Deck 6: Macroeconomics: the Big Picture
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/128
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: Macroeconomics: the Big Picture
1
A rubber-necking traffic jam an example of:
A) microeconomics in action.
B) individual behavior that has a large aggregate impact.
C) the paradox of thrift.
D) an outcome smaller than the sum of its parts.
A) microeconomics in action.
B) individual behavior that has a large aggregate impact.
C) the paradox of thrift.
D) an outcome smaller than the sum of its parts.
individual behavior that has a large aggregate impact.
2
The topics studied in macroeconomics include:
A) inflation.
B) monopolies.
C) spillovers, such as pollution.
D) mergers.
A) inflation.
B) monopolies.
C) spillovers, such as pollution.
D) mergers.
inflation.
3
Which is a microeconomic question, rather than a macroeconomic question?
A) Will a decrease in the income tax rate lift the nation out of a recession?
B) Will an increase in consumer spending cause inflation?
C) Will a decrease in the income tax rate lead to a government budget deficit?
D) Will an increase in the cigarette tax reduce the number of packs sold?
A) Will a decrease in the income tax rate lift the nation out of a recession?
B) Will an increase in consumer spending cause inflation?
C) Will a decrease in the income tax rate lead to a government budget deficit?
D) Will an increase in the cigarette tax reduce the number of packs sold?
Will an increase in the cigarette tax reduce the number of packs sold?
4
Macroeconomics focuses on:
A) the economy as a whole.
B) individual decisions.
C) wages.
D) the allocation of scarce resources.
A) the economy as a whole.
B) individual decisions.
C) wages.
D) the allocation of scarce resources.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Macroeconomics entails the study of the:
A) overall behavior of the economy.
B) individual decision makers.
C) market structures.
D) cost and production decisions by firms.
A) overall behavior of the economy.
B) individual decision makers.
C) market structures.
D) cost and production decisions by firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the paradox of thrift:
A) firms that are pessimistic about the future lay off the most saving-conscientious workers.
B) when families and business are feeling pessimistic about the future, they spend more.
C) increased saving by individuals increases their chances of becoming unemployed.
D) risky behavior during economic tough times has large negative consequences for society.
A) firms that are pessimistic about the future lay off the most saving-conscientious workers.
B) when families and business are feeling pessimistic about the future, they spend more.
C) increased saving by individuals increases their chances of becoming unemployed.
D) risky behavior during economic tough times has large negative consequences for society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
How the actions of individuals and firms interact to produce a particular economy-wide level of performance is the focus of:
A) macroeconomics.
B) fiscal policy.
C) monetary policy.
D) microeconomics.
A) macroeconomics.
B) fiscal policy.
C) monetary policy.
D) microeconomics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Choose the best answer. The topics studied in macroeconomics include:
A) inflation.
B) unemployment.
C) economic growth.
D) inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.
A) inflation.
B) unemployment.
C) economic growth.
D) inflation, unemployment, and economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A key insight into macroeconomics is that in the short run the combined effect of individual decisions:
A) is always the same as what one individual intended.
B) may be very different from what any one individual intended.
C) is always beneficial to the economy as a whole.
D) is always detrimental to the economy as a whole.
A) is always the same as what one individual intended.
B) may be very different from what any one individual intended.
C) is always beneficial to the economy as a whole.
D) is always detrimental to the economy as a whole.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The concept that the whole is greater than the sum of its parts best characterizes:
A) microeconomics.
B) supply and demand.
C) macroeconomics.
D) business forecasting.
A) microeconomics.
B) supply and demand.
C) macroeconomics.
D) business forecasting.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which question is the MOST appropriate to the study of MICROECONOMICS?
A) How does the aggregate price level affect consumer spending?
B) How does the level of interest rates affect investment spending?
C) How much will Sony charge for the new game system to be introduced later this year?
D) How does the GDP affect overall government spending?
A) How does the aggregate price level affect consumer spending?
B) How does the level of interest rates affect investment spending?
C) How much will Sony charge for the new game system to be introduced later this year?
D) How does the GDP affect overall government spending?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In contrast to the conclusions drawn from microeconomics, many economists argue that in macroeconomics, government:
A) control of rent prices increases overall economic activity.
B) intervention in markets usually leaves society as a whole worse off.
C) taxation of goods and services does not cause a deadweight loss of economic welfare.
D) intervention in markets can prevent or reduce the effects of adverse events on the macroeconomy.
A) control of rent prices increases overall economic activity.
B) intervention in markets usually leaves society as a whole worse off.
C) taxation of goods and services does not cause a deadweight loss of economic welfare.
D) intervention in markets can prevent or reduce the effects of adverse events on the macroeconomy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Promotion of employment and growth in the economy as a whole is the focus of:
A) macroeconomics.
B) fiscal policy.
C) monetary policy.
D) microeconomics.
A) macroeconomics.
B) fiscal policy.
C) monetary policy.
D) microeconomics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which is MOST likely a macroeconomic, not microeconomic, question?
A) Is the national unemployment rate rising or falling?
B) Are consumers buying more bottled water and less fruit juice?
C) Are salaries for nurses rising or falling?
D) Should a tax be levied on each ton of carbon dioxide a factory emits?
A) Is the national unemployment rate rising or falling?
B) Are consumers buying more bottled water and less fruit juice?
C) Are salaries for nurses rising or falling?
D) Should a tax be levied on each ton of carbon dioxide a factory emits?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What do a rubber-necking traffic jam and the paradox of thrift have in common?
A) Individual behavior has large negative consequences for the whole of society.
B) Seemingly bad behavior ends up harming everyone.
C) Seemingly careless behavior leads to good times for all.
D) Government intervention can only make matters worse.
A) Individual behavior has large negative consequences for the whole of society.
B) Seemingly bad behavior ends up harming everyone.
C) Seemingly careless behavior leads to good times for all.
D) Government intervention can only make matters worse.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If all of the households and businesses start saving more during economic hard times, then aggregate income will fall, hurting everyone in the economy. This is known as the:
A) quantity theory.
B) crowding-out theory.
C) paradox of thrift.
D) permanent income hypothesis.
A) quantity theory.
B) crowding-out theory.
C) paradox of thrift.
D) permanent income hypothesis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Which would NOT be classified as a MACROECONOMIC question?
A) How many people are employed in the economy as a whole?
B) What determines the overall level of prices?
C) What determines the overall trade in goods, services, and financial assets between the United States and the rest of the world?
D) What determines a university's cost of offering a new course?
A) How many people are employed in the economy as a whole?
B) What determines the overall level of prices?
C) What determines the overall trade in goods, services, and financial assets between the United States and the rest of the world?
D) What determines a university's cost of offering a new course?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which would most likely be a MICROECONOMIC question?
A) Should I go to business school or take a job?
B) What determines the overall salary levels paid to workers in a given year?
C) What government policies should be adopted to promote full employment and growth?
D) What determines the level of output for the economy as whole?
A) Should I go to business school or take a job?
B) What determines the overall salary levels paid to workers in a given year?
C) What government policies should be adopted to promote full employment and growth?
D) What determines the level of output for the economy as whole?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which question is the MOST appropriate to the study of MACROECONOMICS?
A) How does the aggregate price level affect overall consumer spending?
B) How does the level of interest rates affect Delta's decision to buy a new airplane?
C) How much will Sony charge for the new game system to be introduced later this year?
D) What determines whether Wachovia opens a new office in Beijing?
A) How does the aggregate price level affect overall consumer spending?
B) How does the level of interest rates affect Delta's decision to buy a new airplane?
C) How much will Sony charge for the new game system to be introduced later this year?
D) What determines whether Wachovia opens a new office in Beijing?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The topics studied in macroeconomics include:
A) the price of a motorcycle.
B) the wages of engineers.
C) the general price level in the economy.
D) how much ice cream consumers buy.
A) the price of a motorcycle.
B) the wages of engineers.
C) the general price level in the economy.
D) how much ice cream consumers buy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In 1936 economic theory changed dramatically with the publication of:
A) The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money, by John Maynard Keynes.
B) The Wealth of Nations, by Adam Smith.
C) The Road to Serfdom, by F. A. Hayek.
D) Principles of Economics, by Paul Samuelson.
A) The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money, by John Maynard Keynes.
B) The Wealth of Nations, by Adam Smith.
C) The Road to Serfdom, by F. A. Hayek.
D) Principles of Economics, by Paul Samuelson.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The modern macroeconomic tools used by the government are _____ policy and _____ policy.
A) tax; antitrust
B) fiscal; monetary
C) monetary; exchange rate
D) capital; labor
A) tax; antitrust
B) fiscal; monetary
C) monetary; exchange rate
D) capital; labor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Use of fiscal policy involves changes in:
A) interest rates.
B) government spending.
C) the quantity of money.
D) the quantity of money and interest rates.
A) interest rates.
B) government spending.
C) the quantity of money.
D) the quantity of money and interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Fiscal policy attempts to affect the overall level of spending through:
A) changes in the inflation rate.
B) changes in the quantity of money or the interest rate.
C) changes in tax policy or government spending.
D) discretionary regulation of profits and wages.
A) changes in the inflation rate.
B) changes in the quantity of money or the interest rate.
C) changes in tax policy or government spending.
D) discretionary regulation of profits and wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If macroeconomic policy has been successful over time, it is likely that the economy has NOT seen:
A) any inflation.
B) any severe recessions.
C) any unemployment.
D) a business cycle.
A) any inflation.
B) any severe recessions.
C) any unemployment.
D) a business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Among the tools available to macroeconomic policy makers is:
A) fiscal policy, for use in manipulating government spending and taxation.
B) antitrust policy, to break up monopolies.
C) environmental policy, to clean up the economy.
D) improving standards for food and drugs.
A) fiscal policy, for use in manipulating government spending and taxation.
B) antitrust policy, to break up monopolies.
C) environmental policy, to clean up the economy.
D) improving standards for food and drugs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The economist whose writings in the 1930s argued that the cause of an economic depression is inadequate spending was:
A) Herbert Hoover.
B) John Maynard Keynes.
C) Andrew Mellon.
D) Joseph Schumpeter.
A) Herbert Hoover.
B) John Maynard Keynes.
C) Andrew Mellon.
D) Joseph Schumpeter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Fiscal policy attempts to affect the level of overall spending by making changes in:
A) the interest rate.
B) the money supply.
C) banking regulations.
D) taxes and spending.
A) the interest rate.
B) the money supply.
C) banking regulations.
D) taxes and spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Monetary policy attempts to affect the overall level of spending through:
A) changes in the inflation rate.
B) changes in the quantity of money and the interest rate.
C) changes in tax policy or government spending.
D) discretionary regulation of profits and wages.
A) changes in the inflation rate.
B) changes in the quantity of money and the interest rate.
C) changes in tax policy or government spending.
D) discretionary regulation of profits and wages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The onset of the Great Depression:
A) was not a shock to anyone, since most economists predicted the Roaring Twenties were bound to end in disaster.
B) caused a disagreement between the Hoover administration and conventional economists because Hoover wanted the government to intervene much more quickly than most others.
C) came as a considerable shock to the conventional wisdom of economics at that time and opened the door for critiques of mainstream thought by economists like John Maynard Keynes.
D) was in 1918 at the end of World War I.
A) was not a shock to anyone, since most economists predicted the Roaring Twenties were bound to end in disaster.
B) caused a disagreement between the Hoover administration and conventional economists because Hoover wanted the government to intervene much more quickly than most others.
C) came as a considerable shock to the conventional wisdom of economics at that time and opened the door for critiques of mainstream thought by economists like John Maynard Keynes.
D) was in 1918 at the end of World War I.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Changing the level of government spending is an example of _____ policy.
A) fiscal
B) interest rate
C) monetary
D) exchange rate
A) fiscal
B) interest rate
C) monetary
D) exchange rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When the Great Depression reached its trough in 1933, the unemployment rate was approximately _____%.
A) 5
B) 10
C) 25
D) 50
A) 5
B) 10
C) 25
D) 50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The central mission of modern macroeconomics is to prevent:
A) shortages.
B) surpluses.
C) high gas prices.
D) a deep recession like the Great Depression.
A) shortages.
B) surpluses.
C) high gas prices.
D) a deep recession like the Great Depression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Changing interest rates is an example of _____ policy.
A) fiscal
B) tax
C) monetary
D) exchange rate
A) fiscal
B) tax
C) monetary
D) exchange rate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The view that the government should take an active role in the macroeconomy dates to:
A) the Civil War.
B) World War I.
C) the Great Depression.
D) the Vietnam War.
A) the Civil War.
B) World War I.
C) the Great Depression.
D) the Vietnam War.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
One role of government policy is to:
A) provide insurance to cover damages from macroeconomic fluctuations.
B) attempt to manage short-run macroeconomic fluctuations.
C) subsidize private insurance for businesses to cover harm from macroeconomic fluctuations.
D) avoid Keynesian economics.
A) provide insurance to cover damages from macroeconomic fluctuations.
B) attempt to manage short-run macroeconomic fluctuations.
C) subsidize private insurance for businesses to cover harm from macroeconomic fluctuations.
D) avoid Keynesian economics.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which two types of policy are considered to be macroeconomic?
A) monetary and fiscal policy
B) monetary and regulation policy
C) fiscal and regulation policy
D) fiscal policy and price controls
A) monetary and fiscal policy
B) monetary and regulation policy
C) fiscal and regulation policy
D) fiscal policy and price controls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Use of monetary policy entails changes in:
A) government spending.
B) tax receipts.
C) the quantity of money.
D) tax rates.
A) government spending.
B) tax receipts.
C) the quantity of money.
D) tax rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Fiscal policy refers to changes in _____ to affect overall spending in the economy:
A) interest rates
B) government spending and taxation
C) the quantity of money
D) interest rates and of government spending
A) interest rates
B) government spending and taxation
C) the quantity of money
D) interest rates and of government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Monetary policy attempts to affect the overall level of spending by making changes in:
A) taxes.
B) taxes and spending.
C) taxes and interest rates.
D) interest rates and the quantity of money.
A) taxes.
B) taxes and spending.
C) taxes and interest rates.
D) interest rates and the quantity of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The switching between recessions and expansions is known as the:
A) unemployment rate.
B) long-run economic growth.
C) business cycle.
D) macroeconomy.
A) unemployment rate.
B) long-run economic growth.
C) business cycle.
D) macroeconomy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The short-run alternation between economic downturns and recessions, then economic upturns and expansions is known as the _____ cycle.
A) business
B) contractionary
C) expansionary
D) disequilibrium
A) business
B) contractionary
C) expansionary
D) disequilibrium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Recessions are periods when:
A) output rises.
B) the aggregate price level rises.
C) the unemployment rate is falling.
D) output and employment are falling in many industries.
A) output rises.
B) the aggregate price level rises.
C) the unemployment rate is falling.
D) output and employment are falling in many industries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In a typical business cycle, the trough is immediately followed by the:
A) peak.
B) recession.
C) depression.
D) expansion.
A) peak.
B) recession.
C) depression.
D) expansion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In a typical business cycle, the peak is immediately followed by the:
A) recession.
B) trough.
C) expansion.
D) depression.
A) recession.
B) trough.
C) expansion.
D) depression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A business cycle is a:
A) very deep and prolonged economic downturn.
B) period in which output and employment are rising.
C) period in which output and employment are falling.
D) short-run shift between economic upturns and downturns.
A) very deep and prolonged economic downturn.
B) period in which output and employment are rising.
C) period in which output and employment are falling.
D) short-run shift between economic upturns and downturns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Keynesian economics stressed:
A) the importance of total spending.
B) the self-correcting power of free markets.
C) the long run.
D) that the Depression should run its course to bring down the high cost of living.
A) the importance of total spending.
B) the self-correcting power of free markets.
C) the long run.
D) that the Depression should run its course to bring down the high cost of living.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money was written by:
A) Robert Lucas.
B) David Ricardo.
C) John Maynard Keynes.
D) Thomas Malthus.
A) Robert Lucas.
B) David Ricardo.
C) John Maynard Keynes.
D) Thomas Malthus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For the past several months, per capita output has increased at a slower and slower rate. Over the same period, the unemployment rate has been falling, but it appears that both have leveled off. Where in the business cycle is the economy?
A) peak
B) recession
C) trough
D) expansion
A) peak
B) recession
C) trough
D) expansion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money, written by _____ and published in _____, transformed the way economists thought about macroeconomics.
A) Milton Friedman; 1946
B) Paul Samuelson; 1940
C) John Maynard Keynes; 1936
D) Paul Lucas; 1966
A) Milton Friedman; 1946
B) Paul Samuelson; 1940
C) John Maynard Keynes; 1936
D) Paul Lucas; 1966

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
John Maynard Keynes believed that the government should:
A) actively try to mitigate the effects of recessions by using fiscal and monetary policies.
B) not interfere with the economy but let the economy self-correct.
C) intervene only when there is a boom but let the recession run its course.
D) not use fiscal and monetary policies, as these policies have long-term adverse effects.
A) actively try to mitigate the effects of recessions by using fiscal and monetary policies.
B) not interfere with the economy but let the economy self-correct.
C) intervene only when there is a boom but let the recession run its course.
D) not use fiscal and monetary policies, as these policies have long-term adverse effects.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Changing government spending and taxes to affect overall spending is use of _____ policy.
A) tax-and-spend
B) monetary
C) fiscal
D) free-trade
A) tax-and-spend
B) monetary
C) fiscal
D) free-trade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An economic expansion in the United States is typically associated with a(n):
A) falling inflation rate.
B) increase in the poverty rate.
C) increase in output.
D) decrease in corporate profits.
A) falling inflation rate.
B) increase in the poverty rate.
C) increase in output.
D) decrease in corporate profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
An expansion is a period in which:
A) output declines.
B) the price level falls.
C) output rises.
D) deflation occurs.
A) output declines.
B) the price level falls.
C) output rises.
D) deflation occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A change in the level of overall spending in the economy due to a change in the interest rate, brought about by a change in the quantity of money, is an example of _____ policy.
A) monetary
B) fiscal
C) free-market
D) trickle-down
A) monetary
B) fiscal
C) free-market
D) trickle-down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Economists have identified several consecutive quarters of falling employment, and forecasts for the next few months suggest more of the same. The economy is at the _____ stage of the business cycle.
A) recession
B) expansion
C) peak
D) trough
A) recession
B) expansion
C) peak
D) trough

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
If during several quarters, the economy is simultaneously increasing its levels of output and employment, then the economy is in a(n):
A) depression.
B) expansion.
C) recession.
D) turning point between a recovery and a downturn.
A) depression.
B) expansion.
C) recession.
D) turning point between a recovery and a downturn.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In recent times, the U.S. government has been trying to help the economy through one of the worst economic slumps ever. The policies used are based on _____ theory.
A) Keynesian
B) classical
C) supply-side
D) trickle-down
A) Keynesian
B) classical
C) supply-side
D) trickle-down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Keynesian economics promotes ideas that:
A) government intervention can be destabilizing.
B) the government can help a depressed economy via fiscal and monetary policies.
C) the private sector is perfectly capable of regulating itself.
D) the free market system will always prevail.
A) government intervention can be destabilizing.
B) the government can help a depressed economy via fiscal and monetary policies.
C) the private sector is perfectly capable of regulating itself.
D) the free market system will always prevail.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Periods in which output and employment are falling in many industries are called:
A) recessions.
B) booms.
C) expansions.
D) deflations.
A) recessions.
B) booms.
C) expansions.
D) deflations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The point at which a recession ends and the expansion begins is called the:
A) trough.
B) downturn.
C) peak.
D) lag.
A) trough.
B) downturn.
C) peak.
D) lag.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The most painful effect of a recession is:
A) inflation.
B) unemployment.
C) money neutrality.
D) liquidity trap.
A) inflation.
B) unemployment.
C) money neutrality.
D) liquidity trap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A country's real gross domestic product (GDP), undergoes periodic fluctuations called a(n):
A) recession.
B) business cycle.
C) expansion.
D) trough.
A) recession.
B) business cycle.
C) expansion.
D) trough.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
In many countries, economists adopt the rule that a recession is a period of at least _____ during which aggregate output falls.
A) one quarter
B) two consecutive quarters
C) three consecutive quarters
D) a full year
A) one quarter
B) two consecutive quarters
C) three consecutive quarters
D) a full year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The trough of the business cycle:
A) comes right after the expansion phase.
B) comes before the recession phase.
C) is a temporary maximum level of real GDP.
D) is a temporary minimum level of real GDP.
A) comes right after the expansion phase.
B) comes before the recession phase.
C) is a temporary maximum level of real GDP.
D) is a temporary minimum level of real GDP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The sequence of business cycle phases is:
A) peak, trough, expansion, recession.
B) peak, expansion, trough, recession.
C) peak, recession, trough, expansion.
D) peak, expansion, recession, trough.
A) peak, trough, expansion, recession.
B) peak, expansion, trough, recession.
C) peak, recession, trough, expansion.
D) peak, expansion, recession, trough.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The most widely used indicator of the conditions in the labor market is the:
A) unemployment rate.
B) population growth rate.
C) inflation rate.
D) trade deficit.
A) unemployment rate.
B) population growth rate.
C) inflation rate.
D) trade deficit.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In the United States, recessions are typically associated with a(n):
A) falling unemployment rate.
B) decrease in the number of people living in poverty.
C) decrease in the percentage of Americans with health insurance.
D) increase in corporate profits.
A) falling unemployment rate.
B) decrease in the number of people living in poverty.
C) decrease in the percentage of Americans with health insurance.
D) increase in corporate profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A recession does NOT lead to:
A) higher unemployment.
B) reduced output.
C) reduced income and living standards.
D) higher employment.
A) higher unemployment.
B) reduced output.
C) reduced income and living standards.
D) higher employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the following to answer questions: 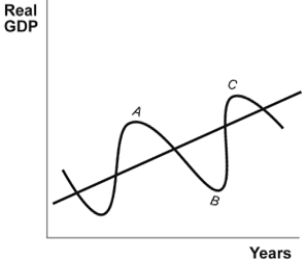
(Figure: The Business Cycle) The movement from point B to C is called a(n):
A) trough.
B) expansion.
C) depression.
D) peak.

(Figure: The Business Cycle) The movement from point B to C is called a(n):
A) trough.
B) expansion.
C) depression.
D) peak.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A period of rising real GDP is a(n)_______in the business cycle:
A) peak.
B) trough.
C) expansion.
D) recession.
A) peak.
B) trough.
C) expansion.
D) recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Rising total output accompanied by increasing employment is generally known as a(n):
A) stagflation.
B) recession.
C) inflation.
D) expansion.
A) stagflation.
B) recession.
C) inflation.
D) expansion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The point on a business cycle when real GDP stops rising and begins falling is a(n):
A) peak.
B) trough.
C) expansion.
D) recession.
A) peak.
B) trough.
C) expansion.
D) recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Use the following to answer questions: 
(Figure: The Business Cycle) Point B on this graph shows a(n):
A) peak.
B) trough.
C) expansion.
D) recession.

(Figure: The Business Cycle) Point B on this graph shows a(n):
A) peak.
B) trough.
C) expansion.
D) recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The most painful consequence of a recession is:
A) rising unemployment.
B) increasing inflation.
C) increasing aggregate output.
D) higher interest rates.
A) rising unemployment.
B) increasing inflation.
C) increasing aggregate output.
D) higher interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A pattern of expansion, then recession, then expansion again is a(n):
A) annual trend.
B) secular trend.
C) business cycle.
D) consumer cycle.
A) annual trend.
B) secular trend.
C) business cycle.
D) consumer cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Choose the best answer. The purpose of macroeconomic policy is to:
A) bring unemployment closer to the natural rate.
B) reduce the severity of recessions.
C) rein in excessively strong expansions.
D) bring unemployment closer to the natural rate, rein in excessively strong expansions, and reduce the severity of recessions.
A) bring unemployment closer to the natural rate.
B) reduce the severity of recessions.
C) rein in excessively strong expansions.
D) bring unemployment closer to the natural rate, rein in excessively strong expansions, and reduce the severity of recessions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The point on a business cycle when real GDP stops falling and begins rising is a(n):
A) peak.
B) expansion.
C) trough.
D) recession.
A) peak.
B) expansion.
C) trough.
D) recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A period of falling real GDP is a(n)________ in the business cycle:
A) peak.
B) trough.
C) expansion.
D) recession.
A) peak.
B) trough.
C) expansion.
D) recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An independent panel of economic experts at the _____ analyzes the macroeconomy and determines when recessions begin and end.
A) Bureau of the Census
B) President's Council of Economic Advisers
C) Treasury Department
D) National Bureau of Economic Research
A) Bureau of the Census
B) President's Council of Economic Advisers
C) Treasury Department
D) National Bureau of Economic Research

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 128 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



