Deck 14: The Impact of Trade Policies
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/36
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: The Impact of Trade Policies
1
"While the imposition by a country's government of an import tariff on a good clearly injures the country's domestic consumers of the good, the tariff helps
domestic import-competing producers and enhances overall country welfare
(i.e., the "net welfare effect" is positive). Similarly, the granting of an export
subsidy by the country's government to home producers of a good also injures
home consumers of the good, but the subsidy helps home producers and enhances overall country welfare."Utilizing traditional supply/demand analysis, illustrate and explain the parts of the above statement that are True (if any) and the parts that are False (if any). (You can use a "small-country" case throughout your answer. Also, assume that there are barriers to the import of the good into the country granting the export subsidy.)
domestic import-competing producers and enhances overall country welfare
(i.e., the "net welfare effect" is positive). Similarly, the granting of an export
subsidy by the country's government to home producers of a good also injures
home consumers of the good, but the subsidy helps home producers and enhances overall country welfare."Utilizing traditional supply/demand analysis, illustrate and explain the parts of the above statement that are True (if any) and the parts that are False (if any). (You can use a "small-country" case throughout your answer. Also, assume that there are barriers to the import of the good into the country granting the export subsidy.)
not answered
2
At the international price of $20/unit, domestic production is 5,000 units and domestic consumption is 6,000 units. With a 20 percent tariff, domestic production increases by 20 percent and domestic consumption decreases by 25 percent. What is the effect of this tariff on the affected parties? What is the net welfare effect on the country as a whole?
not answered
3
Discuss why an exporting country II, if faced with a choice between a 100-unit import quota by importing country I on a given product or a "voluntary" export restriction by II of 100 units of the product, would choose the VER. Might there be a larger import quota (for example, 120 units) that would be preferred by II to a 100-unit VER? In general terms, what considerations would be involved in this latter choice?
not answered
4
In the diagram in Question #19 above, suppose that a subsidy to import-competing Producers is given instead of a tariff being imposed. The subsidy is set to generate the Same amount of domestic production of the good as occurred under the tariff. What Would be the net welfare loss to the country in this situation?
A) $2
B) $6
C) $12
D) $34
A) $2
B) $6
C) $12
D) $34

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Given the information on prices, production, and consumption in Question #15 above, and assuming that demand and supply curves are straight lines, the impact of the imposition of the tariff is that tariff revenue of the government increases by __________. Further, the "net welfare effect" of the imposition of the tariff is a __________.
A) $72; loss of $44
B) $72; gain of $64
C) $180; loss of $44
D) $180; gain of $64
A) $72; loss of $44
B) $72; gain of $64
C) $180; loss of $44
D) $180; gain of $64

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The diagram below shows the situation of a small country with free-trade in an imported product (at a price of $10) and the situation with a tariff on the product (at a price of $11). In this graph, the net welfare loss (or total deadweight loss) to the country from the imposition of the tariff is __________.
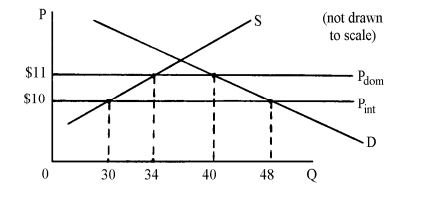
A) $2
B) $6
C) $32
D) $44

A) $2
B) $6
C) $32
D) $44

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the diagram in Question #19 above, what is the amount of tariff revenue collected by the government when the tariff is in place?
A) $3
B) $6
C). $18
D) $40
A) $3
B) $6
C). $18
D) $40

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
"Even if home consumers always have perfectly inelastic demand for a product, at least a portion of the demand curve by those consumers for imports of the product can have the normal downward slope. Further, even if the supply curve of domestic producers is everywhere perfectly inelastic, at least a portion of the supply curve of exports by those producers can have the normal upward slope."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
You are given the following information pertaining to large country B with respect to good W (which is produced at home and also imported), both under free trade and with a $10.00 import tariff in place:
Given this information, and assuming that demand and supply curves are straight lines, what is the loss of consumer surplus in country B that occurs because of the imposition of the tariff?
A) $44
B) $72
C) $448
D) $464
Given this information, and assuming that demand and supply curves are straight lines, what is the loss of consumer surplus in country B that occurs because of the imposition of the tariff?
A) $44
B) $72
C) $448
D) $464

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An import tariff has a similar impact on a country's export good as an export tax. Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
"The imposition of a tariff on a good will always have a negative welfare effect on acountry." Agree? Disagree? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In the following import graph, if horizontal supply line Sm shifts to horizontal line S'm because of the imposition of a tariff,
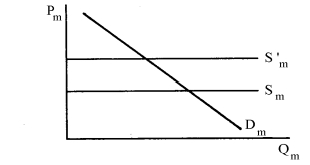
A) the situation must be one of a "large" importing country.
B) the tariff must be a specific tariff.
C) the tariff must be an ad valorem tariff.
D) the tariff can be either a specific or an ad valorem tariff.

A) the situation must be one of a "large" importing country.
B) the tariff must be a specific tariff.
C) the tariff must be an ad valorem tariff.
D) the tariff can be either a specific or an ad valorem tariff.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
(a) Using a demand/supply diagram, illustrate and explain the effects of the imposition of an export tax on a good Y by a home country's government on (i) the home country's consumers of Y, (ii) the home country's producers of Y, and (iii) the home government's tax revenues. (Assume that the country is a "small" country.) Then indicate the "net welfare effect" of the tax on the country. Why might a country want to impose an export tax? Briefly explain.
(b) Suppose now that the country imposing the export tax in part (a) of this question is a "large" country rather than a "small" country. Is it an advantage or a disadvantage for a country to be "large" rather than "small" when it imposes an export tax? Briefly explain. (No diagrams are necessary in this part of the question.)
(b) Suppose now that the country imposing the export tax in part (a) of this question is a "large" country rather than a "small" country. Is it an advantage or a disadvantage for a country to be "large" rather than "small" when it imposes an export tax? Briefly explain. (No diagrams are necessary in this part of the question.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Demonstrate why economists argue that, from a country welfare perspective, a domestic subsidy is preferable to a tariff for assisting a particular industry. Use either a partial or a general equilibrium model to support your argument.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
(a) Suppose that country A wishes to restrict its imports of good X to 900 units per month, which is a reduction from the current quantity of imports. Assume that A also produces good X domestically. In this context, illustrate and explain why the following statement is either True or False.
"The reduction in imports to 900 units per month will have identical effects on product price in A, quantity produced in A, and welfare in A whether the reduction is accomplished by the imposition of an import tariff by country A or by country A's officials persuading foreign governments to 'voluntarily' restrict their exports to A to 900 units per month."
(b) Suppose that country A wishes to expand its home production of good Y (as well as Imployment in country A's Y industry) by 10 percent, and country A is an importer of good Y.In this context, illustrate and explain why the following statement is either True or False.
"The 10 percent increase in home output and employment in the Y industry will be associated with identical effects on product price,quantity of imports of good Y, and welfare in country A whether the 10 percent increase is accomplished by the imposition of an import tariff or by the granting of a subsidy for production and employment to home producers of good Y."
"The reduction in imports to 900 units per month will have identical effects on product price in A, quantity produced in A, and welfare in A whether the reduction is accomplished by the imposition of an import tariff by country A or by country A's officials persuading foreign governments to 'voluntarily' restrict their exports to A to 900 units per month."
(b) Suppose that country A wishes to expand its home production of good Y (as well as Imployment in country A's Y industry) by 10 percent, and country A is an importer of good Y.In this context, illustrate and explain why the following statement is either True or False.
"The 10 percent increase in home output and employment in the Y industry will be associated with identical effects on product price,quantity of imports of good Y, and welfare in country A whether the 10 percent increase is accomplished by the imposition of an import tariff or by the granting of a subsidy for production and employment to home producers of good Y."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Explain, using offer curves, how a tariff affects a large country in the context of general equilibrium. Can a tariff improve the welfare in the tariff-imposing country if both sets of offer curves are elastic in the relevant ranges? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the large-country case, an export tax
A) leads to an increase in the price of the good in the importing country.
B) leads to no change in the price of the good in the importing country.
C) is absorbed totally by the exporting country.
D) increases consumer welfare in both the exporting and the importing country.
A) leads to an increase in the price of the good in the importing country.
B) leads to no change in the price of the good in the importing country.
C) is absorbed totally by the exporting country.
D) increases consumer welfare in both the exporting and the importing country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Given the information on prices, production, and consumption in Question #15 above, and assuming that demand and supply curves are straight lines, what is the gain in producer surplus in country B that occurs because of the imposition of the tariff?
A) $56
B) $140
C) $348
D) $376
A) $56
B) $140
C) $348
D) $376

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
How would an export quota by a home country look in the offer curve diagram? How would a subsequent increase in foreign demand for the export affect the exporting country's terms of trade and quantity of exports?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
For each of the three statements below, illustrate and explain why the statement is either True or False.
(a) "Other things equal, the imposition of a tariff by a (small) country on an imported good will have a less negative net welfare effect on the country than would the use of a'voluntary' export restraint (VER) by supplying countries of the import, even if the effects on domestic price and the quantity of the good imported are the same in the two situations."
(b) "Other things equal, if a country imposes an export tax of a given amount on a good,then the country can potentially enhance its welfare if it is a 'small' country but cannot possibly enhance its welfare if it is a 'large' country."
(c) "Other things equal, if a (small) country elects to assist an import-competing industry in expanding the industry's output by a given amount, the net welfare effect on the country will be the same whether or not the assistance is given in the form of an import tariff or in the form of a production subsidy to the industry."
(a) "Other things equal, the imposition of a tariff by a (small) country on an imported good will have a less negative net welfare effect on the country than would the use of a'voluntary' export restraint (VER) by supplying countries of the import, even if the effects on domestic price and the quantity of the good imported are the same in the two situations."
(b) "Other things equal, if a country imposes an export tax of a given amount on a good,then the country can potentially enhance its welfare if it is a 'small' country but cannot possibly enhance its welfare if it is a 'large' country."
(c) "Other things equal, if a (small) country elects to assist an import-competing industry in expanding the industry's output by a given amount, the net welfare effect on the country will be the same whether or not the assistance is given in the form of an import tariff or in the form of a production subsidy to the industry."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Given the following information pertaining to large country A with respect to good X Under free trade and with a tariff in place:
What is the impact of the tariff upon country A's welfare?
A) loss of $15.
B) loss of $45.
C) gain of $15.
D) gain of $60
What is the impact of the tariff upon country A's welfare?
A) loss of $15.
B) loss of $45.
C) gain of $15.
D) gain of $60

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Given the following information for (small) country A concerning a good X:
A) The government revenue generated by the tariff is $800.
B) The decrease in consumer surplus because of the tariff is $4,000.
C) The increase in producer surplus because of the tariff is $3,200.
D) The net welfare loss for A from the tariff is $600.
A) The government revenue generated by the tariff is $800.
B) The decrease in consumer surplus because of the tariff is $4,000.
C) The increase in producer surplus because of the tariff is $3,200.
D) The net welfare loss for A from the tariff is $600.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Other things equal, a larger share of a tariff is more likely to be "paid" by the foreign exporting country B rather than the domestic importing country A if
A) the supply curve of B's producers is very inelastic.
B) the supply curve of A's producers is very inelastic.
C) the demand curve of B's consumers is very elastic.
D) the demand curve of A's consumers is very inelastic.
A) the supply curve of B's producers is very inelastic.
B) the supply curve of A's producers is very inelastic.
C) the demand curve of B's consumers is very elastic.
D) the demand curve of A's consumers is very inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the general equilibrium graph with a production-possibilities frontier (PPF) and consumer indifference curves,
A) a tariff has the same welfare impact as a subsidy to the import-competing industry (provided domestic production is the same with each alternative instrument).
B) a tariff reduces both real income and the gains from exchange.
C) a tariff reduces consumer welfare only if the tariff is a prohibitive tariff (i.e., Eliminates all imports).
D) protection shifts the PPF outward but reduces consumer welfare.
A) a tariff has the same welfare impact as a subsidy to the import-competing industry (provided domestic production is the same with each alternative instrument).
B) a tariff reduces both real income and the gains from exchange.
C) a tariff reduces consumer welfare only if the tariff is a prohibitive tariff (i.e., Eliminates all imports).
D) protection shifts the PPF outward but reduces consumer welfare.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
In the large country case, the imposition of an import quota
A) will always produce a net loss for the imposing country.
B) can result in a net gain for the importing country if the government employs an Auction quota system to allocate the restricted imports.
C) will produce a net gain for the exporting country.
D) will have no predictable effect on the exporting country.
A) will always produce a net loss for the imposing country.
B) can result in a net gain for the importing country if the government employs an Auction quota system to allocate the restricted imports.
C) will produce a net gain for the exporting country.
D) will have no predictable effect on the exporting country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In the case of nonhomogeneous goods, the imposition of an import tariff
A) produces a transfer from consumers to producers in the domestic market.
B) taxes the domestic product as well as the import product.
C) has no impact on the price of the domestic substitute.
D) results in deadweight losses in both the domestic market and the import market.
A) produces a transfer from consumers to producers in the domestic market.
B) taxes the domestic product as well as the import product.
C) has no impact on the price of the domestic substitute.
D) results in deadweight losses in both the domestic market and the import market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Given the following diagram showing country A's demand for imports schedule for good (Dimports), the supply of exports schedule to A from the rest of the world of good X (SROW), and the supply of exports schedule to A from the rest of the world of good X when country A has imposed a specific tariff on imports of good X (S'ROW):
price
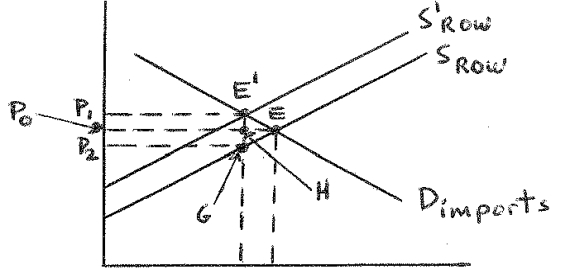
quantity
A) The total tariff revenue collected by country A is indicated by the rectangle P0P1E'H.
B) Distance OP2 indicates the net price received by the foreign suppliers after payment of the tariff.
C) The loss of consumer surplus in country A because of the imposition of the tariff is
indicated by rectangle P2P0HG.
D) Country A is a "small" country.
price

quantity
A) The total tariff revenue collected by country A is indicated by the rectangle P0P1E'H.
B) Distance OP2 indicates the net price received by the foreign suppliers after payment of the tariff.
C) The loss of consumer surplus in country A because of the imposition of the tariff is
indicated by rectangle P2P0HG.
D) Country A is a "small" country.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The imposition of an export tax by a home country will lead to __________ in home Country consumer surplus and will __________ in home country producer surplus.
A) a decrease; also lead to a decrease
B) a decrease; lead to an increase
C) an increase; lead to a decrease
D) an increase; also lead to an increase
A) a decrease; also lead to a decrease
B) a decrease; lead to an increase
C) an increase; lead to a decrease
D) an increase; also lead to an increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Other things equal, a country's consumers' "demand for imports" schedule for a good Tends to be __________ than the country's consumers' overall demand schedule for the Good. In addition, other things equal, a country's producers' "supply of exports" Schedule of a good tends to be __________ than the country's producers' overall supply
Schedule of the good.
A) more elastic; more elastic
B) more elastic; less elastic
C) less elastic; more elastic
D) less elastic; less elastic
Schedule of the good.
A) more elastic; more elastic
B) more elastic; less elastic
C) less elastic; more elastic
D) less elastic; less elastic

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The imposition of an export tax on good X by country A, other things equal,
A) will improve the terms of trade of country A if A is a "small" country.
B) will lead to a lower price of good X in country A's home market if A is a "large" Country but will not affect the price of good X in A's home market if A is a "small" country.
C) will always lead to an improvement in country A's welfare if A is a "large" country.
D) will lead to an increase in consumer surplus in country A.
A) will improve the terms of trade of country A if A is a "small" country.
B) will lead to a lower price of good X in country A's home market if A is a "large" Country but will not affect the price of good X in A's home market if A is a "small" country.
C) will always lead to an improvement in country A's welfare if A is a "large" country.
D) will lead to an increase in consumer surplus in country A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Given the following information pertaining to large country A with respect to good X Under free trade and with a tariff in place:
What is the loss of consumer surplus in country A that occurs because of the imposition of the tariff?
A) $45
B) $150
C) $270
D). $300
What is the loss of consumer surplus in country A that occurs because of the imposition of the tariff?
A) $45
B) $150
C) $270
D). $300

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In Question #26 above, country A
A) can never improve its welfare by the imposition of this tariff.
B) gains welfare from the imposition of this tariff if the area of triangle GHE is larger Than the area of rectangle P0P1E'H.
C) gains welfare from the imposition of this tariff if the area of rectangle P2P0HG is larger Than the area of triangle HE'E.
D) gains welfare if the area of rectangle P0P1E'H is larger than the area of rectangle P2P0HG.
A) can never improve its welfare by the imposition of this tariff.
B) gains welfare from the imposition of this tariff if the area of triangle GHE is larger Than the area of rectangle P0P1E'H.
C) gains welfare from the imposition of this tariff if the area of rectangle P2P0HG is larger Than the area of triangle HE'E.
D) gains welfare if the area of rectangle P0P1E'H is larger than the area of rectangle P2P0HG.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If a small country produces 100 units of product X and consumes 140 units at a price of $2 under free trade, but the imposition of a tariff leads to a situation where domestic price is $2.20, domestic production is 120 units, and domestic consumption is 125 units, then the gain in producer surplus in this country because of the tariff is __________.
A) $1.00
B) $22.00
C) $24.00
D) $26.50
A) $1.00
B) $22.00
C) $24.00
D) $26.50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If a (large) country B puts an export tax on a good, and assuming that world demand for The export from B is not perfectly inelastic, then, because of the tax, the price of the good In country B will __________ and the price of the good on the world market __________.
A) increase; also will increase
B) increase; will decrease
C) decrease; will increase
D) decrease; also will decrease
A) increase; also will increase
B) increase; will decrease
C) decrease; will increase
D) decrease; also will decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The presence of an export subsidy (assuming that foreign demand is not perfectly-Inelastic)
A) will increase the price of the export good in the home market and decrease the well-Being of home consumers.
B) will decrease the price of the export good in the home market and increase the well-Being of home consumers.
C) will lead to a net gain in welfare in the home country since producer surplus is Enhanced.
D) can lead to a higher import price in the importing country in the large-country case.
A) will increase the price of the export good in the home market and decrease the well-Being of home consumers.
B) will decrease the price of the export good in the home market and increase the well-Being of home consumers.
C) will lead to a net gain in welfare in the home country since producer surplus is Enhanced.
D) can lead to a higher import price in the importing country in the large-country case.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In the following offer curve diagram, OCA is the free-trade offer curve of country A, OCB is the free-trade offer curve of country B, and OC'A (which starts at the origin O, goes to point M and then comes back horizontally to point Y') is the offer curve of country A when it has a restrictive trade policy instrument in place (while country B continues with free trade). In this situation, the restrictive instrument that country A has employed is __________, and the resulting equilibrium position E' is __________ equilibrium position.
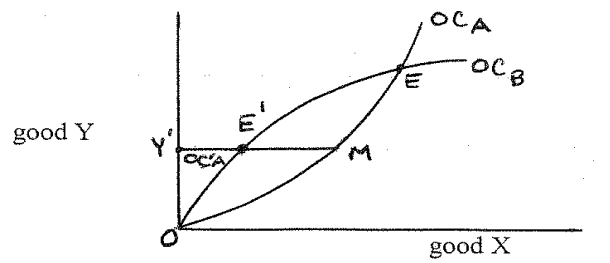
A) a "voluntary" export restraint (VER) on its exports to country B; an unstable
B) a "voluntary" export restraint (VER) on its exports to country B; a stable
C) an import quota; an unstable
D) an import quota; a stable

A) a "voluntary" export restraint (VER) on its exports to country B; an unstable
B) a "voluntary" export restraint (VER) on its exports to country B; a stable
C) an import quota; an unstable
D) an import quota; a stable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



