Deck 10: The Muscular System: the Axial Musculature
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/110
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: The Muscular System: the Axial Musculature
1
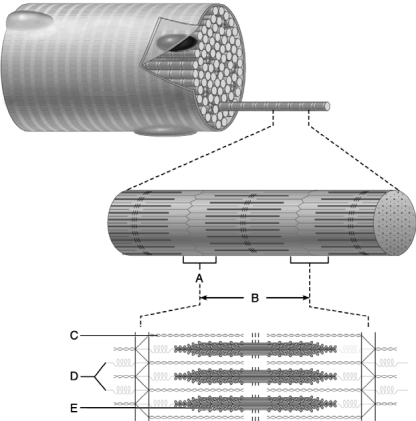 Figure 10.2
Figure 10.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the I band.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
A
2
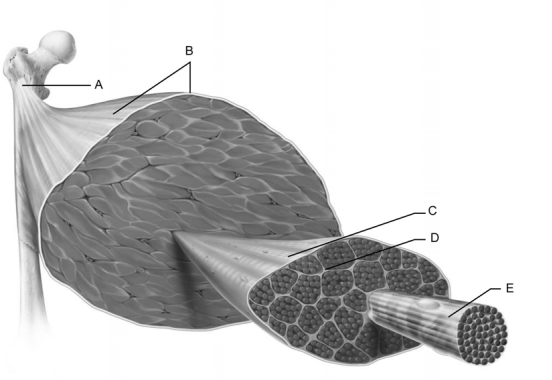 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the endomysium.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
D
3
This type of muscle contains intercalated discs.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
C
4
This type of muscle makes up the walls of hollow organs, such as the stomach and uterus.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Both single-unit smooth muscle and this type of muscle have gap junctions.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Both cardiac muscle and this type of muscle are called involuntary.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
This type of muscle includes the fast oxidative fibers.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
This type of muscle is found in large vessels leading to and from the heart.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
This type of muscle is found in the heart.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
This indicates an individual fascicle.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
 Figure 10.2
Figure 10.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the thin (actin) filament.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The ʺcellsʺ of both skeletal muscle and this muscle type are correctly called muscle fibers.
A) serous muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) serous muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the muscle fiber.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
This type of muscle attaches to bone, but may also attach to skin, cartilage, fascia or a raphe.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
This structure is composed entirely of dense regular connective tissue and connects bone to muscle.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A cell of this type of muscle is striated and can be uninucleated or binucleated.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
 Figure 10.2
Figure 10.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the thick (myosin) filament.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
 Figure 10.2
Figure 10.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
This structure is the basic unit of contraction.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
 Figure 10.2
Figure 10.2Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the titin filament.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
 Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1Use the diagram above to answer the following questions.
Identify the letter that indicates the epimysium.
A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Eccentric contraction
A) generates force without changing the length of the muscle.
B) shortens the muscle.
C) pulls the insertion toward the origin.
D) generates force as the muscle lengthens.
A) generates force without changing the length of the muscle.
B) shortens the muscle.
C) pulls the insertion toward the origin.
D) generates force as the muscle lengthens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The embryonic origin of muscle tissue is from
A) ectoderm.
B) mesoderm.
C) endoderm.
D) epidermis.
A) ectoderm.
B) mesoderm.
C) endoderm.
D) epidermis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which statement about muscle attachments is false?
A) At least one joint is present between an origin and insertion.
B) Insertions are usually distal to the origin.
C) An insertion can be at either attachment point of a muscle, depending on body position and the movement being performed.
D) Upon contraction, the origin is pulled toward the insertion.
A) At least one joint is present between an origin and insertion.
B) Insertions are usually distal to the origin.
C) An insertion can be at either attachment point of a muscle, depending on body position and the movement being performed.
D) Upon contraction, the origin is pulled toward the insertion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Much of the natural elasticity of skeletal muscle tissue is provided by
A) tendons.
B) myosin.
C) actin.
D) connective tissue sheaths.
A) tendons.
B) myosin.
C) actin.
D) connective tissue sheaths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) stores
A) myosin.
B) sodium.
C) ATPase.
D) calcium.
A) myosin.
B) sodium.
C) ATPase.
D) calcium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The biceps and the deltoid muscle are of this type.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A common characteristic of the three types of muscle tissue is that
A) they all have striations.
B) contraction is triggered by the release of calcium.
C) they can all use aerobic and anaerobic methods to utilize energy.
D) they all contain sarcomeres.
A) they all have striations.
B) contraction is triggered by the release of calcium.
C) they can all use aerobic and anaerobic methods to utilize energy.
D) they all contain sarcomeres.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Visceral muscle refers to
A) smooth muscle only.
B) cardiac muscle and smooth muscle.
C) skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle.
D) skeletal muscle and smooth muscle.
A) smooth muscle only.
B) cardiac muscle and smooth muscle.
C) skeletal muscle and cardiac muscle.
D) skeletal muscle and smooth muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
An aponeurosis
A) is a type of direct attachment of muscle to bone.
B) is the junction between the axon terminus of a neuron to an individual muscle fiber.
C) connects a muscle to underlying structures through a flat sheet or web.
D) consists of a neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates.
A) is a type of direct attachment of muscle to bone.
B) is the junction between the axon terminus of a neuron to an individual muscle fiber.
C) connects a muscle to underlying structures through a flat sheet or web.
D) consists of a neuron and all the muscle fibers it innervates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Titin
A) prevents a muscle from being overstretched.
B) connects myosin to actin.
C) forms the Z disk to which actin attaches.
D) limits the degree to which a muscle may contract.
A) prevents a muscle from being overstretched.
B) connects myosin to actin.
C) forms the Z disk to which actin attaches.
D) limits the degree to which a muscle may contract.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Contractions of these muscles are under voluntary control.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Which of these is not in direct contact with thick myofilaments?
A) myosin
B) ATPase
C) actin
D) synaptic vesicles
A) myosin
B) ATPase
C) actin
D) synaptic vesicles

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Delayed-onset muscle soreness is caused by
A) accumulation of lactic acid.
B) overnight cramps that occur after strenuous exercise.
C) microscopic tears and resulting inflammation.
D) depletion of ATP during prolonged activity.
A) accumulation of lactic acid.
B) overnight cramps that occur after strenuous exercise.
C) microscopic tears and resulting inflammation.
D) depletion of ATP during prolonged activity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
This type of muscle, along with cardiac muscle, is called visceral muscle.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
This type of muscle composes the largest share of muscle weight in the human body.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
This type of muscle may be affected by rhabdomyolysis.
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle
A) skeletal muscle
B) smooth muscle
C) cardiac muscle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
As skeletal muscles enlarge in a weight lifter, all of the following occur except
A) myofibrils become more abundant in the muscle cells.
B) muscle cells grow larger.
C) muscle cells divide mitotically.
D) myofilaments become more abundant in the muscle cells.
A) myofibrils become more abundant in the muscle cells.
B) muscle cells grow larger.
C) muscle cells divide mitotically.
D) myofilaments become more abundant in the muscle cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Sarcopenia is
A) a decrease in the amount of actin in the muscle fiber.
B) a decrease in the muscleʹs need for energy.
C) a decrease in the amount of sarcolemma in the muscle fiber.
D) the loss of muscle mass with age.
A) a decrease in the amount of actin in the muscle fiber.
B) a decrease in the muscleʹs need for energy.
C) a decrease in the amount of sarcolemma in the muscle fiber.
D) the loss of muscle mass with age.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Sarcoplasmic reticulum lies
A) between muscles but in myofilaments.
B) between myofibrils but in fibers.
C) between fibers but in myofilaments.
D) between fascicles but outside fibers.
A) between muscles but in myofilaments.
B) between myofibrils but in fibers.
C) between fibers but in myofilaments.
D) between fascicles but outside fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following correctly defines a triad of the sarcomere?
A) actin, troponin, and tropomyosin
B) a T tubule and two adjacent terminal cisterns
C) an axon terminal, synaptic cleft, and sarcolemma
D) actin, myosin, and titin
A) actin, troponin, and tropomyosin
B) a T tubule and two adjacent terminal cisterns
C) an axon terminal, synaptic cleft, and sarcolemma
D) actin, myosin, and titin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The area that contains no thin filaments is known as the
A) A band.
B) H zone.
C) I band.
D) intercalated disc.
A) A band.
B) H zone.
C) I band.
D) intercalated disc.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
When the distance between two adjacent Z disks grows shorter, the muscle fiber is experiencing
A) isometric contraction.
B) concentric contraction.
C) relaxation.
D) eccentric contraction.
A) isometric contraction.
B) concentric contraction.
C) relaxation.
D) eccentric contraction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which type of muscle fiber has no myofibrils?
A) red
B) skeletal
C) smooth
D) cardiac
A) red
B) skeletal
C) smooth
D) cardiac

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which region of the sarcomere does not change in length during contraction?
A) Z disk to Z disk
B) I band
C) A band
D) H zone
A) Z disk to Z disk
B) I band
C) A band
D) H zone

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The type of attachment in which the muscle fibers seem to attach directly to a bone is
A) an aponeurosis.
B) a tendon.
C) an insertion.
D) a fleshy attachment.
A) an aponeurosis.
B) a tendon.
C) an insertion.
D) a fleshy attachment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Myoglobin
A) is released by the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
B) provides energy for contraction.
C) binds and stores oxygen for ATP production.
D) is found within the T tubules.
A) is released by the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
B) provides energy for contraction.
C) binds and stores oxygen for ATP production.
D) is found within the T tubules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which type of muscle fiber has caveolae but no T tubules?
A) white
B) cardiac
C) skeletal
D) smooth
A) white
B) cardiac
C) skeletal
D) smooth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
With intense resistance training,
A) fast oxidative fibers can convert to fast glycolytic fibers.
B) slow oxidative fibers can convert to fast oxidative fibers.
C) slow oxidative fibers can convert to fast glycolytic fibers.
D) fast glycolytic fibers can convert to fast oxidative fibers.
A) fast oxidative fibers can convert to fast glycolytic fibers.
B) slow oxidative fibers can convert to fast oxidative fibers.
C) slow oxidative fibers can convert to fast glycolytic fibers.
D) fast glycolytic fibers can convert to fast oxidative fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The ability of the sarcolemma of muscle cells to conduct an impulse is an example of
A) excitability.
B) contractility.
C) extensibility.
D) elasticity.
A) excitability.
B) contractility.
C) extensibility.
D) elasticity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Of the various types of skeletal muscle fibers, the type containing the most glycogen granules is
A) fast oxidative fibers.
B) slow glycolytic fibers.
C) slow oxidative fibers.
D) fast glycolytic fibers.
A) fast oxidative fibers.
B) slow glycolytic fibers.
C) slow oxidative fibers.
D) fast glycolytic fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Of the various types of skeletal muscle fibers, the type with the most mitochondria is
A) fast oxidative fibers.
B) slow glycolytic fibers.
C) fast glycolytic fibers.
D) slow oxidative fibers.
A) fast oxidative fibers.
B) slow glycolytic fibers.
C) fast glycolytic fibers.
D) slow oxidative fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The sleevelike tubular network within skeletal muscle cells is the
A) rough endoplasmic reticulum.
B) myofibrils.
C) sarcoplasmic reticulum.
D) T tubules.
A) rough endoplasmic reticulum.
B) myofibrils.
C) sarcoplasmic reticulum.
D) T tubules.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The characteristic of muscle tissue that results more from its connective tissue components than from its muscle cells is
A) elasticity.
B) contractility.
C) excitability.
D) extensibility.
A) elasticity.
B) contractility.
C) excitability.
D) extensibility.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Which protein strengthens the sarcolemma by connecting the cytoskeleton with the extracellular matrix?
A) dystrophin
B) titin
C) myosin
D) actin
A) dystrophin
B) titin
C) myosin
D) actin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Age-related loss of muscle mass may be influenced by all of these except:
A) degeneration of muscle fibers because of accumulation of calcium in the sarcoplasm.
B) exhaustion of the supply of muscle satellite cells.
C) an increase in the relative proportion of connective tissue to number of muscle fibers.
D) decrease in the level of testosterone.
A) degeneration of muscle fibers because of accumulation of calcium in the sarcoplasm.
B) exhaustion of the supply of muscle satellite cells.
C) an increase in the relative proportion of connective tissue to number of muscle fibers.
D) decrease in the level of testosterone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Of the various types of skeletal muscle fibers, the type that produces the most power is
A) fast oxidative fibers.
B) fast glycolytic fibers.
C) slow glycolytic fibers.
D) slow oxidative fibers.
A) fast oxidative fibers.
B) fast glycolytic fibers.
C) slow glycolytic fibers.
D) slow oxidative fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
In limbs, the insertions of muscles almost always lie to their origins.
A) posterior
B) lateral
C) distal
D) proximal
A) posterior
B) lateral
C) distal
D) proximal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The only muscle cells that branch are muscle cells.
A) red
B) cardiac
C) skeletal
D) smooth
A) red
B) cardiac
C) skeletal
D) smooth

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Myofascial pain syndrome is best described as a condition in which
A) microscopic tears in muscle fibers result in swelling and inflammation.
B) pain occurs in at least 11 of 18 standardized points across the body.
C) muscle fibers degenerate because of chronic leakage of extracellular calcium.
D) muscle fibers contract when the skin superficial to them is stroked.
A) microscopic tears in muscle fibers result in swelling and inflammation.
B) pain occurs in at least 11 of 18 standardized points across the body.
C) muscle fibers degenerate because of chronic leakage of extracellular calcium.
D) muscle fibers contract when the skin superficial to them is stroked.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Acetylcholine
A) binds to the myosin head, enabling it to form cross-bridges with actin.
B) is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and binds to actin.
C) breaks down the neurotransmitter that activates muscle fibers.
D) binds to the sarcolemma and initiates an impulse in the muscle fiber.
A) binds to the myosin head, enabling it to form cross-bridges with actin.
B) is released from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and binds to actin.
C) breaks down the neurotransmitter that activates muscle fibers.
D) binds to the sarcolemma and initiates an impulse in the muscle fiber.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Of the various types of skeletal muscle fibers, the fibers most resistant to fatigue are
A) slow oxidative fibers.
B) fast glycolytic fibers.
C) fast oxidative fibers.
D) slow glycolytic fibers.
A) slow oxidative fibers.
B) fast glycolytic fibers.
C) fast oxidative fibers.
D) slow glycolytic fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What causes a strain or muscle pull?
A) pain in a muscle due to any muscle disorder
B) a tear in a muscle
C) a sudden involuntary spasm of a muscle
D) a tear in a tendon
A) pain in a muscle due to any muscle disorder
B) a tear in a muscle
C) a sudden involuntary spasm of a muscle
D) a tear in a tendon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Of the three classes of muscle cells, the only one in which the nuclei lie peripherally instead of centrally is
A) smooth.
B) skeletal.
C) cardiac.
D) visceral.
A) smooth.
B) skeletal.
C) cardiac.
D) visceral.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In skeletal muscle fibers, which band or zone contains both thick and thin myofilaments?
A) A
B) I
C) H
D) Z
A) A
B) I
C) H
D) Z

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Muscle tissue can be characterized as being excitable and elastic, but not extensible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
One of the largest and strongest muscles in the body is the gluteus maximus in the buttocks, which is important in these diverse muscular activities: walking, running, and climbing stairs. It must consist of
A) fast oxidative fibers only.
B) slow oxidative fibers only.
C) a mixture of fiber types.
D) fast glycolytic fibers only.
A) fast oxidative fibers only.
B) slow oxidative fibers only.
C) a mixture of fiber types.
D) fast glycolytic fibers only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
In striated muscle, the I band is where
A) thin filaments occur.
B) H zones occur.
C) only thick filaments occur.
D) thick and thin filaments occur.
A) thin filaments occur.
B) H zones occur.
C) only thick filaments occur.
D) thick and thin filaments occur.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Of the surrounding connective tissues of the muscle, the endomysium is the most superficial.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Of the various types of skeletal muscle fibers, the ones with the thinnest myofibrils are
A) slow oxidative fibers.
B) fast glycolytic fibers.
C) fast oxidative fibers.
D) slow glycolytic fibers.
A) slow oxidative fibers.
B) fast glycolytic fibers.
C) fast oxidative fibers.
D) slow glycolytic fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
An aponeurosis is
A) a sheet of dense connective tissue.
B) a nerve to a muscle.
C) clinical pain in a muscle.
D) a large muscle.
A) a sheet of dense connective tissue.
B) a nerve to a muscle.
C) clinical pain in a muscle.
D) a large muscle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
In striated muscle cells, which of these structures stores calcium ions that trigger contraction?
A) T tubules
B) the internal surface of the plasma membrane
C) the myofibrils
D) the terminal cisterns
A) T tubules
B) the internal surface of the plasma membrane
C) the myofibrils
D) the terminal cisterns

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
After a muscle fiber has contracted, the calcium
A) is destroyed.
B) is actively transported into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) is chemically bound to the myofilaments.
D) is secreted by the Golgi apparatus.
A) is destroyed.
B) is actively transported into the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
C) is chemically bound to the myofilaments.
D) is secreted by the Golgi apparatus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
In muscular dystrophy,
A) most forms of the disease do not appear to be inherited.
B) muscle fibers degenerate and atrophy.
C) muscles decrease in size because of loss of fat and connective tissue.
D) most cases appear in young females.
A) most forms of the disease do not appear to be inherited.
B) muscle fibers degenerate and atrophy.
C) muscles decrease in size because of loss of fat and connective tissue.
D) most cases appear in young females.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Of the various types of skeletal muscle fibers, the ones supplied by the most capillaries are
A) slow oxidative fibers.
B) fast glycolytic fibers.
C) fast oxidative fibers.
D) slow glycolytic fibers.
A) slow oxidative fibers.
B) fast glycolytic fibers.
C) fast oxidative fibers.
D) slow glycolytic fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Skeletal muscle fibers are multinucleate, because they arose from a number of embryonic cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Muscle tissue is endowed with all of the following properties except
A) contractibility.
B) extensibility.
C) transmissibility.
D) excitability.
A) contractibility.
B) extensibility.
C) transmissibility.
D) excitability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Skeletal muscle is responsible for movements of the appendages, but not the abdomen.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The origin of a muscle can also be an insertion, depending on the position of the body and the movement being performed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A muscle fascicle is
A) a single muscle cell.
B) a tendon.
C) a bundle of myofilaments.
D) a bundle of cells.
A) a single muscle cell.
B) a tendon.
C) a bundle of myofilaments.
D) a bundle of cells.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Of the various types of skeletal muscle fibers, the fibers that experience fatigue sooner are
A) slow oxidative fibers.
B) fast glycolytic fibers.
C) fast oxidative fibers.
D) slow glycolytic fibers.
A) slow oxidative fibers.
B) fast glycolytic fibers.
C) fast oxidative fibers.
D) slow glycolytic fibers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 110 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



