Deck 12: The Central Nervous System
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/125
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: The Central Nervous System
1
Which description best matches the location of white matter?
A) In the spinal cord, white matter is deep while cerebral white matter is superficial.
B) In both the brain and spinal cord, white matter is superficial.
C) In the spinal cord, white matter is superficial while cerebral white matter is deep.
D) In both the brain and spinal cord, white matter is deep.
A) In the spinal cord, white matter is deep while cerebral white matter is superficial.
B) In both the brain and spinal cord, white matter is superficial.
C) In the spinal cord, white matter is superficial while cerebral white matter is deep.
D) In both the brain and spinal cord, white matter is deep.
C
2
The cerebellum functions in:
A) learning, memory, and personality.
B) the planning and coordination of movement.
C) homeostatic functions such as breathing and heart rate.
D) biological rhythms.
A) learning, memory, and personality.
B) the planning and coordination of movement.
C) homeostatic functions such as breathing and heart rate.
D) biological rhythms.
B
3
An elevated ridge on the surface of the cerebrum is known as a:
A) gyrus.
B) furrow.
C) fissure.
D) sulcus.
A) gyrus.
B) furrow.
C) fissure.
D) sulcus.
A
4
Which lobe is situated posteriorly in each cerebral hemisphere?
A) occipital
B) parietal
C) temporal
D) frontal
A) occipital
B) parietal
C) temporal
D) frontal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The primary motor cortex of the right cerebral hemisphere:
A) integrates senses from multiple different sources.
B) receives and processes sensory input.
C) controls the motor activity on the right side of the body.
D) controls the motor activity on the left side of the body.
A) integrates senses from multiple different sources.
B) receives and processes sensory input.
C) controls the motor activity on the right side of the body.
D) controls the motor activity on the left side of the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What information is received by the primary vestibular cortex?
A) vision
B) taste
C) hearing
D) equilibrium
A) vision
B) taste
C) hearing
D) equilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What is NOT part of the cerebrum?
A) frontal lobe
B) brainstem
C) insula
D) parietal lobe
A) frontal lobe
B) brainstem
C) insula
D) parietal lobe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Where are color, object movement, and depth processed?
A) premotor cortex
B) auditory association cortex
C) precentral gyrus
D) visual association areas
A) premotor cortex
B) auditory association cortex
C) precentral gyrus
D) visual association areas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Bundles of white matter in the cerebrum are known as:
A) nerves.
B) ganglia.
C) tracts.
D) nuclei.
A) nerves.
B) ganglia.
C) tracts.
D) nuclei.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What results when the corpus callosum is cut?
A) communication between a cerebral cortex in one hemisphere with other areas of the same hemisphere would be impaired
B) communication within a single brain hemisphere would be impaired
C) communication between the brain and spinal cord would be impaired
D) communication between the right and left cerebral hemispheres would be impaired
A) communication between a cerebral cortex in one hemisphere with other areas of the same hemisphere would be impaired
B) communication within a single brain hemisphere would be impaired
C) communication between the brain and spinal cord would be impaired
D) communication between the right and left cerebral hemispheres would be impaired

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Select the letter that represents the location of the primary motor cortex. 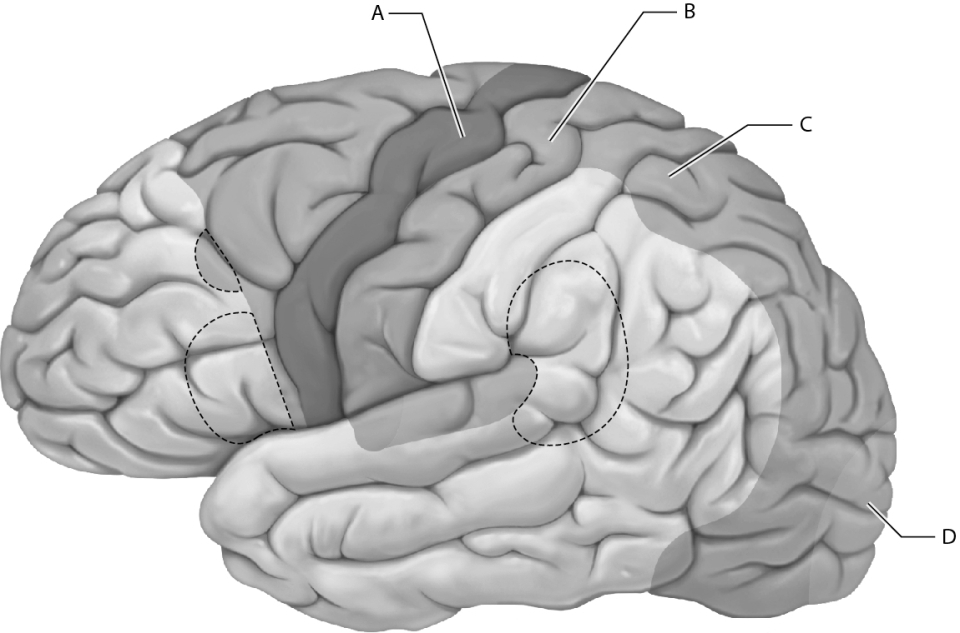
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The brainstem connects the brain and the:
A) eyes.
B) cerebellum.
C) spinal cord.
D) ventricles.
A) eyes.
B) cerebellum.
C) spinal cord.
D) ventricles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The majority of the cerebral cortex is:
A) fiber tracts.
B) cerebellum.
C) white matter.
D) neocortex.
A) fiber tracts.
B) cerebellum.
C) white matter.
D) neocortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What are the three primary brain vesicles that form from the neural tube?
A) midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
B) mesencephalon, telencephalon, diencephalon
C) forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
D) brainstem, diencephalon, cerebellum
A) midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
B) mesencephalon, telencephalon, diencephalon
C) forebrain, midbrain, hindbrain
D) brainstem, diencephalon, cerebellum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What best describes the Broca's area?
A) Broca's area is usually found in the right cerebral hemisphere.
B) Broca's area is housed in the temporal and parietal lobes.
C) Broca's area is a premotor area for speech sounds.
D) Broca's area houses personality, decorum, and behavior.
A) Broca's area is usually found in the right cerebral hemisphere.
B) Broca's area is housed in the temporal and parietal lobes.
C) Broca's area is a premotor area for speech sounds.
D) Broca's area houses personality, decorum, and behavior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is located in the postcentral gyrus of the parietal lobe?
A) primary somatosensory cortex
B) primary visual cortex
C) auditory association area
D) primary auditory cortex
A) primary somatosensory cortex
B) primary visual cortex
C) auditory association area
D) primary auditory cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In 1848, Phineas Gage sustained a brain injury when an iron rod pierced through his left prefrontal cerebral cortex. What do you think was the result?
A) Gage was unable to move the right side of his body.
B) Gage's personality, behavior, and psychological state changed.
C) Gage was unable to produce language.
D) Gage was unable to understand language.
A) Gage was unable to move the right side of his body.
B) Gage's personality, behavior, and psychological state changed.
C) Gage was unable to produce language.
D) Gage was unable to understand language.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What brain region is responsible for learning, memory, and personality?
A) cerebrum
B) cerebellum
C) brainstem
D) diencephalon
A) cerebrum
B) cerebellum
C) brainstem
D) diencephalon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What secondary brain vesicles form from the forebrain?
A) metencephalon and mesencephalon
B) diencephalon and telencephalon
C) metencephalon and myelencephalon
D) telencephalon and metencephalon
A) metencephalon and mesencephalon
B) diencephalon and telencephalon
C) metencephalon and myelencephalon
D) telencephalon and metencephalon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What is the correct pathway of development of the cerebellum?
A) neural tube, forebrain, telencephalon, cerebellum
B) neural tube, midbrain, mesencephalon, cerebellum
C) neural tube, diencephalon, cerebellum
D) neural tube, hindbrain, metencephalon, cerebellum
A) neural tube, forebrain, telencephalon, cerebellum
B) neural tube, midbrain, mesencephalon, cerebellum
C) neural tube, diencephalon, cerebellum
D) neural tube, hindbrain, metencephalon, cerebellum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which meninx touches the brain?
A) subarachnoid space
B) pia mater
C) arachnoid mater
D) dura mater
A) subarachnoid space
B) pia mater
C) arachnoid mater
D) dura mater

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is formed by ________ and reabsorbed through arachnoid  granulations into _.
granulations into _.
A) dural sinuses; ependymal cells
B) astrocytes; ependymal cells
C) choroid plexuses; dural sinuses
D) the cerebral aqueduct; arachnoid villi
 granulations into _.
granulations into _.A) dural sinuses; ependymal cells
B) astrocytes; ependymal cells
C) choroid plexuses; dural sinuses
D) the cerebral aqueduct; arachnoid villi

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Todd was startled when the door slammed shut. What part of the brainstem is responsible?
A) thalamus
B) pons
C) midbrain
D) medulla
A) thalamus
B) pons
C) midbrain
D) medulla

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What is NOT a function of the reticular formation?
A) pain transmission
B) memory
C) breathing
D) sleep
A) pain transmission
B) memory
C) breathing
D) sleep

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Damage to the substantia nigra of the midbrain would be indicated by problems with:
A) heart rate.
B) sense of smell.
C) respiration.
D) movement.
A) heart rate.
B) sense of smell.
C) respiration.
D) movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following should NOT cross the blood -brain barrier with ease?
A) lipid -based molecules
B) glucose
C) large, polar molecules
D) carbon dioxide
A) lipid -based molecules
B) glucose
C) large, polar molecules
D) carbon dioxide

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What would NOT lead to hydrocephalus?
A) deficient CSF production
B) excessive CSF production
C) not enough CSF reabsorbed by the arachnoid granulations
D) blockage of CSF circulation
A) deficient CSF production
B) excessive CSF production
C) not enough CSF reabsorbed by the arachnoid granulations
D) blockage of CSF circulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) circulates through the:
A) dura mater.
B) blood -brain barrier.
C) pia mater.
D) subarachnoid space.
A) dura mater.
B) blood -brain barrier.
C) pia mater.
D) subarachnoid space.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In what dura mater fold is the superior sagittal sinus located?
A) tentorium cerebri
B) tentorium cerebelli
C) falx cerebri
D) falx cerebelli
A) tentorium cerebri
B) tentorium cerebelli
C) falx cerebri
D) falx cerebelli

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What type of fiber carries information from the frontal lobe of the right cerebral hemisphere to the occipital lobe of the same cerebral hemisphere?
A) projection fibers
B) corpus callosum
C) commissural fibers
D) association fibers
A) projection fibers
B) corpus callosum
C) commissural fibers
D) association fibers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The hippocampus and amygdala are parts of the:
A) reticular formation.
B) globus pallidus.
C) limbic system.
D) caudate nucleus.
A) reticular formation.
B) globus pallidus.
C) limbic system.
D) caudate nucleus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The hypothalamus functions in:
A) sending information to the cerebral cortex.
B) coordinating movement.
C) regulating the autonomic nervous system.
D) secreting a hormone called melatonin.
A) sending information to the cerebral cortex.
B) coordinating movement.
C) regulating the autonomic nervous system.
D) secreting a hormone called melatonin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Astrocytes and tight junctions create a barrier to viruses and bacteria known as:
A) dural sinuses.
B) the blood -brain barrier.
C) choroid plexues.
D) meninges.
A) dural sinuses.
B) the blood -brain barrier.
C) choroid plexues.
D) meninges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
What portion of the brainstem blends with the spinal cord after passing through the foramen magnum?
A) hypothalamus
B) pons
C) midbrain
D) medulla oblongata
A) hypothalamus
B) pons
C) midbrain
D) medulla oblongata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What functional brain system participates in memory, learning, emotion, and behavior?
A) anterolateral system
B) medial lemniscal system
C) peripheral nervous system
D) limbic system
A) anterolateral system
B) medial lemniscal system
C) peripheral nervous system
D) limbic system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The thalamus receives information from all of the following afferent fibers EXCEPT for the sense of:
A) vision.
B) smell.
C) hearing.
D) taste.
A) vision.
B) smell.
C) hearing.
D) taste.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The white matter of the cerebellum is known as:
A) cerebellar cortex.
B) arbor vitae.
C) folia.
D) vermis.
A) cerebellar cortex.
B) arbor vitae.
C) folia.
D) vermis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What is NOT part of the diencephalon?
A) thalamus
B) hypothalamus
C) epithalamus
D) medulla oblongata
A) thalamus
B) hypothalamus
C) epithalamus
D) medulla oblongata

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
What is housed in the pyramidal tracts of the medulla oblongata?
A) lower motor neurons of the corticospinal tract
B) upper sensory neurons of the corticospinal tract
C) upper motor neurons of the corticospinal tract
D) lower sensory neurons of the corticospinal tract
A) lower motor neurons of the corticospinal tract
B) upper sensory neurons of the corticospinal tract
C) upper motor neurons of the corticospinal tract
D) lower sensory neurons of the corticospinal tract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) in the third ventricle will drain into the:
A) fourth ventricle.
B) lateral ventricles.
C) dural sinus.
D) choroid plexus.
A) fourth ventricle.
B) lateral ventricles.
C) dural sinus.
D) choroid plexus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The hole in the spinal cord through which CSF flows is the:
A) central canal.
B) vertebral foramen.
C) intervertebral foramen.
D) anterior median fissure.
A) central canal.
B) vertebral foramen.
C) intervertebral foramen.
D) anterior median fissure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What part of the spinal cord carries motor information from the brain?
A) corticospinal tract
B) posterior column
C) anterolateral system
D) spinocerebellar tract
A) corticospinal tract
B) posterior column
C) anterolateral system
D) spinocerebellar tract

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The spinal cord lacks a portion of the dura mater known as the:
A) meningeal layer.
B) subdural space.
C) epidural space.
D) periosteal layer.
A) meningeal layer.
B) subdural space.
C) epidural space.
D) periosteal layer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Where is the sensation of touch processed?
A) primary somatosensory cortex, or S1
B) primary motor cortex
C) prefrontal cortex
D) somatosensory association cortex, or S2
A) primary somatosensory cortex, or S1
B) primary motor cortex
C) prefrontal cortex
D) somatosensory association cortex, or S2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An injury to the spinal cord is not possible below the:
A) fourth cervical vertebra.
B) second lumbar vertebra.
C) second thoracic vertebra.
D) ninth thoracic vertebra.
A) fourth cervical vertebra.
B) second lumbar vertebra.
C) second thoracic vertebra.
D) ninth thoracic vertebra.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
At what point in the brain do upper motor neurons of the corticospinal tracts decussate?
A) midbrain
B) thalamus
C) pons
D) medullary pyramids
A) midbrain
B) thalamus
C) pons
D) medullary pyramids

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Giada experienced damage to a sensory neuron in the PNS. Which neuron sustained damage?
A) first -order neuron
B) third -order neuron
C) interneuron
D) second -order neuron
A) first -order neuron
B) third -order neuron
C) interneuron
D) second -order neuron

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What part of the brain modifies the activity of upper motor neurons to produce voluntary movements and inhibit involuntary ones?
A) primary motor cortex
B) premotor cortex
C) cerebellum
D) basal nuclei
A) primary motor cortex
B) premotor cortex
C) cerebellum
D) basal nuclei

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Where are the cell bodies of lower motor neurons located?
A) brainstem
B) dorsal horn of spinal gray matter
C) anterior horn of spinal gray matter
D) motor area of cerebral cortex
A) brainstem
B) dorsal horn of spinal gray matter
C) anterior horn of spinal gray matter
D) motor area of cerebral cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
In the spinal cord, nerve tracts or funiculi make up the:
A) central canal.
B) white columns.
C) gray commissure.
D) gray horns.
A) central canal.
B) white columns.
C) gray commissure.
D) gray horns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Visual stimuli that arrive in the thalamus are relayed to the:
A) primary visual cortex in the frontal lobe.
B) brainstem nuclei.
C) medulla.
D) primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe.
A) primary visual cortex in the frontal lobe.
B) brainstem nuclei.
C) medulla.
D) primary visual cortex in the occipital lobe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An epidural, or spinal anesthesia, is administered into the CSF flow around the spinal cord. Into what space is this medication injected?
A) subdural space
B) epidural space
C) subarachnoid space
D) dural sinus
A) subdural space
B) epidural space
C) subarachnoid space
D) dural sinus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Sensory information from proprioceptors about joint and muscle positions are carried to the brain by the:
A) anterolateral system (spinothalamic tracts).
B) vestibulospinal tract.
C) reticulospinal tract.
D) spinocerebellar tracts.
A) anterolateral system (spinothalamic tracts).
B) vestibulospinal tract.
C) reticulospinal tract.
D) spinocerebellar tracts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Heidi sustained damage to her spinal cord in a car accident. She has no difficulty moving her arm, but has lost some sensation in her arm. What part of her spinal cord must have been injured?
A) corticospinal tract of spinal white matter
B) anterior horn of spinal gray matter
C) lateral horn of spinal gray matter
D) posterior horn of spinal gray matter
A) corticospinal tract of spinal white matter
B) anterior horn of spinal gray matter
C) lateral horn of spinal gray matter
D) posterior horn of spinal gray matter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Detection of stimuli is a responsibility of the ________ while perception of the stimuli is a responsibility of the _.
A) second -order neuron; first -order neuron
B) upper motor neuron; lower motor neuron
C) PNS; CNS
D) CNS; PNS
A) second -order neuron; first -order neuron
B) upper motor neuron; lower motor neuron
C) PNS; CNS
D) CNS; PNS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Which special sense does NOT travel through the thalamus at any point in its transmission?
A) olfaction
B) gustation
C) vision
D) hearing
A) olfaction
B) gustation
C) vision
D) hearing

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Tactile sensation does NOT refer to:
A) vibrations.
B) light touch.
C) crude touch.
D) two -point discrimination.
A) vibrations.
B) light touch.
C) crude touch.
D) two -point discrimination.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What part of the motor pathway inhibits inappropriate movements?
A) primary motor cortex
B) basal nuclei
C) occipital lobe
D) cerebellum
A) primary motor cortex
B) basal nuclei
C) occipital lobe
D) cerebellum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What is situated inferior to the conus medullaris of the spinal cord?
A) cauda equina
B) cervical enlargement
C) posterior median sulcus
D) lumbar enlargement
A) cauda equina
B) cervical enlargement
C) posterior median sulcus
D) lumbar enlargement

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What role does dopamine play in motor control?
A) Dopamine binds receptors in the cerebral cortex to activate upper motor neurons to produce coordinated and smooth movements.
B) Dopamine enhances the process of motor learning in the cerebellum to reduce motor error.
C) Dopamine binds receptors on the caudate nucleus and putamen, inhibiting the globus pallidus. The upper motor neurons are eventually activated.
D) Dopamine inhibits the substantial nigra of the basal nuclei and inhibits the upper motor neurons from initiating movement.
A) Dopamine binds receptors in the cerebral cortex to activate upper motor neurons to produce coordinated and smooth movements.
B) Dopamine enhances the process of motor learning in the cerebellum to reduce motor error.
C) Dopamine binds receptors on the caudate nucleus and putamen, inhibiting the globus pallidus. The upper motor neurons are eventually activated.
D) Dopamine inhibits the substantial nigra of the basal nuclei and inhibits the upper motor neurons from initiating movement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Which statement best describes the circadian rhythm?
A) In a 24 -hour period of time, we feel the most awake after eating breakfast.
B) In a 24 -hour period of time, adults require at least 8 hours of sleep to feel rested.
C) In a 24 -hour period of time, we feel most sleepy during brightest period of the day.
D) In a 24 -hour period of time, we spend a period of time awake and a period of time asleep.
A) In a 24 -hour period of time, we feel the most awake after eating breakfast.
B) In a 24 -hour period of time, adults require at least 8 hours of sleep to feel rested.
C) In a 24 -hour period of time, we feel most sleepy during brightest period of the day.
D) In a 24 -hour period of time, we spend a period of time awake and a period of time asleep.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The brainstem performs higher level functions dealing with learning and memory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Broca's area is responsible for the ability to produce speech while Wernicke's area is responsible for the ability to understand language.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The hypothalamus integrates emotion, memory, and sensory information and sends it to association areas of the cerebral cortex.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
What part of the brain is the "boss" of the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
A) thalamus
B) pons
C) basal nuclei
D) hypothalamus
A) thalamus
B) pons
C) basal nuclei
D) hypothalamus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
You've looked for your keys for the past ten minutes in several different places. The ability to keep track of the places you've already looked is stored in:
A) long -term memory.
B) short -term (working) memory.
C) immediate memory.
D) long -term potentiation (LTP).
A) long -term memory.
B) short -term (working) memory.
C) immediate memory.
D) long -term potentiation (LTP).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What do you expect to see if the activity of the reticular formation is decreased?
A) increased metabolism
B) decreased level of consciousness
C) fever
D) increased level of consciousness
A) increased metabolism
B) decreased level of consciousness
C) fever
D) increased level of consciousness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The central sulcus separates the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe of the cerebrum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The neurotransmitter orexin plays a role in:
A) the promotion of wakefulness.
B) the promotion of sleepiness.
C) body temperature regulation.
D) the regulation of metabolism.
A) the promotion of wakefulness.
B) the promotion of sleepiness.
C) body temperature regulation.
D) the regulation of metabolism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What part of the cerebral cortex is responsible for personality, the creation of an awareness of self, and the ability to recognize appropriate behavior?
A) parietal association cortex
B) Wernicke's area
C) temporal association cortex
D) prefrontal cortex
A) parietal association cortex
B) Wernicke's area
C) temporal association cortex
D) prefrontal cortex

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which brain nucleus serves as the body's "master clock?"
A) caudate nucleus
B) lentiform nucleus
C) suprachiastmatic nucleus
D) basal nucleus
A) caudate nucleus
B) lentiform nucleus
C) suprachiastmatic nucleus
D) basal nucleus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata of the brainstem all arise from the hindbrain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What part of the brain is responsible for cognition?
A) reticular formation
B) hypothalamus
C) cerebral cortex
D) thalamus
A) reticular formation
B) hypothalamus
C) cerebral cortex
D) thalamus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
What provides a link between the nervous system and the endocrine system?
A) hypothalamus
B) pons
C) cerebellum
D) thalamus
A) hypothalamus
B) pons
C) cerebellum
D) thalamus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
In contrast to the nervous system, the endocrine system accomplishes homeostasis by:
A) producing an immediate effect in target cells.
B) sending action potentials that excite or inhibit target cells.
C) releasing hormones into the blood that regulate the functions of other cells.
D) controlling the activities of the autonomic nervous system (ANS).
A) producing an immediate effect in target cells.
B) sending action potentials that excite or inhibit target cells.
C) releasing hormones into the blood that regulate the functions of other cells.
D) controlling the activities of the autonomic nervous system (ANS).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Cognition is best described as:
A) a reversible and normal suspension of consciousness.
B) encoding and storing learned information in our neural circuitry.
C) the ability to comprehend and produce words.
D) recognizing, processing, planning, and responding to stimuli.
A) a reversible and normal suspension of consciousness.
B) encoding and storing learned information in our neural circuitry.
C) the ability to comprehend and produce words.
D) recognizing, processing, planning, and responding to stimuli.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
What function is NOT lateralized in one of the cerebral hemispheres?
A) emotion
B) language -related recognition
C) creativity
D) facial recognition
A) emotion
B) language -related recognition
C) creativity
D) facial recognition

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The reticular formation is a collection of nuclei in the diencephalon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The deepest stage of sleep is experienced during:
A) stage VI.
B) stage IV.
C) stage I.
D) stage III.
A) stage VI.
B) stage IV.
C) stage I.
D) stage III.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The primary auditory cortex, located in the temporal lobe of the cerebrum, is the first to receive auditory information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 125 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



