Deck 3: Expressions and Interactivity
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/40
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Expressions and Interactivity
1
Which of the following statements doubles the value stored in answer?
A)answer += 2;
B)answer *= 2;
C)answer = answer * 2;
D)All three of the above
E)Both B and C, but not A
A)answer += 2;
B)answer *= 2;
C)answer = answer * 2;
D)All three of the above
E)Both B and C, but not A
E
2
Program code that can be evaluated to a value is called a(n)
A)evaluator.
B)operation.
C)result.
D)line.
E)expression.
A)evaluator.
B)operation.
C)result.
D)line.
E)expression.
E
3
What does the following C++ expression evaluate to? 6 - 6 / 3 + 3
A)0
B)7
C)3
D)5
E)None of the above
A)0
B)7
C)3
D)5
E)None of the above
B
4
To use stream manipulators, you should include the _ header file.
A)iomanip
B)format
C)fstream
D)stream
E)iostream
A)iomanip
B)format
C)fstream
D)stream
E)iostream

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The statement cout << setw(4)<< num4 << " ";
A)outputs the value of num4 rounded to 4 decimal places.
B)outputs the first 4 digits of the number stored in num4.
C)outputs "setw(4)" before the value in the variable num4.
D)outputs the value stored in num4 four times.
E)does none of above.
A)outputs the value of num4 rounded to 4 decimal places.
B)outputs the first 4 digits of the number stored in num4.
C)outputs "setw(4)" before the value in the variable num4.
D)outputs the value stored in num4 four times.
E)does none of above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
can be used to override the rules of operator precedence.
A)Parentheses
B)Associativity
C)Operands
D)Some operators
E)Nothing
A)Parentheses
B)Associativity
C)Operands
D)Some operators
E)Nothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following expressions will evaluate to 2.5?
A)static_cast(5 / 2)
B)5 / static_cast(2)
C)static_cast(5)/ 2
D)All three of the above
E)Both B and C, but not A
A)static_cast
B)5 / static_cast
C)static_cast
D)All three of the above
E)Both B and C, but not A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The stream manipulator can be used to establish a field width for the value immediately following it.
A)setField
B)cin
C)setw
D)width
E)iomanip
A)setField
B)cin
C)setw
D)width
E)iomanip

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When converting some algebraic expressions to C++, you may need to insert and that do not appear in the algebraic expression.
A)operators, calculations
B)values, exponents
C)operands, parentheses
D)operators, parentheses
E)operators, operands
A)operators, calculations
B)values, exponents
C)operands, parentheses
D)operators, parentheses
E)operators, operands

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The object causes data to be input from the keyboard.
A)keyboard buffer
B)cout
C)dataIn
D)cin
E)standard input
A)keyboard buffer
B)cout
C)dataIn
D)cin
E)standard input

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
When an arithmetic expression contains two or more different operators, such as * and +, the order in which the operations is done is determined by
A)the compiler.
B)the programmer.
C)operator associativity.
D)left to right order.
E)operator precedence.
A)the compiler.
B)the programmer.
C)operator associativity.
D)left to right order.
E)operator precedence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When the final value of an expression is assigned to a variable, it will be converted to
A)the largest possible data type.
B)the smallest possible data type.
C)the data type of the variable.
D)the data type of the expression.
E)none of the above.
A)the largest possible data type.
B)the smallest possible data type.
C)the data type of the variable.
D)the data type of the expression.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The following 4 lines of C++ code, use strings. 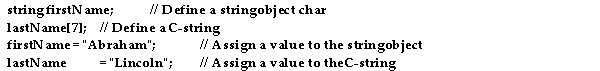 Which of the following statements is /are true?
Which of the following statements is /are true?
A)The C- string is assigned a value correctly, but the string object is not.
B)The string object is defined incorrectly because no size is given for it.
C)The string object is assigned a value correctly, but the C- string is not.
D)The 2 string definitions are correct, but the 2 assignment statements are wrong.
E)All 4 lines of code are correct.
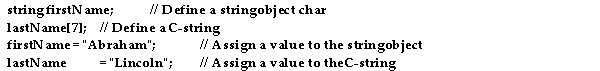 Which of the following statements is /are true?
Which of the following statements is /are true?A)The C- string is assigned a value correctly, but the string object is not.
B)The string object is defined incorrectly because no size is given for it.
C)The string object is assigned a value correctly, but the C- string is not.
D)The 2 string definitions are correct, but the 2 assignment statements are wrong.
E)All 4 lines of code are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In C++, a value can be raised to a power by using
A)the exp operator.
B)the ^ operator.
C)the power operator.
D)the pow function.
E)the square function.
A)the exp operator.
B)the ^ operator.
C)the power operator.
D)the pow function.
E)the square function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following will allow an entire line of text to be read into a string object, even if it contains embedded blanks?
A)cin.get()
B)getline()
C)cin.ignore()
D)cin >>
E)both A and B, but not C or D.
A)cin.get()
B)getline()
C)cin.ignore()
D)cin >>
E)both A and B, but not C or D.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
To use the sqrt()function, or other mathematical library functions, you must #include the header file in your program.
A)cmath
B)mathlib
C)iomanip
D)iostream
E)algebra
A)cmath
B)mathlib
C)iomanip
D)iostream
E)algebra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
causes a program to wait until information is typed at the keyboard and the Enter key is pressed.
A)The cin object
B)A preprocessor
C)An input device
D)The cout object
E)Nothing
A)The cin object
B)A preprocessor
C)An input device
D)The cout object
E)Nothing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Hand tracing a program is
A)a program design technique.
B)a program debugging technique.
C)a program run- time testing technique.
D)creating a drawing of what a program's output screen will look like.
E)none of the above.
A)a program design technique.
B)a program debugging technique.
C)a program run- time testing technique.
D)creating a drawing of what a program's output screen will look like.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following statements about named constants is/are true?
A)The initial value of a named constant, cannot be changed during the program execution.
B)The identifier name of a named constant can only contain capital letters and underscores.
C)A named constant must be initialized with a value at the time it is declared.
D)All 3 of the above statements are true.
E)Statements A and C are true, but B is not.
A)The initial value of a named constant, cannot be changed during the program execution.
B)The identifier name of a named constant can only contain capital letters and underscores.
C)A named constant must be initialized with a value at the time it is declared.
D)All 3 of the above statements are true.
E)Statements A and C are true, but B is not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The cin object must be followed by
A)one or more stream extraction (>>)operators.
B)a single stream extraction (>>)operator.
C)a single stream insertion (<<)operator.
D)no operators.
E)one or more stream insertion operators (<<).
A)one or more stream extraction (>>)operators.
B)a single stream extraction (>>)operator.
C)a single stream insertion (<<)operator.
D)no operators.
E)one or more stream insertion operators (<<).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The setw manipulator is used to set the precision of a number.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The cin object can be used to input more than one value in a single statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Operator associativity is either left to right or
A)front to back.
B)right to left.
C)top to bottom.
D)inside to outside.
E)nothing else; it is always left to right.
A)front to back.
B)right to left.
C)top to bottom.
D)inside to outside.
E)nothing else; it is always left to right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When an operator's operands are of different data types, such as int and double, C++ automatically converts one of them so that they are the same data type.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The following two expressions evaluate to the same thing:
c + a * b c + (a * b)
c + a * b c + (a * b)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The following pair of C++ statements will cause 3.5 to be output.
double number = 7 / 2; cout << number;
double number = 7 / 2; cout << number;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The following C++ statement will assign 1.5 to the result variable.
int result = 3.0 / 2.0;
int result = 3.0 / 2.0;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When an operator has two operands of different data types, C++ always converts them both to double before performing the operation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When a C++ expression is evaluated, binary operations are performed before unary operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The following two statements will assign the same value to result.



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The following statement sets sum1, sum2, and sum3 all to zero.
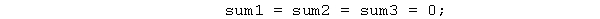
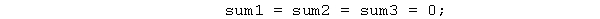

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In any program that uses the cin object, you must #include
A)>> and << operators.
B)the iostream header file.
C)the fstream header file.
D)named constants.
E)none of the above.
A)>> and << operators.
B)the iostream header file.
C)the fstream header file.
D)named constants.
E)none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The cin object lets the user enter a string that contains embedded blanks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The following two statements will assign the same value to answer. answer = a * b / c;
answer = b / c * a;
answer = b / c * a;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The following pair of C++ statements is legal.
const double taxRate; taxRate = .05;
const double taxRate; taxRate = .05;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The following statement sets the value of total to - 3.
total -= 3;
total -= 3;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the value of dollars is 5.0, the following statement will output 5.00 to the monitor:
cout << fixed << showpoint << setprecision(4)<< dollars << endl;
cout << fixed << showpoint << setprecision(4)<< dollars << endl;

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The operator always follows the cin object, and the operator follows the cout object.
A)<< , >>
A)getChar, printChar
B)input, endl
D)>> , <<
E)>> , >>
A)<< , >>
A)getChar, printChar
B)input, endl
D)>> , <<
E)>> , >>

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
In C++, the 5 basic arithmetic operators are
addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/), and exponentiation (^).
addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/), and exponentiation (^).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The only difference between C- strings and string objects is how they are declared and internally stored. They are used exactly the same way.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 40 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



