Deck 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/110
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
1
These regions of a neuron are also referred to as terminal boutons.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
B
2
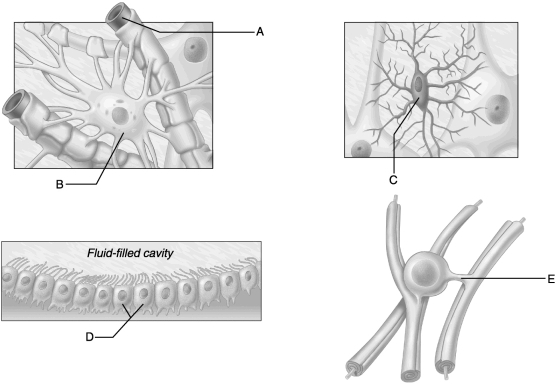 Figure 12.2
Figure 12.2Use the diagrams above to answer the following questions.
Identify which diagram represents cells that produce and circulate cerebrospinal fluid.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
D
3
 Figure 12.2
Figure 12.2Use the diagrams above to answer the following questions.
Identify which diagram represents a microglial cell.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
C
4
 Figure 12.2
Figure 12.2Use the diagrams above to answer the following questions.
Identify which letter represents an oligodendrocyte.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
 Figure 12.2
Figure 12.2Use the diagrams above to answer the following questions.
Identify which diagram represents a cell that produces a myelin sheath in the central nervous system.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
 Figure 12.2
Figure 12.2Use the diagrams above to answer the following questions.
Identify which letter represents the most abundant category of glial cells in the CNS.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In an axodendritic synapse, the region of the postsynaptic neuron that binds the released neurotransmitter is the
A) synapse.
B) axon terminal.
C) axon.
D) cell body.
E) dendrite.
A) synapse.
B) axon terminal.
C) axon.
D) cell body.
E) dendrite.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
An axosomatic synapse occurs between the axon terminals of one neuron and the of a proximal neuron.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
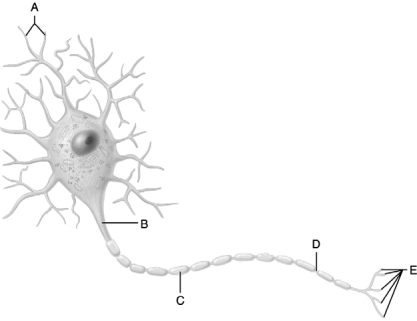 Figure 12.1
Figure 12.1Use the diagram pictured above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the region of a neuron with a name that means ʺlittle hill.ʺ
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
These regions of a neuron are characterized by numerous, short cytoplasmic extensions and are often referred to as receiving regions.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
This tends to be the longest cytoplasmic projection from a neuron.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
This is the site of communication between neurons.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
 Figure 12.1
Figure 12.1Use the diagram pictured above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the gaps between Schwann cells that are known as myelin sheath gaps (nodes of Ranvier).
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
 Figure 12.1
Figure 12.1Use the diagram pictured above to answer the following questions.
Axodendritic synapses occur between letter ʺEʺ on the diagram and this region on a proximal neuron.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Mitochondria are particularly abundant here.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
 Figure 12.1
Figure 12.1Use the diagram pictured above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates a Schwann cell.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Chemical signals diffuse between neurons at this location.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The of a presynaptic neuron associates with the dendrite of a postsynaptic neuron.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
 Figure 12.1
Figure 12.1Use the diagram pictured above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the region of a neuron where neurotransmitters are released.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
This region of the neuron contains a single nucleus surrounded by cytoplasm.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of the following statements about neurotransmitters is false?
A) They are waves of positive charges that travel down axons.
B) They diffuse across the synaptic cleft.
C) They alter the permeability of the postsynaptic cell membrane.
D) They are released from synaptic vesicles.
A) They are waves of positive charges that travel down axons.
B) They diffuse across the synaptic cleft.
C) They alter the permeability of the postsynaptic cell membrane.
D) They are released from synaptic vesicles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Most synapses transmit communicating signals using
A) physical contact between adjacent neurons.
B) chemical signaling molecules released from neuroglia.
C) electrical impulses travelling through gap junctions.
D) chemical signaling molecules-neurotransmitters.
A) physical contact between adjacent neurons.
B) chemical signaling molecules released from neuroglia.
C) electrical impulses travelling through gap junctions.
D) chemical signaling molecules-neurotransmitters.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is the correct path an impulse takes across a synapse?
A) dendrite of presynaptic neuron, synaptic cleft, axon of postsynaptic neuron
B) axon of presynaptic neuron, synaptic cleft, dendrite of postsynaptic neuron
C) axon of postsynaptic neuron, dendrite of presynaptic neuron, synaptic cleft
D) synaptic cleft, dendrite of postsynaptic neuron, axon of presynaptic neuron
A) dendrite of presynaptic neuron, synaptic cleft, axon of postsynaptic neuron
B) axon of presynaptic neuron, synaptic cleft, dendrite of postsynaptic neuron
C) axon of postsynaptic neuron, dendrite of presynaptic neuron, synaptic cleft
D) synaptic cleft, dendrite of postsynaptic neuron, axon of presynaptic neuron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In this part of a neuron, neurofilaments, actin microfilaments, and microtubules are particularly abundant, providing structural support and a transport network.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Most tumors in the brain originate from
A) glial cells.
B) bipolar neurons.
C) multipolar neurons.
D) unipolar neurons.
A) glial cells.
B) bipolar neurons.
C) multipolar neurons.
D) unipolar neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
This part of the neuron may have branching collaterals.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following is not considered a special somatic sense?
A) equilibrium
B) pain
C) smell
D) taste
A) equilibrium
B) pain
C) smell
D) taste

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
This region of a neuron contains chromatophilic substance or Nissl bodies.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which cells are the macrophages of the CNS?
A) ependymal cells
B) Schwann cells
C) satellite cells
D) microglial cells
A) ependymal cells
B) Schwann cells
C) satellite cells
D) microglial cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Interneurons are found
A) only in the visceral nervous system.
B) only in the autonomic nervous system.
C) only in the PNS.
D) only in the CNS.
A) only in the visceral nervous system.
B) only in the autonomic nervous system.
C) only in the PNS.
D) only in the CNS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Of the following, which is the only structure that is in the PNS, as opposed to the CNS?
A) a tract
B) a ganglion
C) white matter
D) gray matter
A) a tract
B) a ganglion
C) white matter
D) gray matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of the following is not a characteristic of neurons?
A) high metabolic rate
B) inability to divide
C) ability to survive without oxygen
D) longevity
A) high metabolic rate
B) inability to divide
C) ability to survive without oxygen
D) longevity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
This neuronal region transmits electrical impulses away from the cell body.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
These regions of the neuron direct electrical currents toward the cell body.
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite
A) synapse
B) axon terminal
C) axon
D) cell body
E) dendrite

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following statements concerning sensory neurons is incorrect?
A) They have peripheral and central processes.
B) Most have their cell bodies in ganglia outside the CNS.
C) Most are pseudounipolar.
D) They contain only dendrites.
A) They have peripheral and central processes.
B) Most have their cell bodies in ganglia outside the CNS.
C) Most are pseudounipolar.
D) They contain only dendrites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The majority of neurons in the body are
A) unipolar.
B) pseudounipolar.
C) bipolar.
D) multipolar.
A) unipolar.
B) pseudounipolar.
C) bipolar.
D) multipolar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Neurofibrils
A) help circulate cerebrospinal fluid.
B) receive incoming stimuli and pass the signal toward the cell body.
C) prevent the neuron from being pulled apart when subjected to tensile forces.
D) form synapses with axons of postsynaptic neurons.
A) help circulate cerebrospinal fluid.
B) receive incoming stimuli and pass the signal toward the cell body.
C) prevent the neuron from being pulled apart when subjected to tensile forces.
D) form synapses with axons of postsynaptic neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements about an axon is false?
A) It has branches.
B) It has a uniform diameter.
C) It carries nerve impulses toward the cell body.
D) It is also referred to as a nerve fiber.
A) It has branches.
B) It has a uniform diameter.
C) It carries nerve impulses toward the cell body.
D) It is also referred to as a nerve fiber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A somatic motor neuron carries
A) motor commands to the skeletal musculature.
B) information from the skin to the CNS.
C) information, such as pain, from the viscera in the ventral cavity to the CNS.
D) information that signals muscle contraction in the organs in the ventral cavity.
A) motor commands to the skeletal musculature.
B) information from the skin to the CNS.
C) information, such as pain, from the viscera in the ventral cavity to the CNS.
D) information that signals muscle contraction in the organs in the ventral cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Ganglia represent
A) groups of dendrites.
B) groups of neuron cell bodies.
C) groups of synapses.
D) groups of axons.
A) groups of dendrites.
B) groups of neuron cell bodies.
C) groups of synapses.
D) groups of axons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
These glial cells arise from embryonic white blood cells.
A) microglia
B) satellite cells
C) ependymal cells
D) oligodendrocytes
A) microglia
B) satellite cells
C) ependymal cells
D) oligodendrocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Nonmyelinated axons
A) occur in the PNS, but not in the CNS.
B) are not associated with any Schwann cells.
C) conduct impulses more slowly than myelinated axons.
D) are thicker than myelinated axons.
A) occur in the PNS, but not in the CNS.
B) are not associated with any Schwann cells.
C) conduct impulses more slowly than myelinated axons.
D) are thicker than myelinated axons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which cells provide the myelin sheath for neurons in the PNS?
A) microglial cells
B) oligodendrocytes
C) astrocytes
D) Schwann cells
A) microglial cells
B) oligodendrocytes
C) astrocytes
D) Schwann cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Motor neurons arise primarily from the
A) ependyma.
B) neural crest.
C) alar plate.
D) basal plate.
A) ependyma.
B) neural crest.
C) alar plate.
D) basal plate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
White matter represents
A) dendrites traveling together in the ANS.
B) myelinated axons traveling together in the CNS.
C) aggregations of neuron cell bodies in the spinal cord.
D) aggregations of neuron cell bodies in the brain.
A) dendrites traveling together in the ANS.
B) myelinated axons traveling together in the CNS.
C) aggregations of neuron cell bodies in the spinal cord.
D) aggregations of neuron cell bodies in the brain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
These glial cells surround the cell bodies of sensory neurons within ganglia of the PNS.
A) Schwann cells
B) satellite cells
C) astrocytes
D) microglia
A) Schwann cells
B) satellite cells
C) astrocytes
D) microglia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
All of the following are characteristics of dendrites except that they
A) typically occur as more than one per cell.
B) are more extensive branching than axons.
C) always conduct action potentials.
D) conduct signals toward the cell body.
A) typically occur as more than one per cell.
B) are more extensive branching than axons.
C) always conduct action potentials.
D) conduct signals toward the cell body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Sensory neurons arise primarily from the
A) neural tube.
B) alar plate.
C) basal plate.
D) neural crest.
A) neural tube.
B) alar plate.
C) basal plate.
D) neural crest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A nerve cell is the same as a
A) nerve.
B) nerve fiber.
C) neuron.
D) neurilemmocyte.
A) nerve.
B) nerve fiber.
C) neuron.
D) neurilemmocyte.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following is the correct arrangement of a reflex arc?
A) receptor, sensory neuron, integration center, motor neuron, effector
B) effector, sensory neuron, integration center, motor neuron, receptor
C) receptor, motor neuron, integration center, effector, sensory neuron
D) integration center, receptor, sensory neuron, motor neuron, effector
A) receptor, sensory neuron, integration center, motor neuron, effector
B) effector, sensory neuron, integration center, motor neuron, receptor
C) receptor, motor neuron, integration center, effector, sensory neuron
D) integration center, receptor, sensory neuron, motor neuron, effector

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Which relatively rare type of neuron has two processes extending from opposite sides of the cell body?
A) multipolar
B) pseudounipolar
C) bipolar
D) unipolar
A) multipolar
B) pseudounipolar
C) bipolar
D) unipolar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Some small neurons in the CNS have no axon, only dendrites, and are
A) unipolar.
B) pseudounipolar.
C) multipolar.
D) bipolar.
A) unipolar.
B) pseudounipolar.
C) multipolar.
D) bipolar.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The complexity of the CNS can be attributed to
A) the large number of sensory neurons carrying information to the CNS.
B) the large number of motor neurons leaving the CNS.
C) the different types of receptors outside the CNS.
D) the large number of interneurons in the CNS.
A) the large number of sensory neurons carrying information to the CNS.
B) the large number of motor neurons leaving the CNS.
C) the different types of receptors outside the CNS.
D) the large number of interneurons in the CNS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A man walking barefoot stepped on a piece of glass. His foot jerked upward in which type of reflex?
A) somatic, polysynaptic withdrawal reflex
B) visceral, polysynaptic withdrawal reflex
C) somatic, monosynaptic withdrawal reflex
D) visceral, monosynaptic stretch reflex
A) somatic, polysynaptic withdrawal reflex
B) visceral, polysynaptic withdrawal reflex
C) somatic, monosynaptic withdrawal reflex
D) visceral, monosynaptic stretch reflex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Myelin on axons functions to
A) store nutrients (fat) for use by the neurons.
B) speed the rate of impulse conduction and insulate neighboring axons from one another.
C) cover nodes of Ranvier.
D) make the axons live longer.
A) store nutrients (fat) for use by the neurons.
B) speed the rate of impulse conduction and insulate neighboring axons from one another.
C) cover nodes of Ranvier.
D) make the axons live longer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Action potentials travel along the
A) dendrite membrane.
B) axon membrane.
C) cell body.
D) myelin.
A) dendrite membrane.
B) axon membrane.
C) cell body.
D) myelin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The peripheral nerve fibers that measure the degree of stretch in the biceps brachii muscle and its tendons are classified as
A) general somatic sensory.
B) general visceral motor.
C) general somatic motor.
D) special visceral sensory.
A) general somatic sensory.
B) general visceral motor.
C) general somatic motor.
D) special visceral sensory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which cells provide the myelin sheath for neurons in the CNS?
A) Schwann cells
B) microglial cells
C) oligodendrocyctes
D) astrocytes
A) Schwann cells
B) microglial cells
C) oligodendrocyctes
D) astrocytes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following most immediately encases the smallest component of a nerve?
A) fascicle
B) epineurium
C) perineurium
D) endoneurium
A) fascicle
B) epineurium
C) perineurium
D) endoneurium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
An example of proprioception is
A) the contraction of the triceps brachii.
B) the sensation you feel during a wake-up stretch.
C) sensing a feather touch the skin.
D) the contraction of pharyngeal arch muscles used in chewing.
A) the contraction of the triceps brachii.
B) the sensation you feel during a wake-up stretch.
C) sensing a feather touch the skin.
D) the contraction of pharyngeal arch muscles used in chewing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The peripheral nerve fibers that speed up the movement of the digestive tract are classified as
A) special somatic motor.
B) general visceral motor (efferent).
C) special visceral sensory.
D) general visceral sensory (afferent).
A) special somatic motor.
B) general visceral motor (efferent).
C) special visceral sensory.
D) general visceral sensory (afferent).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Gray matter in the CNS contains all of the following except
A) fiber tracts.
B) neuroglia.
C) neuron cell bodies.
D) dendrites.
A) fiber tracts.
B) neuroglia.
C) neuron cell bodies.
D) dendrites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In the region of the spinal cord, the cell bodies of most interneurons lie in
A) sensory ganglia.
B) the ventral half of the white matter.
C) the dorsal half of the gray matter.
D) the PNS.
A) sensory ganglia.
B) the ventral half of the white matter.
C) the dorsal half of the gray matter.
D) the PNS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The type of axon that conducts impulses most slowly is
A) thin, myelinated.
B) thin, unmyelinated.
C) thick, myelinated.
D) thick, unmyelinated.
A) thin, myelinated.
B) thin, unmyelinated.
C) thick, myelinated.
D) thick, unmyelinated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The entire nerve is surrounded by a tough fibrous sheath called the
A) ectoneurium.
B) epineurium.
C) perineurium.
D) endoneurium.
A) ectoneurium.
B) epineurium.
C) perineurium.
D) endoneurium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
An axon collateral from one neuron that circles back and synapses with a previous neuron describes
A) a reverberating circuit.
B) serial processing.
C) parallel processing.
D) a converging circuit.
A) a reverberating circuit.
B) serial processing.
C) parallel processing.
D) a converging circuit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
General visceral sensory impulses include pain, temperature, nausea, and hunger.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A node of Ranvier (myelin sheath gap)
A) is one segment of the myelin sheath.
B) occurs in the PNS but not in the CNS.
C) is a bare region of axonal membrane in myelinated axons only.
D) occurs only in ganglia.
A) is one segment of the myelin sheath.
B) occurs in the PNS but not in the CNS.
C) is a bare region of axonal membrane in myelinated axons only.
D) occurs only in ganglia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The covering of a fascicle within a nerve is the
A) ectoneurium.
B) endoneurium.
C) epineurium.
D) perineurium.
A) ectoneurium.
B) endoneurium.
C) epineurium.
D) perineurium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
During embryo development, neurons that make ʺbadʺ connections
A) are turned off by inhibitory synapses in reverberating circuits.
B) die by apoptosis.
C) develop collaterals that seek out appropriate target cells.
D) are inhibited by chemicals released from astrocytes.
A) are turned off by inhibitory synapses in reverberating circuits.
B) die by apoptosis.
C) develop collaterals that seek out appropriate target cells.
D) are inhibited by chemicals released from astrocytes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Regeneration of peripheral axons requires
A) formation of a tube by Schwann cells to guide growth.
B) deposition of neurofilaments to bridge the gap between the original axon fragments.
C) construction of a collateral that branches from the point of damage.
D) migration of neural stem cells from the hippocampus.
A) formation of a tube by Schwann cells to guide growth.
B) deposition of neurofilaments to bridge the gap between the original axon fragments.
C) construction of a collateral that branches from the point of damage.
D) migration of neural stem cells from the hippocampus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
All of the neuronʹs organelles are localized to the cell body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A monosynaptic reflex arc is an example of
A) serial processing.
B) a converging circuit.
C) parallel processing.
D) a reverberating circuit.
A) serial processing.
B) a converging circuit.
C) parallel processing.
D) a reverberating circuit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The chemical substance that is released at axon terminals is called a
A) synaptic vesicle.
B) hormone.
C) neurotransmitter.
D) Nissl body.
A) synaptic vesicle.
B) hormone.
C) neurotransmitter.
D) Nissl body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Most neurons in the body are multipolar neurons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Ciliated neuroglial cells that form an epithelium and play an active role in forming and moving cerebrospinal fluid are
A) astrocytes.
B) Schwann cells.
C) oligodendrocytes.
D) ependymal cells.
A) astrocytes.
B) Schwann cells.
C) oligodendrocytes.
D) ependymal cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Vesicles containing neurotransmitters are located in
A) the nodes of Ranvier.
B) axon terminals.
C) a synaptic cleft.
D) the postsynaptic region of dendrites.
A) the nodes of Ranvier.
B) axon terminals.
C) a synaptic cleft.
D) the postsynaptic region of dendrites.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The difference between myelinated and unmyelinated axons is that
A) Schwann cells wrap around myelinated axons in concentric layers.
B) Schwann cells form more widely spaced nodes of Ranvier in unmyelinated axons.
C) Schwann cells simultaneously surround multiple axons in myelinated axons.
D) Schwann cells are not associated with unmyelinated axons.
A) Schwann cells wrap around myelinated axons in concentric layers.
B) Schwann cells form more widely spaced nodes of Ranvier in unmyelinated axons.
C) Schwann cells simultaneously surround multiple axons in myelinated axons.
D) Schwann cells are not associated with unmyelinated axons.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Special somatic senses have receptors that are located mostly in the head, including hearing and balance and vision.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A neuron is a collection of nerve fibers in the PNS.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



