Deck 24: The Digestive System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 24: The Digestive System
1
Place the following in the correct order, as found in the muscularis layer of the stomach, from outermost to innermost: 1. oblique layer
2) circular layer
3) longitudinal layer
A) 2, 1, 3
B) 3, 1, 2
C) 1, 2, 3
D) 3, 2, 1
2) circular layer
3) longitudinal layer
A) 2, 1, 3
B) 3, 1, 2
C) 1, 2, 3
D) 3, 2, 1
D
2
The head of the pancreas is located closest to the:
A) curve of the duodenum.
B) lesser curvature of the stomach.
C) inferior surface of the liver.
D) medial surface of the spleen.
A) curve of the duodenum.
B) lesser curvature of the stomach.
C) inferior surface of the liver.
D) medial surface of the spleen.
A
3
A portal triad in the liver consists of which three basic structures:
A) a common bile duct, and branches of the right and left hepatic ducts.
B) a branch of the hepatic portal vein, a branch of the hepatic artery, and a bile duct.
C) branches of the hepatic portal vein, hepatic vein, and hepatic artery.
D) branches of the hepatic artery, central vein, and hepatic vein.
A) a common bile duct, and branches of the right and left hepatic ducts.
B) a branch of the hepatic portal vein, a branch of the hepatic artery, and a bile duct.
C) branches of the hepatic portal vein, hepatic vein, and hepatic artery.
D) branches of the hepatic artery, central vein, and hepatic vein.
B
4
The functions of the esophagus include:
A) secretion of enzymes.
B) mixing of food and secretions.
C) absorption of H2O and small nutrients.
D) none of these choices
A) secretion of enzymes.
B) mixing of food and secretions.
C) absorption of H2O and small nutrients.
D) none of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is an intrinsic muscle of the tongue?
A) longitudinalis superior
B) hyoglossus
C) genioglossus
D) styloglossus
A) longitudinalis superior
B) hyoglossus
C) genioglossus
D) styloglossus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following does NOT drive the contents of the colon into the rectum?
A) peristalsis
B) mass peristalsis
C) segmentation
D) haustral churning
A) peristalsis
B) mass peristalsis
C) segmentation
D) haustral churning

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following is NOT a function of the gallbladder?
A) concentrate bile
B) store bile
C) eject bile into the cystic duct
D) synthesize bile
A) concentrate bile
B) store bile
C) eject bile into the cystic duct
D) synthesize bile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Bile helps accomplish which of the following? 1. chemical (enzymatic) breakdown of protein
2) emulsification of large lipid globules
3) absorption of digested lipids
4) maintenance of an alkaline pH in the duodenum
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 1, 2, 3
C) 2, 3
D) 1, 3, 4
2) emulsification of large lipid globules
3) absorption of digested lipids
4) maintenance of an alkaline pH in the duodenum
A) 1, 2, 3, 4
B) 1, 2, 3
C) 2, 3
D) 1, 3, 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The layer of areolar connective tissue underlying the epithelium of the mucosa of the GI tract is called the _____.
A) adventitia
B) lamina propria
C) submucosa
D) peritoneum
A) adventitia
B) lamina propria
C) submucosa
D) peritoneum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The structure attached to the soft palate that helps close off the nasopharynx during swallowing is the _____.
A) fauces
B) uvula
C) epiglottis
D) tongue
A) fauces
B) uvula
C) epiglottis
D) tongue

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The salivary glands whose ducts open on either side of the lingual frenulum are the:
A) parotid glands.
B) sublingual glands.
C) submandibular glands.
D) buccal glands.
A) parotid glands.
B) sublingual glands.
C) submandibular glands.
D) buccal glands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Liver cells called _____ produce bile.
A) stellate reticuloendothelial cells
B) phagocytes
C) hepatocytes
D) endothelial cells
A) stellate reticuloendothelial cells
B) phagocytes
C) hepatocytes
D) endothelial cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The bonelike substance that attaches the root of a tooth to the periodontal ligament is _____.
A) dentin
B) enamel
C) cementum
D) gingiva
A) dentin
B) enamel
C) cementum
D) gingiva

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The peritoneal fold situated as a "fatty apron" anterior to the small intestine is the _____.
A) mesentery
B) falciform ligament
C) lesser omentum
D) greater omentum
A) mesentery
B) falciform ligament
C) lesser omentum
D) greater omentum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is an anatomical feature of the small intestine that serves to increase the surface area for digestion and absorption?
A) lacteals
B) microvilli
C) rugae
D) all of these choices
A) lacteals
B) microvilli
C) rugae
D) all of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Peristaltic contractions:
A) occur in the stomach, esophagus, small intestine, and large intestine.
B) are primarily responsible for mixing the food with the digestive juices.
C) are of similar strength throughout the digestive tract.
D) all of these choices
A) occur in the stomach, esophagus, small intestine, and large intestine.
B) are primarily responsible for mixing the food with the digestive juices.
C) are of similar strength throughout the digestive tract.
D) all of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Contraction of which of the following aid in defecation? 1. external anal sphincter
2) circular colon muscles
3 longitudinal rectal muscles
4) internal anal sphincter
5) diaphragm
6) abdominal muscles
A) 2, 3, 5, 6
B) 1, 2, 3, 4
C) 1, 2, 4
D) 3, 5, 6
2) circular colon muscles
3 longitudinal rectal muscles
4) internal anal sphincter
5) diaphragm
6) abdominal muscles
A) 2, 3, 5, 6
B) 1, 2, 3, 4
C) 1, 2, 4
D) 3, 5, 6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The sphincter of the hepatopancreatic ampulla (sphincter of Oddi) directly controls the flow of bile between:
A) the liver and the gallbladder.
B) the liver and the common bile duct
C) the gallbladder and the cystic duct
D) the common bile duct and the duodenum
A) the liver and the gallbladder.
B) the liver and the common bile duct
C) the gallbladder and the cystic duct
D) the common bile duct and the duodenum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The _____ of the stomach is/are responsible for the production of gastric juice.
A) rugae
B) gastric glands
C) fundus
D) serosa
A) rugae
B) gastric glands
C) fundus
D) serosa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The stomach occupies the following abdominal region(s):
A) umbilical.
B) left hypochondriac.
C) epigastric.
D) all of these choices
A) umbilical.
B) left hypochondriac.
C) epigastric.
D) all of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Antacid tablets (e.g. TUMS, ROLAIDS) are used to help neutralize the acidity of gastric contents. What cells are responsible for this acidity?
A) chief
B) mucus
C) rugae
D) parietal
A) chief
B) mucus
C) rugae
D) parietal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In the wall of the GI tract, the mucosa and muscularis layers both contain smooth muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The hepatic veins deliver nutrient-rich blood to the sinusoids of the liver.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the permanent dentition, the teeth that have two cusps and commonly two roots are the upper first premolars (bicuspids).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which dome-shaped region of the stomach is located under the diaphragm?
A) fundus
B) cardia
C) greater curvature
D) pylorus
A) fundus
B) cardia
C) greater curvature
D) pylorus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The secretory activity of the salivary glands is controlled via vasoconstriction and vasodilation of their blood vessels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Mucus in the small intestine is secreted by goblet cells in the mucosa and by duodenal glands (Brunner's glands) in the submucosa of the duodenum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The tongue is attached to the floor of the oral cavity by a fold of mucous membrane called the labial frenulum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The greater curvature of the stomach is closer to the liver than is the lesser curvature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The opening of the accessory pancreatic duct (duct of Santorini) into the duodenum is inferior to the opening of the hepatopancreatic ampulla (ampulla of Vater).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Paneth cells, circular folds (plicae circulares), brush border enzymes and lacteals are all characteristics of the small intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Bile secreted from the gallbladder and pancreatic juice secreted from the pancreas enter which portion of the GI tract?
A) cecum
B) duodenum
C) ileum
D) jejunum
A) cecum
B) duodenum
C) ileum
D) jejunum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
As a result of the action of pancreatic enzymes, the following are digested in the lumen of the small intestine: carbohydrates (starches), proteins, triglycerides (fats and oils), nucleic acids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Enzymatic breakdown of food is a form of mechanical digestion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The pancreas is the largest internal organ and heaviest gland of the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The palatine tonsils are located in the uvula, at the posterior border of the soft palate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Most pancreatic tissue is exocrine in function and is arranged in cell clusters called acini.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Advancing a gastric tube from the oral cavity to the oropharynx requires passing through the:
A) fauces
B) parotid gland
C) chonae
D) inferior meatus
A) fauces
B) parotid gland
C) chonae
D) inferior meatus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The muscularis layer of the esophagus contains skeletal muscle superiorly and changes to smooth muscle inferiorly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The four main regions of the stomach are cardia, fundus, cecum, and pylorus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following substances need to undergo digestion before being absorbed into the cells lining the alimentary canal?
A) water
B) vitamins
C) minerals
D) proteins
E) cholesterols
A) water
B) vitamins
C) minerals
D) proteins
E) cholesterols

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What is the structure indicated in the figure? 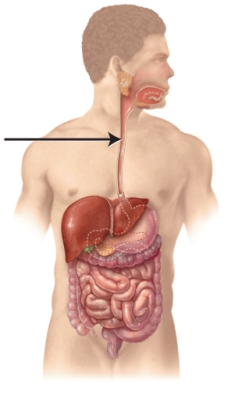
A) stomach
B) pancreas
C) esophagus
D) pharynx

A) stomach
B) pancreas
C) esophagus
D) pharynx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The esophagus is not suspended in a cavity and therefore will not have a true serous membrane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Describe the teeth of the permanent dentition in order from anterior to posterior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Describe the route traveled by bile from the time it is secreted until it enters the duodenum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following is an accessory digestive organ?
A) tongue
B) mouth
C) esophagus
D) small intestine
E) large intestine
A) tongue
B) mouth
C) esophagus
D) small intestine
E) large intestine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The gastrointestinal (GI) tract is found in the thoracic, abdominal and pelvic cavities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Trace the route most commonly traveled by pancreatic juice, from its production until it is in the lumen of the intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The type of epithelial tissue found in the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, and anal canal is keratinized stratified squamous epithelium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Describe the structure of a tooth and illustrate your answer with a labeled diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Describe the route traveled by chyme from the time it leaves the ileum until it is expelled as feces from the body. As you mention the regions of the large intestine, state which are retroperitoneal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Pouches of the large intestine that give it a puckered appearance are called epiploic (omental) appendices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
From the primitive gut, the endodermal layer gives rise to the epithelial lining and glands of most of the GI tract, whereas the smooth muscle and connective tissue develop from the mesodermal layer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
What is the structure the arrow is pointing to? 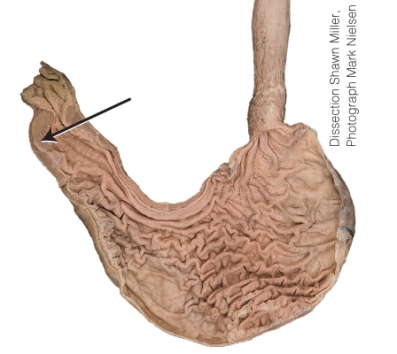
A) rugae
B) fundus
C) cardia
D) pyloric sphincter

A) rugae
B) fundus
C) cardia
D) pyloric sphincter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The length of the GI tract is longer after death because of a lack of _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Identify the structure indicated in the figure. 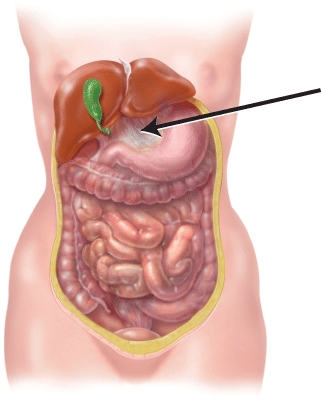
A) gallbladder
B) sigmoid colon
C) greater omentum
D) lesser omentum

A) gallbladder
B) sigmoid colon
C) greater omentum
D) lesser omentum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What structure is the arrow is pointing to? 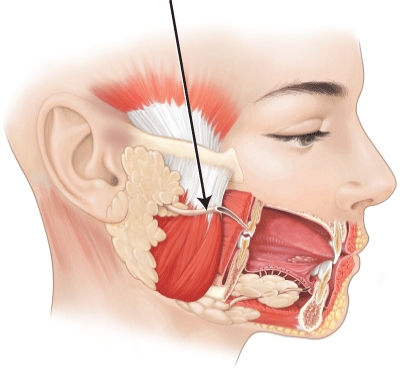
A) parotid duct
B) mylohyoid duct
C) submandibular duct
D) sublingual duct

A) parotid duct
B) mylohyoid duct
C) submandibular duct
D) sublingual duct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The release of hydrochloric acid (HCl) into the lumen of the stomach is which basic process of digestion?
A) ingestion
B) secretion
C) absorption
D) defecation
E) mastication
A) ingestion
B) secretion
C) absorption
D) defecation
E) mastication

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Describe the gross anatomy of the stomach. Illustrate your answer with a labeled diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The cells of the serous layer of the alimentary canal come in contact with food.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the small intestine, segmentation begins with the contraction of this muscle layer.
A) longitudinal
B) circular
C) oblique
A) longitudinal
B) circular
C) oblique

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The esophagus lies anterior to the trachea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The greater omentum attaches to which two organs in the abdominopelvic cavity?
A) liver and lesser curvature of the stomach
B) greater curvature of the stomach and transverse colon
C) ascending colon and duodenum
D) pancreas and kidney
A) liver and lesser curvature of the stomach
B) greater curvature of the stomach and transverse colon
C) ascending colon and duodenum
D) pancreas and kidney

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Common changes in the digestive organs in the elderly include decreased mobility, increased mucosal secretions, and malabsoprtion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Substances secreted from the pancreas gives pancreatic juice a slightly alkaline pH which buffers the acids in the chyme.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The cecum directs waste into which structure of the large intestine?
A) descending colon
B) transverse colon
C) ascending colon
D) sigmoid colon
A) descending colon
B) transverse colon
C) ascending colon
D) sigmoid colon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Deglutition occurs in the pharynx when _____ muscles contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which region of the GI track receives a bolus from oral cavity and passes it into the esophagus?
A) oropharynx
B) laryngopharynx
C) nasopharynx
D) oropharynx and laryngopharynx are correct
E) oropharynx and nasopharynx are correct
A) oropharynx
B) laryngopharynx
C) nasopharynx
D) oropharynx and laryngopharynx are correct
E) oropharynx and nasopharynx are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Which of the following substances are not absorbed in the large intestine?
A) water
B) vitamins
C) soluble fiber
D) electrolytes
A) water
B) vitamins
C) soluble fiber
D) electrolytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which type of papillae of the tongue lack taste buds and are used to detect touch rather than taste?
A) fungiform papillae
B) vallate (circumvallate) papillae
C) foliate papillae
D) filiform papillae
A) fungiform papillae
B) vallate (circumvallate) papillae
C) foliate papillae
D) filiform papillae

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The upper esophageal sphincter is composed of a circular band of skeletal muscle. The lower esophageal sphincter is composed of a circular band of smooth muscle.
A) Both statements are true.
B) Both statements are false.
C) The first statement is true; the second is false.
D) The second statement is true; the first is false.
A) Both statements are true.
B) Both statements are false.
C) The first statement is true; the second is false.
D) The second statement is true; the first is false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
During fetal development, which structure develops from the foregut?
A) appendix
B) jejunum
C) pharynx
D) sigmoid colon
E) anal canal
A) appendix
B) jejunum
C) pharynx
D) sigmoid colon
E) anal canal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The parietal peritoneum lines the outside of the organs in the abdominopelvic cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which structure of the peritoneum is the only one to attach to the anterior body wall?
A) lesser omentum
B) greater omentum
C) mesentery
D) falciform ligament
E) mesocolon
A) lesser omentum
B) greater omentum
C) mesentery
D) falciform ligament
E) mesocolon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The majority of nutrient digestion and absorption occurs in the small intestine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



