Deck 9: Joints
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: Joints
1
Which of the following terms could describe a joint at which flexion and extension are the only movements? 1. pivot joint
2) hinge joint
3) monaxial joint
4) biaxial joint
A) 1 and 3
B) 2 and 3
C) 1 and 4
D) 2 and 4
2) hinge joint
3) monaxial joint
4) biaxial joint
A) 1 and 3
B) 2 and 3
C) 1 and 4
D) 2 and 4
B
2
Fibrous connective tissue firmly holds the articular surfaces of bones together in
A) fibrous joints
B) cartilaginous joints
C) synovial joints
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) fibrous joints
B) cartilaginous joints
C) synovial joints
D) All of the choices are correct.
A
3
A _____ is a type of joint in which two bones are held together by a disc of fibrocartilage.
A) symphysis
B) synchondrosis
C) suture
D) synovial joint
A) symphysis
B) synchondrosis
C) suture
D) synovial joint
A
4
Which of the following statements about joint classification is true?
A) All synchondroses are synarthrotic.
B) All synovial joints are diarthrotic.
C) All symphyses are amphiarthrotic.
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) All synchondroses are synarthrotic.
B) All synovial joints are diarthrotic.
C) All symphyses are amphiarthrotic.
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Structures that are most responsible for holding bones together at a synovial joint are
A) tendons.
B) articular cartilages.
C) synovial membranes.
D) ligaments.
A) tendons.
B) articular cartilages.
C) synovial membranes.
D) ligaments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The articular cartilage 1. consists of two layers: an outer layer of dense fibrous connective tissue and an inner layer of loose connective tissue.
2) firmly binds the articulating bones.
3) covers the surfaces of the articulating bones at a synovial joint.
4) helps absorb shock and reduces friction at a synovial joint.
A) 1, 2, and 3
B) 2, 3, and 4
C) 3 and 4 only
D) 1 and 2 only
2) firmly binds the articulating bones.
3) covers the surfaces of the articulating bones at a synovial joint.
4) helps absorb shock and reduces friction at a synovial joint.
A) 1, 2, and 3
B) 2, 3, and 4
C) 3 and 4 only
D) 1 and 2 only

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Articular discs of synovial joints
A) are pads of hyaline cartilage.
B) move freely within the joint cavity.
C) are found in the space between the ends of the bones.
D) are found in all synovial joints.
A) are pads of hyaline cartilage.
B) move freely within the joint cavity.
C) are found in the space between the ends of the bones.
D) are found in all synovial joints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The surfaces of the bones at a gliding joint perform the movement(s) of
A) side-to-side movement.
B) rotation.
C) flexion and extension.
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) side-to-side movement.
B) rotation.
C) flexion and extension.
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The action that moves the palm of the hand into anatomical position is
A) pronation.
B) supination.
C) inversion.
D) eversion.
A) pronation.
B) supination.
C) inversion.
D) eversion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Alternating the turning of the palm of the hand toward the ceiling and then turning it toward the floor is a movement of the forearm. This movement
A) includes pronation.
B) includes supination.
C) occurs at the radiocarpal joint.
D) all except occurs at the radiocarpal joint.
A) includes pronation.
B) includes supination.
C) occurs at the radiocarpal joint.
D) all except occurs at the radiocarpal joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If a joint is enclosed in a tough connective tissue capsule and if it contains a joint cavity, it is classified as
A) synovial.
B) fibrous.
C) cartilaginous.
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) synovial.
B) fibrous.
C) cartilaginous.
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following pairs of terms is most closely associated or matched?
A) atlanto-occipital, synchondrosis
B) vertebrocostal, synarthrosis
C) talocrural (ankle), diarthrosis
D) sacroiliac, synarthrosis
A) atlanto-occipital, synchondrosis
B) vertebrocostal, synarthrosis
C) talocrural (ankle), diarthrosis
D) sacroiliac, synarthrosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Epiphyseal plates of growing bones may be classified as
A) cartilaginous joints.
B) synarthrotic joints.
C) synchondroses.
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) cartilaginous joints.
B) synarthrotic joints.
C) synchondroses.
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A good description for a condyloid (ellipsoidal) joint is
A) flat or slightly curved articulating surfaces.
B) one articulating surface is convex and fits into the other surface which is concave.
C) oval-shaped projection fits into an oval depression.
D) one bone articulates with another like a rider in a saddle.
E) the only synovial joint that allows triaxial movement.
A) flat or slightly curved articulating surfaces.
B) one articulating surface is convex and fits into the other surface which is concave.
C) oval-shaped projection fits into an oval depression.
D) one bone articulates with another like a rider in a saddle.
E) the only synovial joint that allows triaxial movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What structure(s) of the synovial joint absorb(s) shock from external forces that are placed on it?
A) articular cartilage
B) synovial fluid
C) hyaline cartilage covering the articulating surface of bones
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) articular cartilage
B) synovial fluid
C) hyaline cartilage covering the articulating surface of bones
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The articular capsule of the hip joint is one of the strongest in the body. It consists partially of
A) transverse humeral ligament.
B) pubofemoral ligament.
C) glenoid labrum.
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) transverse humeral ligament.
B) pubofemoral ligament.
C) glenoid labrum.
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which type of joint has the most movement?
A) synarthrosis
B) diarthrosis
C) gomphosis
D) syndesmosis
A) synarthrosis
B) diarthrosis
C) gomphosis
D) syndesmosis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Concerning diarthroses, one may speculate that as mobility increases, _____ decreases.
A) the thickness of articular cartilage
B) the amount of synovial fluid
C) range of motion (ROM)
D) stability
A) the thickness of articular cartilage
B) the amount of synovial fluid
C) range of motion (ROM)
D) stability

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The primary type of movement permitted at a pivot joint is
A) rotation.
B) circumduction.
C) abduction and adduction.
D) All of the choices are correct.
A) rotation.
B) circumduction.
C) abduction and adduction.
D) All of the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements about aging and joints is false?
A) Production of synovial fluid decreases.
B) Ligaments shorten and become less flexible.
C) Articular cartilage thickens.
D) Osteoarthritis is evident in almost everyone over age 70.
A) Production of synovial fluid decreases.
B) Ligaments shorten and become less flexible.
C) Articular cartilage thickens.
D) Osteoarthritis is evident in almost everyone over age 70.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The joint between two bodies of adjacent vertebrae is a synchondrosis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which joint could be called a saddle joint?
A) wrist joint
B) knee joint
C) hip joint
D) between atlas and dens of axis
E) between trapezium and first metacarpal
A) wrist joint
B) knee joint
C) hip joint
D) between atlas and dens of axis
E) between trapezium and first metacarpal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
All symphyses occur in the midline of the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which feature goes with the elbow joint?
A) medial and lateral menisci
B) glenoid labrum
C) radial collateral ligament
D) zona orbicularis
E) acetabular labrum
A) medial and lateral menisci
B) glenoid labrum
C) radial collateral ligament
D) zona orbicularis
E) acetabular labrum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which feature goes with the temporomandibular joint?
A) sphenomandibular ligament
B) glenoid labrum
C) radial annular ligament
D) zona orbicularis
E) acetabular labrum
A) sphenomandibular ligament
B) glenoid labrum
C) radial annular ligament
D) zona orbicularis
E) acetabular labrum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which joint shows a hinge motion?
A) between tarsal bones
B) elbow joint
C) hip joint
D) between atlas and dens of axis
E) between trapezium and first metacarpal
A) between tarsal bones
B) elbow joint
C) hip joint
D) between atlas and dens of axis
E) between trapezium and first metacarpal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In an x-ray of a young person's skeleton, what are easily seen as thin dark areas between the white-appearing bone tissue?
A) synovial joints
B) interosseous membranes
C) sutures
D) synchondroses
A) synovial joints
B) interosseous membranes
C) sutures
D) synchondroses

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Which joint shows a pivot motion?
A) between tarsal bones
B) knee joint
C) hip joint
D) between atlas and dens of axis
E) between trapezium and first metacarpal
A) between tarsal bones
B) knee joint
C) hip joint
D) between atlas and dens of axis
E) between trapezium and first metacarpal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which feature goes with the hip (coxal) joint?
A) medial and lateral menisci
B) glenoid labrum
C) radial annular ligament
D) zona orbicularis
E) arcuate popliteal ligament
A) medial and lateral menisci
B) glenoid labrum
C) radial annular ligament
D) zona orbicularis
E) arcuate popliteal ligament

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A good description for a plane joint is
A) flat or slightly curved articulating surfaces.
B) one articulating surface is convex and fits into the other surface which is concave.
C) oval-shaped projection fits into an oval depression.
D) one bone articulates with another like a rider in a saddle.
E) the only synovial joint that allows triaxial movement.
A) flat or slightly curved articulating surfaces.
B) one articulating surface is convex and fits into the other surface which is concave.
C) oval-shaped projection fits into an oval depression.
D) one bone articulates with another like a rider in a saddle.
E) the only synovial joint that allows triaxial movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
An acute or chronic inflammation of a bursa, i.e bursitis can be caused by
A) repeated, excessive exertion of a joint.
B) rheumatoid arthritis.
C) infection.
D) All the choices are correct.
A) repeated, excessive exertion of a joint.
B) rheumatoid arthritis.
C) infection.
D) All the choices are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The joints between the sternum and ribs 2-7 are syndesmoses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A good description for a ball-and-socket joint is
A) a bone rotates around its long axis as it articulates within a ring of bone and ligament.
B) one articulating surface is convex and fits into the other surface which is concave.
C) oval-shaped projection fits into an oval depression.
D) one bone articulates with another like a rider in a saddle.
E) the only synovial joint that allows triaxial movement.
A) a bone rotates around its long axis as it articulates within a ring of bone and ligament.
B) one articulating surface is convex and fits into the other surface which is concave.
C) oval-shaped projection fits into an oval depression.
D) one bone articulates with another like a rider in a saddle.
E) the only synovial joint that allows triaxial movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which joint allows a gliding movement to occur?
A) between tarsal bones
B) knee joint
C) hip joint
D) between atlas and dens of axis
E) between trapezium and first metacarpal
A) between tarsal bones
B) knee joint
C) hip joint
D) between atlas and dens of axis
E) between trapezium and first metacarpal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which joint is the most frequently injured of the major joints of the body?
A) acromioclavicular
B) knee
C) intertarsal
D) interphalangeal
E) ankle (talocrural)
A) acromioclavicular
B) knee
C) intertarsal
D) interphalangeal
E) ankle (talocrural)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which joint shows the motion called rotation?
A) acromioclavicular
B) wrist
C) intertarsal
D) interphalangeal
E) radioulnar
A) acromioclavicular
B) wrist
C) intertarsal
D) interphalangeal
E) radioulnar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which feature goes with the knee joint?
A) medial and lateral menisci
B) glenoid labrum
C) radial annular ligament
D) zona orbicularis
E) acetabular labrum
A) medial and lateral menisci
B) glenoid labrum
C) radial annular ligament
D) zona orbicularis
E) acetabular labrum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which joint shows the motions called elevation and depression?
A) temporomandibular
B) knee
C) intertarsal
D) interphalangeal
E) ankle (talocrural)
A) temporomandibular
B) knee
C) intertarsal
D) interphalangeal
E) ankle (talocrural)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Which joint shows the motions called inversion and eversion?
A) temporomandibular
B) knee
C) intertarsal
D) interphalangeal
E) ankle (talocrural)
A) temporomandibular
B) knee
C) intertarsal
D) interphalangeal
E) ankle (talocrural)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which feature goes with the shoulder (humeroscapular) joint?
A) sphenomandibular ligament
B) glenoid labrum
C) radial annular ligament
D) zona orbicularis
E) acetabular labrum
A) sphenomandibular ligament
B) glenoid labrum
C) radial annular ligament
D) zona orbicularis
E) acetabular labrum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The shoulder joint is an example of a triaxial joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Interphalangeal joints are synovial joints at which flexion and extension occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Define the terms synarthrosis and diarthrosis and give an example of each.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Bursae are connective tissue sacs that are responsible for reducing friction during the movement of some joints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Bending the ankle so that the foot moves downward is the movement called plantar flexion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Both joints of the clavicle, the acromioclavicular and the sternoclavicular, are synovial joints.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Articular cartilage receives nutrients and oxygen from the _____ _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Abduction occurs when a bone moves toward the midline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The distal tibiofibular joint, which allows some movement, is classified structurally as a _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
List and describe six factors that affect the range of motion possible at a joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Outline the ACI (Autologous Chondrocyte Implantation) procedure, which is used as an alternative to total knee replacement for damaged cartilage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Medial and lateral menisci are found in the joint cavity of the elbow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Explain the benefits of using ice in the treatment of sprains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In order to fully understand kinesiology (study of movement), one would be advised to study _____ (scientific study of joints) first.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A separated shoulder is an injury to the shoulder (glenohumeral joint).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The name of the type of joint where a tooth fits into a socket is _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Synovial fluid is a somewhat viscous liquid that contains hyaluronic acid and fluid formed from blood plasma.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The general anatomical term for the regions of contact between bones is _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Describe the following features of a synovial joint and state the function of each: articular cartilage, fibrous membrane, synovial membrane, synovial fluid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Give the structural classification, list the possible movements, and name the articular surfaces of the bones for
a) the shoulder joint,
b) the metacarpophalangeal joints,
c) the hip joint.
a) the shoulder joint,
b) the metacarpophalangeal joints,
c) the hip joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A structure that consists of parallel bundles of collagen fibers and is part of the fibrous membrane of some synovial joints is called a/an _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The goal of arthroplasty is to relieve pain and increase _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Name the joint shown below. 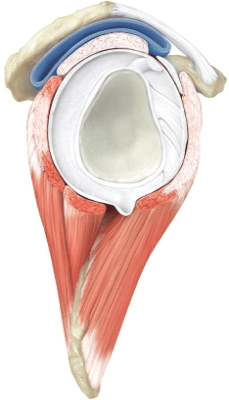


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Give the structural classification, list the possible movements, and name the articular surfaces of the bones for
a) the shoulder joint,
b) the metacarpophalangeal joints,
c) the hip joint.
a) the shoulder joint,
b) the metacarpophalangeal joints,
c) the hip joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The line is pointing to the _____ ligaments. 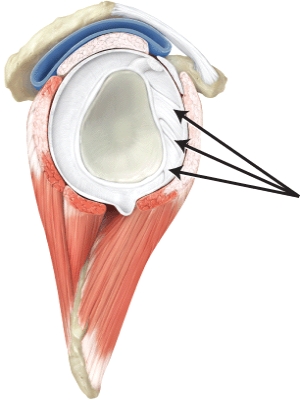


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The knee joint, the largest joint, is actually three joints: two tibiofemoral joints and one _____ joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The line is pointing to the _____. 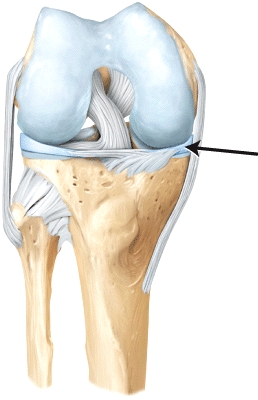


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Name the joint shown. 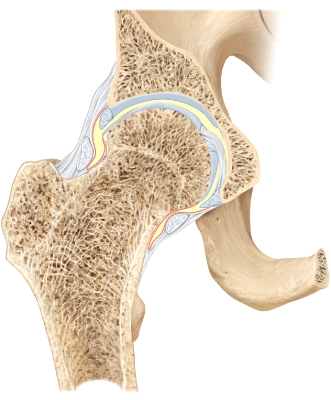


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Give the structural classification, list the possible movements, and name the articular surfaces of the bones for
a) the shoulder joint,
b) the metacarpophalangeal joints,
c) the hip joint.
a) the shoulder joint,
b) the metacarpophalangeal joints,
c) the hip joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The movement of the mandible in a forward direction parallel to the ground is called _____.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The line is pointing to the _____ ligament.] ![The line is pointing to the _____ ligament.]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7892/11eae20c_3fe1_5c46_ad0d_2b60f6ef0a2a_TB7892_00.jpg)
![The line is pointing to the _____ ligament.]](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB7892/11eae20c_3fe1_5c46_ad0d_2b60f6ef0a2a_TB7892_00.jpg)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The _____ _____ligament limits hyperextension of the knee and prevents the anterior sliding of the tibia on the femur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The joint that allows rotation of the head is the _____ joint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The line is pointing to the _____ ligament. 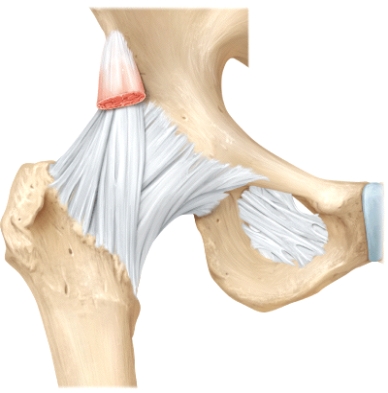


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The line is pointing to the _____ ligament. 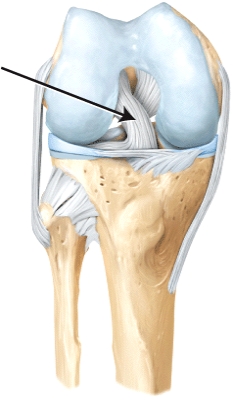


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



