Deck 2: The Economic Problem
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/129
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: The Economic Problem
1
A person who has an absolute advantage in the production of all goods will
A)have a production possibilities frontier with a constant slope.
B)have a comparative advantage in the production of some goods but not in the production of others.
C)also have a comparative advantage in the production of all goods.
D)not be able to gain from specialisation and exchange.
A)have a production possibilities frontier with a constant slope.
B)have a comparative advantage in the production of some goods but not in the production of others.
C)also have a comparative advantage in the production of all goods.
D)not be able to gain from specialisation and exchange.
have a comparative advantage in the production of some goods but not in the production of others.
2
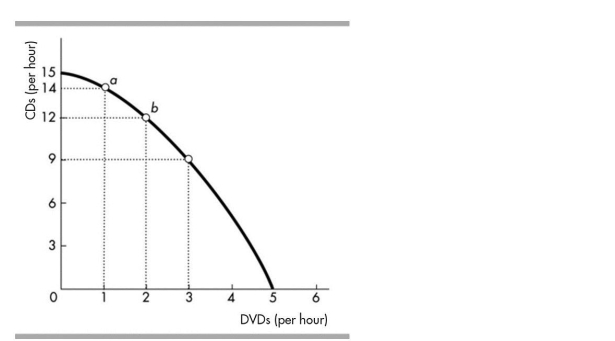
In the above figure, at point a, what is the opportunity cost of producing one more CD?
A)2 DVDs.
B)1 DVD.
C)14 DVDs.
D)There is no opportunity cost.
1 DVD.
3
When the production possibilities frontier is bowed outwards, the opportunity cost of producing more of one good
A)decreases in terms of the amount forgone of the other good.
B)remains constant.
C)increases in terms of the amount forgone of the other good.
D)cannot be determined.
A)decreases in terms of the amount forgone of the other good.
B)remains constant.
C)increases in terms of the amount forgone of the other good.
D)cannot be determined.
increases in terms of the amount forgone of the other good.
4
The principle of decreasing marginal benefit implies that the
A)additional benefit from obtaining one more of a good or service decreases as more is consumed.
B)total benefit from obtaining more of a good or service decreases as more is consumed.
C)total benefit from obtaining more of a good or service remains the same as more is consumed.
D)additional benefit from obtaining one more of a good or service increases as more is consumed.
A)additional benefit from obtaining one more of a good or service decreases as more is consumed.
B)total benefit from obtaining more of a good or service decreases as more is consumed.
C)total benefit from obtaining more of a good or service remains the same as more is consumed.
D)additional benefit from obtaining one more of a good or service increases as more is consumed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Moving from one point on the production possibilities frontier to another
A)involves an opportunity cost but no tradeoff.
B)involves a tradeoff and incurs an opportunity cost.
C)involves a tradeoff but does not incur an opportunity cost.
D)involves no tradeoff but it does incur an opportunity cost.
A)involves an opportunity cost but no tradeoff.
B)involves a tradeoff and incurs an opportunity cost.
C)involves a tradeoff but does not incur an opportunity cost.
D)involves no tradeoff but it does incur an opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
One of the opportunity costs of economic growth is
A)reduced current consumption.
B)technological change.
C)the gain in future consumption.
D)capital accumulation.
A)reduced current consumption.
B)technological change.
C)the gain in future consumption.
D)capital accumulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Scarcity is represented on a production possibilities frontier figure by
A)the amount of the good on the horizontal axis forgone.
B)technological progress.
C)the fact that there are only two goods in the diagram.
D)the fact that there are attainable and unattainable points.
A)the amount of the good on the horizontal axis forgone.
B)technological progress.
C)the fact that there are only two goods in the diagram.
D)the fact that there are attainable and unattainable points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
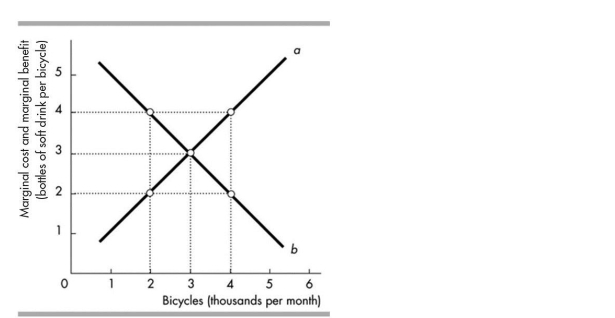
In the above figure, when 2000 bicycles are produced each month, we can see that
A)the marginal benefit from another bicycle is greater than the marginal cost of another bicycle.
B)more bicycles should be produced to reach the allocatively efficient level of output.
C)the economy is very efficient at the production of bicycles because the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost.
D)Both answers A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9

In the figure above, both Joe and Jill initially produce at point A. If Joe and Jill realise that they each possess a comparative advantage, which outcome can we expect?
A)Joe will specialise in shirts and Jill will specialise in pants.
B)Joe will specialise in pants and Jill will specialise in shirts.
C)Joe and Jill each will be able to consume more than 2 shirts and 2 pairs of pants.
D)Both answers B and C are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Markets
A)allow traders to enjoy gains from trade.
B)coordinate price information between buyers and sellers.
C)facilitate trade.
D)All of the above answers are correct.
A)allow traders to enjoy gains from trade.
B)coordinate price information between buyers and sellers.
C)facilitate trade.
D)All of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A marginal cost curve
A)is upward sloping.
B)shows that as more of a good is produced, opportunity costs of producing another unit increase.
C)is bowed inward so that its slope can become negative.
D)Both answers A and B are correct.
A)is upward sloping.
B)shows that as more of a good is produced, opportunity costs of producing another unit increase.
C)is bowed inward so that its slope can become negative.
D)Both answers A and B are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12

In the figure above, the marginal cost of the second computer is
A)2 television sets.
B)30 television sets.
C)5 television sets.
D)3 television sets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13

In the above figure, in order for this country to move from production possibilities frontier PPF1 to
PPF2, it might
A)engage in exchange with other nations.
B)increase the average level of prices for all goods produced and consumed.
C)increase the skills and productivity of its work force.
D)put all unemployed resources to work producing desired output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
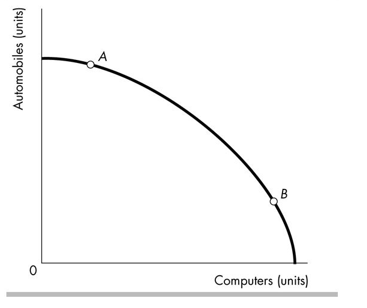
According to the figure above, the opportunity cost of producing another computer is
A)higher at A.
B)higher at B.
C)the same at every point along the frontier.
D)different at most points along the frontier but equal at points A and B because they are equally distant from the axes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Capital accumulation definitely
A)shifts the production possibilities frontier inward.
B)shifts the production possibilities frontier outward.
C)has no impact on the production possibilities frontier.
D)makes the production possibilities frontier steeper.
A)shifts the production possibilities frontier inward.
B)shifts the production possibilities frontier outward.
C)has no impact on the production possibilities frontier.
D)makes the production possibilities frontier steeper.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An increase in the production of capital goods
A)shifts the production possibilities frontier outward in the future.
B)must increase the current production of consumer goods.
C)must decrease the future production of consumer goods.
D)shifts the production possibilities frontier inward in the future.
A)shifts the production possibilities frontier outward in the future.
B)must increase the current production of consumer goods.
C)must decrease the future production of consumer goods.
D)shifts the production possibilities frontier inward in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
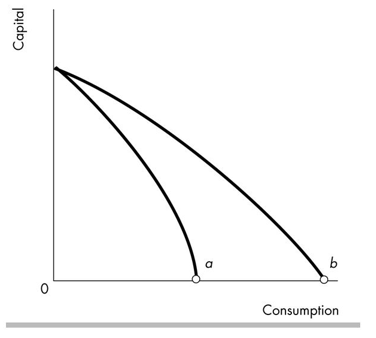
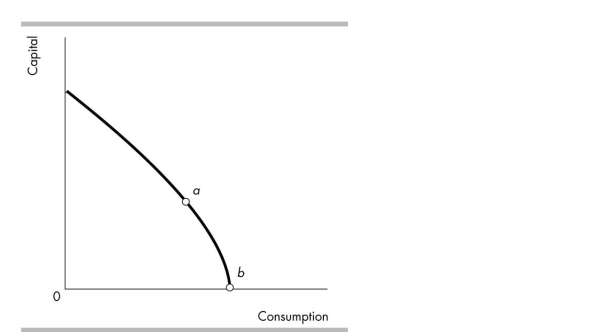
The opportunity cost of producing a unit of consumption goods at point b in the figure _ point a.
A)is greater than at
B)is the same as
C)is less than at
D)cannot be compared with

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Economic growth can be represented by
A)a movement down the production possibilities frontier (PPF).
B)an inward shift of the production possibilities frontier (PPF).
C)a movement up the production possibilities frontier (PPF).
D)an outward shift of the production possibilities frontier (PPF).
A)a movement down the production possibilities frontier (PPF).
B)an inward shift of the production possibilities frontier (PPF).
C)a movement up the production possibilities frontier (PPF).
D)an outward shift of the production possibilities frontier (PPF).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The production possibilities frontier itself illustrates
A)all goods that can be produced by an economy.
B)all possible production of capital goods.
C)all goods and services that are desired but cannot be produced due to scarce resources.
D)the combination of goods and services that can be produced efficiently.
A)all goods that can be produced by an economy.
B)all possible production of capital goods.
C)all goods and services that are desired but cannot be produced due to scarce resources.
D)the combination of goods and services that can be produced efficiently.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements regarding the production possibilities frontier is true?
A)Points inside the frontier are attainable.
B)Points outside the frontier are attainable.
C)Points on the frontier are less efficient than points inside the frontier.
D)None of the above because all of the above statements are false.
A)Points inside the frontier are attainable.
B)Points outside the frontier are attainable.
C)Points on the frontier are less efficient than points inside the frontier.
D)None of the above because all of the above statements are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Production efficiency occurs when production
A)is on the production possibilities frontier.
B)is on the production possibilities frontier or inside it.
C)is at any attainable point.
D)is at a point beyond the production possibilities frontier.
A)is on the production possibilities frontier.
B)is on the production possibilities frontier or inside it.
C)is at any attainable point.
D)is at a point beyond the production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A tradeoff is
A)a transaction at a price either above or below the equilibrium price.
B)a constraint that requires giving up one thing to get another.
C)represented by a point outside a PPF.
D)represented by a point inside a PPF.
A)a transaction at a price either above or below the equilibrium price.
B)a constraint that requires giving up one thing to get another.
C)represented by a point outside a PPF.
D)represented by a point inside a PPF.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Resource use is allocatively efficient when
A)we produce the amount of the different goods we value most highly.
B)we produce the goods with the lowest opportunity cost.
C)we cannot produce more goods and services.
D)we produce the goods with the highest opportunity cost.
A)we produce the amount of the different goods we value most highly.
B)we produce the goods with the lowest opportunity cost.
C)we cannot produce more goods and services.
D)we produce the goods with the highest opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Some time ago the government of China required many highly skilled technicians and scientists to engage in unskilled agricultural labour in order to develop "proper social attitudes." This policy probably caused China to produce
A)inside its production possibilities frontier with respect to food, but outside with respect to high- technology goods.
B)inside its production possibilities frontier.
C)outside its production possibilities frontier with respect to food, but inside with respect to high- technology goods.
D)at an inappropriate point along its production possibilities frontier.
A)inside its production possibilities frontier with respect to food, but outside with respect to high- technology goods.
B)inside its production possibilities frontier.
C)outside its production possibilities frontier with respect to food, but inside with respect to high- technology goods.
D)at an inappropriate point along its production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If an economy is operating at a point inside the production possibilities frontier, then
A)the PPF curve will shift inward.
B)society's resources are being inefficiently utilised.
C)economic policy must retard further growth of the economy.
D)society's resources are being used to produce too many consumer goods.
A)the PPF curve will shift inward.
B)society's resources are being inefficiently utilised.
C)economic policy must retard further growth of the economy.
D)society's resources are being used to produce too many consumer goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Homer and Teddy are stranded on a desert island. To feed themselves each day they can either catch fish or pick fruit. In a day, Teddy could pick 60 pieces of fruit or catch 20 fish. Homer could pick 100 pieces of fruit or catch 150 fish. Which of the following statements is correct?
A)Homer has an absolute advantage in picking fruit and Teddy has an absolute advantage in catching fish.
B)Teddy has an absolute advantage in both catching fish and picking fruit.
C)Homer has an absolute advantage in catching fish and Teddy has an absolute advantage in picking fruit.
D)Homer has an absolute advantage in both catching fish and picking fruit.
A)Homer has an absolute advantage in picking fruit and Teddy has an absolute advantage in catching fish.
B)Teddy has an absolute advantage in both catching fish and picking fruit.
C)Homer has an absolute advantage in catching fish and Teddy has an absolute advantage in picking fruit.
D)Homer has an absolute advantage in both catching fish and picking fruit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Suppose Joe can prepare 20 sandwiches or 10 pizzas in an hour and Beth can produce 36 sandwiches or 27 pizzas. The concept of comparative advantage concludes that
A)Beth should produce both goods because she can produce more of both goods in an hour than can Joe.
B)Beth should produce both goods and Joe should produce sandwiches.
C)Beth should produce sandwiches and Joe should produce pizza.
D)Beth should produce pizza and Joe should produce sandwiches.
A)Beth should produce both goods because she can produce more of both goods in an hour than can Joe.
B)Beth should produce both goods and Joe should produce sandwiches.
C)Beth should produce sandwiches and Joe should produce pizza.
D)Beth should produce pizza and Joe should produce sandwiches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
According to the principle of comparative advantage, if a rich country trades with a poor country, then
A)the rich country will lose and the poor country will benefit.
B)the rich country will benefit and the poor country will lose.
C)both countries will benefit.
D)neither of the countries will benefit.
A)the rich country will lose and the poor country will benefit.
B)the rich country will benefit and the poor country will lose.
C)both countries will benefit.
D)neither of the countries will benefit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
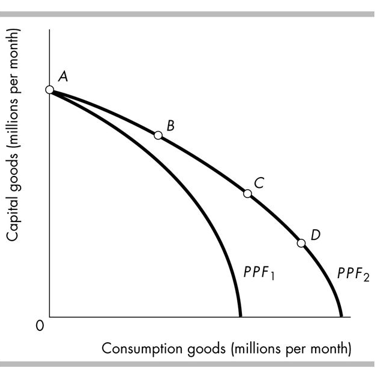
In the above figure, once on PPF2, a country would grow slowest by producing at point
A)C.
B)B.
C)D.
D)A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In goods markets and in factor markets _ .
A)firms sell to households; households sell to firms
B)households sell to firms; firms sell to households
C)households sell to firms; households sell to firms
D)firms sell to households; firms sell to households
A)firms sell to households; households sell to firms
B)households sell to firms; firms sell to households
C)households sell to firms; households sell to firms
D)firms sell to households; firms sell to households

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
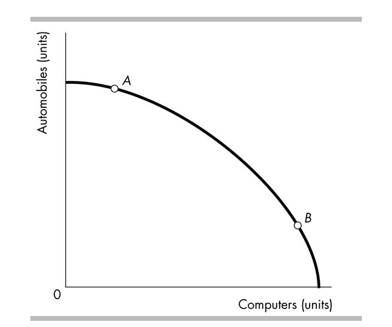
The bowed outward shape of the production possibilities frontier in the above figure indicates that
A)computer technology is subject to the principle of decreasing costs.
B)some resources are better suited for producing computers.
C)the opportunity cost of producing more computers decreases as more computers are produced.
D)All of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Two countries, Alpha and Beta, have identical production possibilities frontiers. If Alpha produces at point a and Beta produces at point b, then
A)Alpha's and Beta's economic growth rates will be the same.
B)Beta's economic growth rate will exceed Alpha's.
C)Beta's future consumption will be greater than Alpha's.
D)Alpha consumes less than Beta today, but it will grow faster than Beta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
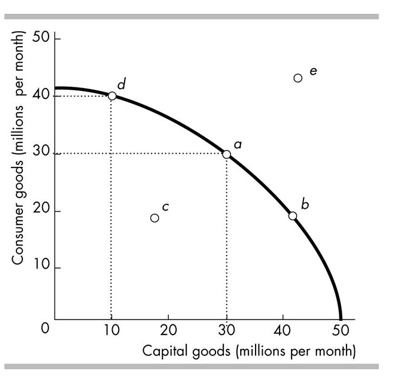
Refer to the production possibilities frontier in the figure above. Which production point is unattainable?
A)Point a
B)Point b
C)Point c
D)Point e

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
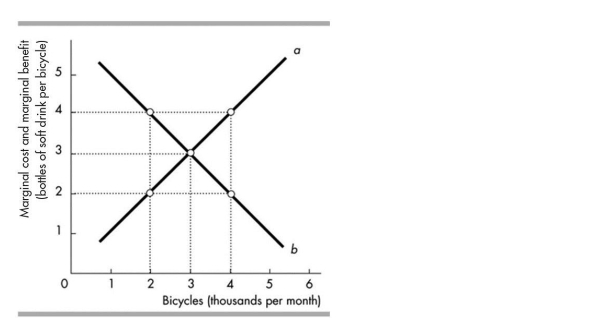
In the above figure, curve b shows the
A)bottles of cola that people are willing to forgo to get another bicycle.
B)benefits of producing more bicycles is greater than the benefits of producing more cola.
C)bottles of cola that people must forgo to get another bicycle.
D)benefits of producing more cola is greater than the benefits of producing more bicycles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
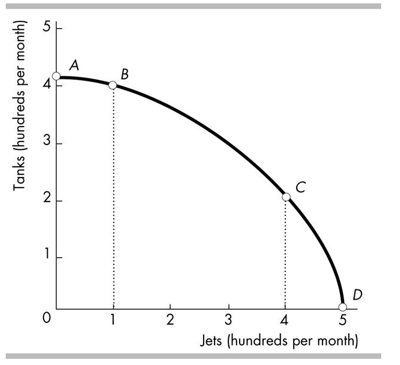
In the above figure, which of the following is true regarding the movements from point A to B and from point C to D?
A)I and II
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Suppose a scientific breakthrough made free solar power available in unlimited quantities in Australia. The effect of this invention would be to move
A)the Australian production possibilities frontier outward.
B)Australia beyond its production possibilities frontier.
C)Australia inside its production possibilities frontier.
D)the Australian production possibilities frontier inward.
A)the Australian production possibilities frontier outward.
B)Australia beyond its production possibilities frontier.
C)Australia inside its production possibilities frontier.
D)the Australian production possibilities frontier inward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A person has a comparative advantage in producing a particular good if that person
A)has higher productivity in producing it than anyone else has.
B)has less desire to consume that good than anyone else has.
C)can produce it at lower opportunity cost than anyone else can.
D)has more human capital related to that good than anyone else has.
A)has higher productivity in producing it than anyone else has.
B)has less desire to consume that good than anyone else has.
C)can produce it at lower opportunity cost than anyone else can.
D)has more human capital related to that good than anyone else has.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A PPF bows outward because
A)not all resources are equally productive in all activities.
B)resources are used inefficiently.
C)entrepreneurial talent is more abundant than human capital.
D)consumers prefer about equal amounts of the different goods.
A)not all resources are equally productive in all activities.
B)resources are used inefficiently.
C)entrepreneurial talent is more abundant than human capital.
D)consumers prefer about equal amounts of the different goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When resources are assigned to inappropriate tasks, the result will be producing at a point
A)outside the PPF.
B)where the slope of the PPF is zero.
C)inside the PPF.
D)where the slope of the PPF is positive.
A)outside the PPF.
B)where the slope of the PPF is zero.
C)inside the PPF.
D)where the slope of the PPF is positive.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Betty and Ann live on a desert island. With a day's labour, Ann can produce 8 fish or 4 coconuts; Betty can produce 6 fish or 2 coconuts. Ann's opportunity cost of producing 1 coconut is and she should specialise in the production of .
A)0 fish per coconut; coconuts
B)6 fish per coconut; coconuts
C)8 fish per coconut; fish
D)2 fish per coconut; coconuts
A)0 fish per coconut; coconuts
B)6 fish per coconut; coconuts
C)8 fish per coconut; fish
D)2 fish per coconut; coconuts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
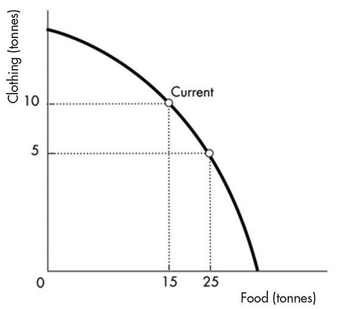
The above figure illustrates that if this country wishes to move from its current production point (labelled "Current")and have 10 more tonnes of food, it can do this by producing
A)10 more tonnes of clothing.
B)5 more tonnes of clothing.
C)10 fewer tonnes of clothing.
D)5 fewer tonnes of clothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Suppose that the government is trying to decide between allocating its resources to build more dams or to build more freeways. In terms of forgone dams, as more freeways are constructed, the marginal benefit of additional freeways _ and the marginal cost of additional freeways
.
A)increases; decreases
B)increases; increases
C)decreases; decreases
D)decreases; increases
.
A)increases; decreases
B)increases; increases
C)decreases; decreases
D)decreases; increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
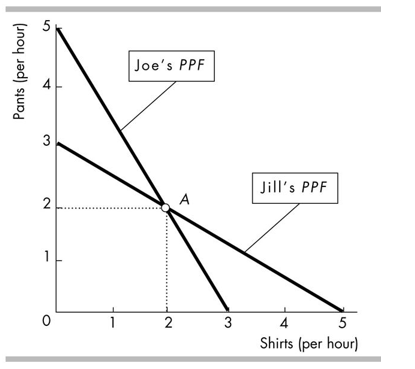
In the figure above, Joe is producing at point A. Joe's opportunity cost of producing one shirt is
A)2 pairs of pants per shirt.
B)3/5 of a pair of pants per shirt.
C)5 pairs of pants per shirt.
D)5/3 of a pair of pants per shirt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Marginal cost is the one more unit of a good and of the good increases.
A)price that must be paid to consume; increases as consumption
B)opportunity cost of producing; increases as production
C)opportunity cost of producing; decreases as production
D)price that must be paid to consume; decreases as consumption
A)price that must be paid to consume; increases as consumption
B)opportunity cost of producing; increases as production
C)opportunity cost of producing; decreases as production
D)price that must be paid to consume; decreases as consumption

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Betty and Ann live on a desert island. With a day's labour, Ann can produce 6 fish or 4 coconuts; Betty can produce 3 fish or 1 coconut. Betty's opportunity cost of producing 1 fish is , and she should specialise in the production of .
A)1 coconut per fish; fish
B)4 coconuts per fish; fish
C)2/3 coconut per fish; coconuts
D)1/3 coconut per fish; fish
A)1 coconut per fish; fish
B)4 coconuts per fish; fish
C)2/3 coconut per fish; coconuts
D)1/3 coconut per fish; fish

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
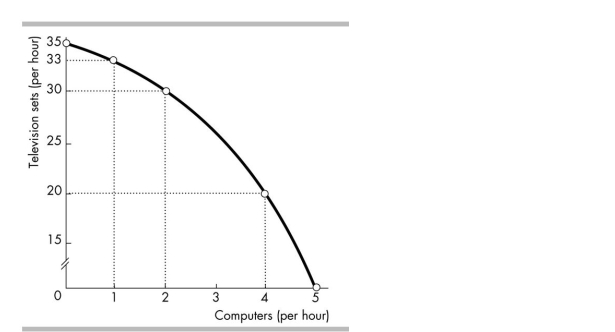
In the figure above, the marginal cost of producing a computer
A)is the same as the marginal cost of producing a television set.
B)stays the same as more computers are produced.
C)increases as more computers are produced.
D)decreases as more computers are produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
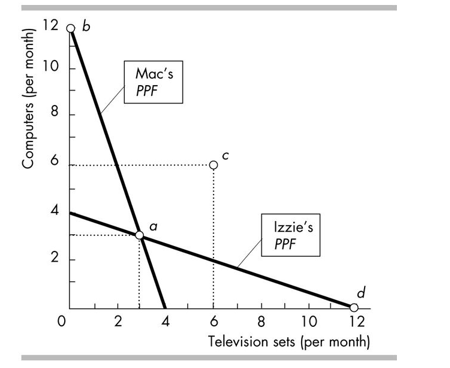
In the figure above, suppose that Mac and Izzie specialise and trade to reach point c. Mac sends Izzie
A)12 computers in exchange for 6 TVs.
B)6 computers in exchange for 12 TVs.
C)12 computers in exchange for 12 TVs.
D)6 computers in exchange for 6 TVs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Resource use is allocatively efficient when marginal benefit is
A)less than marginal cost.
B)greater than marginal cost.
C)equal to marginal cost.
D)at its maximum value.
A)less than marginal cost.
B)greater than marginal cost.
C)equal to marginal cost.
D)at its maximum value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Economic growth is the result of all of the following EXCEPT
A)opportunity cost.
B)technological change.
C)capital accumulation.
D)investment in human capital.
A)opportunity cost.
B)technological change.
C)capital accumulation.
D)investment in human capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
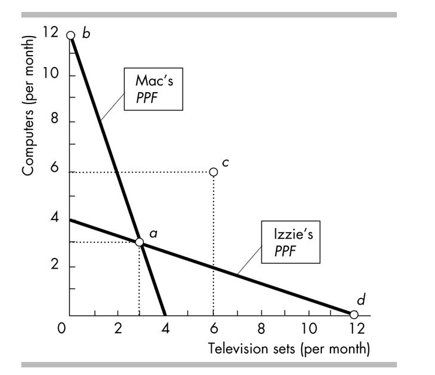
In the figure above, suppose that Mac and Izzie trade and reach point c. Then
A)Mac should produce at point b and Izzie should produce at point d.
B)Mac should produce at point d and Izzie should produce at point b.
C)Mac and Izzie should both produce at point a.
D)Mac and Izzie should both produce at point c.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A nation's production possibilities frontier is bowed outward. Suppose that the government decides to increase the production of armaments by $20 billion, and that as a result the output of consumer goods falls by $20 billion. If a further $20 billion increase beyond the initial $20 billion increase in armaments output is sought, we can expect that the output of consumer goods and services will fall further by
A)less than $20 billion.
B)more than $20 billion.
C)$20 billion.
D)There is not enough information to determine the answer.
A)less than $20 billion.
B)more than $20 billion.
C)$20 billion.
D)There is not enough information to determine the answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Marginal cost
A)remains constant as more is produced.
B)decreases as marginal benefits decrease.
C)increases as more is produced.
D)decreases as more is produced.
A)remains constant as more is produced.
B)decreases as marginal benefits decrease.
C)increases as more is produced.
D)decreases as more is produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
When economic growth occurs, the
A)production possibilities frontier shifts outward.
B)production possibilities frontier becomes steeper.
C)economy moves along its production possibilities frontier.
D)production possibilities frontier shifts outward but no longer limits the amount that can be produced.
A)production possibilities frontier shifts outward.
B)production possibilities frontier becomes steeper.
C)economy moves along its production possibilities frontier.
D)production possibilities frontier shifts outward but no longer limits the amount that can be produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
As an economy's capital stock increases, the economy
A)gains an absolute advantage in the production of capital goods.
B)experiences economic growth.
C)generally decides to engage in international trade.
D)generally experiences increased unemployment of other resources, such as labour.
A)gains an absolute advantage in the production of capital goods.
B)experiences economic growth.
C)generally decides to engage in international trade.
D)generally experiences increased unemployment of other resources, such as labour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A computer software program is most strongly an example of
A)intellectual property.
B)real property.
C)vicarious property.
D)fiat property.
A)intellectual property.
B)real property.
C)vicarious property.
D)fiat property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Tom takes 20 minutes to cook an egg and 5 minutes to make a sandwich. Jerry takes 15 minutes to cook an egg and 3 minutes to make a sandwich. Both individuals will be better off if
A)they don't trade as no one has the comparative advantage in either of the two goods.
B)they trade, no matter who trades sandwiches and who eggs.
C)Jerry trades sandwiches in exchange for eggs.
D)Tom trades sandwiches in exchange for eggs.
A)they don't trade as no one has the comparative advantage in either of the two goods.
B)they trade, no matter who trades sandwiches and who eggs.
C)Jerry trades sandwiches in exchange for eggs.
D)Tom trades sandwiches in exchange for eggs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In March a factory used new technology to produce its output. Then in August a fire destroyed half the factory. The new technology shifted the factory's PPF _ and the fire shifted it _.
A)outward; outward
B)inward; outward
C)outward; inward
D)inward; inward
A)outward; outward
B)inward; outward
C)outward; inward
D)inward; inward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Individual economic decisions are coordinated by
A)governments through adjustments in income taxes.
B)governments through adjustments in sales taxes.
C)markets through adjustments in sales levels.
D)markets through adjustments in prices.
A)governments through adjustments in income taxes.
B)governments through adjustments in sales taxes.
C)markets through adjustments in sales levels.
D)markets through adjustments in prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If property rights are not clearly defined and enforced, then
A)resources are devoted to protecting possessions rather than to production.
B)incentives for specialisation based on comparative advantage are weakened.
C)some potential gains from specialisation and trade are lost.
D)All of the above answers are correct.
A)resources are devoted to protecting possessions rather than to production.
B)incentives for specialisation based on comparative advantage are weakened.
C)some potential gains from specialisation and trade are lost.
D)All of the above answers are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The production possibilities frontier is the boundary between
A)those wants that are limited and those that are unlimited.
B)those combinations of goods and services that can be produced and those that can be consumed.
C)those resources that are limited and those that are unlimited.
D)those combinations of goods and services that can be produced and those that cannot.
A)those wants that are limited and those that are unlimited.
B)those combinations of goods and services that can be produced and those that can be consumed.
C)those resources that are limited and those that are unlimited.
D)those combinations of goods and services that can be produced and those that cannot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Marginal cost curves slope
A)downward because of increasing opportunity cost.
B)downward because of decreasing opportunity cost.
C)upward because of increasing opportunity cost.
D)upward because of decreasing opportunity cost.
A)downward because of increasing opportunity cost.
B)downward because of decreasing opportunity cost.
C)upward because of increasing opportunity cost.
D)upward because of decreasing opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Harry produces two balloon rides and four boat rides an hour. Harry could produce more balloon rides but to do so he must produce fewer boat rides. Harry is his production possibilities frontier.
A)producing either inside or on
B)producing inside
C)producing on
D)producing outside
A)producing either inside or on
B)producing inside
C)producing on
D)producing outside

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
When we cannot produce more of any good without giving up some other good that we value more highly, we have achieved
A)the production point where the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost by as much as possible.
B)equity.
C)allocative efficiency.
D)economic growth.
A)the production point where the marginal benefit exceeds the marginal cost by as much as possible.
B)equity.
C)allocative efficiency.
D)economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When operating on its PPF, a country can produce two tonnes of butter and 200 cars OR three tonnes of butter and 150 cars. The opportunity cost of one tonne of butter is cars per tonne of butter.
A)50
B)0.75
C)300
D)200
A)50
B)0.75
C)300
D)200

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
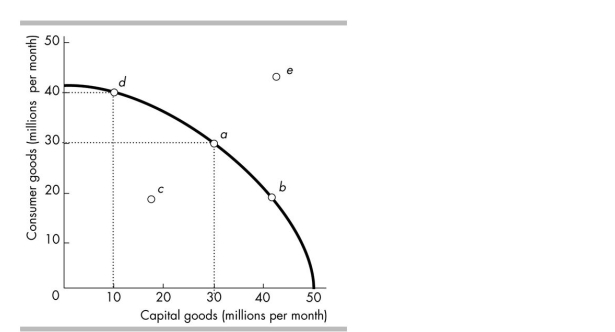
Refer to the production possibilities frontier in the figure above. Suppose a country is producing at point a. A movement to point means that the country .
A)b; is producing at an inefficient point.
B)e; is not operating efficiently
C)d; gives up 10 million consumer goods.
D)d; must give up 20 million capital goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
We measure the marginal _ of a good by what a for another unit of the good.
A)cost; person's preferences are
B)cost; person is willing to pay
C)benefit; person must pay
D)benefit; person is willing to pay
A)cost; person's preferences are
B)cost; person is willing to pay
C)benefit; person must pay
D)benefit; person is willing to pay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Comparative advantage is
A)the ability to perform an activity at a lower opportunity cost than anyone else.
B)the ability to perform an activity at a zero opportunity cost.
C)the ability to perform an activity at a higher opportunity cost than anyone else.
D)another name for absolute advantage.
A)the ability to perform an activity at a lower opportunity cost than anyone else.
B)the ability to perform an activity at a zero opportunity cost.
C)the ability to perform an activity at a higher opportunity cost than anyone else.
D)another name for absolute advantage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Jane produces only corn and cloth. Taking account of her preferences for corn and cloth
A)makes her production possibilities frontier flatter.
B)makes her production possibilities frontier steeper.
C)makes her production possibilities frontier straighter.
D)does not affect her production possibilities frontier.
A)makes her production possibilities frontier flatter.
B)makes her production possibilities frontier steeper.
C)makes her production possibilities frontier straighter.
D)does not affect her production possibilities frontier.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The production possibilities frontier separates
A)the combinations of goods that people value and those that they don't.
B)the types of goods that can be attained from those that can't be attained.
C)the goods and services people want from those they do not want.
D)the quantities of goods and services that can be produced from those that cannot be produced.
A)the combinations of goods that people value and those that they don't.
B)the types of goods that can be attained from those that can't be attained.
C)the goods and services people want from those they do not want.
D)the quantities of goods and services that can be produced from those that cannot be produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Economic growth comes from
A)capital accumulation and the avoidance of opportunity cost.
B)people willing to increase their skills, in which case, economic growth is free.
C)producing more goods than people want to consume.
D)capital accumulation and technological advance.
A)capital accumulation and the avoidance of opportunity cost.
B)people willing to increase their skills, in which case, economic growth is free.
C)producing more goods than people want to consume.
D)capital accumulation and technological advance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
If the marginal benefit of a good exceeds its marginal cost,
A)we should produce less to achieve the allocatively efficient use of resources.
B)we should produce more to achieve the allocatively efficient use of resources.
C)we've achieved efficient resource use.
D)we cannot tell if more or less should be produced to achieve the allocatively efficient use of resources.
A)we should produce less to achieve the allocatively efficient use of resources.
B)we should produce more to achieve the allocatively efficient use of resources.
C)we've achieved efficient resource use.
D)we cannot tell if more or less should be produced to achieve the allocatively efficient use of resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The term "market" refers to
A)physical structures only.
B)trading arrangements that have been approved by the government.
C)locations where buyers and sellers physically meet.
D)any arrangement that enables buyers and sellers to get information and trade with one another.
A)physical structures only.
B)trading arrangements that have been approved by the government.
C)locations where buyers and sellers physically meet.
D)any arrangement that enables buyers and sellers to get information and trade with one another.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Allocative efficiency occurs when
A)we cannot produce more of any good without giving up some other good that we value more highly.
B)opportunity costs are decreasing.
C)marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost.
D)we cannot produce more of any one good without giving up some other good.
A)we cannot produce more of any good without giving up some other good that we value more highly.
B)opportunity costs are decreasing.
C)marginal benefit exceeds marginal cost.
D)we cannot produce more of any one good without giving up some other good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
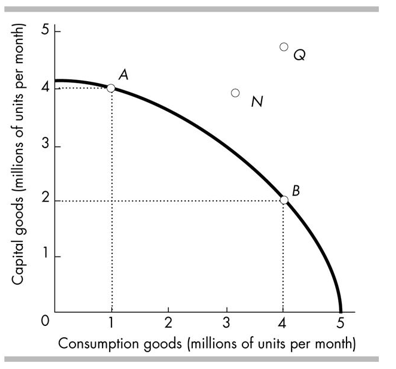
In 2006, Country X and Country Y had the same production possibilities, illustrated in the figure above. Country X chose to produce at point A, while country Y chose to produce at point B. In 2012, most likely, Country X will be at a point such as _ while Country Y will be at a point such as .
A)N; Q
B)A; B
C)Q; N
D)B; A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Which of the following is NOT illustrated by a production possibilities frontier?
A)Opportunity cost
B)The necessity for choice
C)Who gets the goods
D)Scarcity
A)Opportunity cost
B)The necessity for choice
C)Who gets the goods
D)Scarcity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
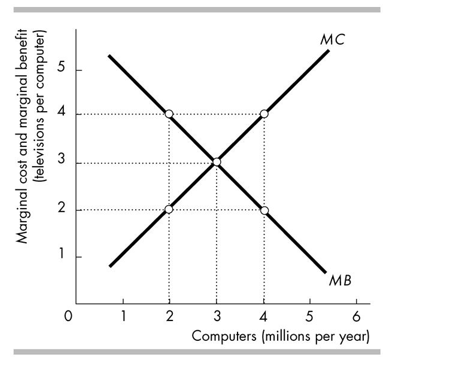
In the figure above, at the allocatively efficient level of computer production consumers are willing to give up
A)3 televisions per computer.
B)more than 3 televisions per computer.
C)0 televisions per computer.
D)between 0 and 3 televisions per computer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Susan likes to drink colas. The cola Susan drinks, the of the last cola.
A)less; higher the opportunity cost
B)more; higher the marginal benefit
C)less; lower the marginal benefit
D)more; lower the marginal benefit
A)less; higher the opportunity cost
B)more; higher the marginal benefit
C)less; lower the marginal benefit
D)more; lower the marginal benefit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78

In the above figure, the curve labelled a is the curve and the curve labelled b is the
Curve.
A)marginal cost; marginal benefit
B)production possibilities frontier; trade line
C)marginal benefit; trade line
D)marginal cost; trade line

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
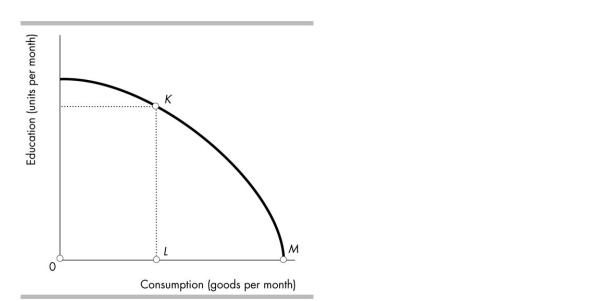
Molly just graduated from high school. The figure shows her possibilities frontier. If Molly goes to university, she will move from point M to point K. In terms of consumption goods, Molly's opportunity cost of going to university is
A)OL.
B)MK.
C)LM.
D)KL.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following is true regarding markets?
A)I only
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II and III
A)I only
B)I and III
C)II and III
D)I, II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 129 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



