Deck 25: The Urinary System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/100
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 25: The Urinary System
1
Cortical nephrons lack one portion of the renal tubule that is found in juxtamedullary nephrons, the:
A) thick segment of the ascending limb of the nephron loop (loop of Henle).
B) thin segment of the ascending limb of the nephron loop (loop of Henle).
C) proximal convoluted tubule.
D) distal convoluted tubule.
A) thick segment of the ascending limb of the nephron loop (loop of Henle).
B) thin segment of the ascending limb of the nephron loop (loop of Henle).
C) proximal convoluted tubule.
D) distal convoluted tubule.
B
2
Which structure(s) is/are made of skeletal muscle?
A) detrusor muscle (intermediate muscularis)
B) internal urethral sphincter
C) external urethral sphincter
D) detrusor muscle (intermediate muscularis) and external urethral sphincter
A) detrusor muscle (intermediate muscularis)
B) internal urethral sphincter
C) external urethral sphincter
D) detrusor muscle (intermediate muscularis) and external urethral sphincter
C
3
The concave border of the kidney faces the
A) vertebral column
B) diaphragm
C) pelvis
D) urinary bladder
A) vertebral column
B) diaphragm
C) pelvis
D) urinary bladder
A
4
The visceral layer of the glomerular capsule (Bowman's capsule):
A) forms the outermost (superficial) wall of the capsule.
B) contains cells called podocytes.
C) consists of extracellular material.
D) none of these choices
A) forms the outermost (superficial) wall of the capsule.
B) contains cells called podocytes.
C) consists of extracellular material.
D) none of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The two portions of a nephron that commonly contribute to the juxtaglomerular apparatus are the:
A) glomerulus and distal convoluted tubule.
B) descending limb of nephron loop (loop of Henle) and efferent arteriole.
C) final part of ascending limb of nephron loop (loop of Henle) and afferent arteriole.
D) glomerulus and collecting duct.
A) glomerulus and distal convoluted tubule.
B) descending limb of nephron loop (loop of Henle) and efferent arteriole.
C) final part of ascending limb of nephron loop (loop of Henle) and afferent arteriole.
D) glomerulus and collecting duct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following structures normally transport blood? 1. glomerular (Bowman's) capsule
2) glomerulus
3) efferent arteriole
4) nephron loop (loop of Henle)
5) collecting duct
6) vasa recta
A) 1, 4 and 5
B) 2, 3 and 6
C) 4 and 5 only
D) 3 and 6 only
2) glomerulus
3) efferent arteriole
4) nephron loop (loop of Henle)
5) collecting duct
6) vasa recta
A) 1, 4 and 5
B) 2, 3 and 6
C) 4 and 5 only
D) 3 and 6 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which of the following structures is NOT a portion of a nephron?
A) vasa recta
B) nephron loop (loop of Henle)
C) distal convoluted tubule
D) proximal convoluted tubule
A) vasa recta
B) nephron loop (loop of Henle)
C) distal convoluted tubule
D) proximal convoluted tubule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Juxtaglomerular cells:
A) have receptors for both antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and aldosterone.
B) are found in the macula densa.
C) are modified smooth muscle fibers (cells) in the wall of the afferent arteriole.
D) are found in the distal convoluted tubules and collecting duct.
A) have receptors for both antidiuretic hormone (ADH) and aldosterone.
B) are found in the macula densa.
C) are modified smooth muscle fibers (cells) in the wall of the afferent arteriole.
D) are found in the distal convoluted tubules and collecting duct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Trace the route of an oxygenated red blood cell from the time it passes into the kidney in a renal artery until it enters a venule as a deoxygenated red blood cell by placing the following vessels in their correct order: 1. segmental artery
2) arcuate artery
3) interlobar artery
4) peritubular capillary
5) afferent arteriole
6) peritubular venule
7) efferent arteriole
8) cortical radiate artery
9) glomerular capillaries
A) 1, 3, 2, 8, 5, 9, 7, 4, 6
B) 3, 2, 1, 8, 4, 7, 9, 5, 6
C) 1, 8, 2, 3, 7, 9, 5, 4, 6
D) 1, 2, 3, 8, 5, 9, 7, 6, 4
2) arcuate artery
3) interlobar artery
4) peritubular capillary
5) afferent arteriole
6) peritubular venule
7) efferent arteriole
8) cortical radiate artery
9) glomerular capillaries
A) 1, 3, 2, 8, 5, 9, 7, 4, 6
B) 3, 2, 1, 8, 4, 7, 9, 5, 6
C) 1, 8, 2, 3, 7, 9, 5, 4, 6
D) 1, 2, 3, 8, 5, 9, 7, 6, 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The shortest portion of the male urethra is the _____.
A) spongy urethra
B) membranous (intermediate) urethra
C) prostatic urethra
D) penile urethra
A) spongy urethra
B) membranous (intermediate) urethra
C) prostatic urethra
D) penile urethra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Three layers of tissue surround each kidney. They are, in order from innermost (deepest) to outermost (most superficial): 1. renal capsule
2) visceral peritoneum (serosa)
3) adipose capsule
4) renal fascia
A) 1, 3, 4
B) 2, 3, 4
C) 1, 3, 2
D) 4, 3, 1
2) visceral peritoneum (serosa)
3) adipose capsule
4) renal fascia
A) 1, 3, 4
B) 2, 3, 4
C) 1, 3, 2
D) 4, 3, 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The urinary bladder is posterior to the pubic symphysis in males. In females, the urinary bladder is posterior to the vagina.
A) Both statements are true.
B) Both statements are false.
C) The first statement is true; the second is false.
D) The second statement is true; the first is false.
A) Both statements are true.
B) Both statements are false.
C) The first statement is true; the second is false.
D) The second statement is true; the first is false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which of the following is NOT true regarding the location of the kidneys?
A) They are partially protected by the floating ribs (11th and 12th pairs).
B) The left kidney is slightly lower than the right.
C) They are located between the peritoneum and the posterior wall of the abdomen.
D) They are situated between the levels of the last thoracic and third lumbar vertebrae.
A) They are partially protected by the floating ribs (11th and 12th pairs).
B) The left kidney is slightly lower than the right.
C) They are located between the peritoneum and the posterior wall of the abdomen.
D) They are situated between the levels of the last thoracic and third lumbar vertebrae.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Normally, urine is prevented from backing up into the ureters from a full bladder due to:
A) gravity.
B) hydrostatic pressure from the renal pelvis.
C) sphincters (anatomical valves) at the junctions of the ureters and bladder.
D) physiological valves where pressure in the bladder compresses oblique openings into the ureters.
A) gravity.
B) hydrostatic pressure from the renal pelvis.
C) sphincters (anatomical valves) at the junctions of the ureters and bladder.
D) physiological valves where pressure in the bladder compresses oblique openings into the ureters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The right kidney is slightly lower than the left due to the position of which organ?
A) spleen
B) pancreas
C) lung
D) liver
A) spleen
B) pancreas
C) lung
D) liver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In severe cases of urinary incontinence, a suprapubic catheter (a tube placed in the bladder from the anterior abdominal wall) is used to aid in voiding urine. With the placement of this catheter, urine does not pass through the:
A) nephron
B) ureters
C) urethra
D) renal pelvis
A) nephron
B) ureters
C) urethra
D) renal pelvis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The internal urethral sphincter is formed by circular smooth muscle. The external urethral sphincter is derived from voluntary skeletal muscle.
A) Both statements are true.
B) Both statements are false.
C) The first statement is true; the second is false.
D) The second statement is true; the first is false.
A) Both statements are true.
B) Both statements are false.
C) The first statement is true; the second is false.
D) The second statement is true; the first is false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following structures would not be located entering/exiting the renal hilum?
A) blood vessel
B) lymphatic vessel
C) nerve
D) urethra
A) blood vessel
B) lymphatic vessel
C) nerve
D) urethra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A nephron consists of two parts:
A) renal corpuscle and renal tubule.
B) glomerulus and glomerular capsule.
C) proximal and distal convoluted tubules.
D) glomerulus and collecting duct.
A) renal corpuscle and renal tubule.
B) glomerulus and glomerular capsule.
C) proximal and distal convoluted tubules.
D) glomerulus and collecting duct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The lining of the male urethra contains:
A) transitional epithelium.
B) pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
C) stratified squamous epithelium.
D) all of these choices
A) transitional epithelium.
B) pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
C) stratified squamous epithelium.
D) all of these choices

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
There are three openings into the urinary bladder: a pair of ureteral openings and an internal urethral orifice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
_____ is an enzyme released by the kidney which indirectly causes an increase in blood pressure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The renal corpuscle, proximal convoluted tubule, and distal convoluted tubule of a nephron are located within the renal cortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The female urethra opens between the clitoris and the vaginal opening.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
All nephron loops (loops of Henle) receive their blood supply from the vasa recta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The indentation on the concave border of each kidney is the renal _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The distal (last) region of a ureter has only two layers of smooth muscle in the muscularis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A patient who suffers from chronic bladder infections could eventually develop a more serious kidney infection. Which structure is responsible for the spread of the inflammation?
A) urethra
B) physiological valve between bladder and ureter
C) external urethral sphincter
D) internal urethral sphincter
A) urethra
B) physiological valve between bladder and ureter
C) external urethral sphincter
D) internal urethral sphincter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The kidneys contain more cortical nephrons than juxtamedullary nephrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two urethras, one urinary bladder, and one ureter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A renal papilla is located at the base (wider end) of each renal pyramid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The process of tubular reabsorption rids the body of some materials such as hydrogen ions and ammonium ions and some drugs such as penicillin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The renal cortex contains the renal corpuscles and most parts of the renal tubules except for the nephron loops (loops of Henle) of the juxtamedullary nephrons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Approximately 50% of the resting cardiac output is received by the kidneys.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The kidneys release glucose to maintain normal blood glucose levels.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
List the functions of the urinary system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The kidneys are located within peritoneum cavity of the abdomen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The fetal kidneys begin excreting urine by the third month of development, thus contributing most of the volume of the amniotic fluid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The kidneys produce two hormones: calcitrol and calcitonin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The filtration membrane consists of the glomerular capillaries and the podocytes that surround the glomerulus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When mesangial cells relax, the surface area of the glomerulus increases causing glomerular filtration to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
At the base of each renal pyramid, the interlobar arteries arch between the medulla and cortex to become the _____ arteries.
A) cortical radiate
B) arcuate
C) segmental
D) renal
A) cortical radiate
B) arcuate
C) segmental
D) renal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Describe the three coats that make up the wall of the urinary bladder, from innermost (deepest) to outermost (most superficial).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The renal cortex is deep to the renal medulla.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
After birth, growth of nephrons is due to hypertrophy not hyperplasia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What is the structure or area that the arrow is pointing to? 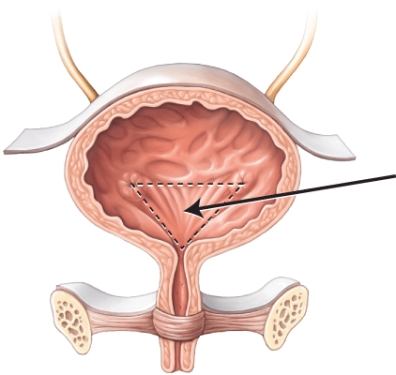
A) peritoneum
B) internal urethral sphincter
C) detrusor muscle
D) trigone

A) peritoneum
B) internal urethral sphincter
C) detrusor muscle
D) trigone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The major blood vessel that supplies the kidney with blood from the heart is the renal artery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Urine formation involves three processes. Define them and name the regions of the nephron and blood supply involved in each process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Describe the layers through which a substance will pass when moving from glomerular blood into filtrate of the capsular space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is the structure indicated in the diagram? 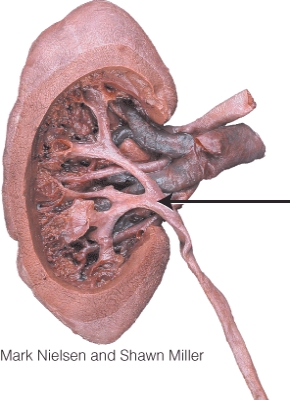
A) renal pelvis
B) minor calyx
C) renal vein
D) major calyx

A) renal pelvis
B) minor calyx
C) renal vein
D) major calyx

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The first branch of the renal artery is the
A) arcuate artery
B) interlobar artery
C) segmental artery
D) efferent arteriole
A) arcuate artery
B) interlobar artery
C) segmental artery
D) efferent arteriole

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Potassium ions (K+) secreted from tubule cells into the tubular fluids help control blood pH.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The proximal convoluted tubule cells have microvilli on their apical surface to assist in reabsorption and secretion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Aldosterone and antidiuretic hormone target the principle cells of the proximal convoluted tubule?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The portion of the renal cortex that extends between the renal pyramids are the
A) renal papilla
B) renal columns
C) renal medulla
D) papillary duct
A) renal papilla
B) renal columns
C) renal medulla
D) papillary duct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What is the structure indicated in the diagram? 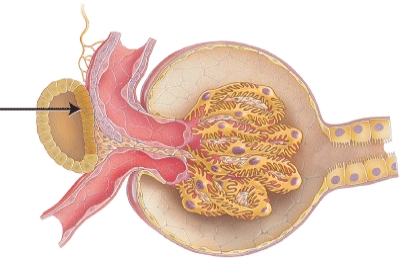
A) mesangial cells
B) pedicels
C) parietal layer of capsule
D) macula densa

A) mesangial cells
B) pedicels
C) parietal layer of capsule
D) macula densa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What structure is the arrow is pointing to? 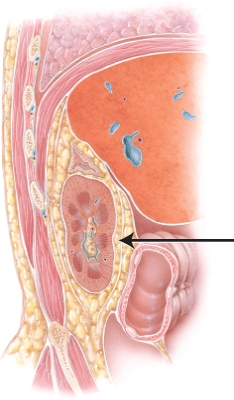
A) suprarenal gland
B) adipose capsule
C) quadratus lumborum
D) peritoneum

A) suprarenal gland
B) adipose capsule
C) quadratus lumborum
D) peritoneum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The kidney has more major calyces than minor calyces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What is the structure that is indicated on the diagram? 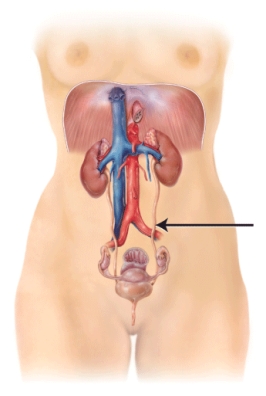
A) right renal artery
B) left renal vein
C) left ureter
D) left urethra

A) right renal artery
B) left renal vein
C) left ureter
D) left urethra

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Filtration of blood plasma occurs at the
A) renal corpuscle
B) renal tubule
C) nephron loop
D) collecting duct
A) renal corpuscle
B) renal tubule
C) nephron loop
D) collecting duct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The movement of water and solutes across blood capillaries into the renal capsule is
A) glomerular filtration
B) tubular reabsorption
C) tubular secretion
A) glomerular filtration
B) tubular reabsorption
C) tubular secretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Each nephron consist of a renal corpuscle and a renal
A) tubule
B) duct
C) limb
D) gland
A) tubule
B) duct
C) limb
D) gland

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
One single collecting duct receives fluid from
A) several distal convoluted tubules
B) several proximal convoluted tubules
C) one distal convoluted tubule
D) several proximal convoluted tubules
A) several distal convoluted tubules
B) several proximal convoluted tubules
C) one distal convoluted tubule
D) several proximal convoluted tubules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The internal urethral sphincter is composed of which arrangement and type of muscle fibers? 1. circular
2) longitudinal
3) oblique
4) smooth
5) skeletal
A) 1 and 4
B) 2 and 4
C) 2 and 5
D) 1, 2, and 5
E) 1, 3 and 5
2) longitudinal
3) oblique
4) smooth
5) skeletal
A) 1 and 4
B) 2 and 4
C) 2 and 5
D) 1, 2, and 5
E) 1, 3 and 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Waste passes from the renal pelvis into this structure, which removes the waste from the kidney.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The movement of water and solutes from the kidney tubules into the bloodstream is
A) glomerular filtration
B) tubular reabsorption
C) tubular secretion
A) glomerular filtration
B) tubular reabsorption
C) tubular secretion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the following substances would be least likely to pass through the fenestrations in the endothelial cells of the glomerulus?
A) sodium ions
B) water
C) proteins
D) glucose
A) sodium ions
B) water
C) proteins
D) glucose

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The _____ _____ is a layer of material between the endothelium of the glomerulus and the podocytes. It contains a negatively charged glycoprotein matrix, which repels larger negatively charged proteins.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
______ is defined by excess excretion of glucose in the urine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A common effect of aging is _____, increased frequency of urination at night.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following is least likely to affect urine flow in the ureters?
A) peristaltic contractions
B) hydrostatic pressure
C) blood pressure
D) gravity
A) peristaltic contractions
B) hydrostatic pressure
C) blood pressure
D) gravity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Which segment of the renal tubule is composed of simple squamous epithelium?
A) proximal convoluted tubule (CT)
B) nephron loop: descending limb and thin ascending limb
C) nephron loop: thick ascending limb
D) distal convoluted tubule
A) proximal convoluted tubule (CT)
B) nephron loop: descending limb and thin ascending limb
C) nephron loop: thick ascending limb
D) distal convoluted tubule

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The inner lining of the ureter secretes _____ to prevent the cells lining the ureter from being damaged by urine.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The mass of the kidney decreases in size as an individual ages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Peritubulular capillaries surround parts of the nephron in the renal cortex. The vasa recta surrounds portions of the nephron in the renal medulla.
A) Both statements are true.
B) Both statements are false.
C) The first statement is true; the second is false.
D) The second statement is true; the first is false.
A) Both statements are true.
B) Both statements are false.
C) The first statement is true; the second is false.
D) The second statement is true; the first is false.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
The functional unit of the kidney is the ___________________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Collecting ducts in the renal cortex and renal medulla drain directly into
A) papillary ducts
B) nephron loops
C) distal convoluted tubules
D) glomerular capsules
A) papillary ducts
B) nephron loops
C) distal convoluted tubules
D) glomerular capsules

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The movement of substances through the epithelial cells and then into the peritubular capillaries is _____ reabsorption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which of the following is least likely to affect filtration in the glomerulus?
A) efferent arteriole diameter is smaller than afferent arteriole.
B) large surface area of the glomerulus.
C) fenestrations cause the membrane to be leaky.
D) low blood pressure in the glomerulus.
A) efferent arteriole diameter is smaller than afferent arteriole.
B) large surface area of the glomerulus.
C) fenestrations cause the membrane to be leaky.
D) low blood pressure in the glomerulus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 100 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



