Deck 18: Aids and Other Immune Disorders
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 18: Aids and Other Immune Disorders
1
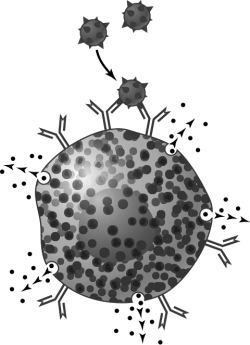 The events illustrated in the figure are part of a(n) disorder.
The events illustrated in the figure are part of a(n) disorder.A) type I hypersensitivity
B) type II hypersensitivity
C) type III hypersensitivity
D) immunodeficiency
E) autoimmune
A
2
If circulating immune complexes are deposited in the glomeruli, the ensuing type III hypersensitivity reaction can result in
A) kidney damage.
B) allergic contact dermatitis.
C) rheumatoid arthritis.
D) pneumonitis.
E) multiple sclerosis.
A) kidney damage.
B) allergic contact dermatitis.
C) rheumatoid arthritis.
D) pneumonitis.
E) multiple sclerosis.
A
3
Which of the following blood types can be safely transfused into someone with O blood type?
A) O
B) A
C) B
D) A and O
E) A, B, and O
A) O
B) A
C) B
D) A and O
E) A, B, and O
A
4
Which of the following reactions is the result of type IV (delayed) hypersensitivity?
A) breathing difficulties after exposure to mold spores
B) dermatitis in response to latex gloves
C) skin irritation after wearing wool
D) sensitivity to pet dander
E) runny nose triggered by pollen
A) breathing difficulties after exposure to mold spores
B) dermatitis in response to latex gloves
C) skin irritation after wearing wool
D) sensitivity to pet dander
E) runny nose triggered by pollen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The destruction of tissue cells resulting from severe allergic reaction is due to the release of
A) proteases.
B) leukotrienes.
C) histamines.
D) kinins.
E) prostaglandins.
A) proteases.
B) leukotrienes.
C) histamines.
D) kinins.
E) prostaglandins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following could result in hemolytic disease of the newborn?
A) Rh-positive mother and Rh-positive father
B) Rh-negative mother and Rh-positive father
C) Rh-negative mother and Rh-negative father
D) Rh-positive mother and Rh-negative father
E) either Rh-positive mother and Rh-negative father or Rh-negative mother and Rh-positive father
A) Rh-positive mother and Rh-positive father
B) Rh-negative mother and Rh-positive father
C) Rh-negative mother and Rh-negative father
D) Rh-positive mother and Rh-negative father
E) either Rh-positive mother and Rh-negative father or Rh-negative mother and Rh-positive father

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Immediate hypersensitivity reactions result when a first exposure to antigen results in
A) activation of IgG-producing B cells.
B) activation of IgE-producing B cells.
C) the activation of CTL.
D) an elevation of eosinophils.
E) activation of IgA-producing B cells.
A) activation of IgG-producing B cells.
B) activation of IgE-producing B cells.
C) the activation of CTL.
D) an elevation of eosinophils.
E) activation of IgA-producing B cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The redness, swelling and itching of urticaria is due to release.
A) kinin
B) protease
C) kinin and protease
D) leukotriene
E) histamine
A) kinin
B) protease
C) kinin and protease
D) leukotriene
E) histamine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following is an example of a type I hypersensitivity reaction?
A) destruction of red blood cells after an incompatible blood transfusion
B) farmerʹs lung
C) the tuberculin response
D) watery eyes after exposure to animal dander
E) deposition of immune complexes in the glomeruli of the kidneys
A) destruction of red blood cells after an incompatible blood transfusion
B) farmerʹs lung
C) the tuberculin response
D) watery eyes after exposure to animal dander
E) deposition of immune complexes in the glomeruli of the kidneys

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
When mast cells degranulate and release histamine, which of the following events may occur?
A) constriction of small blood vessels
B) increased mucus production
C) bronchial spasms
D) both constriction of small blood vessels and bronchial spasms
E) both bronchial spasms and increased mucus production
A) constriction of small blood vessels
B) increased mucus production
C) bronchial spasms
D) both constriction of small blood vessels and bronchial spasms
E) both bronchial spasms and increased mucus production

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The constriction of the airways and mucus production of asthma is the result of a(n) response.
A) type II hypersensitivity
B) delayed hypersensitivity
C) autoimmune
D) type III hypersensitivity
E) type I hypersensitivity
A) type II hypersensitivity
B) delayed hypersensitivity
C) autoimmune
D) type III hypersensitivity
E) type I hypersensitivity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How is hemolytic disease of the newborn prevented?
A) treating with glucocorticoids throughout pregnancy
B) administering anti-IgG antibodies during pregnancy
C) immunizing a woman against Rh factor prior to pregnancy
D) administering anti-Rh IgG late in pregnancy and after pregnancy ends
E) treating with cytokines to prevent B cell activation late in pregnancy
A) treating with glucocorticoids throughout pregnancy
B) administering anti-IgG antibodies during pregnancy
C) immunizing a woman against Rh factor prior to pregnancy
D) administering anti-Rh IgG late in pregnancy and after pregnancy ends
E) treating with cytokines to prevent B cell activation late in pregnancy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A small amount of antigen is injected under the skin of a patient. After 30 minutes there is no apparent change at the injection site, but 36 hours later the patient reports that the area is red and swollen. This type of response is due to
A) type I hypersensitivity.
B) type II hypersensitivity.
C) type III hypersensitivity.
D) type IV hypersensitivity.
E) immunodeficiency.
A) type I hypersensitivity.
B) type II hypersensitivity.
C) type III hypersensitivity.
D) type IV hypersensitivity.
E) immunodeficiency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A person with no siblings or children receives a kidney transplant. The kidney is an example of a(n)
A) xenograft.
B) autograft.
C) dermograft.
D) allograft.
E) isograft.
A) xenograft.
B) autograft.
C) dermograft.
D) allograft.
E) isograft.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is NOT considered a hypersensitivity reaction?
A) dermatitis at the site of a metal watchband
B) a rash caused by poison ivy
C) breaking into hives after eating strawberries
D) itchy eyes and a runny nose in a dusty environment
E) immune system attack on the thyroid gland
A) dermatitis at the site of a metal watchband
B) a rash caused by poison ivy
C) breaking into hives after eating strawberries
D) itchy eyes and a runny nose in a dusty environment
E) immune system attack on the thyroid gland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Jess has A- blood type, has never received a blood transfusion, and has never been pregnant. Antibodies against what blood antigens will be present in Jessʹ blood?
A) O and Rh antigens
B) B and Rh antigens
C) B antigens
D) O antigens
E) A antigens
A) O and Rh antigens
B) B and Rh antigens
C) B antigens
D) O antigens
E) A antigens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An agricultural worker experiences difficulty breathing, which becomes progressively worse. Tests show inflammation and damage of the lung tissue, but IgE antibodies and granulocytes are in the normal ranges. With which disorder of the immune system are these signs and symptoms consistent?
A) type III (immune complex-mediated) hypersensitivity
B) acquired immunodeficiency
C) autoimmunity
D) type IV (delayed) hypersensitivity
E) allergic reaction
A) type III (immune complex-mediated) hypersensitivity
B) acquired immunodeficiency
C) autoimmunity
D) type IV (delayed) hypersensitivity
E) allergic reaction

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The glycoprotein and glycolipid molecules on the surface of red blood cells
A) stimulate the production of antibodies that contribute to a transfusion reaction.
B) cause degranulation of the cell when it is exposed to allergens.
C) act to transport glucose and ions across the cytoplasmic membrane.
D) function as a binding site for IgD.
E) act as receptors for foreign antigens and trigger an early immune response.
A) stimulate the production of antibodies that contribute to a transfusion reaction.
B) cause degranulation of the cell when it is exposed to allergens.
C) act to transport glucose and ions across the cytoplasmic membrane.
D) function as a binding site for IgD.
E) act as receptors for foreign antigens and trigger an early immune response.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
An accident victim receives a blood transfusion. Shortly thereafter, he begins to have difficulty breathing, develops a fever, and experiences nausea and vomiting. Which of the following is the most likely interpretation of these events?
A) The blood transfusion was mismatched and contained pyrogens.
B) The blood transfusion was mismatched.
C) The recipient had previously been exposed to foreign blood group antigens.
D) The blood transfusion contained pyrogens.
E) The blood transfusion was mismatched and the recipient had previously been exposed to the foreign blood group antigens.
A) The blood transfusion was mismatched and contained pyrogens.
B) The blood transfusion was mismatched.
C) The recipient had previously been exposed to foreign blood group antigens.
D) The blood transfusion contained pyrogens.
E) The blood transfusion was mismatched and the recipient had previously been exposed to the foreign blood group antigens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following immunoglobulins is produced by plasma cells in response to an allergen?
A) IgM
B) IgE
C) IgD
D) IgG
E) IgA
A) IgM
B) IgE
C) IgD
D) IgG
E) IgA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Hypotheses explaining the development of autoimmune disease include
A) hormonal stimulation of cytotoxic T cells.
B) anaphylactic shock triggered by molecular mimicry.
C) molecular mimicry.
D) genetic factors.
E) molecular mimicry, genetic factors, and hormonal stimulation of cytotoxic T cells.
A) hormonal stimulation of cytotoxic T cells.
B) anaphylactic shock triggered by molecular mimicry.
C) molecular mimicry.
D) genetic factors.
E) molecular mimicry, genetic factors, and hormonal stimulation of cytotoxic T cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The disease known as is a disorder in which phagocytes are inefficient at killing bacteria.
A) chronic granulomatous disease
B) immune thrombocytopenic purpura
C) autoimmune hemolytic anemia
D) severe combined immunodeficiency disease
E) hemolytic disease of the newborn
A) chronic granulomatous disease
B) immune thrombocytopenic purpura
C) autoimmune hemolytic anemia
D) severe combined immunodeficiency disease
E) hemolytic disease of the newborn

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements concerning rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is TRUE?
A) The onset of disease is clearly correlated with having been infected with a specific microbe.
B) Accumulations of antibody complexes lead to inflammation in and destruction of the joints.
C) The symptoms are due to damage caused by cytotoxic T cells.
D) There is no genetic influence on the likelihood of developing RA.
E) It occurs in humans and animals.
A) The onset of disease is clearly correlated with having been infected with a specific microbe.
B) Accumulations of antibody complexes lead to inflammation in and destruction of the joints.
C) The symptoms are due to damage caused by cytotoxic T cells.
D) There is no genetic influence on the likelihood of developing RA.
E) It occurs in humans and animals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following statements concerning allografts is TRUE?
A) They induce strong type IV hypersensitivity reactions and must be treated with immunosuppressive drugs.
B) They are the best type of transplants because they are not associated with rejection.
C) They are impossible to perform because the antigens between donor and recipient are so different.
D) They are the rarest type of transplants.
E) They always require complete destruction of the recipientʹs bone marrow cells.
A) They induce strong type IV hypersensitivity reactions and must be treated with immunosuppressive drugs.
B) They are the best type of transplants because they are not associated with rejection.
C) They are impossible to perform because the antigens between donor and recipient are so different.
D) They are the rarest type of transplants.
E) They always require complete destruction of the recipientʹs bone marrow cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Monoclonal antibodies that bind the IL-2 receptor have been successfully used to reverse graft rejection. Why is this approach effective?
A) B cells are suppressed by exposure to IL-2.
B) IL-2 suppresses Th 2 cells.
C) IL-2 stimulates the activity of CTL.
D) IL-2 is an immunosuppressive cytokine.
E) IL-2 contributes to type VI hypersensitivity responses.
A) B cells are suppressed by exposure to IL-2.
B) IL-2 suppresses Th 2 cells.
C) IL-2 stimulates the activity of CTL.
D) IL-2 is an immunosuppressive cytokine.
E) IL-2 contributes to type VI hypersensitivity responses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Primary immunodeficiency diseases
A) develop later in life.
B) are never associated with genetic defects.
C) may be caused by malnutrition.
D) are sometimes caused by severe stress.
E) are detectable close to birth.
A) develop later in life.
B) are never associated with genetic defects.
C) may be caused by malnutrition.
D) are sometimes caused by severe stress.
E) are detectable close to birth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A young woman comes into the clinic complaining of itchy, red skin and swelling on her arms and legs. She had not been in any parks or wooded areas recently, but she had been shopping. A blood sample reveals elevated levels of granulocytes. What treatment is the physician likely to prescribe at this point?
A) antihistamines
B) interferon
C) corticosteroids
D) cyclophosphamide
E) methotrexate
A) antihistamines
B) interferon
C) corticosteroids
D) cyclophosphamide
E) methotrexate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which of the following would test positive for the tuberculin response?
A) someone who has previously been injected subcutaneously with tuberculin
B) someone who has previously had tuberculosis
C) someone who has been immunized with the tuberculosis vaccine
D) someone who has been immunized with the tuberculosis vaccine or has previously had tuberculosis
E) someone who has been immunized with the tuberculosis vaccine or previously been injected subcutaneously with tuberculin
A) someone who has previously been injected subcutaneously with tuberculin
B) someone who has previously had tuberculosis
C) someone who has been immunized with the tuberculosis vaccine
D) someone who has been immunized with the tuberculosis vaccine or has previously had tuberculosis
E) someone who has been immunized with the tuberculosis vaccine or previously been injected subcutaneously with tuberculin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which condition occurs when antibodies bind to and stimulate receptors that elicit production of thyroid hormone and growth of the thyroid gland?
A) DiGeorge syndrome
B) multiple sclerosis
C) farmerʹs lung
D) type I diabetes
E) Gravesʹ disease
A) DiGeorge syndrome
B) multiple sclerosis
C) farmerʹs lung
D) type I diabetes
E) Gravesʹ disease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What is the underlying problem in most acquired immunodeficiencies?
A) production of autoantibodies
B) anemia
C) declining humoral immunity
D) declining cell-mediated immunity
E) eosinophilia
A) production of autoantibodies
B) anemia
C) declining humoral immunity
D) declining cell-mediated immunity
E) eosinophilia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The responses observed in type IV hypersensitivities result from the action of
A) IgE antibodies and mast cells.
B) IgG and complement.
C) inflammatory chemicals.
D) T cells and phagocytes.
E) autoantibodies.
A) IgE antibodies and mast cells.
B) IgG and complement.
C) inflammatory chemicals.
D) T cells and phagocytes.
E) autoantibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
An acquired immunodeficiency may result from treatment with
A) antihistamine.
B) RhoGAM.
C) azathioprine.
D) corticosteroids.
E) interferon.
A) antihistamine.
B) RhoGAM.
C) azathioprine.
D) corticosteroids.
E) interferon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The production of cytotoxic T cells specific for the myelin sheath of neurons leads to the disorder known as
A) type 1 diabetes mellitus.
B) Graveʹs disease.
C) systemic lupus erythematosus.
D) multiple sclerosis.
E) autoimmune neuralgia.
A) type 1 diabetes mellitus.
B) Graveʹs disease.
C) systemic lupus erythematosus.
D) multiple sclerosis.
E) autoimmune neuralgia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The name systemic lupus erythematosus refers in part to the distinctive rash resulting from
A) the release of histamines and kinins in response to sunburn.
B) CTL attack on connective tissue fibroblasts.
C) CTL attack on skin cells altered by sun damage.
D) antibody-antigen complexes accumulating in the skin.
E) autoantibodies causing mast cell degranulation.
A) the release of histamines and kinins in response to sunburn.
B) CTL attack on connective tissue fibroblasts.
C) CTL attack on skin cells altered by sun damage.
D) antibody-antigen complexes accumulating in the skin.
E) autoantibodies causing mast cell degranulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The tuberculin response is mediated by
A) memory T cells.
B) B lymphocytes.
C) mast cells.
D) plasma cells.
E) eosinophils.
A) memory T cells.
B) B lymphocytes.
C) mast cells.
D) plasma cells.
E) eosinophils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A person comes to the clinic complaining of aching joints and muscles, swelling, and a decrease in urine output. The clinician also notes a rash on the skin of the face. A probable diagnosis is
A) pneumonitis.
B) Gravesʹ disease.
C) systemic lupus erythematosus.
D) immunodeficiency.
E) dermatitis.
A) pneumonitis.
B) Gravesʹ disease.
C) systemic lupus erythematosus.
D) immunodeficiency.
E) dermatitis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If a T cell is exposed to a ʺhiddenʺ antigen, what kind of immune reaction will result?
A) an autoimmune disease
B) an allergy
C) a cytotoxic hypersensitivity reaction
D) a delayed hypersensitivity reaction
E) allergic contact dermatitis
A) an autoimmune disease
B) an allergy
C) a cytotoxic hypersensitivity reaction
D) a delayed hypersensitivity reaction
E) allergic contact dermatitis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A child has a history of repeated severe infections and frequently has recurring infections with the same bacterial pathogen. A blood sample shows some lymphopenia and serological tests are negative. Based on this information, which of the following is the likeliest diagnosis for this child?
A) systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
B) Bruton-type agammaglobulinemia
C) severe combined immune deficiency (SCID)
D) hemolytic disease of the newborn
E) DiGeorge syndrome
A) systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
B) Bruton-type agammaglobulinemia
C) severe combined immune deficiency (SCID)
D) hemolytic disease of the newborn
E) DiGeorge syndrome

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A combination of genetic predisposition and viral infection is suspected in the development of
A) Bruton-type agammaglobulinemia.
B) type 1 diabetes mellitus.
C) autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
D) rheumatoid arthritis.
E) glomerulonephritis.
A) Bruton-type agammaglobulinemia.
B) type 1 diabetes mellitus.
C) autoimmune hemolytic anemia.
D) rheumatoid arthritis.
E) glomerulonephritis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Antigen-antibody complexes trapped in tissues and triggering complement activation or mast cell degranulation are characteristic of
A) type I hypersensitivity.
B) type II hypersensitivity.
C) type III hypersensitivity.
D) graft rejection.
E) autoimmunity.
A) type I hypersensitivity.
B) type II hypersensitivity.
C) type III hypersensitivity.
D) graft rejection.
E) autoimmunity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
All autoimmune diseases have a genetic cause.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Rheumatoid arthritis is a type (I/II/III/IV) hypersensitivity reaction that results when B cells produce autoantibodies that damage the cartilage in the joints. (Be sure to use Roman numerals in your answer.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Anaphylactic shock is a type III hypersensitivity disorder.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Contact dermatitis is a type (I/II/III/IV) hypersensitivity disorder. (Be sure to use Roman numerals in your answer.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Xenografts are tissue transplants from one individual to another within the same species.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If an Rh-positive woman marries an Rh-negative man, their children are at risk for hemolytic disease of the newborn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Severe malnutrition may lead to immunodeficiency by
A) preventing to proliferation of B cells.
B) promoting the development of food allergies.
C) decreasing the ability of the body to produce phagocytes.
D) triggering an inflammatory response.
E) triggering the proliferation of T cells.
A) preventing to proliferation of B cells.
B) promoting the development of food allergies.
C) decreasing the ability of the body to produce phagocytes.
D) triggering an inflammatory response.
E) triggering the proliferation of T cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Type I hypersensitivity reactions are also commonly known as (allergies/autoimmunities/inflammation).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
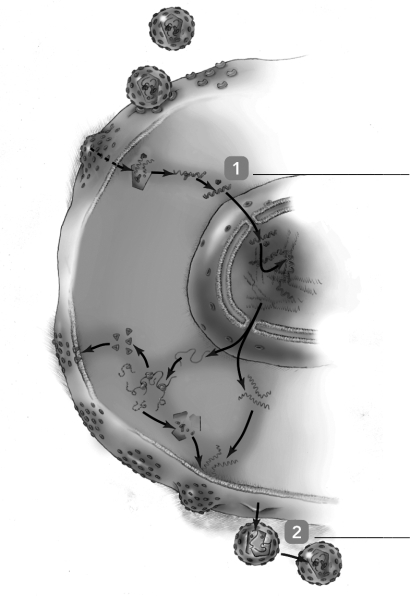 The figure represents the HIV infection cycle. What virus-specified proteins are required for the
The figure represents the HIV infection cycle. What virus-specified proteins are required for theEvents indicated by 1 and 2? (Be sure they are in the correct sequence.)
A) reverse transcriptase, protease
B) RNA polymerase, gp120
C) integrase, protease
D) gp41, protease
E) integrase, gp120

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Infection with certain viruses may lead to the development of type I diabetes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The syndrome known as AIDS is characterized by
A) the presence of HIV.
B) an opportunistic disease resulting from herpesvirus reactivation.
C) one or more opportunistic diseases and the presence of HIV.
D) CTL attack on CD4 T cells.
E) the presence of anti-HIV antibodies.
A) the presence of HIV.
B) an opportunistic disease resulting from herpesvirus reactivation.
C) one or more opportunistic diseases and the presence of HIV.
D) CTL attack on CD4 T cells.
E) the presence of anti-HIV antibodies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is a disease resulting from accumulation of immune complexes in various organs and tissues.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Normally, complement-activating immune complexes are eliminated from the body by phagocytosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
MHC genes are significant genetic factors in predisposition to develop autoimmune disease.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Although autoantibodies to nucleic acids are characteristic of (HIV/GVH/SLE), many other autoantibodies are produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Graft rejection can be reduced by
A) preventing T cell proliferation.
B) preventing B cell activation.
C) antiphagocytic factors.
D) epinephrine.
E) antihistamines.
A) preventing T cell proliferation.
B) preventing B cell activation.
C) antiphagocytic factors.
D) epinephrine.
E) antihistamines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Opportunistic infections typical of AIDS but rare otherwise include
A) tuberculosis.
B) Pneumocystis pneumonia.
C) tuberculosis and shingles.
D) Pneumocystis pneumonia and Kaposiʹs sarcoma.
E) Kaposiʹs sarcoma.
A) tuberculosis.
B) Pneumocystis pneumonia.
C) tuberculosis and shingles.
D) Pneumocystis pneumonia and Kaposiʹs sarcoma.
E) Kaposiʹs sarcoma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Children with Bruton-type agammaglobulinemia are highly susceptible to recurrent bacterial infections.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
In most cases, production of antibodies against foreign ABO antigens is stimulated by exposure to foreign blood cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Critically low levels of CD4 lymphocytes are a key diagnostic indicator of (AIDS/SCID/SLE).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Failure of the (spleen/thymus/thyroid) to develop results in DiGeorge syndrome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Hashimotoʹs thyroiditis and Gravesʹ disease are autoimmune diseases involving the thyroid, but Hashimotoʹs results in hypothyroidism (low thyroid function), whereas Gravesʹ results in hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid). Both diseases are characterized by antithyroid antibodies. Discuss ways in which the autoimmune responses may produce the different outcomes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The (histamines/leukotrienes/prostaglandins/proteases) released in an immediate hypersensitivity reaction leads to the destruction of nearby cells and the activation of the complement system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A positive response on a tuberculin test is an example of a type (I/II/III/IV) hypersensitivity response. (Be sure to use Roman numerals in your answer.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A graft that is from one identical twin to another is an (allograft/autograft/isograft).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A recent news story claimed a man was cured of AIDS by a bone marrow transplant he had received three years previously for treatment of leukemia. The donor bone marrow cells lacked the fusin (CCR) protein. Discuss basis for this claim and whether or not it is reasonable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A person with (A/B/AB/O) blood type can safely receive any blood type for transfusion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
One feature of hemolytic disease of the newborn is excessive (erythrocytes/bilirubin/hemoglobin), which leads to jaundice in the newborn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A patient arrives at a hospital suffering from serious difficulty breathing and shortness of breath. Initial tests indicate none of the standard respiratory infectious agents are present. The physician suspects an immune disorder. What clinical indicators would distinguish between asthma, pneumonitis and Pneumocystic pneumonia?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Compare and contrast type I hypersensitivity with type IV hypersensitivity with respect to reaction time, mediators, and cells involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
One of the important inherited defects in the second line of immune defense is a condition called chronic granulomatous disease. What is this disease, and how is it caused?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Stress may result in the production of (corticosteroids/leukotrienes/interleukins), which may lead to acquired immunodeficiency disease.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Type 1 diabetes mellitus is the result of CTL attack on the (kidney/pancreas/thyroid).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Binding of IgE to the surface of sensitized cells leads to (activation/degranulation/lysis) of the cell, releasing many inflammatory chemicals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The damage caused by mismatched blood transfusions results from the activation of (antibody/complement/histamine) proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



