Deck 23: Minerals and Mining
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/35
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 23: Minerals and Mining
1
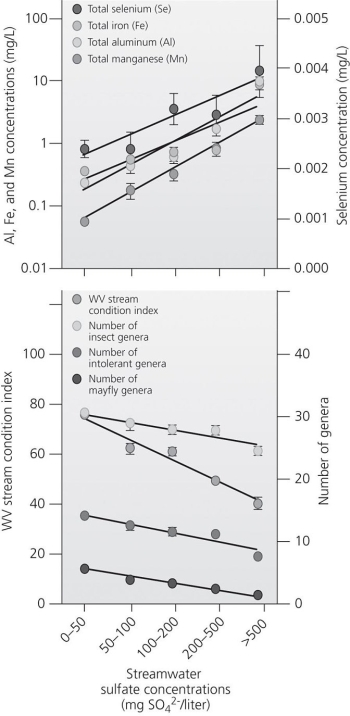 Use the accompanying figure to answer the following questions.
Use the accompanying figure to answer the following questions.The top portion of the graph tells us that selenium .
A)is increasing much more rapidly than the other pollutants
B)is increasing at the same rate as other pollutants
C)had a greater initial concentration than the other pollutants
D)increases with increased sulfate concentration
E)is increasing linearly, while other pollutants are increasing more exponentially
D
2
Read the following scenario and answer the questions below.
In 2010, geologists working for the U.S. military operations in Afghanistan discovered a literal treasure- trove of mineral deposits with a preliminary estimated value at nearly U.S. $1 trillion. So far, no proposals have been made for extracting these resources, but already parallels have been drawn to the many dimensions of human rights issues that have plagued coltan production in the Congo, oil drilling in Nigeria, and the "blood diamonds" of Sierra Leone.
You have been appointed as a delegate to the U.N.- initiated Afghan Minerals Development Council, which will convene in the next few months. The goals of the council are to oversee the extraction and export of resources and to ensure economic benefits, social and environmental justice, as well as environmental protection for the Afghan people.
All of the following could be sensible appointments for the U.N. Council, except perhaps .
A)representatives of banking, marketing and corporate law from developed nations
B)mining corporation engineers and university geologists from developed nations
C)experts in environmental and social justice from the Arab League of Nations
D)mining engineers from Afghanistan and neighboring nations
E)regional economists without corporate ties
In 2010, geologists working for the U.S. military operations in Afghanistan discovered a literal treasure- trove of mineral deposits with a preliminary estimated value at nearly U.S. $1 trillion. So far, no proposals have been made for extracting these resources, but already parallels have been drawn to the many dimensions of human rights issues that have plagued coltan production in the Congo, oil drilling in Nigeria, and the "blood diamonds" of Sierra Leone.
You have been appointed as a delegate to the U.N.- initiated Afghan Minerals Development Council, which will convene in the next few months. The goals of the council are to oversee the extraction and export of resources and to ensure economic benefits, social and environmental justice, as well as environmental protection for the Afghan people.
All of the following could be sensible appointments for the U.N. Council, except perhaps .
A)representatives of banking, marketing and corporate law from developed nations
B)mining corporation engineers and university geologists from developed nations
C)experts in environmental and social justice from the Arab League of Nations
D)mining engineers from Afghanistan and neighboring nations
E)regional economists without corporate ties
A
3
At today's rate of consumption, the world's known reserves of tantalum will last about more years at today's rate of consumption, but if everyone in the world began consuming tantalum at the rate of U.S. citizens, then it would last for only years.
A)15; 5
B)200; 50
C)50; 5
D)200; 15
E)50; 15
A)15; 5
B)200; 50
C)50; 5
D)200; 15
E)50; 15
D
4
Sustainable mineral use and longer projected lifetimes for scarce minerals can be achieved with all of the following, except .
A)recycling
B)increasing demand and lowering prices for products using these minerals
C)researching more efficient and environmentally friendly techniques of extraction
D)exploring for new reserves
E)finding more available substitutes for scarce minerals
A)recycling
B)increasing demand and lowering prices for products using these minerals
C)researching more efficient and environmentally friendly techniques of extraction
D)exploring for new reserves
E)finding more available substitutes for scarce minerals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Examples of valuable nonmetallic minerals extracted by mining are .
A)lead, cadmium, mercury
B)gold, platinum, copper
C)radon, radium, sodium
D)sand, gravel, phosphate
E)nitrogen, hydrogen, neon
A)lead, cadmium, mercury
B)gold, platinum, copper
C)radon, radium, sodium
D)sand, gravel, phosphate
E)nitrogen, hydrogen, neon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In Appalachia, many miners are out of work because .
A)coal extraction has decreased because the region is beginning to run out of coal
B)they were fired for protesting mountaintop removal
C)of local protests that shut down mining operations
D)of a moratorium on mountaintop removal
E)mountaintop removal is highly mechanized, and thus they are not needed
A)coal extraction has decreased because the region is beginning to run out of coal
B)they were fired for protesting mountaintop removal
C)of local protests that shut down mining operations
D)of a moratorium on mountaintop removal
E)mountaintop removal is highly mechanized, and thus they are not needed

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The newest bonanza for recycling scarce and toxic metals is to recover them from .
A)car batteries
B)compact discs, LPs and 8- track tapes
C)landfills from the 1960s
D)construction dump sites
E)e- wastes such as computers
A)car batteries
B)compact discs, LPs and 8- track tapes
C)landfills from the 1960s
D)construction dump sites
E)e- wastes such as computers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Read the following scenario and answer the questions below.
In 2010, geologists working for the U.S. military operations in Afghanistan discovered a literal treasure- trove of mineral deposits with a preliminary estimated value at nearly U.S. $1 trillion. So far, no proposals have been made for extracting these resources, but already parallels have been drawn to the many dimensions of human rights issues that have plagued coltan production in the Congo, oil drilling in Nigeria, and the "blood diamonds" of Sierra Leone.
You have been appointed as a delegate to the U.N.- initiated Afghan Minerals Development Council, which will convene in the next few months. The goals of the council are to oversee the extraction and export of resources and to ensure economic benefits, social and environmental justice, as well as environmental protection for the Afghan people.
Coltan ore contains .
A)tantalum
B)uranium
C)cobalt
D)aluminum
E)platinum
In 2010, geologists working for the U.S. military operations in Afghanistan discovered a literal treasure- trove of mineral deposits with a preliminary estimated value at nearly U.S. $1 trillion. So far, no proposals have been made for extracting these resources, but already parallels have been drawn to the many dimensions of human rights issues that have plagued coltan production in the Congo, oil drilling in Nigeria, and the "blood diamonds" of Sierra Leone.
You have been appointed as a delegate to the U.N.- initiated Afghan Minerals Development Council, which will convene in the next few months. The goals of the council are to oversee the extraction and export of resources and to ensure economic benefits, social and environmental justice, as well as environmental protection for the Afghan people.
Coltan ore contains .
A)tantalum
B)uranium
C)cobalt
D)aluminum
E)platinum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
 Use the accompanying figure to answer the following questions.
Use the accompanying figure to answer the following questions.Heavy landscape damage and water pollution have occurred in as a result of _ .
A)Canada; subsurface mining for oil sands
B)San Francisco; placer mining for gold
C)Appalachia; mountaintop removal mining for coal
D)Mississippi; strip mining for uranium
E)Florida; subsurface mining for limestone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Read the following scenario and answer the questions below.
In 2010, geologists working for the U.S. military operations in Afghanistan discovered a literal treasure- trove of mineral deposits with a preliminary estimated value at nearly U.S. $1 trillion. So far, no proposals have been made for extracting these resources, but already parallels have been drawn to the many dimensions of human rights issues that have plagued coltan production in the Congo, oil drilling in Nigeria, and the "blood diamonds" of Sierra Leone.
You have been appointed as a delegate to the U.N.- initiated Afghan Minerals Development Council, which will convene in the next few months. The goals of the council are to oversee the extraction and export of resources and to ensure economic benefits, social and environmental justice, as well as environmental protection for the Afghan people.
A(n)is formed by the fusion of a metal with another metal or a nonmetal.
A)ore
B)alloy
C)smelting
D)flance
E)tailing
In 2010, geologists working for the U.S. military operations in Afghanistan discovered a literal treasure- trove of mineral deposits with a preliminary estimated value at nearly U.S. $1 trillion. So far, no proposals have been made for extracting these resources, but already parallels have been drawn to the many dimensions of human rights issues that have plagued coltan production in the Congo, oil drilling in Nigeria, and the "blood diamonds" of Sierra Leone.
You have been appointed as a delegate to the U.N.- initiated Afghan Minerals Development Council, which will convene in the next few months. The goals of the council are to oversee the extraction and export of resources and to ensure economic benefits, social and environmental justice, as well as environmental protection for the Afghan people.
A(n)is formed by the fusion of a metal with another metal or a nonmetal.
A)ore
B)alloy
C)smelting
D)flance
E)tailing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The relationship between recycling, economics, and energy consumption is demonstrated in the case of aluminum, where .
A)it costs more than 10 times as much to produce items from recycled aluminum than from virgin ore
B)the U.S. failure to recycle aluminum has caused energy to be lost in mining new ore
C)new cheap mining technologies and huge newly discovered aluminum deposits have made recycling unprofitable
D)all of the metal recycling industries in the United States went bankrupt by 2009
E)it requires over 20 times more energy to mine and extract aluminum from bauxite ore than from recycled materials
A)it costs more than 10 times as much to produce items from recycled aluminum than from virgin ore
B)the U.S. failure to recycle aluminum has caused energy to be lost in mining new ore
C)new cheap mining technologies and huge newly discovered aluminum deposits have made recycling unprofitable
D)all of the metal recycling industries in the United States went bankrupt by 2009
E)it requires over 20 times more energy to mine and extract aluminum from bauxite ore than from recycled materials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Read the following scenario and answer the questions below.
In 2010, geologists working for the U.S. military operations in Afghanistan discovered a literal treasure- trove of mineral deposits with a preliminary estimated value at nearly U.S. $1 trillion. So far, no proposals have been made for extracting these resources, but already parallels have been drawn to the many dimensions of human rights issues that have plagued coltan production in the Congo, oil drilling in Nigeria, and the "blood diamonds" of Sierra Leone.
You have been appointed as a delegate to the U.N.- initiated Afghan Minerals Development Council, which will convene in the next few months. The goals of the council are to oversee the extraction and export of resources and to ensure economic benefits, social and environmental justice, as well as environmental protection for the Afghan people.
The dwindling supplies of rare strategic metals such as indium, tantalum, and platinum may be extended if we rigorously .
A)relax environmental requirements for mining
B)recycle existing supplies
C)reduce demands for social and economic justice
D)increase demand for the products in which they are used
E)exploit known deposits more efficiently
In 2010, geologists working for the U.S. military operations in Afghanistan discovered a literal treasure- trove of mineral deposits with a preliminary estimated value at nearly U.S. $1 trillion. So far, no proposals have been made for extracting these resources, but already parallels have been drawn to the many dimensions of human rights issues that have plagued coltan production in the Congo, oil drilling in Nigeria, and the "blood diamonds" of Sierra Leone.
You have been appointed as a delegate to the U.N.- initiated Afghan Minerals Development Council, which will convene in the next few months. The goals of the council are to oversee the extraction and export of resources and to ensure economic benefits, social and environmental justice, as well as environmental protection for the Afghan people.
The dwindling supplies of rare strategic metals such as indium, tantalum, and platinum may be extended if we rigorously .
A)relax environmental requirements for mining
B)recycle existing supplies
C)reduce demands for social and economic justice
D)increase demand for the products in which they are used
E)exploit known deposits more efficiently

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Read the following scenario and answer the questions below.
In 2010, geologists working for the U.S. military operations in Afghanistan discovered a literal treasure- trove of mineral deposits with a preliminary estimated value at nearly U.S. $1 trillion. So far, no proposals have been made for extracting these resources, but already parallels have been drawn to the many dimensions of human rights issues that have plagued coltan production in the Congo, oil drilling in Nigeria, and the "blood diamonds" of Sierra Leone.
You have been appointed as a delegate to the U.N.- initiated Afghan Minerals Development Council, which will convene in the next few months. The goals of the council are to oversee the extraction and export of resources and to ensure economic benefits, social and environmental justice, as well as environmental protection for the Afghan people.
As far as costs of restoration and reclamation of mining sites, you should strongly recommend that .
A)the U.S. EPA should oversee the operation and pay for it
B)the Afghan central government should take responsibility
C)any corporation wishing to invest should post a bond for reclamation and hire Afghans to do the work
D)the U.S. military should take responsibility
E)the costs be shared by the Afghan central government and also by the most powerful tribal leaders
In 2010, geologists working for the U.S. military operations in Afghanistan discovered a literal treasure- trove of mineral deposits with a preliminary estimated value at nearly U.S. $1 trillion. So far, no proposals have been made for extracting these resources, but already parallels have been drawn to the many dimensions of human rights issues that have plagued coltan production in the Congo, oil drilling in Nigeria, and the "blood diamonds" of Sierra Leone.
You have been appointed as a delegate to the U.N.- initiated Afghan Minerals Development Council, which will convene in the next few months. The goals of the council are to oversee the extraction and export of resources and to ensure economic benefits, social and environmental justice, as well as environmental protection for the Afghan people.
As far as costs of restoration and reclamation of mining sites, you should strongly recommend that .
A)the U.S. EPA should oversee the operation and pay for it
B)the Afghan central government should take responsibility
C)any corporation wishing to invest should post a bond for reclamation and hire Afghans to do the work
D)the U.S. military should take responsibility
E)the costs be shared by the Afghan central government and also by the most powerful tribal leaders

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
One drawback of in- situ recovery techniques is .
A)the potential for soil compaction from the heavy equipment requires
B)that the land is often not reclaimable after mining operations cease
C)that although the techniques are scientifically feasible, they are not economically feasible
D)the potential for leakage of acids into groundwater
E)that the technique often results in severe erosion, especially in steep areas
A)the potential for soil compaction from the heavy equipment requires
B)that the land is often not reclaimable after mining operations cease
C)that although the techniques are scientifically feasible, they are not economically feasible
D)the potential for leakage of acids into groundwater
E)that the technique often results in severe erosion, especially in steep areas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Many types of mining, such as for coal, produce a specific type of water pollution called .
A)chlorinated pesticides
B)acid drainage
C)radon gas
D)eutrophication
E)suspended limestone particles
A)chlorinated pesticides
B)acid drainage
C)radon gas
D)eutrophication
E)suspended limestone particles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The U.S. General Mining Act of 1872, although encouraging of the domestic mining industry, also .
A)has pollution and remediation clauses that are too strict
B)makes mining unprofitable except for the largest corporations
C)gives away resources located on public land almost for free
D)opens mining rights to foreign nations which stake claims on U.S. land
E)has allowed mining in urban centers with dense commercial development
A)has pollution and remediation clauses that are too strict
B)makes mining unprofitable except for the largest corporations
C)gives away resources located on public land almost for free
D)opens mining rights to foreign nations which stake claims on U.S. land
E)has allowed mining in urban centers with dense commercial development

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which of the following is an effect of high selenium concentrations in stream water?
A)Selenium mining companies will want to extract the selenium and thus damage the aquatic ecosystem.
B)There are no negative effects from selenium, but high selenium levels generally indicate high levels of substances that are harmful.
C)The selenium will react with potassium isocyanate, resulting in cyanide poisoning of organisms living in the stream.
D)Selenium causes birth defects in fish.
E)Selenium reacts with oxygen, thus suffocating fish and other aquatic organisms.
A)Selenium mining companies will want to extract the selenium and thus damage the aquatic ecosystem.
B)There are no negative effects from selenium, but high selenium levels generally indicate high levels of substances that are harmful.
C)The selenium will react with potassium isocyanate, resulting in cyanide poisoning of organisms living in the stream.
D)Selenium causes birth defects in fish.
E)Selenium reacts with oxygen, thus suffocating fish and other aquatic organisms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If a mineral is opaque, lustrous, malleable and can conduct heat and electricity, it is a(n).
A)gemstone
B)radioactive element
C)crystal
D)metal
E)element
A)gemstone
B)radioactive element
C)crystal
D)metal
E)element

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Subsurface mining is used extensively in the extraction of .
A)coltan
B)organic soils for landscaping
C)oil sands
D)limestone, natural gas, peat
E)coal, phosphate, diamonds, gold
A)coltan
B)organic soils for landscaping
C)oil sands
D)limestone, natural gas, peat
E)coal, phosphate, diamonds, gold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Read the following scenario and answer the questions below.
In 2010, geologists working for the U.S. military operations in Afghanistan discovered a literal treasure- trove of mineral deposits with a preliminary estimated value at nearly U.S. $1 trillion. So far, no proposals have been made for extracting these resources, but already parallels have been drawn to the many dimensions of human rights issues that have plagued coltan production in the Congo, oil drilling in Nigeria, and the "blood diamonds" of Sierra Leone.
You have been appointed as a delegate to the U.N.- initiated Afghan Minerals Development Council, which will convene in the next few months. The goals of the council are to oversee the extraction and export of resources and to ensure economic benefits, social and environmental justice, as well as environmental protection for the Afghan people.
A useful benefit from mining profits could be .
A)permanent enclaves of foreign scientists and mine managers located near mining sites
B)creation of improved roads into and around mining sites for corporate transport and mining machinery
C)establishing high- end tourist hotels for visiting foreign mine executives and their families
D)using the U.S. military to provide security at mines
E)training for Afghan mining technicians and establishing Afghan mining institutes
In 2010, geologists working for the U.S. military operations in Afghanistan discovered a literal treasure- trove of mineral deposits with a preliminary estimated value at nearly U.S. $1 trillion. So far, no proposals have been made for extracting these resources, but already parallels have been drawn to the many dimensions of human rights issues that have plagued coltan production in the Congo, oil drilling in Nigeria, and the "blood diamonds" of Sierra Leone.
You have been appointed as a delegate to the U.N.- initiated Afghan Minerals Development Council, which will convene in the next few months. The goals of the council are to oversee the extraction and export of resources and to ensure economic benefits, social and environmental justice, as well as environmental protection for the Afghan people.
A useful benefit from mining profits could be .
A)permanent enclaves of foreign scientists and mine managers located near mining sites
B)creation of improved roads into and around mining sites for corporate transport and mining machinery
C)establishing high- end tourist hotels for visiting foreign mine executives and their families
D)using the U.S. military to provide security at mines
E)training for Afghan mining technicians and establishing Afghan mining institutes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Tantalum from African coltan is used primarily for the manufacture of .
A)plastics
B)aerospace engines and aircraft hulls
C)pesticides, fertilizers, and biodiesel fuel
D)high- quality steel
E)electronics such as cell phones, computers, digital cameras
A)plastics
B)aerospace engines and aircraft hulls
C)pesticides, fertilizers, and biodiesel fuel
D)high- quality steel
E)electronics such as cell phones, computers, digital cameras

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The General Mining Act of 1872 .
A)officially legalized mountaintop removal
B)encouraged the prospecting for minerals on federal lands
C)legalized the mining for gold in California
D)requires remediation and reclamation of areas damaged by mining operations
E)was named after a Civil War general who died at the Battle of Gettysburg
A)officially legalized mountaintop removal
B)encouraged the prospecting for minerals on federal lands
C)legalized the mining for gold in California
D)requires remediation and reclamation of areas damaged by mining operations
E)was named after a Civil War general who died at the Battle of Gettysburg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Match the following.
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Discuss the major environmental impacts of mining operations.
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Discuss the major environmental impacts of mining operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Match the following.
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Tunneling deep underground to extract minerals
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Tunneling deep underground to extract minerals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In 2010, geologists from the U.S. military discovered nearly $1 trillion worth of minerals in .
A)Nevada
B)Peru
C)Afghanistan
D)Iraq
E)Vietnam
A)Nevada
B)Peru
C)Afghanistan
D)Iraq
E)Vietnam

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Discuss the facets of sustainable mineral use.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The U.S. Surface Mining Control and Reclamation Act of 1977 requires .
A)mining companies to post bonds to cover restoration of mined areas before permits are granted
B)restoration of the identical ecosystem and biodiversity present before mining began
C)20% of sales revenues to be donated to national park maintenance
D)no remediation of water pollution, except in the case of uranium mining
E)all mined minerals to be processed and sold only within the United States
A)mining companies to post bonds to cover restoration of mined areas before permits are granted
B)restoration of the identical ecosystem and biodiversity present before mining began
C)20% of sales revenues to be donated to national park maintenance
D)no remediation of water pollution, except in the case of uranium mining
E)all mined minerals to be processed and sold only within the United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Match the following.
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Sifting through sand and silt in riverbeds for minerals using flowing water
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Sifting through sand and silt in riverbeds for minerals using flowing water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A naturally occurring solid chemical element with a distinct composition and a crystal structure is a(n).
A)horizon
B)organic nutrient
C)rock
D)sediment
E)mineral
A)horizon
B)organic nutrient
C)rock
D)sediment
E)mineral

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Match the following.
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Restoration of mined areas to premining conditions
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Restoration of mined areas to premining conditions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A(n)_ is a solid aggregate of _.
A)crystal; rocks
B)rock; minerals
C)mineral; rocks
D)element; crystals
E)mineral; crystals
A)crystal; rocks
B)rock; minerals
C)mineral; rocks
D)element; crystals
E)mineral; crystals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Match the following.
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Excavating a giant hole in the landscape to remove widely spread mineral deposits
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Excavating a giant hole in the landscape to remove widely spread mineral deposits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Smelting of iron ore involves .
A)washing the ore with acid to extract iron
B)heating beyond iron's melting point and combining the material with carbon
C)dissolving the ore in hot water to separate iron and aluminum
D)crushing and heating the ore to its melting point
E)oxidizing iron to ferric oxide and then adding silicon and boron
A)washing the ore with acid to extract iron
B)heating beyond iron's melting point and combining the material with carbon
C)dissolving the ore in hot water to separate iron and aluminum
D)crushing and heating the ore to its melting point
E)oxidizing iron to ferric oxide and then adding silicon and boron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Match the following.
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Mineral extraction by removing several hundred vertical feet from hill and mountaintops
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Mineral extraction by removing several hundred vertical feet from hill and mountaintops

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Match the following.
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Removing surface layers to expose and extract horizontal mineral deposits
A)mountaintop removal mining
B)recreation
C)open pit mining
D)solution mining
E)prospecting
F)strip mining
G)placer mining
H)subsurface mining
I)reclamation
Removing surface layers to expose and extract horizontal mineral deposits

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 35 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



