cover the shortfall.
D)borrow money from abroad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
If the prices in Australia rise faster than those in other countries,
A)then interest rate parity must not hold.
B)the exchange rate falls.
C)the interest rate in Australia falls.
D)the exchange rate rises.
A)then interest rate parity must not hold.
B)the exchange rate falls.
C)the interest rate in Australia falls.
D)the exchange rate rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Suppose the Australian government gives foreign aid to Indonesia. This transaction would directly
A)increase the Australian current account.
B)decrease the Australian capital and financial account.
C)decrease the Australian current account.
D)increase the Australian capital and financial account.
A)increase the Australian current account.
B)decrease the Australian capital and financial account.
C)decrease the Australian current account.
D)increase the Australian capital and financial account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The law of demand in the foreign exchange market refers to the relationship between the
A)Australian price level and the exchange rate.
B)interest rate and the quantity of Australian dollars demanded.
C)exchange rate and the quantity of Australian dollars demanded.
D)interest rate and the exchange rate.
A)Australian price level and the exchange rate.
B)interest rate and the quantity of Australian dollars demanded.
C)exchange rate and the quantity of Australian dollars demanded.
D)interest rate and the exchange rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
According to purchasing power parity, a rise in inflation in Australia relative to the rest of the world will lead to
A)an exchange rate appreciation.
B)a balance of payments surplus.
C)an exchange rate depreciation.
D)a balance of payments deficit.
A)an exchange rate appreciation.
B)a balance of payments surplus.
C)an exchange rate depreciation.
D)a balance of payments deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The demand for Australian dollars in the foreign exchange market will decrease and the demand curve will shift leftward if
A)the exchange rate for the Australian dollar rises.
B)the Australian interest rate differential decreases.
C)the expected future exchange rate rises.
D)None of the above answers is correct.
A)the exchange rate for the Australian dollar rises.
B)the Australian interest rate differential decreases.
C)the expected future exchange rate rises.
D)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Given the Australian price level P, the foreign country price level P*, and the nominal exchange rate E in foreign currency per Australian dollar, the real exchange rate RER is given by
A)RER = E × (P/P*)
B)RER = (P/P*)/ E
C)RER = E × (P*/P)
D)RER = P × (E/P*)
A)RER = E × (P/P*)
B)RER = (P/P*)/ E
C)RER = E × (P*/P)
D)RER = P × (E/P*)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If Australia's current account balance is - $500 billion and the capital and financial account balance is +$510 billion,
A)foreign investment in Australia is smaller than Australian investment abroad.
B)the Australian government's holdings of foreign currency increase by $10 billion.
C)Australian exports are greater than Australian imports.
D)the Australian reserve assets account balance is $10 billion.
A)foreign investment in Australia is smaller than Australian investment abroad.
B)the Australian government's holdings of foreign currency increase by $10 billion.
C)Australian exports are greater than Australian imports.
D)the Australian reserve assets account balance is $10 billion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A negative balance in the capital and financial account means the economy is
A)running a capital account surplus.
B)lending to the rest of the world.
C)importing more than it is exporting.
D)borrowing from the rest of the world.
A)running a capital account surplus.
B)lending to the rest of the world.
C)importing more than it is exporting.
D)borrowing from the rest of the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Adjusted for risk, interest rate parity
A)holds only between Australian and New Zealand.
B)holds only when purchasing parity holds.
C)always holds.
D)holds only for larger countries.
A)holds only between Australian and New Zealand.
B)holds only when purchasing parity holds.
C)always holds.
D)holds only for larger countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the expected future exchange rate rises, the currency's
A)exchange rate falls.
B)supply decreases.
C)quantity supplied increases.
D)supply increases.
A)exchange rate falls.
B)supply decreases.
C)quantity supplied increases.
D)supply increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the pound- dollar exchange rate changes from £0.60 per dollar to £0.65 per dollar, then the pound has _ against the dollar and the dollar has _ against the pound.
A)depreciated; appreciated
B)depreciated; depreciated
C)appreciated; depreciated
D)appreciated; appreciated
A)depreciated; appreciated
B)depreciated; depreciated
C)appreciated; depreciated
D)appreciated; appreciated

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In the figure above, the shift in the supply curve for Australian dollars from S0 to S2 could occur when
A)the current exchange rate rises.
B)the expected future exchange rate rises.
C)the expected future exchange rate falls.
D)the current exchange rate falls.
A)the current exchange rate rises.
B)the expected future exchange rate rises.
C)the expected future exchange rate falls.
D)the current exchange rate falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If there are equal rates of return between assets in two currencies, then there is
A)interest rate parity.
B)foreign exchange parity.
C)parity of exchange.
D)purchasing power parity.
A)interest rate parity.
B)foreign exchange parity.
C)parity of exchange.
D)purchasing power parity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A factor determining the supply of Australian dollars in the foreign exchange market is
A)the expected future exchange rate.
B)the expected future interest rate in foreign countries.
C)the expected future interest rate in Australia.
D)Australia's supply of exports.
A)the expected future exchange rate.
B)the expected future interest rate in foreign countries.
C)the expected future interest rate in Australia.
D)Australia's supply of exports.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
When the Australian exchange rate rises, foreign goods become _ and Australian imports
.
A)less expensive; decrease
B)less expensive; increase
C)more expensive; decrease
D)more expensive; increase
.
A)less expensive; decrease
B)less expensive; increase
C)more expensive; decrease
D)more expensive; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following exchange rate policies uses a target exchange rate, but allows the target to change?
A)Flexible exchange rate
B)Crawling peg
C)Moving target
D)Fixed exchange rate
A)Flexible exchange rate
B)Crawling peg
C)Moving target
D)Fixed exchange rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
When the Australian exchange rate falls, Australian goods become _ to foreign residents and Australian exports .
A)more expensive; increase
B)less expensive; decrease
C)less expensive; increase
D)more expensive; decrease
A)more expensive; increase
B)less expensive; decrease
C)less expensive; increase
D)more expensive; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A country's balance of payments accounts record
A)the international trading, borrowing and lending positions of a country over a period of time.
B)only official transactions between governments over a period of time.
C)only the goods and services purchases among countries over a period of time.
D)the flow of human and non- human capital among countries over a period of time.
A)the international trading, borrowing and lending positions of a country over a period of time.
B)only official transactions between governments over a period of time.
C)only the goods and services purchases among countries over a period of time.
D)the flow of human and non- human capital among countries over a period of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
By fixing its exchange rate, China is most likely
A)keeping its export prices low.
B)making it easier to compete in world markets.
C)achieving a low inflation rate by anchoring to the U.S. inflation rate.
D)Both answers B and C
A)keeping its export prices low.
B)making it easier to compete in world markets.
C)achieving a low inflation rate by anchoring to the U.S. inflation rate.
D)Both answers B and C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
In the figure above, the shift in the demand curve for Australian dollars from D0 to D1 could occur when
A)the Australian interest rate rises.
B)the expected future exchange rate decreases.
C)foreign interest rates increase.
D)people expect that the dollar will depreciate.
A)the Australian interest rate rises.
B)the expected future exchange rate decreases.
C)foreign interest rates increase.
D)people expect that the dollar will depreciate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A reserve assets account balance of - $5,000 means
A)the country is exporting more than it is importing.
B)official reserves of foreign currency increased by $5,000.
C)the country is importing more than it is exporting.
D)official reserves of foreign currency decreased by $5,000.
A)the country is exporting more than it is importing.
B)official reserves of foreign currency increased by $5,000.
C)the country is importing more than it is exporting.
D)official reserves of foreign currency decreased by $5,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
can intervene directly in the foreign exchange market by buying or selling Australian dollars.
A)The International Monetary Fund
B)The Reserve Bank of Australia
C)The Australian Treasury department
D)The Parliament
A)The International Monetary Fund
B)The Reserve Bank of Australia
C)The Australian Treasury department
D)The Parliament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If a country is importing more than it is exporting, the current account will have a _ _ balance and the capital and financial account will have a balance.
A)positive; positive
B)negative; positive
C)positive; negative
D)negative; negative
A)positive; positive
B)negative; positive
C)positive; negative
D)negative; negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
If the Reserve Bank sets a target exchange rate that is higher than the current exchange rate, then
A)the Reserve Bank must buy dollars.
B)the Reserve Bank must sell dollars.
C)the Reserve Bank will try to print more dollars for foreign distribution.
D)the Reserve Bank can do nothing in the short run.
A)the Reserve Bank must buy dollars.
B)the Reserve Bank must sell dollars.
C)the Reserve Bank will try to print more dollars for foreign distribution.
D)the Reserve Bank can do nothing in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Other things remaining the same, if the expected future exchange rate rises, the demand curve for Australian dollars shifts and the supply curve of Australian dollars shifts .
A)rightward; rightward
B)leftward; leftward
C)leftward; rightward
D)rightward; leftward
A)rightward; rightward
B)leftward; leftward
C)leftward; rightward
D)rightward; leftward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The account that records the receipts from exports of goods and services sold abroad, the payments for imports of goods and services from abroad, net interest income paid abroad, and net transfers is the .
A)international capital account
B)current account
C)official settlements account
D)capital and financial account
A)international capital account
B)current account
C)official settlements account
D)capital and financial account

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the foreign exchange market, the supply curve for dollars slopes upwards because
A)supply curves always slope upwards.
B)as the exchange rate rises, imports become cheaper, and more dollars are supplied to pay for the increase in the quantity of imports.
C)as the exchange rate rises, imports become more expensive, and more dollars are supplied to pay for the imports.
D)as the exchange rate rises, more dollars are supplied since the profit from selling dollars falls.
A)supply curves always slope upwards.
B)as the exchange rate rises, imports become cheaper, and more dollars are supplied to pay for the increase in the quantity of imports.
C)as the exchange rate rises, imports become more expensive, and more dollars are supplied to pay for the imports.
D)as the exchange rate rises, more dollars are supplied since the profit from selling dollars falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The Reserve Bank of Australia
A)sells Australian dollars to China in an attempt to depreciate the Australian dollar.
B)has no influence on the exchange rate.
C)allows a flexible exchange rate, though their actions can impact on the exchange rate.
D)alternates between a flexible, fixed and crawling peg exchange rate policy depending on economic conditions.
A)sells Australian dollars to China in an attempt to depreciate the Australian dollar.
B)has no influence on the exchange rate.
C)allows a flexible exchange rate, though their actions can impact on the exchange rate.
D)alternates between a flexible, fixed and crawling peg exchange rate policy depending on economic conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Australians demand Japanese yen in order to
A)allow the Japanese to buy Australian products.
B)sell Japanese products.
C)supply Australian goods in Japanese markets.
D)buy Japanese products.
A)allow the Japanese to buy Australian products.
B)sell Japanese products.
C)supply Australian goods in Japanese markets.
D)buy Japanese products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If the price level in Australia is 120, the price level in South Africa is 140, and the nominal exchange rate is 7 South African rand per Australian dollar, then the real exchange rate is
A)9.8 South African goods per Australian good.
B)6 South African goods per Australian good.
C)8.4 South African goods per Australian good.
D)1.4 South African goods per Australian good.
A)9.8 South African goods per Australian good.
B)6 South African goods per Australian good.
C)8.4 South African goods per Australian good.
D)1.4 South African goods per Australian good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Hyundai is a large South Korean company that produces finished steel products. Hyundai plans to buy raw steel from Australia. As a result, the
A)demand curve for Australian dollars shifts rightward.
B)demand curve for Australian dollars shifts leftward.
C)demand curve for South Korean won shifts leftward.
D)demand curve for South Korean won shifts rightward.
A)demand curve for Australian dollars shifts rightward.
B)demand curve for Australian dollars shifts leftward.
C)demand curve for South Korean won shifts leftward.
D)demand curve for South Korean won shifts rightward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Suppose the Reserve Bank wants to fix the Australian dollar/Philippine peso rate at 11 pesos per dollar under a fixed exchange rate policy. If the exchange rate falls to 10 pesos per Australian dollar, the Reserve Bank can
A)attempt to freeze all sales of Australian dollars.
B)buy Australian dollars.
C)sell Australian dollars.
D)Any of the above actions could take place.
A)attempt to freeze all sales of Australian dollars.
B)buy Australian dollars.
C)sell Australian dollars.
D)Any of the above actions could take place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A change in which of the following changes the supply of dollars and shifts the supply curve of dollars?
I. An increase in the exchange rate
II. A change in interest rates
III. A decrease in the expected future exchange rate
A)I
B)I and II
C)II and III
D)I, II and III
I. An increase in the exchange rate
II. A change in interest rates
III. A decrease in the expected future exchange rate
A)I
B)I and II
C)II and III
D)I, II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The private sector surplus or deficit equals
A)investment minus saving.
B)government purchases minus net taxes.
C)saving minus investment.
D)net taxes minus government purchases.
A)investment minus saving.
B)government purchases minus net taxes.
C)saving minus investment.
D)net taxes minus government purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If interest rates in Japan rise and those in Australia do not change, there is
A)a downward movement along the supply curve for Australian dollars.
B)a decrease in the supply of Australian dollars.
C)an increase in the supply of Australian dollars.
D)None of the above answers is correct.
A)a downward movement along the supply curve for Australian dollars.
B)a decrease in the supply of Australian dollars.
C)an increase in the supply of Australian dollars.
D)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The current account balance is equal to
A)net exports - net interest income - net transfers.
B)net interest income + net transfers - net exports.
C)net exports + net interest income + net transfers.
D)net exports + net interest income - net transfers.
A)net exports - net interest income - net transfers.
B)net interest income + net transfers - net exports.
C)net exports + net interest income + net transfers.
D)net exports + net interest income - net transfers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Suppose that the Australian interest rate is 5 per cent and the Japanese interest rate is 1 per cent. The effect of this difference in the foreign exchange market is that
A)investors expect the yen to appreciate against the dollar.
B)a Japanese investor is guaranteed to make an additional 4 per cent in yen terms by investing in Australia.
C)investors expect the yen to depreciate against the dollar.
D)all funds flow to Australia to get the higher interest rate.
A)investors expect the yen to appreciate against the dollar.
B)a Japanese investor is guaranteed to make an additional 4 per cent in yen terms by investing in Australia.
C)investors expect the yen to depreciate against the dollar.
D)all funds flow to Australia to get the higher interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The current account records all transactions below EXCEPT for
A)net interest income.
B)net transfers.
C)net exports of goods and services.
D)net foreign investment.
A)net interest income.
B)net transfers.
C)net exports of goods and services.
D)net foreign investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The quantity of Australian dollars demanded by foreign nations increases as
A)Australian residents purchase more foreign goods.
B)foreigners purchase more Australian goods.
C)Australian exports fall.
D)more Australian residents travel abroad.
A)Australian residents purchase more foreign goods.
B)foreigners purchase more Australian goods.
C)Australian exports fall.
D)more Australian residents travel abroad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When Australia imports goods and services from the rest of the world,
A)we decrease our inflation rate.
B)we receive payments from the rest of the world.
C)we increase our inflation rate.
D)we make payments to the rest of the world.
A)we decrease our inflation rate.
B)we receive payments from the rest of the world.
C)we increase our inflation rate.
D)we make payments to the rest of the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Australians demand Japanese yen in order to
A)buy Japanese products.
B)balance the current account.
C)supply Australian goods in Japanese markets.
D)allow the Japanese to buy Australian products.
A)buy Japanese products.
B)balance the current account.
C)supply Australian goods in Japanese markets.
D)allow the Japanese to buy Australian products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In the foreign exchange market, which of the following results in a movement along the supply curve of dollars?
A)A change in the expected future exchange rate.
B)A change in the current exchange rate.
C)A change in the Australian interest rate.
D)None of the above answers is correct.
A)A change in the expected future exchange rate.
B)A change in the current exchange rate.
C)A change in the Australian interest rate.
D)None of the above answers is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The nominal exchange rate is
A)a measure of the quantity of the nominal GDP of other countries that we get per unit of Australia's nominal GDP.
B)the real exchange rate multiplied by the ratio of the Australian price level to the foreign price level.
C)the relative price of Australian- produced goods to foreign- produced goods.
D)the value of the Australian dollar expressed in units of foreign currency per Australian dollar.
A)a measure of the quantity of the nominal GDP of other countries that we get per unit of Australia's nominal GDP.
B)the real exchange rate multiplied by the ratio of the Australian price level to the foreign price level.
C)the relative price of Australian- produced goods to foreign- produced goods.
D)the value of the Australian dollar expressed in units of foreign currency per Australian dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If net interest and net transfers are zero, and a country's exports exceed its imports, the country definitely has _ _.
A)a reserve assets account surplus
B)a capital and financial account surplus
C)a current account deficit
D)a current account surplus
A)a reserve assets account surplus
B)a capital and financial account surplus
C)a current account deficit
D)a current account surplus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When there is a current account deficit and the reserve assets account equals 0, then
A)the country has a budget surplus.
B)exports exceed imports for the country.
C)the country is an exporter of capital.
D)the capital and financial account has a surplus.
A)the country has a budget surplus.
B)exports exceed imports for the country.
C)the country is an exporter of capital.
D)the capital and financial account has a surplus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In the foreign exchange market, a change in which of the following will result in a movement along the demand curve for Australian dollars?
A)The interest rate in the foreign country
B)The Australian interest rate
C)The expected future exchange rate
D)The exchange rate
A)The interest rate in the foreign country
B)The Australian interest rate
C)The expected future exchange rate
D)The exchange rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Epsilon is a country whose unit of currency is the omega. New information leads people to expect that the omega will appreciate next year. To keep the foreign exchange value of the omega fairly steady, the Bank of Epsilon will enough omegas on the foreign exchange market so that the omegas will .
A)buy; demand for; increase
B)buy; demand for; decrease
C)buy; supply of; decrease
D)sell; supply of; increase
A)buy; demand for; increase
B)buy; demand for; decrease
C)buy; supply of; decrease
D)sell; supply of; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A net exports deficit or surplus equals
A)net worth plus the government sector balance minus the private sector balance.
B)the government sector balance plus the private sector balance.
C)net lending by both the private and public sector plus savings minus investment.
D)taxes minus savings plus public and private investment.
A)net worth plus the government sector balance minus the private sector balance.
B)the government sector balance plus the private sector balance.
C)net lending by both the private and public sector plus savings minus investment.
D)taxes minus savings plus public and private investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is correct?
A)Net exports equals the current account plus the capital account plus the official settlements account.
B)The private sector balance equals net exports plus the government sector balance.
C)The government sector balance equals net exports plus the private sector balance.
D)Net exports equals the government sector balance plus the private sector balance.
A)Net exports equals the current account plus the capital account plus the official settlements account.
B)The private sector balance equals net exports plus the government sector balance.
C)The government sector balance equals net exports plus the private sector balance.
D)Net exports equals the government sector balance plus the private sector balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which factor can change expectations about the exchange rate?
A)Interest rate parity
B)Purchasing power parity
C)Real GDP parity
D)Both answers A and B are correct.
A)Interest rate parity
B)Purchasing power parity
C)Real GDP parity
D)Both answers A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Other things remaining the same, the the exchange rate for Australian dollars, the greater the in the foreign exchange market.
A)lower; value of Australian imports
B)higher; quantity of Australian dollars demanded
C)higher; expected profits from holding Australian dollars
D)higher; quantity of Australian dollars supplied
A)lower; value of Australian imports
B)higher; quantity of Australian dollars demanded
C)higher; expected profits from holding Australian dollars
D)higher; quantity of Australian dollars supplied

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The current account
A)does not account for interest payments paid to and received from the rest of the world.
B)is part of GDP.
C)measures our imports minus our exports.
D)measures our exports minus our imports, taking into account interest payments paid to and received from the rest of the world.
A)does not account for interest payments paid to and received from the rest of the world.
B)is part of GDP.
C)measures our imports minus our exports.
D)measures our exports minus our imports, taking into account interest payments paid to and received from the rest of the world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A country's balance of payments accounts include all of the following EXCEPT the
A)reserve assets account.
B)capital and financial account.
C)Australian government deficit or surplus.
D)current account.
A)reserve assets account.
B)capital and financial account.
C)Australian government deficit or surplus.
D)current account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Other things remaining the same, the Australian interest rate differential increases if the Australian interest rate
A)falls and foreign interest rates rise.
B)remains constant and foreign interest rates rise.
C)rises and foreign interest rates remain constant.
D)falls and foreign interest rates remain constant.
A)falls and foreign interest rates rise.
B)remains constant and foreign interest rates rise.
C)rises and foreign interest rates remain constant.
D)falls and foreign interest rates remain constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
In the above figure, suppose the demand for dollars permanently decreases to D2. To maintain the target, the Reserve Bank
A)must decrease the nation's net exports.
B)can buy dollars.
C)can sell dollars.
D)The Reserve Bank cannot permanently maintain the exchange rate target of 150 yen per dollar.
A)must decrease the nation's net exports.
B)can buy dollars.
C)can sell dollars.
D)The Reserve Bank cannot permanently maintain the exchange rate target of 150 yen per dollar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If Australia sells beef to Japan, the Australian beef producer is paid with
A)international monetary credits.
B)yen, the Japanese currency.
C)Australian dollars.
D)euros, or any other third currency.
A)international monetary credits.
B)yen, the Japanese currency.
C)Australian dollars.
D)euros, or any other third currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
As the value of Australian exports , the quantity of _ demanded increases.
A)increases; Australian dollars
B)decreases; Australian dollars
C)increases; foreign currencies
D)None of the above is correct because the value of Australian exports has nothing to do with the quantity of dollars or foreign currency.
A)increases; Australian dollars
B)decreases; Australian dollars
C)increases; foreign currencies
D)None of the above is correct because the value of Australian exports has nothing to do with the quantity of dollars or foreign currency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 154 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



