Deck 2: The Chemistry of Microbiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: The Chemistry of Microbiology
1
A research microbiologist wants to determine whether a microbe can metabolize a new synthetic organic molecule composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen. Which of the following would be useful in tracing the fate of the compound?
A) the 2H isotope
B) the 13C isotope
C) a 13C+ ion.
D) the 14C isotope
E) the 12C isotope
A) the 2H isotope
B) the 13C isotope
C) a 13C+ ion.
D) the 14C isotope
E) the 12C isotope
D
2
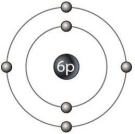 The outer ring in Figure 2-1 represents
The outer ring in Figure 2-1 representsA) a neutron.
B) the nucleus.
C) an electron.
D) an isotope.
E) an electron shell.
E
3
Compounds that readily dissociate in water are
A) ionic.
B) polar.
C) nonpolar.
D) either polar or ionic.
E) never polar or ionic.
A) ionic.
B) polar.
C) nonpolar.
D) either polar or ionic.
E) never polar or ionic.
D
4
A hydroxyl acts as a base.
A) salt
B) group
C) anion
D) atom
E) cation
A) salt
B) group
C) anion
D) atom
E) cation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A stable atom has in its valence shell.
A) 4 electrons
B) 2 neutrons
C) 10 electrons
D) 8 protons
E) 8 electrons
A) 4 electrons
B) 2 neutrons
C) 10 electrons
D) 8 protons
E) 8 electrons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following is a CORRECT pairing of metabolic terms?
A) hydrolysis: decomposition
B) synthesis: exothermic
C) synthesis: catabolism
D) catabolism: endothermic
E) dehydration: decomposition
A) hydrolysis: decomposition
B) synthesis: exothermic
C) synthesis: catabolism
D) catabolism: endothermic
E) dehydration: decomposition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Matter composed of a single type of atom is known as a(n)
A) mineral.
B) electron.
C) molecule.
D) element.
E) compound.
A) mineral.
B) electron.
C) molecule.
D) element.
E) compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The type(s) of bond produced when atoms with somewhat different electronegativities share electrons is/are
A) an ionic bond.
B) a nonpolar covalent bond.
C) a polar covalent bond.
D) a hydrogen bond.
E) both nonpolar covalent and ionic bonds.
A) an ionic bond.
B) a nonpolar covalent bond.
C) a polar covalent bond.
D) a hydrogen bond.
E) both nonpolar covalent and ionic bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The reaction described below is consistent with 
A) a catabolic reaction.
B) an exchange reaction.
C) a synthesis reaction.
D) a decomposition reaction.
E) both synthesis and decomposition.

A) a catabolic reaction.
B) an exchange reaction.
C) a synthesis reaction.
D) a decomposition reaction.
E) both synthesis and decomposition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is a property of water?
A) It is a nonpolar molecule.
B) It has a high capacity for heat.
C) It is not a good solvent.
D) It is liquid in a very narrow temperature range.
E) It is not a common reactant in metabolic reactions.
A) It is a nonpolar molecule.
B) It has a high capacity for heat.
C) It is not a good solvent.
D) It is liquid in a very narrow temperature range.
E) It is not a common reactant in metabolic reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The chemical formula of a solid indicates it contains two groups with different electronegativities. This substance is most likely
A) radioactive.
B) a nonpolar molecule.
C) a salt.
D) non-ionic.
E) a mixture.
A) radioactive.
B) a nonpolar molecule.
C) a salt.
D) non-ionic.
E) a mixture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An acid dissociates in water to release
A) hydroxyl groups.
B) anions.
C) cations.
D) hydrogen ions.
E) both anions and hydrogen ions.
A) hydroxyl groups.
B) anions.
C) cations.
D) hydrogen ions.
E) both anions and hydrogen ions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is a particle found in the nucleus of an atom and that has no electrical charge?
A) neutron
B) element
C) electron
D) isotope
E) proton
A) neutron
B) element
C) electron
D) isotope
E) proton

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Nucleic acid polymers, proteins, and complex carbohydrates are all produced by
A) dehydration synthesis.
B) exchange reactions.
C) hydrogen bonding.
D) hydrolytic reactions.
E) catabolic reactions.
A) dehydration synthesis.
B) exchange reactions.
C) hydrogen bonding.
D) hydrolytic reactions.
E) catabolic reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which parts of the atoms interact in a chemical reaction?
A) ions
B) electrons
C) neutrons
D) isotopes
E) protons
A) ions
B) electrons
C) neutrons
D) isotopes
E) protons

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
You are performing an experiment in your chemistry lab class. The directions advise caution because the reaction is exothermic. Which of the following is the hazard the directions warn about?
A) The reaction may cause the container to become dangerously hot.
B) The reaction will produce a noxious vapor.
C) The reaction will generate enough light to require eye protection.
D) The reaction may cause the container to freeze and break.
E) The reaction will generate radiation.
A) The reaction may cause the container to become dangerously hot.
B) The reaction will produce a noxious vapor.
C) The reaction will generate enough light to require eye protection.
D) The reaction may cause the container to freeze and break.
E) The reaction will generate radiation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The valence of an atom represents its
A) electronegativity.
B) ability to interact with other atoms.
C) radioactivity.
D) ability to interact with water.
E) ability to attract electrons.
A) electronegativity.
B) ability to interact with other atoms.
C) radioactivity.
D) ability to interact with water.
E) ability to attract electrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Unstable isotopes can be useful
A) in medical diagnosis.
B) in vitamins.
C) in the formation of hydrogen bonds.
D) catalysts.
E) as buffers.
A) in medical diagnosis.
B) in vitamins.
C) in the formation of hydrogen bonds.
D) catalysts.
E) as buffers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The reverse of a dehydration synthesis reaction is a(n) reaction.
A) anabolic
B) endothermic
C) exchange
D) metabolic
E) hydrolysis
A) anabolic
B) endothermic
C) exchange
D) metabolic
E) hydrolysis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The type(s) of bonds produced when atoms share electrons equally is/are
A) a hydrogen bond.
B) a nonpolar covalent bond.
C) an ionic bond.
D) a polar covalent bond.
E) both polar covalent and ionic bonds.
A) a hydrogen bond.
B) a nonpolar covalent bond.
C) an ionic bond.
D) a polar covalent bond.
E) both polar covalent and ionic bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Proteins contain both acidic and basic R groups, and can therefore function as
A) catalysts.
B) structural macromolecules.
C) energy storage macromolecules.
D) buffers.
E) genetic material.
A) catalysts.
B) structural macromolecules.
C) energy storage macromolecules.
D) buffers.
E) genetic material.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
All of the following are components of an amino acid EXCEPT a(n)
A) carboxyl group.
B) pentose group.
C) amino group.
D) R group.
E) α-carbon.
A) carboxyl group.
B) pentose group.
C) amino group.
D) R group.
E) α-carbon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins involves bonds.
A) ionic
B) nonpolar covalent
C) polar covalent
D) hydrogen
E) hydrogen, ionic, polar, and nonpolar covalent
A) ionic
B) nonpolar covalent
C) polar covalent
D) hydrogen
E) hydrogen, ionic, polar, and nonpolar covalent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is found in nucleic acids?
A) carboxylic acid
B) purines
C) glycerol
D) R group
E) amino groups
A) carboxylic acid
B) purines
C) glycerol
D) R group
E) amino groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A(n) is an arrangement of atoms found in a variety of macromolecules.
A) salt
B) functional group
C) buffer
D) isotope
E) stereoisomer
A) salt
B) functional group
C) buffer
D) isotope
E) stereoisomer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Research suggests taking antacids may make people more susceptible to infection with Vibrio vulnificus by making the stomach environment more tolerable to the bacteria. Based on this information and the name ʺantacid,ʺ which of the following are antacids likely to be?
A) acids
B) non-polar compounds
C) buffers
D) bases
E) either base or buffer
A) acids
B) non-polar compounds
C) buffers
D) bases
E) either base or buffer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All of the following are associated with ATP molecules EXCEPT
A) high-energy bonds.
B) a recyclable energy supply.
C) a long-term energy supply.
D) formation of coenzymes.
E) three phosphate groups.
A) high-energy bonds.
B) a recyclable energy supply.
C) a long-term energy supply.
D) formation of coenzymes.
E) three phosphate groups.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following lipids has the lowest ratio of hydrogens to carbons?
A) monounsaturated fats
B) polyunsaturated fats
C) saturated fats
D) both saturated and monounsaturated fats
E) Saturated, unsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats have equal ratios of hydrogens to carbons.
A) monounsaturated fats
B) polyunsaturated fats
C) saturated fats
D) both saturated and monounsaturated fats
E) Saturated, unsaturated, and polyunsaturated fats have equal ratios of hydrogens to carbons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Hydrogen bonds are found in all of the following EXCEPT
A) in the DNA double helix between nucleotides.
B) between the R groups of amino acids in proteins.
C) in the structure of complex polysaccharides.
D) between water molecules.
E) between phosphates in ATP.
A) in the DNA double helix between nucleotides.
B) between the R groups of amino acids in proteins.
C) in the structure of complex polysaccharides.
D) between water molecules.
E) between phosphates in ATP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following are examples of pyrimidines?
A) cytosine and guanine
B) cytosine and thymine
C) uracil and adenine
D) thymine and guanine
E) thymine and adenine
A) cytosine and guanine
B) cytosine and thymine
C) uracil and adenine
D) thymine and guanine
E) thymine and adenine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A macromolecule containing two fatty acids and a phosphate group is a
A) glycerol.
B) wax.
C) phospholipid.
D) steroid.
E) saturated fatty acid.
A) glycerol.
B) wax.
C) phospholipid.
D) steroid.
E) saturated fatty acid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Plant cell walls are composed of held together by .
A) polysaccharides; hydrogen bonds
B) amino acids; peptide bonds
C) fatty acids; polar covalent bonds
D) peptidoglycan; ionic bonds
E) disaccharides; hydrophobic interactions
A) polysaccharides; hydrogen bonds
B) amino acids; peptide bonds
C) fatty acids; polar covalent bonds
D) peptidoglycan; ionic bonds
E) disaccharides; hydrophobic interactions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which of the following is an INCORRECT pairing?
A) secondary structure; β-pleated sheets
B) secondary structure; disulfide bridges
C) primary structure; amino acid sequence
D) tertiary structure; covalent bonds
E) quaternary structure; two or more polypeptides
A) secondary structure; β-pleated sheets
B) secondary structure; disulfide bridges
C) primary structure; amino acid sequence
D) tertiary structure; covalent bonds
E) quaternary structure; two or more polypeptides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is an example of a polysaccharide?
A) glycogen
B) fructose
C) glucose
D) sucrose
E) deoxyribose
A) glycogen
B) fructose
C) glucose
D) sucrose
E) deoxyribose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is TRUE of both DNA and RNA?
A) They are highly hydrophobic macromolecules.
B) They contain adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine.
C) The ʺbackboneʺ is composed of riboses and phosphates.
D) The purines and pyrimidines form hydrogen-bonded pairs.
E) They are usually double-stranded helices.
A) They are highly hydrophobic macromolecules.
B) They contain adenine, cytosine, guanine and thymine.
C) The ʺbackboneʺ is composed of riboses and phosphates.
D) The purines and pyrimidines form hydrogen-bonded pairs.
E) They are usually double-stranded helices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The ʺbackboneʺ of the DNA molecule is composed of
A) pentoses.
B) phosphates.
C) amino acids.
D) alternating phosphates and pentoses.
E) nitrogenous bases.
A) pentoses.
B) phosphates.
C) amino acids.
D) alternating phosphates and pentoses.
E) nitrogenous bases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is characteristic of proteins?
A) Their secondary structure is composed of β-helices.
B) They have multiple layers of structural organization.
C) They are composed of carbohydrate.
D) They are primarily hydrophobic.
E) They are composed of nucleic acids.
A) Their secondary structure is composed of β-helices.
B) They have multiple layers of structural organization.
C) They are composed of carbohydrate.
D) They are primarily hydrophobic.
E) They are composed of nucleic acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Lipids found in the membranes of most eukaryotic cells are
A) phospholipids.
B) waxes.
C) steroids.
D) triglycerides.
E) polyunsaturated fats.
A) phospholipids.
B) waxes.
C) steroids.
D) triglycerides.
E) polyunsaturated fats.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following would NOT normally be found as a component of a cellʹs nucleic acids?
A) cytosine ribonucleotides
B) adenine deoxyribonucleotides
C) adenine ribonucleotides
D) thymine deoxyribonucleotides
E) uracil deoxyribonucleotides
A) cytosine ribonucleotides
B) adenine deoxyribonucleotides
C) adenine ribonucleotides
D) thymine deoxyribonucleotides
E) uracil deoxyribonucleotides

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Decomposition reactions are commonly reactions.
A) anabolic
B) exchange
C) endothermic
D) exothermic
E) dehydration
A) anabolic
B) exchange
C) endothermic
D) exothermic
E) dehydration

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The phosphorylation of a protein by ATP is a(n) (exchange/transfer/group) reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The electron shells of atoms hold eight electrons each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A reaction requires water as a reactant and produces heat. What type of reaction is likely to be involved?
A) a decomposition reaction
B) a synthesis reaction
C) a hydrolysis reaction
D) an exchange reaction
E) The answer cannot be determined with the available information.
A) a decomposition reaction
B) a synthesis reaction
C) a hydrolysis reaction
D) an exchange reaction
E) The answer cannot be determined with the available information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Salts are produced from exchange reactions in which acids and bases neutralize each other.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Amylose is a(n) carbohydrate.
A) polymer
B) ionic
C) monomer
D) simple
E) nucleotide
A) polymer
B) ionic
C) monomer
D) simple
E) nucleotide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Radioactive iodine is sometimes used to treat thyroid cancer. This is an example of the use of (isotopes/elements/radiation) in medical treatment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The smallest chemical units of matter are elements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The side groups of amino acids can interact with each other and with other molecules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Glycolipids are an example of a mixture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Anna is conducting an experiment using a pH indicator that is red at low pH, green at neutral pH, and purple at high pH. She starts with a green solution. When she adds compound X to her solution it turns purple. Then she adds compound Z to the solution and it turns green. She adds more Z and the solution remains green. These observations suggest X is and Z is .
A) a base; a strong acid
B) a base; a buffer
C) a buffer; a base
D) an acid; a base
E) an acid; a buffer
A) a base; a strong acid
B) a base; a buffer
C) a buffer; a base
D) an acid; a base
E) an acid; a buffer

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A molecule composed of carbon and hydrogen is a compound.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An organic molecule with the chemical formula C4H5O1N3 is probably a pyrimidine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Denaturation of a protein is always permanent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
DNA is composed of repeating units of sugars, phosphates, and nucleic acids. This is an example of a
A) micelle.
B) polymer.
C) salt.
D) lipid.
E) monomer.
A) micelle.
B) polymer.
C) salt.
D) lipid.
E) monomer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Carbon atoms have four valence electrons and typically form polar covalent bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Bacterial cell walls are composed of
A) peptides.
B) waxes.
C) peptides and polysaccharides.
D) carbohydrates and waxes.
E) polysaccharides.
A) peptides.
B) waxes.
C) peptides and polysaccharides.
D) carbohydrates and waxes.
E) polysaccharides.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Neon generally does not react with other atoms because it has (2/4/6/8) electrons in its outer shell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
An atom or molecule becomes a(n) (anion/ion/cation) when it loses an electron to a more electronegative molecule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
One of the products of dehydration synthesis reactions is water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What functional groups are present in ALL amino acids?
A) amino groups
B) carboxyl groups
C) hydroxyl groups.
D) amino and sulfhydryl groups.
E) amino and carboxyl groups
A) amino groups
B) carboxyl groups
C) hydroxyl groups.
D) amino and sulfhydryl groups.
E) amino and carboxyl groups

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A student is given a compound to identify in an organic chemistry class. The first thing she notices is that it is not soluble in pure water or saline. Analysis of the ratios of atoms indicates the ratio of carbon to hydrogen to oxygen is 1:1.5:0.05. There is no nitrogen. Based on this information, what class of biological macromolecule is the student working with? Justify your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
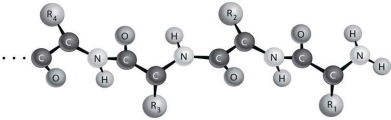 Figure 2-2 depicts the (primary/secondary/tertiary) structure of a protein.
Figure 2-2 depicts the (primary/secondary/tertiary) structure of a protein.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A fatty acid with two double bonds is a (saturated/monounsaturated/polyunsaturated) fat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A chemical reaction that traps energy within newly formed chemical bonds is an (exothermic/endothermic) reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Discuss the importance of hydrogen bonds in the chemistry of the cell.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A(n) (catalyst/enzyme/protein) is any molecule that speeds up a chemical reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A(n) (indicator/base/buffer) is a substance that maintains the pH even when the amounts of acid and/or base are changing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Max is exploring the properties of various compounds. Some of his explorations involve the use of a pH indicator that is red at low pH, yellow-green at neutral pH, and blue to purple at high pH. He sets up several tubes containing water and the pH indicator and then begins to add some of the compounds he is characterizing in various combinations. His results are shown on the Figure 2.3.
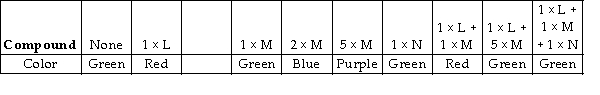 What can Max conclude about his compounds based on these results? Describe the likely events in terms of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions.
What can Max conclude about his compounds based on these results? Describe the likely events in terms of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions.
 What can Max conclude about his compounds based on these results? Describe the likely events in terms of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions.
What can Max conclude about his compounds based on these results? Describe the likely events in terms of hydrogen and hydroxyl ions.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A(n) (base/acid) is a molecule that binds with hydrogen ions when it is dissolved in water.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The (atoms/isotopes/stereoisomers) of an element vary in the number of neutrons in the nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The functional group of a monosaccharide is a(n) (amino/carboxyl/hydroxyl/carbonyl)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A chemical reaction in which a water molecule is a reactant is known as a (dehydration/hydrolysis) reaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Nitrogen is an essential element for living things, as demonstrated by the fact that nearly all fertilizers contain nitrogenous compounds. Discuss why nitrogen is essential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The ʺdouble helixʺ of DNA is the result of (covalent/ionic/hydrogen) bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Compare and contrast synthesis reactions with decomposition reactions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The folding of a polypeptide into a three -dimensional shape is its (secondary/tertiary/quaternary) structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



