Deck 1: Introduction to Anatomy Physiology
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/101
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 1: Introduction to Anatomy Physiology
1
Which organ system produces movement and generates heat?
A) skeletal system
B) digestive system
C) endocrine system
D) muscular system
A) skeletal system
B) digestive system
C) endocrine system
D) muscular system
D
2
In laboratory, you will study tissues. This area of study is known as:
A) cytology.
B) gross anatomy.
C) physiology.
D) histology.
A) cytology.
B) gross anatomy.
C) physiology.
D) histology.
D
3
What is a good way to manage time in preparation for your anatomy and physiology class?
A) I study only on the weekends when I have many hours of free time.
B) I should stay up all night the night before the test to maximize what is stored in short -term memory.
C) I should delay studying until the day or two before the test to best remember the material.
D) I make a schedule and budget my time.
A) I study only on the weekends when I have many hours of free time.
B) I should stay up all night the night before the test to maximize what is stored in short -term memory.
C) I should delay studying until the day or two before the test to best remember the material.
D) I make a schedule and budget my time.
D
4
How could you use the Learning Outcomes in this book to help you study?
A) Read through the Learning Outcomes after you have completed a section.
B) Write down the answers to the Learning Outcomes.
C) Rewrite each Learning Outcome in your notes.
D) Recite the Learning Outcomes until you have them memorized.
A) Read through the Learning Outcomes after you have completed a section.
B) Write down the answers to the Learning Outcomes.
C) Rewrite each Learning Outcome in your notes.
D) Recite the Learning Outcomes until you have them memorized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following is the correct sequence, from simplest to most complex, in the levels of structural organization of the human body?
A) chemical level, tissue level, cellular level, organ system level, organ level, organismal level
B) cellular level, tissue level, chemical level, organ level, organ system level, organismal level
C) cellular level, chemical level, tissue level, organ level, organ system level, organismal level
D) chemical level, cellular level, tissue level, organ level, organ system level, organismal level
A) chemical level, tissue level, cellular level, organ system level, organ level, organismal level
B) cellular level, tissue level, chemical level, organ level, organ system level, organismal level
C) cellular level, chemical level, tissue level, organ level, organ system level, organismal level
D) chemical level, cellular level, tissue level, organ level, organ system level, organismal level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In laboratory, you will study the overall structure and shape of the femur bone without the aid of a microscope. This is a study known as:
A) microscopic anatomy.
B) systemic anatomy.
C) regional anatomy.
D) gross anatomy.
A) microscopic anatomy.
B) systemic anatomy.
C) regional anatomy.
D) gross anatomy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Which organ system includes blood vessels and the heart?
A) lymphatic system
B) endocrine system
C) respiratory system
D) cardiovascular system
A) lymphatic system
B) endocrine system
C) respiratory system
D) cardiovascular system

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What is a major function of the respiratory system?
A) digest food and absorb nutrients into the blood
B) deliver oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide from the body
C) return excess tissue fluid to the cardiovascular system
D) produce vitamin D and retain water
A) digest food and absorb nutrients into the blood
B) deliver oxygen to the blood and remove carbon dioxide from the body
C) return excess tissue fluid to the cardiovascular system
D) produce vitamin D and retain water

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What does the SQ3R method stand for?
A) share, quiz, query, question, and read
B) search, quiet, research, read, and remember
C) survey, question, read, recite, and review
D) sort, query, read, recite, and review
A) share, quiz, query, question, and read
B) search, quiet, research, read, and remember
C) survey, question, read, recite, and review
D) sort, query, read, recite, and review

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What type of learner performs best with study groups?
A) any type of visual learner
B) visual/nonverbal learner
C) visual/verbal learner
D) tactile/kinesthetic learner
A) any type of visual learner
B) visual/nonverbal learner
C) visual/verbal learner
D) tactile/kinesthetic learner

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
What is the smallest level of structural organization in the human body?
A) chemical level
B) tissue level
C) organ level
D) cellular level
A) chemical level
B) tissue level
C) organ level
D) cellular level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Sierra says she learns more from reading the textbook for class than from sitting in lecture. She must be a(n):
A) visual/nonverbal learner.
B) tactile/kinesthetic learner.
C) visual/verbal learner.
D) auditory/verbal learner.
A) visual/nonverbal learner.
B) tactile/kinesthetic learner.
C) visual/verbal learner.
D) auditory/verbal learner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What characteristic of life involves the removal of waste products that result from metabolic processes?
A) irritability
B) reproduction
C) excretion
D) growth
A) irritability
B) reproduction
C) excretion
D) growth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which learner thrives in an environment with a practical -based laboratory or hands -on activities?
A) auditory/verbal
B) visual/nonverbal
C) visual/verbal
D) tactile/kinesthetic
A) auditory/verbal
B) visual/nonverbal
C) visual/verbal
D) tactile/kinesthetic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following is the most complex structural level of organization?
A) organ level
B) cellular level
C) chemical level
D) tissue level
A) organ level
B) cellular level
C) chemical level
D) tissue level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What is a good strategy for class or laboratory preparation?
A) Only read after you have attended class or laboratory.
B) Read and prepare notes before attending your class or laboratory.
C) Avoid reading before class as you may get confused.
D) Focus on reading your materials on the weekends when you have hours to spend.
A) Only read after you have attended class or laboratory.
B) Read and prepare notes before attending your class or laboratory.
C) Avoid reading before class as you may get confused.
D) Focus on reading your materials on the weekends when you have hours to spend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Why should a student use the SQ3R method?
A) The SQ3R method provides a student with a strategy for taking notes during lecture class.
B) The SQ3R method provides a plan for a student to improve textbook reading skills.
C) The SQ3R method provides a student with a strategy for improving test taking skills.
D) The SQ3R method provides a student with ways to improve time management skills.
A) The SQ3R method provides a student with a strategy for taking notes during lecture class.
B) The SQ3R method provides a plan for a student to improve textbook reading skills.
C) The SQ3R method provides a student with a strategy for improving test taking skills.
D) The SQ3R method provides a student with ways to improve time management skills.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When we imagine a person exhibiting anatomical position, the palms of the hands are assumed to be facing:
A) down.
B) forward.
C) to the side.
D) backward.
A) down.
B) forward.
C) to the side.
D) backward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Jesse felt comfortable using the microscope after listening to directions from his lab professor. His learning style preference must be:
A) visual/nonverbal learner.
B) auditory/verbal learner.
C) visual/verbal learner.
D) tactile/kinesthetic learner.
A) visual/nonverbal learner.
B) auditory/verbal learner.
C) visual/verbal learner.
D) tactile/kinesthetic learner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which two organ systems include the pancreas as a component?
A) digestive and urinary systems
B) endocrine and lymphatic systems
C) respiratory and cardiovascular systems
D) digestive and endocrine systems
A) digestive and urinary systems
B) endocrine and lymphatic systems
C) respiratory and cardiovascular systems
D) digestive and endocrine systems

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Select the appropriate directional term to complete this sentence: The elbow is ________ to the wrist.
A) superficial
B) proximal
C) inferior (caudal)
D) distal
A) superficial
B) proximal
C) inferior (caudal)
D) distal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What best describes the directional term proximal?
A) toward the head
B) closer to the midline of the body
C) toward the front
D) closer to the point of origin
A) toward the head
B) closer to the midline of the body
C) toward the front
D) closer to the point of origin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
On which body surface is the sural region?
A) anterior (ventral)
B) posterior (dorsal)
C) medial
D) superficial
A) anterior (ventral)
B) posterior (dorsal)
C) medial
D) superficial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which directional term indicates the front side of the body?
A) anterior (ventral)
B) posterior (dorsal)
C) superior (cranial)
D) medial
A) anterior (ventral)
B) posterior (dorsal)
C) superior (cranial)
D) medial

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What are the two subcavities of the dorsal body cavity?
A) abdominal and pelvic cavities
B) pleural and pericardial cavities
C) cranial and vertebral (spinal) cavities
D) thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities
A) abdominal and pelvic cavities
B) pleural and pericardial cavities
C) cranial and vertebral (spinal) cavities
D) thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The vertebral region is superior to the:
A) sacral region.
B) cephalic region.
C) cervical region.
D) occipital region.
A) sacral region.
B) cephalic region.
C) cervical region.
D) occipital region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
In anatomical position, the palms are on the:
A) lateral surface.
B) posterior (dorsal) surface.
C) anterior (ventral) surface.
D) superior (cranial) surface.
A) lateral surface.
B) posterior (dorsal) surface.
C) anterior (ventral) surface.
D) superior (cranial) surface.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What major organs are housed in the thoracic cavity?
A) stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas
B) urinary bladder, reproductive organs
C) lungs, heart, esophagus, trachea
D) brain and spinal cord
A) stomach, intestines, liver, pancreas
B) urinary bladder, reproductive organs
C) lungs, heart, esophagus, trachea
D) brain and spinal cord

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which regions of the abdominopelvic cavity are situated medially?
A) right and left lumbar regions and the umbilical region
B) right and left hypochondriac regions, and the epigastric region
C) epigastric, umbilical, hypogastric regions
D) right hypochondriac, right lumbar, and right iliac (inguinal) regions
A) right and left lumbar regions and the umbilical region
B) right and left hypochondriac regions, and the epigastric region
C) epigastric, umbilical, hypogastric regions
D) right hypochondriac, right lumbar, and right iliac (inguinal) regions

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The hand is also known as the:
A) plantar region.
B) acromial region.
C) pedal region.
D) manual region.
A) plantar region.
B) acromial region.
C) pedal region.
D) manual region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A person in anatomical position is visualized to be:
A) laying down on his or her back.
B) sitting down.
C) laying down on the stomach.
D) standing upright.
A) laying down on his or her back.
B) sitting down.
C) laying down on the stomach.
D) standing upright.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Dr. Mitchell performs open heart surgery. The incision he makes through the sternal region of his patient divides the thoracic cavity into equal left and right parts. This incision must be made along a:
A) transverse (horizontal) plane.
B) sagittal plane.
C) midsagittal (median) plane.
D) frontal (coronal) plane.
A) transverse (horizontal) plane.
B) sagittal plane.
C) midsagittal (median) plane.
D) frontal (coronal) plane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Select the appropriate directional term to complete this sentence: The mouth is nose.
A) inferior (caudal)
B) posterior (dorsal)
C) distal
D) superior (cranial)
A) inferior (caudal)
B) posterior (dorsal)
C) distal
D) superior (cranial)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A person who is standing facing forward with hands at the sides, palms facing forward, is in the:
A) anatomical position.
B) supine position.
C) frontal position.
D) sagittal position.
A) anatomical position.
B) supine position.
C) frontal position.
D) sagittal position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The thoracic cavity is situated superior to the abdominopelvic cavity and separated by the diaphragm. Therefore, the diaphragm creates a:
A) frontal (coronal) plane.
B) parasagittal plane.
C) transverse (horizontal) plane or cross section.
D) midsagittal (median) plane.
A) frontal (coronal) plane.
B) parasagittal plane.
C) transverse (horizontal) plane or cross section.
D) midsagittal (median) plane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What smaller cavity within the thoracic cavity houses the heart, great blood vessels, esophagus, and trachea?
A) diaphragm
B) peritoneal cavity
C) mediastinum
D) abdominal cavity
A) diaphragm
B) peritoneal cavity
C) mediastinum
D) abdominal cavity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A directional term that means the same as posterior is:
A) ventral.
B) sagittal.
C) anterior.
D) dorsal.
A) ventral.
B) sagittal.
C) anterior.
D) dorsal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominopelvic cavity?
A) mediastinum
B) diaphragm
C) pericardium
D) pleura
A) mediastinum
B) diaphragm
C) pericardium
D) pleura

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The shoulder is also known as the:
A) digital region.
B) brachial region.
C) antebrachial region.
D) acromial region.
A) digital region.
B) brachial region.
C) antebrachial region.
D) acromial region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts is known as a:
A) sagittal plane.
B) frontal (coronal) plane.
C) transverse (horizontal) plane.
D) midsagittal (median) plane.
A) sagittal plane.
B) frontal (coronal) plane.
C) transverse (horizontal) plane.
D) midsagittal (median) plane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A cell or organ that responds to the directions of the control center in a negative feedback loop is termed a(n):
A) stimulus.
B) regulator.
C) receptor.
D) effector.
A) stimulus.
B) regulator.
C) receptor.
D) effector.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A mother breastfeeds her infant. As long as the baby suckles his mother's breast, the mother's mammary glands produce milk. Suckling, the stimulus, increases milk production, the response. This scenario is best described as:
A) a positive feedback loop.
B) a negative feedback loop.
C) anatomical position.
D) principle of complementarity of structure and function.
A) a positive feedback loop.
B) a negative feedback loop.
C) anatomical position.
D) principle of complementarity of structure and function.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The innermost serous membrane attached to the heart muscle is called the:
A) visceral pleura.
B) visceral pericardium.
C) parietal pericardium.
D) visceral peritoneum.
A) visceral pleura.
B) visceral pericardium.
C) parietal pericardium.
D) visceral peritoneum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What are the two major methods by which cells communicate to coordinate their functions?
A) temperature gradients and pressure gradients
B) positive feedback loops and negative feedback loops
C) effectors and responses
D) chemical messengers and/or electrical signals
A) temperature gradients and pressure gradients
B) positive feedback loops and negative feedback loops
C) effectors and responses
D) chemical messengers and/or electrical signals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
How does the effector restore homeostasis in a negative feedback loop?
A) The effector increases and reinforces the initial stimulus.
B) The effector amplifies the response, but does not continue indefinitely.
C) The effector opposes the initial stimulus and shuts off when conditions return to the normal range.
D) The effector causes a rapid change in a variable.
A) The effector increases and reinforces the initial stimulus.
B) The effector amplifies the response, but does not continue indefinitely.
C) The effector opposes the initial stimulus and shuts off when conditions return to the normal range.
D) The effector causes a rapid change in a variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What part of a feedback loop causes physiological responses to return the variable to the normal homeostatic range?
A) stimulus
B) effector
C) control center
D) receptor (sensor)
A) stimulus
B) effector
C) control center
D) receptor (sensor)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Serous membranes line certain cavities within the:
A) dorsal cavities.
B) vertebral (spinal) cavity.
C) ventral cavities.
D) cranial cavity.
A) dorsal cavities.
B) vertebral (spinal) cavity.
C) ventral cavities.
D) cranial cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
What is a gradient?
A) equilibrium or balance between two unconnected areas
B) equal amounts of something exist in areas that are connected
C) maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment
D) more of something exists in one area than another and the two areas are connected
A) equilibrium or balance between two unconnected areas
B) equal amounts of something exist in areas that are connected
C) maintenance of a relatively stable internal environment
D) more of something exists in one area than another and the two areas are connected

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What would a needle travel through as it enters the right lung?
A) parietal pleura, serous fluid, visceral pleura, right lung
B) visceral pericardium, serous fluid, parietal pericardium, right lung
C) visceral pleura, serous fluid, parietal pleura, right lung
D) parietal pleura, serous fluid, right lung, visceral pleura
A) parietal pleura, serous fluid, visceral pleura, right lung
B) visceral pericardium, serous fluid, parietal pericardium, right lung
C) visceral pleura, serous fluid, parietal pleura, right lung
D) parietal pleura, serous fluid, right lung, visceral pleura

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The type of feedback that increases or enhances the effects of the variable is:
A) positive.
B) neutral.
C) responsive.
D) negative.
A) positive.
B) neutral.
C) responsive.
D) negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What is NOT one of the four core principles related to homeostasis?
A) feedback loops
B) cell -cell communication
C) metabolism
D) gradients
A) feedback loops
B) cell -cell communication
C) metabolism
D) gradients

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Select the letter that represents the left iliac (inguinal) region.
A) B
B) C
C) A
D) D
A) B
B) C
C) A
D) D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A nerve cell releases chemical messengers to trigger changes in a nearby muscle cell. This is example of a core principle known as:
A) principle of complementarity of structure and function.
B) cell -cell communication.
C) gradients.
D) feedback loops.
A) principle of complementarity of structure and function.
B) cell -cell communication.
C) gradients.
D) feedback loops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which serous membrane covers the abdominal organs?
A) mediastinum
B) peritoneum
C) pleura
D) pericardium
A) mediastinum
B) peritoneum
C) pleura
D) pericardium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What of the following best summarizes the principle of complementarity of structure and function?
A) structure drives function
B) function follows structure
C) maintenance of a stable internal environment
D) form follows function
A) structure drives function
B) function follows structure
C) maintenance of a stable internal environment
D) form follows function

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Blood pressure in arteries is higher than the blood pressure in capillaries. Blood flows from arteries to capillaries due to the presence of a:
A) negative feedback loop.
B) positive feedback loop.
C) homeostatic imbalance.
D) gradient.
A) negative feedback loop.
B) positive feedback loop.
C) homeostatic imbalance.
D) gradient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment is termed:
A) effector control.
B) positive feedback.
C) integration.
D) homeostasis.
A) effector control.
B) positive feedback.
C) integration.
D) homeostasis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which region of the abdominopelvic cavity lies between the right and left lumbar regions?
A) epigastric region
B) umbilical region
C) right lumbar region
D) hypogastric region
A) epigastric region
B) umbilical region
C) right lumbar region
D) hypogastric region

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
When you go outside on a hot summer day, your body temperature heats up above the normal range. Receptors in your brain detect the change in body temperature. The brain activates nerve cells that send messages to sweat glands, causing the body temperature to fall as the sweat evaporates from the skin. What part of this feedback loop is the effector?
A) sweat glands
B) brain
C) nerve cells
D) increased body temperature
A) sweat glands
B) brain
C) nerve cells
D) increased body temperature

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
When you go outside on a hot summer day, your body temperature heats up above the normal range. Receptors in your brain detect the change in body temperature. The brain activates nerve cells that send messages to sweat glands, causing the body temperature to fall as the sweat evaporates from the skin. What part of this feedback loop is the stimulus?
A) increased body temperature
B) brain
C) sweat glands
D) nerve cells
A) increased body temperature
B) brain
C) sweat glands
D) nerve cells

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
According to the principle of complementarity of structure and function, structure and function are related only at the cellular level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The transverse (horizontal plane or cross section) plane divides the body into anterior and posterior parts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Patients are always examined while they are standing in anatomical position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Match the following with the correct body cavity or subdivision.
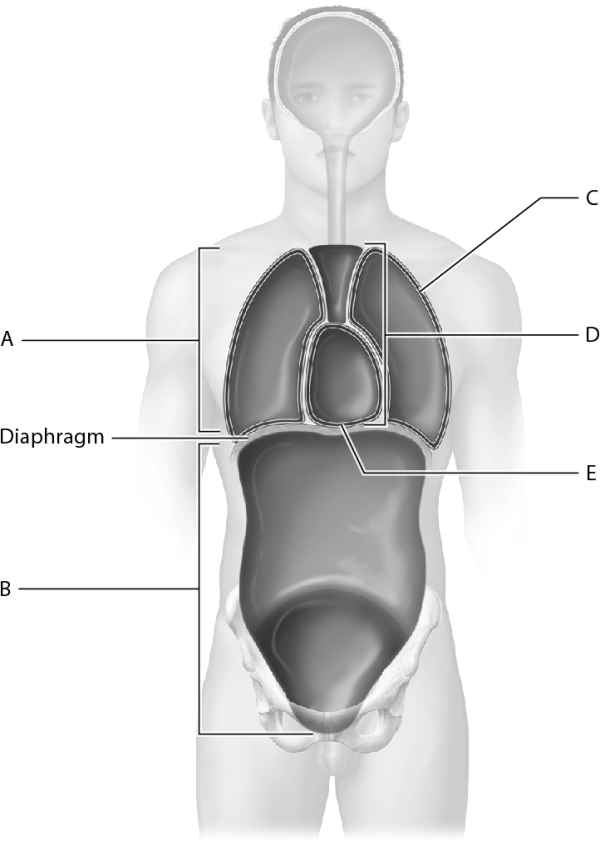
Identify the cavity where the left lung is housed.

Identify the cavity where the left lung is housed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Match the following with the correct body cavity or subdivision.

Identify the thoracic cavity.

Identify the thoracic cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Match the following with the correct regional anatomical term.
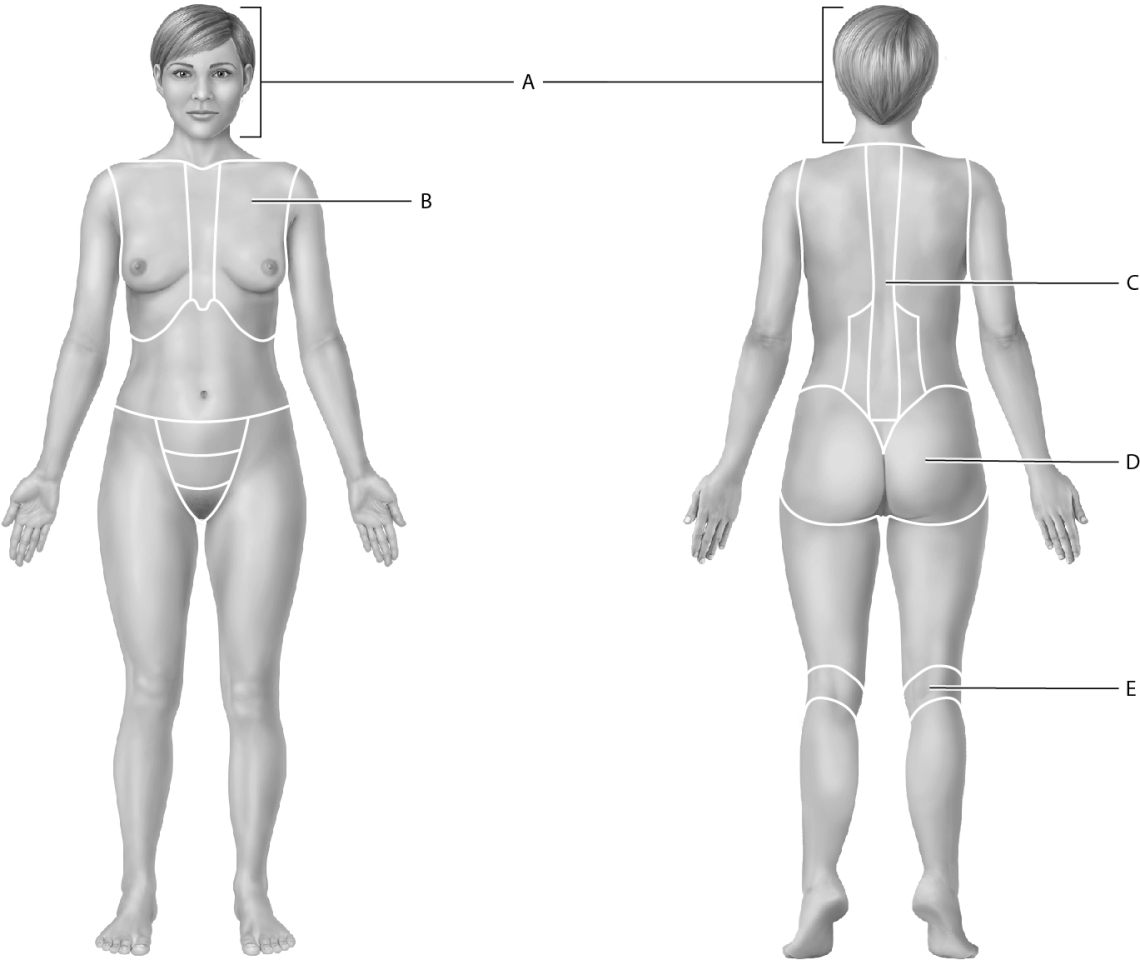
Identify the cephalic region.

Identify the cephalic region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Match the following with the correct regional anatomical term.

Identify the gluteal region.

Identify the gluteal region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Serous fluid lubricates around organs and reduces friction as the organ moves against adjacent structures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Match the following with the correct regional anatomical term.

Identify the thoracic region.

Identify the thoracic region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Match the following with the correct regional anatomical term.

Identify the popliteal region.

Identify the popliteal region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
You should wait to read the textbook until you have heard the material presented in lecture or laboratory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The simplest level of organization in the human body is the cellular level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The popliteal region is posterior (dorsal) to the patellar region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Match the following with the correct regional anatomical term.

Identify the vertebral region.

Identify the vertebral region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match the following with the correct body cavity or subdivision.

Identify the abdominopelvic cavity.

Identify the abdominopelvic cavity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The thymus is a component of both the endocrine and lymphatic systems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
When studying, you should actively read the textbook by taking notes and making diagrams.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Negative feedback loops produce responses in the opposite direction of the initial stimulus while positive feedback loops produce responses in the same direction of the initial stimulus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Match the following with the correct body cavity or subdivision.

Identify the mediastinum.

Identify the mediastinum.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Match the following with the correct body cavity or subdivision.

Identify the cavity that houses the heart.

Identify the cavity that houses the heart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 101 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



