Deck 14: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: The Cardiovascular System: Blood Vessels
1
Blood in pulmonary circulation travels from the _____, then through arteries, capillaries, and veins, to the _____.
A) left ventricle, right atrium
B) left atrium, right ventricle
C) left atrium, right atrium
D) right ventricle, left atrium
A) left ventricle, right atrium
B) left atrium, right ventricle
C) left atrium, right atrium
D) right ventricle, left atrium
D
2
Which of the following is NOT a part of the hepatic portal system?
A) splenic vein
B) superior mesenteric vein
C) hepatic veins
D) inferior mesenteric vein
A) splenic vein
B) superior mesenteric vein
C) hepatic veins
D) inferior mesenteric vein
C
3
What is the correct route that a drop of blood would follow as it flows through the following vessels? 1. ulnar vein
2) palmar venous arch
3) brachial vein
4) subclavian vein
5) axillary vein
6) brachiocephalic vein
A) 2, 1, 3, 5, 4, 6
B) 2, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6
C) 2, 3, 1, 5, 4, 6
D) 6, 5, 4, 3, 1, 2
2) palmar venous arch
3) brachial vein
4) subclavian vein
5) axillary vein
6) brachiocephalic vein
A) 2, 1, 3, 5, 4, 6
B) 2, 1, 3, 4, 5, 6
C) 2, 3, 1, 5, 4, 6
D) 6, 5, 4, 3, 1, 2
A
4
Which of the following statements about sinusoids is TRUE?
A) Their walls have large intercellular clefts that allow proteins and blood cells to pass between tissue and the bloodstream.
B) Sinusoids are found in the liver, spleen and red bone marrow.
C) Sinusoids function as capillaries, but are wider and more winding than other capillaries.
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) Their walls have large intercellular clefts that allow proteins and blood cells to pass between tissue and the bloodstream.
B) Sinusoids are found in the liver, spleen and red bone marrow.
C) Sinusoids function as capillaries, but are wider and more winding than other capillaries.
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The _____ contain(s) the largest volume of blood when the body is at rest.
A) arteries and arterioles
B) veins and venules
C) heart
D) systemic capillaries
A) arteries and arterioles
B) veins and venules
C) heart
D) systemic capillaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The branches of the arch of the aorta, in correct order, are: 1. brachiocephalic trunk
2) left common carotid
3) left subclavian
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 1, 3, 2
C) 2, 1, 3
D) 3, 2, 1
2) left common carotid
3) left subclavian
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 1, 3, 2
C) 2, 1, 3
D) 3, 2, 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Epithelial tissue forms part of which layer(s) of an artery wall? 1. tunica interna (intima)
2) tunica media
3) tunica externa
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 1 only
C) 1, 3 only
D) 1, 2 only
2) tunica media
3) tunica externa
A) 1, 2, 3
B) 1 only
C) 1, 3 only
D) 1, 2 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is the correct route that a drop of blood would follow as it flows through the following vessels? 1. inferior vena cava
2) thoracic aorta
3) renal artery
4) abdominal aorta
5) renal vein
A) 1, 3, 5, 4, 2
B) 2, 3, 5, 4, 1
C) 2, 3, 4, 5, 1
D) 2, 4, 3, 5, 1
2) thoracic aorta
3) renal artery
4) abdominal aorta
5) renal vein
A) 1, 3, 5, 4, 2
B) 2, 3, 5, 4, 1
C) 2, 3, 4, 5, 1
D) 2, 4, 3, 5, 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Materials move between capillary blood and interstitial fluid through
A) fenestrations
B) intercellular clefts
C) pinocytic vesicles
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) fenestrations
B) intercellular clefts
C) pinocytic vesicles
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Blood in systemic circulation travels from the _____, then through arteries, capillaries, and veins, to the _____.
A) left ventricle, right atrium
B) left atrium, right ventricle
C) left atrium, right atrium
D) right ventricle, left atrium
A) left ventricle, right atrium
B) left atrium, right ventricle
C) left atrium, right atrium
D) right ventricle, left atrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The gastric, pancreatic, and splenic veins are part of the
A) coronary circulation
B) hepatic portal circulation
C) pulmonary circulation
D) fetal circulation only
A) coronary circulation
B) hepatic portal circulation
C) pulmonary circulation
D) fetal circulation only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A difference between veins and arteries is
A) arteries have three layers (tunics); veins have only two layers (tunics)
B) venous blood is under more pressure than is arterial blood
C) arteries have their own blood supply (vasa vasorum); veins do not
D) the tunica interna (intima) and tunica media are thinner in veins than in arteries
A) arteries have three layers (tunics); veins have only two layers (tunics)
B) venous blood is under more pressure than is arterial blood
C) arteries have their own blood supply (vasa vasorum); veins do not
D) the tunica interna (intima) and tunica media are thinner in veins than in arteries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The thinnest-walled blood vessels in the body are
A) capillaries
B) veins
C) venules
D) arterioles
A) capillaries
B) veins
C) venules
D) arterioles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Abundant capillary networks are located in the
A) epidermis of the skin
B) lens of the eye
C) tendons
D) liver
A) epidermis of the skin
B) lens of the eye
C) tendons
D) liver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What is the correct route that a drop of blood would follow as it flows through the following vessels? 1. superior vena cava
2) internal jugular vein
3) sigmoid sinuses
4) subclavian vein
5) brachiocephalic vein
A) 3, 2, 4, 5, 1
B) 1, 2, 5, 3, 4
C) 2, 3, 1, 4, 5
D) 3, 2, 5, 4, 1
2) internal jugular vein
3) sigmoid sinuses
4) subclavian vein
5) brachiocephalic vein
A) 3, 2, 4, 5, 1
B) 1, 2, 5, 3, 4
C) 2, 3, 1, 4, 5
D) 3, 2, 5, 4, 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Pulmonary circulation differs from systemic circulation in that
A) blood passes first through veins, then capillaries, and then arteries
B) arteries carry deoxygenated blood and veins carry oxygenated blood
C) all of the blood in pulmonary circulation is oxygenated blood
D) low oxygen levels cause pulmonary vessels to dilate, but cause systemic vessels to constrict
A) blood passes first through veins, then capillaries, and then arteries
B) arteries carry deoxygenated blood and veins carry oxygenated blood
C) all of the blood in pulmonary circulation is oxygenated blood
D) low oxygen levels cause pulmonary vessels to dilate, but cause systemic vessels to constrict

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What is the correct route that a drop of blood would follow as it flows through the following vessels? 1. external iliac artery
2) popliteal artery
3) anterior tibial artery
4) common iliac artery
5) femoral artery
6) dorsalis pedis (right dorsal artery of foot) artery
A) 1, 4, 5, 3, 6, 2
B) 4, 1, 5, 2, 3, 6
C) 4, 1, 2, 5, 3, 6
D) 6, 3, 2, 1, 5, 4
2) popliteal artery
3) anterior tibial artery
4) common iliac artery
5) femoral artery
6) dorsalis pedis (right dorsal artery of foot) artery
A) 1, 4, 5, 3, 6, 2
B) 4, 1, 5, 2, 3, 6
C) 4, 1, 2, 5, 3, 6
D) 6, 3, 2, 1, 5, 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Blood flows through the following vessels in what order? 1. arteriole
2) capillary
3) thoroughfare channel
4) metarteriole
5) venule
A) 1, 2, 4, 5
B) 1, 4, 2, 5
C) 5, 2, 3, 1
D) 1, 2, 3, 4
2) capillary
3) thoroughfare channel
4) metarteriole
5) venule
A) 1, 2, 4, 5
B) 1, 4, 2, 5
C) 5, 2, 3, 1
D) 1, 2, 3, 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The layer(s) of an artery wall that is/are responsible for vasoconstriction and vasodilation is/are the
A) tunica externa
B) tunica interna (intima)
C) tunica media
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) tunica externa
B) tunica interna (intima)
C) tunica media
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Elastic arteries
A) are medium-sized arteries
B) restrict blood flow due to the force needed to stretch their walls
C) are also called distributing arteries
D) include the largest diameter arteries in the body
A) are medium-sized arteries
B) restrict blood flow due to the force needed to stretch their walls
C) are also called distributing arteries
D) include the largest diameter arteries in the body

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A tunica interna (intima) of endothelium is found only in arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The blood that sustains lung tissue is supplied by the systemic circulation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Trace the path of a drop of blood through pulmonary circulation, starting as it leaves the heart. 1. left atrium
2) right ventricle
3) pulmonary vein
4) pulmonary artery
5) pulmonary capillaries
6) pulmonary trunk
A) 1, 6, 3, 5, 4, 2
B) 1, 6, 4, 5, 3, 2
C) 2, 6, 3, 5, 4, 1
D) 2, 6, 4, 5, 3, 1
2) right ventricle
3) pulmonary vein
4) pulmonary artery
5) pulmonary capillaries
6) pulmonary trunk
A) 1, 6, 3, 5, 4, 2
B) 1, 6, 4, 5, 3, 2
C) 2, 6, 3, 5, 4, 1
D) 2, 6, 4, 5, 3, 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which position is most likely to place the greatest pressure on the inferior vena cava, thereby hindering the return of venous blood from the lower limb (causing swelling)?
A) person lying in the supine position
B) person lying in the prone position
C) person with his/her neck hyperextended
D) person with his/her ankle in dorsiflexion
A) person lying in the supine position
B) person lying in the prone position
C) person with his/her neck hyperextended
D) person with his/her ankle in dorsiflexion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A blockage in an end artery is more serious than in an anastomosing artery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Is the aorta an elastic (conducting) or a muscular (distributing) artery? Compare the structure of the wall of the aorta to an artery that is of the other type.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Blood in an umbilical artery travels from the fetus to the placenta.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
At about the level of the fourth lumbar vertebra, the abdominal aorta divides into left and right common iliac arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is NOT considered a change in the cardiovascular system due to aging?
A) 50% decrease in renal blood flow
B) decreased compliance (elasticity) of the aorta
C) decreased size of cardiac muscle cells (fibers)
D) an increase in maximum heart rate
A) 50% decrease in renal blood flow
B) decreased compliance (elasticity) of the aorta
C) decreased size of cardiac muscle cells (fibers)
D) an increase in maximum heart rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Diagram a portion of a capillary network, labeling the features that are found between the arteriole and the venule. Draw the smooth muscle fibers in a representative area that indicates where they are located. Label the zone of oxygenated blood. State the function of each portion or feature of the capillary network that you have labeled.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The superior and inferior vena cavae are both located to the right of the midline of the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In an artery wall, the tunica media contains smooth muscle and elastic fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Which artery can be palpated inferior to the hamstring tendons, superior to the heads of the gastrocnemius muscle and deep posterior to the patella?
A) inguinal
B) iliac
C) popliteal
D) dorsalis pedis
A) inguinal
B) iliac
C) popliteal
D) dorsalis pedis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Describe the three layers that make up the wall of an artery. Using this as a standard, compare artery walls to capillary and vein walls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Obstruction (blockage) in the radial artery will restrict ALL blood flow to the hand resulting in "blue fingernails" (a tell-tale sign of cyanosis).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Blindness or other visual disturbances will arise following a blockage of the posterior cerebral arteries. These arteries branch directly from the
A) internal carotid arteries
B) basilar artery
C) vertebral arteries
D) external carotid arteries
A) internal carotid arteries
B) basilar artery
C) vertebral arteries
D) external carotid arteries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Describe the routes by which blood is supplied to the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A thrombus (blood clot) formed in the knee during knee surgery has the potential to travel to the lung causing a pulmonary embolism (PE) via which of the following circulatory route?
A) popliteal vein; anterior tibial vein; dorsalis pedal vein
B) popliteal vein; common iliac vein; inferior vena cava; pulmonary trunk
C) popliteal vein; femoral vein; superior vena cava; aorta
D) popliteal vein; common iliac vein; external iliac vein; internal iliac vein
A) popliteal vein; anterior tibial vein; dorsalis pedal vein
B) popliteal vein; common iliac vein; inferior vena cava; pulmonary trunk
C) popliteal vein; femoral vein; superior vena cava; aorta
D) popliteal vein; common iliac vein; external iliac vein; internal iliac vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Drugs used to treat hypertension include calcium channel blockers, vasodilators, diuretics, and ACE inhibitors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Three different types of capillaries include continuous capillaries, fenestrated capillaries, and sinusoids.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In the fetus, what two structures allow most blood to bypass the lungs?
A) fossa ovalis and ligamentum arteriosum
B) foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus
C) fossa ovalis and ductus arteriosus
D) foramen ovale and ligamentum arteriosum
A) fossa ovalis and ligamentum arteriosum
B) foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus
C) fossa ovalis and ductus arteriosus
D) foramen ovale and ligamentum arteriosum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The thickest layer of an artery wall is the tunica
A) externa
B) interna
C) media
D) intima
A) externa
B) interna
C) media
D) intima

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The superior mesenteric vein empties into the
A) popliteal vein
B) hepatic vein
C) hepatic portal vein
D) superior vena cava
A) popliteal vein
B) hepatic vein
C) hepatic portal vein
D) superior vena cava

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The superior mesenteric artery branches from the
A) ascending aorta
B) abdominal aorta
C) arch of the aorta
D) thoracic aorta
A) ascending aorta
B) abdominal aorta
C) arch of the aorta
D) thoracic aorta

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The basilar artery is formed by the union of the right and left internal carotid arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The external iliac vein is formed by the union of the _____ vein and the _____vein.
A) femoral; internal iliac
B) internal jugular; subclavian
C) great saphenous; femoral
D) popliteal; great saphenous
A) femoral; internal iliac
B) internal jugular; subclavian
C) great saphenous; femoral
D) popliteal; great saphenous

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Describe the damaging effects of untreated hypertension on the cardiovascular system, brain, and kidneys.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Arteries that do not anastomose are known as
A) venules
B) end arteries
C) arterioles
D) sinuses
A) venules
B) end arteries
C) arterioles
D) sinuses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The first two vessels to branch from the ascending aorta are the
A) brachiocephalic and left common carotid
B) right common carotid and right subclavian
C) right coronary and left coronary
D) right coronary and brachiocephalic
A) brachiocephalic and left common carotid
B) right common carotid and right subclavian
C) right coronary and left coronary
D) right coronary and brachiocephalic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The largest diameter vein in the body is the
A) inferior vena cava
B) superior vena cava
C) internal jugular vein
D) coronary sinus
A) inferior vena cava
B) superior vena cava
C) internal jugular vein
D) coronary sinus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Contraction of smooth muscle in the vessel wall produces _____ which is a _____ in the diameter of the vessel lumen.
A) vasoconstriction; decrease
B) vasodilation; decrease
C) vasoconstriction; increase
D) vasodilation; increase
A) vasoconstriction; decrease
B) vasodilation; decrease
C) vasoconstriction; increase
D) vasodilation; increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The umbilical cord contains three blood vessels; one umbilical vein and two umbilical arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The brachiocephalic trunk gives rise directly to the
A) left subclavian artery
B) right subclavian artery
C) left vertebral artery
D) right internal carotid artery
A) left subclavian artery
B) right subclavian artery
C) left vertebral artery
D) right internal carotid artery

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Arteries that anastomose are able to provide a collateral circulation to a tissue in order to prevent necrosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The most distal muscle cells of the _____ form the precapillary sphincters which monitor blood flow into the capillary.
A) venules
B) metarteriole
C) sinusoids
D) thoroughfare channels
A) venules
B) metarteriole
C) sinusoids
D) thoroughfare channels

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Direct branches of the _____ artery and the _____ artery contribute to the palmar arches.
A) brachial; basilic
B) basilic; cephalic
C) radial; brachial
D) ulnar; radial
A) brachial; basilic
B) basilic; cephalic
C) radial; brachial
D) ulnar; radial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The _____ artery is located in the cervical transverse foramina.
A) vertebral
B) internal carotid
C) basilar
D) external carotid
A) vertebral
B) internal carotid
C) basilar
D) external carotid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Extensions of the _____ of veins form valves that help prevent the backflow of blood.
A) tunica interna (intima)
B) tunica media
C) tunica externa
A) tunica interna (intima)
B) tunica media
C) tunica externa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Define portal system. Explain how the hepatic portal system fits your definition and describe its function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The hollow center of a blood vessel is called the endothelium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The internal jugular vein is primarily responsible for directly draining the parotid gland and scalp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which two arteries most significantly contribute to the cerebral arterial circle (Circle of Willis) supplying blood to the brain?
A) vertebral and external carotid
B) internal carotid and posterior cerebral
C) external carotid and internal jugular
D) basilar and internal carotid
A) vertebral and external carotid
B) internal carotid and posterior cerebral
C) external carotid and internal jugular
D) basilar and internal carotid

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
This blood vessel tissue layer is most responsible for 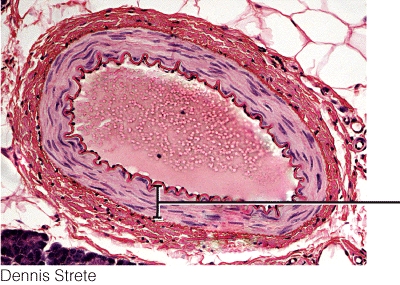
A) regulating blood flow and blood pressure
B) helping to limit the loss of blood when vessels are damaged
C) regulating the diameter of the lumen wall
D) All of the choices are correct.

A) regulating blood flow and blood pressure
B) helping to limit the loss of blood when vessels are damaged
C) regulating the diameter of the lumen wall
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The left testicular (or ovarian) vein drains into the _____, whereas the right testicular (or ovarian) vein drains into the _____. 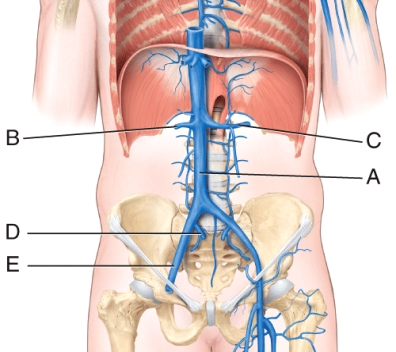
A) A; B
B) B; C
C) D; E
D) C; A

A) A; B
B) B; C
C) D; E
D) C; A

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Which of these vessels of the neck contributes directly to the formation of the basilar artery? 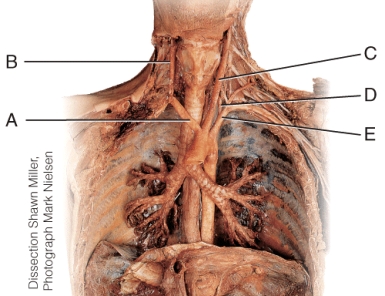
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The renal artery supplies the _____ with blood.
A) liver
B) spleen
C) pancreas
D) kidney
A) liver
B) spleen
C) pancreas
D) kidney

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the veins of the upper limb is commonly punctured for an injection, transfusion, or removal of a blood sample?
A) brachial
B) radial
C) ulnar
D) median cubital
E) cephalic
A) brachial
B) radial
C) ulnar
D) median cubital
E) cephalic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Which of the vessels of the neck are NOT direct branches of the arch of the aorta? 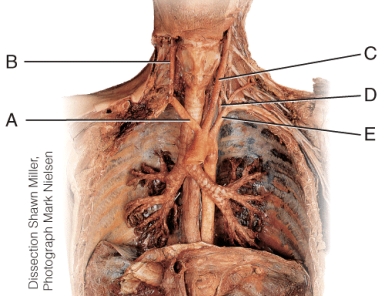
A) B and C
B) B and D
C) C and D
D) D and E

A) B and C
B) B and D
C) C and D
D) D and E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Venous blood from the adrenal gland is returned via the
A) superior mesenteric vein
B) suprarenal vein
C) azygos vein
D) gastric vein
A) superior mesenteric vein
B) suprarenal vein
C) azygos vein
D) gastric vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The great saphenous vein drains the medial aspect of the leg and thigh, the groin, external genitals, and abdominal wall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Blood supply for the pancreas, spleen and stomach comes from the _____ artery.
A) hepatic
B) inferior mesenteric
C) superior mesenteric
D) splenic
A) hepatic
B) inferior mesenteric
C) superior mesenteric
D) splenic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The chest muscles and diaphragm are supplied with blood by the bronchial arteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Venous blood from the buttocks, urinary bladder, uterus, and prostate gland is returned via the
A) internal iliac vein
B) femoral vein
C) great saphenous vein
D) external iliac vein
A) internal iliac vein
B) femoral vein
C) great saphenous vein
D) external iliac vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Venous blood from the liver reaches the inferior vena cava via the
A) hepatic veins
B) splenic vein
C) hepatic portal vein
D) superior mesenteric vein
A) hepatic veins
B) splenic vein
C) hepatic portal vein
D) superior mesenteric vein

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The lumbar arteries supply blood to the spinal cord and meninges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



