Deck 6: Bone Tissue
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Bone Tissue
1
Which of the following are true of yellow bone marrow? 1. It is the main site of blood cell production.
2) It is located in the medullary (marrow) cavities of long bones.
3) It is located in hipbones, sternum, ribs, and vertebrae.
4) It is a site of energy storage in the form of triglycerides.
5) It becomes more abundant relative to red bone marrow with increasing age due to the conversion of red bone marrow to yellow bone marrow.
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 2
C) 1, 2, and 5
D) 2, 4, and 5
2) It is located in the medullary (marrow) cavities of long bones.
3) It is located in hipbones, sternum, ribs, and vertebrae.
4) It is a site of energy storage in the form of triglycerides.
5) It becomes more abundant relative to red bone marrow with increasing age due to the conversion of red bone marrow to yellow bone marrow.
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 2
C) 1, 2, and 5
D) 2, 4, and 5
D
2
Appearance of the epiphyseal line means
A) the end of lengthwise growth of that bone
B) total replacement of epiphyseal plate by bone
C) all chondrocytes of the epiphyseal plate are dead
D) all of these choices
A) the end of lengthwise growth of that bone
B) total replacement of epiphyseal plate by bone
C) all chondrocytes of the epiphyseal plate are dead
D) all of these choices
D
3
In the diagram of bone tissue, which label is on the central canal? 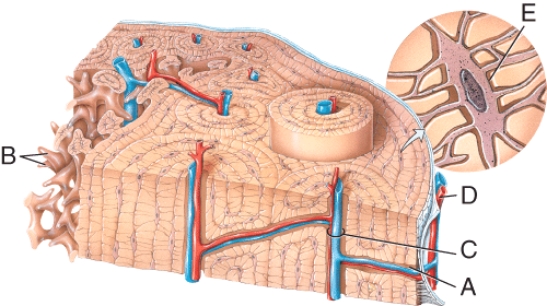
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C
4
A characteristic of osteocytes is that they
A) maintain the daily metabolism of bone tissue
B) are responsible for the formation of matrix
C) undergo mitosis and develop into osteoblasts
D) undergo mitosis and develop into osteoclasts
E) are responsible for the destruction (resorption) of matrix and the release of calcium into the bloodstream
A) maintain the daily metabolism of bone tissue
B) are responsible for the formation of matrix
C) undergo mitosis and develop into osteoblasts
D) undergo mitosis and develop into osteoclasts
E) are responsible for the destruction (resorption) of matrix and the release of calcium into the bloodstream

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Normal bone growth and replacement depend on the presence of
A) the vitamins A, B12, C, and D
B) the minerals calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, boron, and manganese
C) calcitonin, parathyroid hormone, human growth hormone, sex hormones, and thyroid hormones
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) the vitamins A, B12, C, and D
B) the minerals calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, boron, and manganese
C) calcitonin, parathyroid hormone, human growth hormone, sex hormones, and thyroid hormones
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The nutrient artery of a long bone
A) divides into branches that supply the marrow and the inner portion of the diaphysis
B) travels through Volkmann's (perforating) canals
C) supplies the marrow and bony tissue of the epiphysis
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) divides into branches that supply the marrow and the inner portion of the diaphysis
B) travels through Volkmann's (perforating) canals
C) supplies the marrow and bony tissue of the epiphysis
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Functions of the skeletal system do NOT include
A) protection of vital organs such as heart, lungs, and brain
B) blood cell production
C) control of body temperature
D) energy storage in the form of adipose tissue
A) protection of vital organs such as heart, lungs, and brain
B) blood cell production
C) control of body temperature
D) energy storage in the form of adipose tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The hardness of bone is due to crystallized inorganic mineral salts such as calcium phosphate. The flexibility and tensile strength of bone are due to organic molecules such as collagen fibers.
A) Both statements are true.
B) The first statement is true; the second is false.
C) The first statement is false; the second is true.
D) Both statements are false.
A) Both statements are true.
B) The first statement is true; the second is false.
C) The first statement is false; the second is true.
D) Both statements are false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A characteristic of osteoclasts is that they
A) maintain the daily metabolism of bone tissue
B) are responsible for the formation of matrix
C) undergo mitosis and develop into osteoblasts
D) are responsible for the destruction (resorption) of matrix and the release of calcium into the bloodstream
A) maintain the daily metabolism of bone tissue
B) are responsible for the formation of matrix
C) undergo mitosis and develop into osteoblasts
D) are responsible for the destruction (resorption) of matrix and the release of calcium into the bloodstream

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following is not true of periosteum?
A) It consists of two layers, the inner osteogenic and outer fibrous layers.
B) It assists in fracture repair.
C) It covers and protects the articular cartilages.
D) It serves as a point of attachment for tendons and ligaments.
A) It consists of two layers, the inner osteogenic and outer fibrous layers.
B) It assists in fracture repair.
C) It covers and protects the articular cartilages.
D) It serves as a point of attachment for tendons and ligaments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A good description of a medullary (marrow) cavity is that it
A) is located in spaces between trabeculae
B) allows movement of nutrients between osteocytes
C) is a region of bone that contains yellow bone marrow
D) is a region of bone that contains red bone marrow
A) is located in spaces between trabeculae
B) allows movement of nutrients between osteocytes
C) is a region of bone that contains yellow bone marrow
D) is a region of bone that contains red bone marrow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What bone disorder is best described as inadequate calcification of the extracellular matrix, usually caused by a vitamin D deficiency?
A) rickets
B) osteomalacia
C) all of these choices
D) none of these choices
A) rickets
B) osteomalacia
C) all of these choices
D) none of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Put the following in correct order for endochondral ossification. 1. Mesenchymal cells of the embryo develop into cartilage-producing cells.
2) The periosteum (formerly perichondrium) begins to produce a thin layer of compact bone.
3) A hyaline cartilage model of the future bone is formed.
4) Cartilage in the midregion of the model becomes calcified.
5) Spongy bone tissue develops at the primary ossification center.
6) Secondary ossification centers produce spongy bone tissue of the epiphyses.
7) Medullary cavity is formed.
A) 1, 3, 4, 2, 5, 7, 6
B) 7, 2, 3, 1, 4, 5, 6
C) 3, 1, 2, 6, 7, 4, 5
D) 1, 3, 2, 4, 6, 5, 7
2) The periosteum (formerly perichondrium) begins to produce a thin layer of compact bone.
3) A hyaline cartilage model of the future bone is formed.
4) Cartilage in the midregion of the model becomes calcified.
5) Spongy bone tissue develops at the primary ossification center.
6) Secondary ossification centers produce spongy bone tissue of the epiphyses.
7) Medullary cavity is formed.
A) 1, 3, 4, 2, 5, 7, 6
B) 7, 2, 3, 1, 4, 5, 6
C) 3, 1, 2, 6, 7, 4, 5
D) 1, 3, 2, 4, 6, 5, 7

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The areas between neighboring osteons contain
A) interstitial lamellae.
B) circumferential lamellae.
C) yellow bone marrow.
D) red bone marrow.
A) interstitial lamellae.
B) circumferential lamellae.
C) yellow bone marrow.
D) red bone marrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which one of the following is characteristic of spongy bone tissue, but not of compact bone tissue?
A) trabeculae
B) haversian systems
C) osteocytes in lacunae
D) lamellae
A) trabeculae
B) haversian systems
C) osteocytes in lacunae
D) lamellae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Osteocytes are the mature bone cells that develop directly from _____.
A) osteogenic cells
B) osteoblasts
C) osteoclasts
D) white blood cells
A) osteogenic cells
B) osteoblasts
C) osteoclasts
D) white blood cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Growth in length as a long bone develops is called _____ growth.
A) intramembranous
B) interstitial
C) appositional
D) periosteal
A) intramembranous
B) interstitial
C) appositional
D) periosteal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The strength of the diaphysis of a long bone is due to 1. the presence of compact bone.
2) the longitudinal orientation of the osteons.
3) the presence of trabeculae.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2 are both correct
2) the longitudinal orientation of the osteons.
3) the presence of trabeculae.
A) 1 only
B) 2 only
C) 3 only
D) 1 and 2 are both correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A major change in bone tissue that occurs with aging and that leads to increased brittleness is _____.
A) demineralization
B) decreased protein synthesis
C) increased bone remodeling
D) all of these choices
A) demineralization
B) decreased protein synthesis
C) increased bone remodeling
D) all of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Intramembranous ossification is the process that
A) produces most bones.
B) produces only flat bones of the cranium.
C) results in growth in length of long bones.
D) none of these choices.
A) produces most bones.
B) produces only flat bones of the cranium.
C) results in growth in length of long bones.
D) none of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following best describes a facet?
A) prominent border or ridge
B) large, rounded, usually roughened surface for muscle attachment
C) large projection for muscle attachment on the femur
D) smooth, flat surface
E) rounded articular surface
A) prominent border or ridge
B) large, rounded, usually roughened surface for muscle attachment
C) large projection for muscle attachment on the femur
D) smooth, flat surface
E) rounded articular surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following is an organic part of bone matrix that gives bone its flexibility and tensile strength?
A) calcium
B) osteoclasts
C) osteocytes
D) hydroxyapatites
E) collagen
A) calcium
B) osteoclasts
C) osteocytes
D) hydroxyapatites
E) collagen

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following best describes an epicondyle?
A) prominence above or beside a condyle
B) tube-like passageway
C) depression
D) rounded articular surface
E) smooth, flat surface
A) prominence above or beside a condyle
B) tube-like passageway
C) depression
D) rounded articular surface
E) smooth, flat surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The epiphyseal plate is
A) in a young bone, the site of growth in length
B) a structural unit of compact bone
C) a thin plate of bone in spongy bone
D) essential for growth in diameter of a long bone
A) in a young bone, the site of growth in length
B) a structural unit of compact bone
C) a thin plate of bone in spongy bone
D) essential for growth in diameter of a long bone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An osteon (haversian system) is
A) in a young bone, the site of growth in length
B) a structural unit of compact bone
C) a region of bone that contains yellow bone marrow
D) a region of bone that contains red bone marrow
A) in a young bone, the site of growth in length
B) a structural unit of compact bone
C) a region of bone that contains yellow bone marrow
D) a region of bone that contains red bone marrow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Bone matrix contains crystallized mineral salts called hydroxyapatite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following best describes a crest?
A) prominent border or ridge
B) large, rounded, usually roughened surface for muscle attachment
C) large projection for muscle attachment on the femur
D) smooth, flat surface
E) rounded articular surface
A) prominent border or ridge
B) large, rounded, usually roughened surface for muscle attachment
C) large projection for muscle attachment on the femur
D) smooth, flat surface
E) rounded articular surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The femur and humerus contain
A) red bone marrow in the proximal epiphysis
B) articular cartilage on the diaphysis
C) a growth area in the metaphysis of an adult bone
D) compact bone in the center of the epiphyses
A) red bone marrow in the proximal epiphysis
B) articular cartilage on the diaphysis
C) a growth area in the metaphysis of an adult bone
D) compact bone in the center of the epiphyses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following best describes a condyle?
A) prominent border or ridge
B) large, rounded, usually roughened surface for muscle attachment
C) large projection for muscle attachment on the femur
D) smooth, flat surface
E) rounded articular surface
A) prominent border or ridge
B) large, rounded, usually roughened surface for muscle attachment
C) large projection for muscle attachment on the femur
D) smooth, flat surface
E) rounded articular surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A lamella is
A) in a young bone, the site of growth in length
B) a structural unit of compact bone
C) a ring of matrix
D) a region of bone that contains red bone marrow
A) in a young bone, the site of growth in length
B) a structural unit of compact bone
C) a ring of matrix
D) a region of bone that contains red bone marrow

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following best describes a fossa?
A) prominence above or beside a condyle
B) tube-like passageway
C) depression
D) rounded articular surface
E) smooth, flat surface
A) prominence above or beside a condyle
B) tube-like passageway
C) depression
D) rounded articular surface
E) smooth, flat surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following best describes a meatus?
A) prominence above or beside a condyle
B) tube-like passageway
C) depression
D) rounded articular surface
E) smooth, flat surface
A) prominence above or beside a condyle
B) tube-like passageway
C) depression
D) rounded articular surface
E) smooth, flat surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Canaliculi allow nutrients to diffuse to mature bone cells located within lacunae of the osteon. Which of the following are those mature bone cells?
A) osteoblasts
B) osteoclasts
C) osteocytes
D) osteogenic cells
E) chondrocytes
A) osteoblasts
B) osteoclasts
C) osteocytes
D) osteogenic cells
E) chondrocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following best describes a tuberosity?
A) prominent border or ridge
B) large, rounded, usually roughened surface for muscle attachment
C) large projection for muscle attachment on the femur
D) smooth, flat surface
E) rounded articular surface
A) prominent border or ridge
B) large, rounded, usually roughened surface for muscle attachment
C) large projection for muscle attachment on the femur
D) smooth, flat surface
E) rounded articular surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following best describes a trochanter?
A) prominent border or ridge
B) large, rounded, usually roughened surface for muscle attachment
C) large projection for muscle attachment on the femur
D) smooth, flat surface
E) rounded articular surface
A) prominent border or ridge
B) large, rounded, usually roughened surface for muscle attachment
C) large projection for muscle attachment on the femur
D) smooth, flat surface
E) rounded articular surface

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Spongy bone is located
A) in the epiphyses of long bones
B) in the diploe of flat bones
C) in the ribs and sternum
D) all of these choices
A) in the epiphyses of long bones
B) in the diploe of flat bones
C) in the ribs and sternum
D) all of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Activity of which of these cells is responsible for the remodeling of the bony callus as the final step in fracture repair?
A) Osteoblasts
B) Osteoclasts
C) Osteocytes
D) Osteogenic cells
E) Chondrocytes
A) Osteoblasts
B) Osteoclasts
C) Osteocytes
D) Osteogenic cells
E) Chondrocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A good description of a perforating canal is that it
A) is located in spaces between trabeculae
B) allows movement of nutrients between osteocytes
C) contains yellow bone marrow
D) allows blood vessels and nerves to penetrate compact bone tissue
A) is located in spaces between trabeculae
B) allows movement of nutrients between osteocytes
C) contains yellow bone marrow
D) allows blood vessels and nerves to penetrate compact bone tissue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which of the following is a true statement about bone surface markings?
A) Most are not present at birth but develop as forces are exerted on bones and are most prominent during adult life.
B) Processes and outgrowths are the result of tension from tendons and ligaments on the periosteum of a bone.
C) Surface markings on skeletal remains may provide information related to age and sex.
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) Most are not present at birth but develop as forces are exerted on bones and are most prominent during adult life.
B) Processes and outgrowths are the result of tension from tendons and ligaments on the periosteum of a bone.
C) Surface markings on skeletal remains may provide information related to age and sex.
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The connective tissue found on the articular surface at the end of a bone is called endosteum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The vertebrae are classed according to shape as short bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A Colles' fracture involves the distal end of the lateral forearm bone (radius).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Osteopenia is a decrease in bone mass below normal, as occurs in osteoporosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Following completion of ossification, bone replacement occurs only if bone tissue is injured.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The perichondrium of the cartilage model becomes the periosteum of compact bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Draw a diagram of a typical mature long bone shown in sagittal section. Label the regions and tissues and identify the sites for red and yellow bone marrow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Briefly describe the structure and function of each of the four zones of cartilage of the epiphyseal plate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
At birth, all bones are cartilaginous. Ossification occurs only after birth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The nutrient artery of a long bone branches into proximal, distal, epiphyseal, and metaphyseal branches, and therefore supplies the entire bone with blood.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Explain why damage to the epiphyseal plate in childhood may result in the fractured bone being shorter than normal once adult stature is reached.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Explain what is meant by "hot spots" and "cold spots" seen on a diagnostic bone scan.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Microscopic canals that run longitudinally through bone tissue and that contain blood vessels and nerves are called perforating (Volkmann's) canals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Sesamoid and sutural bones are the two types of bones that are the most variable in number in the human body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Cigarette smoking is a risk factor for developing Osteoporosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In matrix formation, calcification precedes the secretion of collagen by osteoblasts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Most bones develop in a process whereby hyaline cartilage models are replaced by bone tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
As a long bone grows in length, new cartilage cells are produced on the epiphyseal side of the epiphyseal plate and bone replaces cartilage on the diaphyseal side of the plate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What factors are necessary for normal bone growth and replacement?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The bone tissue of the distal region of the femur is replaced about every 4 months, whereas some regions of the shaft of the femur may never be replaced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Primary ossification proceeds from the external surfaces inward; secondary ossification proceeds from the interior outward toward the external surface of a bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
On the basis of shape, the femur is an example of a _____ bone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The epiphyseal plate separates the epiphysis and diaphysis of a growing bone. The four zones of cartilage found here, in order from epiphyseal edge to diaphyseal edge are _____, _____, _____, and _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In aging females, decreasing levels of estrogen accelerate the loss of _____ from bone tissue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The process by which bone tissue replaces hyaline cartilage is _____ ossification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The spaces in bone tissue that contain osteocytes are called _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The lifelong replacement and redistribution of bone matrix is referred to as _____ __________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Mechanical stress on bone is due to the contraction of skeletal muscles and due to _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A bone fracture in which the broken ends of the bone can be seen protruding from the skin is called a/an _____ fracture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The region of a long bone where the epiphysis and diaphysis join is called the _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
According to shape classification, the phalanges of the fingers and toes are _____ bones.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The artery entering near the center of the diaphysis is the _____ artery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Medications used to treat osteoporosis are generally of two types: _____ and _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The process of _____ ossification produces flat bones of the skull and the lower jawbone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
For bones to unite properly, the fractured ends must be brought into alignment. In _____, the fractured ends of a bone are brought into alignment by manual manipulation, and the skin remains intact. In _____, the fractured ends of a bone are brought into alignment by a surgical procedure using internal fixation devices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Explain why bedridden patients can lose bone mass.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



