Deck 13: Technological Progress: the Short, the Medium and the Long Run
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/59
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Technological Progress: the Short, the Medium and the Long Run
1
Since the early 1980s in Australia, which group of workers has experienced decreasing relative wage?
A) Workers that completed high school.
B) Workers with trade qualification or diploma.
C) Workers with university degrees.
D) Workers with incomplete high school qualification.
E) Foreign migrant workers.
A) Workers that completed high school.
B) Workers with trade qualification or diploma.
C) Workers with university degrees.
D) Workers with incomplete high school qualification.
E) Foreign migrant workers.
Workers with incomplete high school qualification.
2
Employment growth will increase as a result of an increase in productivity when which of the following occurs?
A) The AS curve shifts downward.
B) The AS curve shifts downward and the AD curve shifts to the right.
C) Output growth exceeds productivity growth.
D) The AD curve shifts to the right.
E) Productivity growth exceeds output growth.
A) The AS curve shifts downward.
B) The AS curve shifts downward and the AD curve shifts to the right.
C) Output growth exceeds productivity growth.
D) The AD curve shifts to the right.
E) Productivity growth exceeds output growth.
Output growth exceeds productivity growth.
3
Which of the following statements about Australia during the 1996- 2011 period is correct?
A) Output has increased largely due to monetary and fiscal policy.
B) Output has increased largely due to tax and exchange rate policy.
C) Output growth has been approximately equal to employment growth.
D) Output growth has been slower than employment growth.
E) Output growth has been faster than employment growth.
A) Output has increased largely due to monetary and fiscal policy.
B) Output has increased largely due to tax and exchange rate policy.
C) Output growth has been approximately equal to employment growth.
D) Output growth has been slower than employment growth.
E) Output growth has been faster than employment growth.
Output growth has been faster than employment growth.
4
Which of the following represents the wage- setting relation when changes in labour productivity are allowed to occur?
A)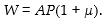
B)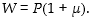
C)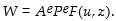
D)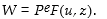
E)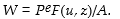
A)
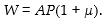
B)
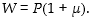
C)
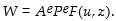
D)
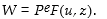
E)
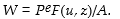

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Employment will remain constant as a result of an increase in productivity when which of the following occurs?
A) Productivity growth exceeds output growth.
B) Productivity growth is equal to output growth.
C) Output growth exceeds productivity growth.
D) The AS curve shifts downward.
E) The AD curve shifts to the right.
A) Productivity growth exceeds output growth.
B) Productivity growth is equal to output growth.
C) Output growth exceeds productivity growth.
D) The AS curve shifts downward.
E) The AD curve shifts to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Suppose the aggregate production function is represented by Y = AN. Which of the following expressions represents the number of additional workers required to increase production by one unit?
A) 1/A.
B) 1/N.
C) 1/Y.
D) A.
E) Y/N.
A) 1/A.
B) 1/N.
C) 1/Y.
D) A.
E) Y/N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Assume an economy experiences, for a given period, a 1% increase in output and a 5% increase in productivity. Given this information, we know that which of the following occurred for this economy during this economy?
A) Employment has decreased during this period.
B) Employment has increased during this period.
C) Employment has not changed during this period.
D) Employment initially decreased then increased during this period.
E) The effects on employment are ambiguous.
A) Employment has decreased during this period.
B) Employment has increased during this period.
C) Employment has not changed during this period.
D) Employment initially decreased then increased during this period.
E) The effects on employment are ambiguous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In recent years, the increasing relative wage of skilled labour has been mostly due to:
A) government laws promoting the hiring of skilled labour.
B) government subsidies provided to college students.
C) a decrease in the supply of, and increase in the demand for, skilled labour.
D) an increase in the demand for skilled labour that exceeds the increase in supply.
E) a decrease in the supply of skilled labour that exceeds the decrease in demand.
A) government laws promoting the hiring of skilled labour.
B) government subsidies provided to college students.
C) a decrease in the supply of, and increase in the demand for, skilled labour.
D) an increase in the demand for skilled labour that exceeds the increase in supply.
E) a decrease in the supply of skilled labour that exceeds the decrease in demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Assume that expectations of P and A are correct. Now suppose that there is a 1.6% increase in A. Given this information, which of the following will occur?
A) A 1.6% increase in the real wage and an increase in the natural rate of unemployment.
B) No change in the real wage and an increase in the natural rate of unemployment.
C) A 1.6% increase in the real wage and no change in the natural rate of unemployment.
D) No change in the real wage and a decrease in the natural rate of unemployment.
E) A 1.6% increase in the real wage and a decrease in the natural rate of unemployment.
A) A 1.6% increase in the real wage and an increase in the natural rate of unemployment.
B) No change in the real wage and an increase in the natural rate of unemployment.
C) A 1.6% increase in the real wage and no change in the natural rate of unemployment.
D) No change in the real wage and a decrease in the natural rate of unemployment.
E) A 1.6% increase in the real wage and a decrease in the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In recent years in Australia, relative wages of the least educated workers:
A) have decreased, but by less than the relative wages of university- educated workers.
B) have increased faster than the relative wages of university- educated workers.
C) have decreased at about the same rate as the relative wages of university- educated workers.
D) have decreased, while the relative wages of university- educated workers also decreased.
E) have increased, but by less than the relative wages of university- educated workers.
A) have decreased, but by less than the relative wages of university- educated workers.
B) have increased faster than the relative wages of university- educated workers.
C) have decreased at about the same rate as the relative wages of university- educated workers.
D) have decreased, while the relative wages of university- educated workers also decreased.
E) have increased, but by less than the relative wages of university- educated workers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A major explanation for the decline in employment in the textiles industry in Australia is:
A) shifts in production toward low- wage countries.
B) inaccurate expectations about the price level.
C) increases in income.
D) inaccurate expectations about productivity growth.
E) social problems in Australia.
A) shifts in production toward low- wage countries.
B) inaccurate expectations about the price level.
C) increases in income.
D) inaccurate expectations about productivity growth.
E) social problems in Australia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Suppose an economy experiences an increase in technological progress. This increase in technological progress will:
A) lead to changes in the types of goods produced.
B) allow the same amount of output to be produced with fewer workers.
C) allow more output to be produced with the same number of workers.
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.
A) lead to changes in the types of goods produced.
B) allow the same amount of output to be produced with fewer workers.
C) allow more output to be produced with the same number of workers.
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Technological unemployment is a macroeconomic phenomenon that occurs when:
A) hysteresis.
B) unemployment changes due to the effects of technology in high- technology industries.
C) unemployment changes due to the effects of monetary and fiscal policy in the New Economy.
D) Eurosclerosis.
E) unemployment changes as a result of technological change.
A) hysteresis.
B) unemployment changes due to the effects of technology in high- technology industries.
C) unemployment changes due to the effects of monetary and fiscal policy in the New Economy.
D) Eurosclerosis.
E) unemployment changes as a result of technological change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Assume an economy experiences an increase in productivity that occurs as a result of a more widespread implementation of a major technological breakthrough. Given this information, we would expect which of the following to occur?
A) Aggregate demand would shift to the left.
B) Aggregate demand would not change.
C) Aggregate demand would shift to the right.
D) Both the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves would shift to the right.
E) Both the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves would shift to the left.
A) Aggregate demand would shift to the left.
B) Aggregate demand would not change.
C) Aggregate demand would shift to the right.
D) Both the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves would shift to the right.
E) Both the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves would shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
"Churning" refers to:
A) the increase in productivity caused by an increase in output.
B) changes in the real wage over the business cycle.
C) changes in the markup over the business cycle.
D) the increase in output caused by an increase in productivity.
E) structural change associated with technological progress.
A) the increase in productivity caused by an increase in output.
B) changes in the real wage over the business cycle.
C) changes in the markup over the business cycle.
D) the increase in output caused by an increase in productivity.
E) structural change associated with technological progress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Assume that expectations of P and A are correct. Now suppose that there is a 4% increase in A. Given this
Information, which of the following will occur?
A) The PS relation will shift up by 4%.
B) The PS relation will shift up by less than 4%.
C) The WS relation will shift down by 4%.
D) The PS relation will shift down by 4%.
E) The WS relation will shift up by less than 4%.
Information, which of the following will occur?
A) The PS relation will shift up by 4%.
B) The PS relation will shift up by less than 4%.
C) The WS relation will shift down by 4%.
D) The PS relation will shift down by 4%.
E) The WS relation will shift up by less than 4%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose workers expectations of prices and productivity are accurate. For this economy, an increase in productivity will cause which of the following?
A) An increase in both the real wage and the natural rate of unemployment.
B) A decrease in both the real wage and the natural rate of unemployment.
C) An increase in the real wage and no change to the natural rate of unemployment.
D) An increase in the real wage and a decrease in the natural rate of unemployment.
E) A decrease in the real wage and an increase in the natural rate of unemployment.
A) An increase in both the real wage and the natural rate of unemployment.
B) A decrease in both the real wage and the natural rate of unemployment.
C) An increase in the real wage and no change to the natural rate of unemployment.
D) An increase in the real wage and a decrease in the natural rate of unemployment.
E) A decrease in the real wage and an increase in the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Assume that expectations of the price level and productivity are accurate. Now suppose that the economy experiences an increase in productivity. Which of the following will occur in the medium run?
A) A decrease in unemployment.
B) An increase in unemployment.
C) An increase in employment.
D) No change in unemployment.
E) A decrease in employment.
A) A decrease in unemployment.
B) An increase in unemployment.
C) An increase in employment.
D) No change in unemployment.
E) A decrease in employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Based on our understanding of the price- setting equation, which of the following will not cause a decrease in the price level?
A) A decrease in the nominal wage.
B) A decrease in productivity.
C) An increase in productivity.
D) A decrease in the markup.
E) A decrease in nominal wage to productivity ratio.
A) A decrease in the nominal wage.
B) A decrease in productivity.
C) An increase in productivity.
D) A decrease in the markup.
E) A decrease in nominal wage to productivity ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Assume an economy experiences, for a given period, a 4% increase in output and a 4% increase in productivity. Given this information, we know that which of the following occurred for this economy during this economy?
A) Employment has increased during this period.
B) The employment growth rate is negative during this period.
C) Employment has not changed during this period.
D) The effects on employment are ambiguous.
E) Employment has decreased during this period.
A) Employment has increased during this period.
B) The employment growth rate is negative during this period.
C) Employment has not changed during this period.
D) The effects on employment are ambiguous.
E) Employment has decreased during this period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Assume that expectations of P and A are correct. Based on the wage- setting behaviour, the real wage will be equal to which of the following?
A) P(1 + m).
B) APF(u, z).
C) AP(1 + µ).
D) A(1 + m).
E) AF(u, z).
A) P(1 + m).
B) APF(u, z).
C) AP(1 + µ).
D) A(1 + m).
E) AF(u, z).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Assume that expectations of productivity are slow to adjust. Further assume that A had been increasing by 6% a year. Now suppose that A only increases by 2% in period t. This slowdown in productivity growth will cause:
A) the WS relation to shift up more than the PS relation.
B) the PS and WS relations to shift up by the same amount.
C) the real wage to fall.
D) the PS relation to shift up more than the WS relation.
E) the natural rate of unemployment to fall.
A) the WS relation to shift up more than the PS relation.
B) the PS and WS relations to shift up by the same amount.
C) the real wage to fall.
D) the PS relation to shift up more than the WS relation.
E) the natural rate of unemployment to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Suppose the aggregate production function is represented by Y = AN. Given this information, labour productivity is given by:
A) Y/A.
B) Y.
C) A/N.
D) A.
E) N/A.
A) Y/A.
B) Y.
C) A/N.
D) A.
E) N/A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is not true about technological progress?
A) Cause a decrease in unemployment in the medium run.
B) Lead to the disappearance of old goods.
C) Cause a decrease in unemployment in the short run.
D) Allow for the production of a larger quantity of goods using the same number of workers.
E) Lead to the production of new goods.
A) Cause a decrease in unemployment in the medium run.
B) Lead to the disappearance of old goods.
C) Cause a decrease in unemployment in the short run.
D) Allow for the production of a larger quantity of goods using the same number of workers.
E) Lead to the production of new goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Assume that the aggregate production function is represented by Y = AN. Which of the following represents the marginal cost of producing an additional unit of output?
A) (1 + A)W.
B) W/A.
C) A/W.
D) 1/W.
E) W.
A) (1 + A)W.
B) W/A.
C) A/W.
D) 1/W.
E) W.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following institutional arrangements foster economic growth?
A) A judicial system that resolves disputes.
B) An anti- trust body scrutinising market competition.
C) A political system that protects its citizens.
D) All of the above.
E) Only A and B.
A) A judicial system that resolves disputes.
B) An anti- trust body scrutinising market competition.
C) A political system that protects its citizens.
D) All of the above.
E) Only A and B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Which of the following represents the broad definition of good institutions for economic growth?
A) Strong sense of patriotism.
B) Protection of property rights.
C) Heavy punishments for violations of laws.
D) Tax incentives for investments.
E) Highly regulated markets.
A) Strong sense of patriotism.
B) Protection of property rights.
C) Heavy punishments for violations of laws.
D) Tax incentives for investments.
E) Highly regulated markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Assume that expectations of productivity are slow to adjust. An increase in productivity growth from 2% to 5% will cause:
A) an increase in the real wage of 2% and an increase in un.
B) an increase in the real wage of 2% and a decrease in un.
C) an increase in the real wage of 3% and a decrease in un.
D) an increase in the real wage of 5% and an increase in un.
E) an increase in the real wage of 5% and a decrease in un.
A) an increase in the real wage of 2% and an increase in un.
B) an increase in the real wage of 2% and a decrease in un.
C) an increase in the real wage of 3% and a decrease in un.
D) an increase in the real wage of 5% and an increase in un.
E) an increase in the real wage of 5% and a decrease in un.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Assume that expectations of productivity growth adjust slowly over time. For this economy, a decrease in productivity will most likely cause which of the following to occur?
A) An increase in the natural rate of unemployment.
B) A decrease in the markup over labour costs.
C) An increase in the markup over labour costs.
D) A decrease in the natural rate of unemployment.
E) A decrease in the real wage.
A) An increase in the natural rate of unemployment.
B) A decrease in the markup over labour costs.
C) An increase in the markup over labour costs.
D) A decrease in the natural rate of unemployment.
E) A decrease in the real wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Assume that the aggregate production function is represented by Y = AN. Which of the following represents the price- setting relation for this economy?
A) W/P.
B) (1 + m)W.
C) W/A.
D) (1 + m)(W/A).
E) (1 + m)(A/W).
A) W/P.
B) (1 + m)W.
C) W/A.
D) (1 + m)(W/A).
E) (1 + m)(A/W).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Suppose an economy experiences an increase in productivity. The AD curve will most likely shift to the right when this increase in productivity is the result of which of the following?
A) Government subsidies for higher education.
B) An increase in human capital.
C) New tax incentives for R&D spending.
D) A reorganisation of production designed to reduce costs with existing technology.
E) Implementation of major technological breakthrough.
A) Government subsidies for higher education.
B) An increase in human capital.
C) New tax incentives for R&D spending.
D) A reorganisation of production designed to reduce costs with existing technology.
E) Implementation of major technological breakthrough.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A decrease in productivity will cause which of the following to occur in the labour market model?
A) Both the wage- setting and price- setting curves to shift upward.
B) The wage- setting curve to shift downward, and the price- setting curve to shift upward.
C) Both the wage- setting and price- setting curves to shift downward.
D) The wage- setting curve to shift upward, and the price- setting curve to shift downward.
E) The price- setting curve to shift downward, and no shift in the wage- setting curve.
A) Both the wage- setting and price- setting curves to shift upward.
B) The wage- setting curve to shift downward, and the price- setting curve to shift upward.
C) Both the wage- setting and price- setting curves to shift downward.
D) The wage- setting curve to shift upward, and the price- setting curve to shift downward.
E) The price- setting curve to shift downward, and no shift in the wage- setting curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When was the last year that GDP per capita in North Korea was approximately equal to GDP per capita in South Korea?
A) 1950.
B) 1970.
C) 1990.
D) 2000.
E) 2010.
A) 1950.
B) 1970.
C) 1990.
D) 2000.
E) 2010.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Because of labour hoarding, a reduction in output may signal:
A) a decrease in employment.
B) no change in productivity.
C) an increase in productivity.
D) a decrease in productivity.
E) an increase in employment.
A) a decrease in employment.
B) no change in productivity.
C) an increase in productivity.
D) a decrease in productivity.
E) an increase in employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Assume an economy experiences, for a given period, a 4% increase in output and a 2% increase in productivity. Given this information, we know that which of the following occurred for this economy during this economy?
A) The employment growth rate is negative during this period.
B) The effects on employment are ambiguous.
C) Employment has increased during this period.
D) Employment has decreased during this period.
E) Employment has not changed during this period.
A) The employment growth rate is negative during this period.
B) The effects on employment are ambiguous.
C) Employment has increased during this period.
D) Employment has decreased during this period.
E) Employment has not changed during this period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Assume that the production function for an economy is represented by Y = AN. Which of the following expressions is equal to labour productivity for this economy?
A) A/N.
B) AN.
C) 1/A.
D) A.
E) Y/A.
A) A/N.
B) AN.
C) 1/A.
D) A.
E) Y/A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following is believed to cause recent increases in wage inequality?
A) Skill- biased technological progress.
B) International trade.
C) The weakening of trade unions.
D) Both A and C.
E) Both B and C.
A) Skill- biased technological progress.
B) International trade.
C) The weakening of trade unions.
D) Both A and C.
E) Both B and C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Some believe that technological progress leads to higher unemployment in the medium run. This claim that technological progress results in an increase in unemployment in the medium run is supported by:
A) economic theory, but contradicted by the evidence.
B) neither theory nor evidence.
C) both theory and evidence.
D) the evidence, but contradicted by theory.
E) evidence from Australia only.
A) economic theory, but contradicted by the evidence.
B) neither theory nor evidence.
C) both theory and evidence.
D) the evidence, but contradicted by theory.
E) evidence from Australia only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Assume that expectations of productivity are slow to adjust. Further assume that A had been increasing by 2% a year. Now suppose that A increases by 6% in period t. This increase in productivity growth will cause:
A) the real wage to rise and no change in the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the PS and WS relations to shift up by the same amount.
C) the WS relation to shift up more than the PS relation.
D) the real wage to fall.
E) the natural rate of unemployment to fall.
A) the real wage to rise and no change in the natural rate of unemployment.
B) the PS and WS relations to shift up by the same amount.
C) the WS relation to shift up more than the PS relation.
D) the real wage to fall.
E) the natural rate of unemployment to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The evidence suggests that recent technological change:
A) is different from past technological change, in that it has no impact on productivity.
B) has increased the wage gap between skilled and unskilled workers.
C) has increased productivity in the service sector only.
D) has increased productivity in the manufacturing sector only.
E) permanently increased the natural rate of unemployment.
A) is different from past technological change, in that it has no impact on productivity.
B) has increased the wage gap between skilled and unskilled workers.
C) has increased productivity in the service sector only.
D) has increased productivity in the manufacturing sector only.
E) permanently increased the natural rate of unemployment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An increase in productivity will cause which of the following according to the price- setting behaviour of firms?
A) An increase in the markup set by firms.
B) An increase in the level of employment protection set by the government.
C) An increase in the prices set by firms.
D) An increase in the minimum wage paid by firms.
E) An increase in the real wage paid by firms.
A) An increase in the markup set by firms.
B) An increase in the level of employment protection set by the government.
C) An increase in the prices set by firms.
D) An increase in the minimum wage paid by firms.
E) An increase in the real wage paid by firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Assume that expectations of productivity growth adjust slowly. Now, suppose that there is a 5% decrease in productivity. Explain how this 5% decrease in productivity can cause changes in the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Assume that expectations of the price level and productivity are accurate. For this economy, we know that the natural rate of unemployment should depend on which of the following?
A) Neither the level of productivity nor its rate of growth.
B) The level of productivity, but not its rate of growth.
C) Both the level of productivity and its rate of growth.
D) The level of productivity, its rate of growth, and the history of its recent change.
E) The rate of growth of productivity, but not its level.
A) Neither the level of productivity nor its rate of growth.
B) The level of productivity, but not its rate of growth.
C) Both the level of productivity and its rate of growth.
D) The level of productivity, its rate of growth, and the history of its recent change.
E) The rate of growth of productivity, but not its level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Suppose an economy experiences a decrease in productivity. Explain both the short- run and medium- run effects of this productivity decrease on output, employment, and the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Based on our understanding of the wage- setting equation, which of the following will not cause a decrease in the nominal wage?
A) A decrease in expected productivity.
B) An increase in unemployment.
C) A decrease in unemployment benefits.
D) A decrease in the expected price level.
E) An increase in the minimum wage.
A) A decrease in expected productivity.
B) An increase in unemployment.
C) A decrease in unemployment benefits.
D) A decrease in the expected price level.
E) An increase in the minimum wage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Joseph Schumpeter argued that growth was a process of creative destruction. Explain what is meant by the phrase, "creative destruction".

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Some commentators will argue that increases in productivity may have no effect or even a negative effect on employment in the short run. Explain what must occur for an increase in productivity to have no effect or even a negative effect on employment in short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Explain how technological change can cause changes in wage inequality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Because of labour hoarding, an increase in output may signal:
A) a decrease in productivity.
B) no change in productivity.
C) an increase in employment.
D) an increase in productivity.
E) a decrease in employment.
A) a decrease in productivity.
B) no change in productivity.
C) an increase in employment.
D) an increase in productivity.
E) a decrease in employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
There are some concerns that technological progress can lead to an increase in unemployment. Explain the two related but separate dimensions of technological progress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What are the three explanations researchers have offered for why China's transition from a planned economy to a market- oriented one is smoother than central and eastern European countries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Assume that expectations of productivity growth adjust slowly. Now, suppose that there is a 4% increase in productivity. Explain how this 4% increase in productivity can cause changes in the unemployment rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Explain what effect a decrease in productivity has on wage- setting behaviour, price- setting behaviour, the equilibrium real wage, the natural rate of unemployment, and the natural level of output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Using the AS- AD model, graphically illustrate and explain the short- run and medium- run effects of a decrease in productivity. In your graph, clearly label all curves and equilibria. For simplicity, assume that the change in productivity has no effect on aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following would increase the gap in wages between skilled and unskilled workers?
A) International trade forces companies to relocate to low- cost countries.
B) An increase in the costs of going to university.
C) New types of production technology that require workers to have more skills.
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.
A) International trade forces companies to relocate to low- cost countries.
B) An increase in the costs of going to university.
C) New types of production technology that require workers to have more skills.
D) All of the above.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Assume an economy experiences an increase in productivity that occurs as a result of the more efficient use of existing technologies. Given this information, we would expect which of the following to occur?
A) Aggregate demand would shift to the right.
B) Both the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves would shift to the right.
C) Aggregate demand would not change.
D) Both the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves would shift to the left.
E) Aggregate demand would shift to the left.
A) Aggregate demand would shift to the right.
B) Both the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves would shift to the right.
C) Aggregate demand would not change.
D) Both the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves would shift to the left.
E) Aggregate demand would shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Explain some of the causes of increased wage inequality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Assume that expectations of P and A are correct. Now suppose that there is a 4% decrease in A. Given this information, which of the following will occur?
A) The WS relation will shift down by 4%.
B) The WS relation will shift down by more than 4%.
C) The PS relation will shift down by less than 4%.
D) The PS relation will shift up by 4%.
E) The WS relation will shift down by less than 4%.
A) The WS relation will shift down by 4%.
B) The WS relation will shift down by more than 4%.
C) The PS relation will shift down by less than 4%.
D) The PS relation will shift up by 4%.
E) The WS relation will shift down by less than 4%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The empirical evidence suggests that periods of high productivity growth will cause which of the following in the medium run?
A) Lower unemployment.
B) Higher markups.
C) Greater equality in wages.
D) Very little churning.
E) Constant real wages.
A) Lower unemployment.
B) Higher markups.
C) Greater equality in wages.
D) Very little churning.
E) Constant real wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 59 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



