Deck 17: Macroeconomics: Events and Ideas
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/283
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Macroeconomics: Events and Ideas
1
The predominant economic thinking up to the 1930s was:
A) monetarism.
B) classical economics.
C) Keynesian economics.
D) rational expectations theory.
A) monetarism.
B) classical economics.
C) Keynesian economics.
D) rational expectations theory.
classical economics.
2
Prior to the 1930s, the _____ model dominated thinking about how the economy worked.
A) Keynesian
B) classical
C) monetarist
D) real business cycle
A) Keynesian
B) classical
C) monetarist
D) real business cycle
classical
3
Which year is often described as the worst year of the Great Depression?
A) 1913
B) 1933
C) 1953
D) 1973
A) 1913
B) 1933
C) 1953
D) 1973
1933
4
In the classical model, an increase in the money supply will result in:
A) inflation only, without affecting aggregate output.
B) economic expansion, as aggregate output will increase.
C) higher interest rates, lower investment, and ultimately lower aggregate output.
D) recession only, without affecting the aggregate price level.
A) inflation only, without affecting aggregate output.
B) economic expansion, as aggregate output will increase.
C) higher interest rates, lower investment, and ultimately lower aggregate output.
D) recession only, without affecting the aggregate price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Adam believes that in the long run all prices are flexible and that any increase in the money supply will lead only to inflation, not to an increase in aggregate output. Because the economy would self-correct to long-run equilibrium output, there is no role for either fiscal or monetary policy. Adam is best described as a:
A) supply-sider.
B) Keynesian.
C) classical economist.
D) monetarist.
A) supply-sider.
B) Keynesian.
C) classical economist.
D) monetarist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In response to the Great Depression, the classical economists:
A) stressed the use of monetary policy over fiscal policy.
B) tried to tame the "animal spirits" that caused the recession in the first place.
C) stressed the use of fiscal policy over monetary policy.
D) did not advocate any action because of the lack of consensus about the consequences of policy.
A) stressed the use of monetary policy over fiscal policy.
B) tried to tame the "animal spirits" that caused the recession in the first place.
C) stressed the use of fiscal policy over monetary policy.
D) did not advocate any action because of the lack of consensus about the consequences of policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
According to the classical model:
A) the aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
B) increases in the money supply lead to proportional increases in the price level but not to change in real output.
C) increases in the money supply lead to proportional changes in output but no change in the price level.
D) we are all dead in the long run.
A) the aggregate supply curve is horizontal.
B) increases in the money supply lead to proportional increases in the price level but not to change in real output.
C) increases in the money supply lead to proportional changes in output but no change in the price level.
D) we are all dead in the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When other things are equal and using the classical model, an increase in the money supply leads to an equal proportional _____ in the aggregate _____, with no effect on aggregate _____.
A) rise; output; price level
B) fall; price level; output
C) rise; price level; output
D) fall; output; price level
A) rise; output; price level
B) fall; price level; output
C) rise; price level; output
D) fall; output; price level

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The classical school of economics:
A) emphasizes the short run.
B) emphasizes the flexibility of wages and prices.
C) has a problem with potential output, since potential output cannot be achieved without active policy.
D) advocates the use of discretionary fiscal policy.
A) emphasizes the short run.
B) emphasizes the flexibility of wages and prices.
C) has a problem with potential output, since potential output cannot be achieved without active policy.
D) advocates the use of discretionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If wages and prices are perfectly flexible, a decrease in aggregate demand will cause a(n) _____ in the price level and _____ in unemployment.
A) increase; an increase
B) decrease; a decrease
C) increase; no change
D) decrease; no change
A) increase; an increase
B) decrease; a decrease
C) increase; no change
D) decrease; no change

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
According to the classical model of the price level, the short-run aggregate supply curve is:
A) flat.
B) negatively sloped.
C) vertical.
D) unstable.
A) flat.
B) negatively sloped.
C) vertical.
D) unstable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Classical macroeconomics was based largely on the foundation of:
A) flexible wages and prices.
B) persistent unemployment.
C) government intervention in the market.
D) Adam Smith's model of imperfectly competitive markets.
A) flexible wages and prices.
B) persistent unemployment.
C) government intervention in the market.
D) Adam Smith's model of imperfectly competitive markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In the classical model of the price level, prices are _____, the short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical, and as a result, a decrease in the money supply leads to _____ in the aggregate price level.
A) sticky; a more than proportional decrease
B) flexible; a proportional decrease
C) sticky; a more than proportional increase
D) flexible; a proportional increase
A) sticky; a more than proportional decrease
B) flexible; a proportional decrease
C) sticky; a more than proportional increase
D) flexible; a proportional increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Because classical economists stressed the long run, they:
A) perceived the economy as being mostly self-adjusting.
B) favored the use of fiscal policy over monetary policy.
C) expected the government to purge the rot from the system.
D) favored the use of monetary policy over fiscal policy.
A) perceived the economy as being mostly self-adjusting.
B) favored the use of fiscal policy over monetary policy.
C) expected the government to purge the rot from the system.
D) favored the use of monetary policy over fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Policy makers before the Great Depression were:
A) uncertain about the appropriate measure to use against a recession in the absence of any clear theory about the cause of business cycles.
B) using both fiscal and monetary policies to combat the harmful effects of recession on output and employment.
C) against using monetary policies to fight the economic downturns caused by business cycles.
D) in favor of using only fiscal policies to fight the economic booms caused by business cycles.
A) uncertain about the appropriate measure to use against a recession in the absence of any clear theory about the cause of business cycles.
B) using both fiscal and monetary policies to combat the harmful effects of recession on output and employment.
C) against using monetary policies to fight the economic downturns caused by business cycles.
D) in favor of using only fiscal policies to fight the economic booms caused by business cycles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Classical economists focused mainly on:
A) unemployment.
B) the short run.
C) the long run.
D) government economic policy.
A) unemployment.
B) the short run.
C) the long run.
D) government economic policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Classical economists point out that:
A) there is a trade-off between unemployment and inflation.
B) an increase in the money supply leads to a proportional rise in the price level.
C) government spending can affect aggregate demand.
D) there is a possibility of a liquidity trap.
A) there is a trade-off between unemployment and inflation.
B) an increase in the money supply leads to a proportional rise in the price level.
C) government spending can affect aggregate demand.
D) there is a possibility of a liquidity trap.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The school of economics that predominated prior to the Great Depression was the:
A) business cycle theorists.
B) classical school.
C) post-Keynesian school.
D) Marxists.
A) business cycle theorists.
B) classical school.
C) post-Keynesian school.
D) Marxists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
According to the classical model, prices are _____, making the aggregate supply curve _____ in the short run.
A) sticky; upward sloping
B) flexible; vertical
C) flexible; downward sloping
D) sticky; vertical
A) sticky; upward sloping
B) flexible; vertical
C) flexible; downward sloping
D) sticky; vertical

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The measurement of business cycles was pioneered by:
A) Ragnar Frisch.
B) John Maynard Keynes.
C) Wesley Mitchell.
D) Andrew Mellon.
A) Ragnar Frisch.
B) John Maynard Keynes.
C) Wesley Mitchell.
D) Andrew Mellon.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Keynesian economics emphasizes _____ shifts in aggregate _____.
A) long-run; demand
B) long-run; supply
C) short-run; demand
D) short-run; supply
A) long-run; demand
B) long-run; supply
C) short-run; demand
D) short-run; supply

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money was written by:
A) Adam Smith.
B) Paul Samuelson.
C) Joseph Schumpeter.
D) John Maynard Keynes.
A) Adam Smith.
B) Paul Samuelson.
C) Joseph Schumpeter.
D) John Maynard Keynes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
According to some economic historians, the first true modern recession took place in:
A) the United States in 1854.
B) Britain in 1825.
C) Russia in 1860.
D) Japan in 1890.
A) the United States in 1854.
B) Britain in 1825.
C) Russia in 1860.
D) Japan in 1890.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which statement is FALSE? Keynesian economics:
A) emphasizes the effects of shifts in aggregate demand on aggregate output.
B) focuses the attention of economists on situations in which the short-run aggregate supply curve slopes upward.
C) holds "animal spirits" mainly responsible for business cycles.
D) holds that changes in business confidence have no effect on either the aggregate price level or aggregate output.
A) emphasizes the effects of shifts in aggregate demand on aggregate output.
B) focuses the attention of economists on situations in which the short-run aggregate supply curve slopes upward.
C) holds "animal spirits" mainly responsible for business cycles.
D) holds that changes in business confidence have no effect on either the aggregate price level or aggregate output.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which statement is FALSE? At the time of the Great Depression:
A) the measurement of the business cycle was well advanced.
B) there was no widely accepted theory of the causes of depressions.
C) economists recognized that the economy did not always grow smoothly.
D) the U.S. economy was substantially agricultural.
A) the measurement of the business cycle was well advanced.
B) there was no widely accepted theory of the causes of depressions.
C) economists recognized that the economy did not always grow smoothly.
D) the U.S. economy was substantially agricultural.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Keynesian economics emphasized that economic downturns could be due to:
A) inflation.
B) technological shocks.
C) a decline in business confidence.
D) deflation.
A) inflation.
B) technological shocks.
C) a decline in business confidence.
D) deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Classical economists did NOT believe that:
A) there could be temporary periods of unemployment.
B) emphasis should be on the long run, and in the long run all would be set right because of the smooth functioning of the price system.
C) the Great Depression would be a short-run aberration.
D) monetary policy could tame the business cycle.
A) there could be temporary periods of unemployment.
B) emphasis should be on the long run, and in the long run all would be set right because of the smooth functioning of the price system.
C) the Great Depression would be a short-run aberration.
D) monetary policy could tame the business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Use the following to answer questions: 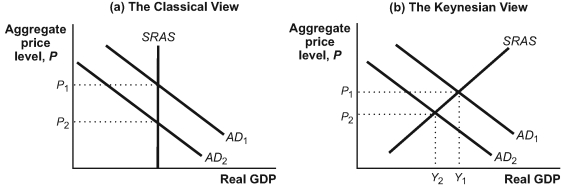
(Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics) Refer to Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics. According to the Keynesian view, if this economy shifts from AD2 to AD1, perhaps because of a large increase in government spending, the price level will _____ and real GDP will _____.
A) rise; fall
B) not change; rise
C) rise; not change
D) rise; rise

(Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics) Refer to Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics. According to the Keynesian view, if this economy shifts from AD2 to AD1, perhaps because of a large increase in government spending, the price level will _____ and real GDP will _____.
A) rise; fall
B) not change; rise
C) rise; not change
D) rise; rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
At the time of the Great Depression, there was:
A) general agreement that monetary policy could help in the short run.
B) no widely accepted theory of the causes of depressions.
C) general agreement that fiscal policy could help in the short run.
D) a consensus about what economic policies to adopt.
A) general agreement that monetary policy could help in the short run.
B) no widely accepted theory of the causes of depressions.
C) general agreement that fiscal policy could help in the short run.
D) a consensus about what economic policies to adopt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The start of an expansion is determined by the:
A) Treasury Department.
B) Federal Reserve.
C) president.
D) National Bureau of Economic Research.
A) Treasury Department.
B) Federal Reserve.
C) president.
D) National Bureau of Economic Research.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Keynes suggested that money is:
A) the most important factor affecting aggregate supply.
B) the most important factor affecting aggregate demand.
C) only one of a variety of factors affecting aggregate supply.
D) only one of a variety of factors affecting aggregate demand.
A) the most important factor affecting aggregate supply.
B) the most important factor affecting aggregate demand.
C) only one of a variety of factors affecting aggregate supply.
D) only one of a variety of factors affecting aggregate demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the Keynesian model, prices and nominal wages are _____, the short-run aggregate supply curve is upward sloping, and as a result, an increase in the money supply leads to _____ in the aggregate price level.
A) sticky; a less than proportional decrease
B) flexible; a proportional decrease
C) sticky; a less than proportional increase
D) flexible; a proportional increase
A) sticky; a less than proportional decrease
B) flexible; a proportional decrease
C) sticky; a less than proportional increase
D) flexible; a proportional increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The _____ has the official role of declaring the beginnings of recessions and expansions.
A) Federal Reserve
B) U.S. Congress
C) National Bureau of Economic Research
D) U.S. president
A) Federal Reserve
B) U.S. Congress
C) National Bureau of Economic Research
D) U.S. president

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
According to Keynesian theory:
A) the long-run and short-run aggregate supply curves are identical.
B) a decrease in aggregate demand leads to decreases in output and prices in the short run.
C) a decrease in aggregate demand will decrease prices but not output in the short run.
D) the short run is relatively unimportant.
A) the long-run and short-run aggregate supply curves are identical.
B) a decrease in aggregate demand leads to decreases in output and prices in the short run.
C) a decrease in aggregate demand will decrease prices but not output in the short run.
D) the short run is relatively unimportant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A fundamental feature of early classical macroeconomics is that:
A) aggregate demand and aggregate income are usually unequal.
B) prices of inputs and outputs are usually relatively rigid.
C) the economy's level of employment can remain substantially below its natural level over a long period.
D) the economy can achieve full employment on its own, though there may be short periods in which employment falls below the natural level.
A) aggregate demand and aggregate income are usually unequal.
B) prices of inputs and outputs are usually relatively rigid.
C) the economy's level of employment can remain substantially below its natural level over a long period.
D) the economy can achieve full employment on its own, though there may be short periods in which employment falls below the natural level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
According to Keynes, changes in "animal spirits" will affect actual output through changes in:
A) business investment spending.
B) government expenditure and taxes.
C) money supply and interest rates.
D) labor productivity and technological progress.
A) business investment spending.
B) government expenditure and taxes.
C) money supply and interest rates.
D) labor productivity and technological progress.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Use the following to answer questions: 
(Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics) Refer to Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics. According to the classical view, if this economy shifts from AD1 to AD2, perhaps because of a large decline in investment spending by businesses, the price level will _____ and real GDP will _____.
A) rise; fall
B) not change; increase
C) fall; not change
D) fall; fall

(Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics) Refer to Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics. According to the classical view, if this economy shifts from AD1 to AD2, perhaps because of a large decline in investment spending by businesses, the price level will _____ and real GDP will _____.
A) rise; fall
B) not change; increase
C) fall; not change
D) fall; fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Use the following to answer questions: 
(Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics) Refer to Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics. According to the Keynesian view, if this economy shifts from AD1 to AD2 because of a large decline in investment spending by businesses, the price level will _____, and real GDP will _____.
A) increase; decrease
B) not change; increase
C) increase; not change
D) decrease; decrease

(Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics) Refer to Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics. According to the Keynesian view, if this economy shifts from AD1 to AD2 because of a large decline in investment spending by businesses, the price level will _____, and real GDP will _____.
A) increase; decrease
B) not change; increase
C) increase; not change
D) decrease; decrease

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The beginning of a recession is declared by the:
A) National Bureau of Economic Research.
B) Treasury Department.
C) Fed.
D) president.
A) National Bureau of Economic Research.
B) Treasury Department.
C) Fed.
D) president.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The economist that warned that any attempt to alleviate the Great Depression with expansionary monetary policy "would, in the end, lead to a collapse worse than the one it was called in to remedy" was:
A) John Maynard Keynes.
B) Milton Friedman.
C) Wesley Mitchel.
D) Joseph Schumpeter.
A) John Maynard Keynes.
B) Milton Friedman.
C) Wesley Mitchel.
D) Joseph Schumpeter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
According to Keynesian economics, a tax cut will _____ aggregate demand and output by _____.
A) increase; decreasing exports
B) decrease; decreasing incentives to work and save
C) increase; increasing income and consumption
D) increase; decreasing government spending
A) increase; decreasing exports
B) decrease; decreasing incentives to work and save
C) increase; increasing income and consumption
D) increase; decreasing government spending

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
During the 1940s, 1950s, and 1960s:
A) the role of the government in the economy increased.
B) the role of the government in the economy decreased.
C) Keynes's ideas were constantly challenged by free-market policies.
D) Keynes's views were accepted only by left-wing socialist economists.
A) the role of the government in the economy increased.
B) the role of the government in the economy decreased.
C) Keynes's ideas were constantly challenged by free-market policies.
D) Keynes's views were accepted only by left-wing socialist economists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The main ideas of Keynesian economics are the importance of the _____ and emphasis on _____.
A) long run over the short run; a vertical SRAS curve
B) long run over the short run; the AD curve and the SRAS curve
C) short run over the long run; the AD curve and a rising SRAS curve
D) free market with no government intervention; monetary policy in the long run
A) long run over the short run; a vertical SRAS curve
B) long run over the short run; the AD curve and the SRAS curve
C) short run over the long run; the AD curve and a rising SRAS curve
D) free market with no government intervention; monetary policy in the long run

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
According to Keynes, the remedy for a recessionary gap was straightforward. The solution was to:
A) increase aggregate supply.
B) increase aggregate demand.
C) control big business.
D) decrease government involvement.
A) increase aggregate supply.
B) increase aggregate demand.
C) control big business.
D) decrease government involvement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Keynesian economics emphasized the:
A) role of money.
B) long run.
C) impact of changes in aggregate demand.
D) impact of changes in aggregate supply.
A) role of money.
B) long run.
C) impact of changes in aggregate demand.
D) impact of changes in aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Macroeconomic policy activism:
A) is the use of political activism made popular by liberal economists.
B) mandates a balanced government budget.
C) is the use of monetary and fiscal policy to smooth out the business cycle.
D) was the tool used by classical economists.
A) is the use of political activism made popular by liberal economists.
B) mandates a balanced government budget.
C) is the use of monetary and fiscal policy to smooth out the business cycle.
D) was the tool used by classical economists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The idea of sticky wages and prices is most closely associated with:
A) monetarism.
B) classical economics.
C) Keynesian economics.
D) rational expectations theory.
A) monetarism.
B) classical economics.
C) Keynesian economics.
D) rational expectations theory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
We now typically refer to the Keynesian term "animal spirits" as:
A) rational expectation.
B) business confidence.
C) adaptive expectation.
D) irrational exuberance.
A) rational expectation.
B) business confidence.
C) adaptive expectation.
D) irrational exuberance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Macroeconomic policy activism:
A) is the use of monetary and fiscal policy to smooth out the business cycle.
B) is the primary theory of classical economics.
C) gives the Federal Reserve the sole responsibility for economic policy.
D) advocates that all of the people in a democracy should decide what type of economic policy is appropriate.
A) is the use of monetary and fiscal policy to smooth out the business cycle.
B) is the primary theory of classical economics.
C) gives the Federal Reserve the sole responsibility for economic policy.
D) advocates that all of the people in a democracy should decide what type of economic policy is appropriate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Keynes believed that wages and prices were sticky. Therefore, a rightward shift of the aggregate demand curve would cause a(n):
A) decrease in the level of income.
B) increase in the unemployment level.
C) change in the long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) increase in employment, production, and income.
A) decrease in the level of income.
B) increase in the unemployment level.
C) change in the long-run aggregate supply curve.
D) increase in employment, production, and income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money is:
A) the first economics textbook of the 1980s.
B) a defense of fiscal policy written by Milton Friedman.
C) an analysis of the Great Depression.
D) an explanation of globalization.
A) the first economics textbook of the 1980s.
B) a defense of fiscal policy written by Milton Friedman.
C) an analysis of the Great Depression.
D) an explanation of globalization.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money, written by _____ and published in _____, transformed the way economists thought about macroeconomics.
A) Milton Friedman; 1946
B) Paul Samuelson; 1940
C) John Maynard Keynes; 1936
D) Paul Lucas; 1966
A) Milton Friedman; 1946
B) Paul Samuelson; 1940
C) John Maynard Keynes; 1936
D) Paul Lucas; 1966

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Keynes believed that to end the Great Depression:
A) only a government takeover of industry could save the economy.
B) the capitalist system needed only a narrow technical fix.
C) a decrease in government spending would increase the budget deficit.
D) a decrease in the money supply would cause inflation.
A) only a government takeover of industry could save the economy.
B) the capitalist system needed only a narrow technical fix.
C) a decrease in government spending would increase the budget deficit.
D) a decrease in the money supply would cause inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use the following to answer questions: 
(Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics) Refer to Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics. According to the classical view, if this economy shifts from AD2 to AD1, perhaps because of a large increase in government spending, the price level will _____ and real GDP will _____.
A) rise; fall
B) rise; not change
C) not change; rise
D) fall; fall

(Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics) Refer to Figure: Classical Versus Keynesian Macroeconomics. According to the classical view, if this economy shifts from AD2 to AD1, perhaps because of a large increase in government spending, the price level will _____ and real GDP will _____.
A) rise; fall
B) rise; not change
C) not change; rise
D) fall; fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Keynesian economics stresses the role of:
A) aggregate demand.
B) aggregate supply.
C) the long run.
D) both aggregate demand and the long run.
A) aggregate demand.
B) aggregate supply.
C) the long run.
D) both aggregate demand and the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Keynes argued that the surest way to bring the economy out of the Great Depression was to:
A) keep the economy in a liquidity trap until antitrust policy could be enforced.
B) use expansionary fiscal policy.
C) increase taxes and spend less.
D) leave the economy alone, and flexible wages and prices would eventually lead to increases in income and employment.
A) keep the economy in a liquidity trap until antitrust policy could be enforced.
B) use expansionary fiscal policy.
C) increase taxes and spend less.
D) leave the economy alone, and flexible wages and prices would eventually lead to increases in income and employment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
According to a Keynesian economist, a recessionary gap should be fixed with:
A) a monetary rule.
B) supply-side tax increases to balance the budget.
C) decreases in government spending.
D) discretionary fiscal policy.
A) a monetary rule.
B) supply-side tax increases to balance the budget.
C) decreases in government spending.
D) discretionary fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which statement is TRUE?
A) Keynes treated short-run macroeconomics as a minor issue.
B) Keynes emphasized the short-run effects of shifts in aggregate demand on aggregate output, employment, and prices, whereas the classical economists focused on the long-run determination of the aggregate price level.
C) The classical economists believed that the short-run aggregate supply curve was upward sloping.
D) The classical economists emphasized the short-run effects of shifts in aggregate demand on aggregate output, whereas Keynes focused on the long-run determination of the aggregate price level.
A) Keynes treated short-run macroeconomics as a minor issue.
B) Keynes emphasized the short-run effects of shifts in aggregate demand on aggregate output, employment, and prices, whereas the classical economists focused on the long-run determination of the aggregate price level.
C) The classical economists believed that the short-run aggregate supply curve was upward sloping.
D) The classical economists emphasized the short-run effects of shifts in aggregate demand on aggregate output, whereas Keynes focused on the long-run determination of the aggregate price level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
_____ was a _____ economist who believed that _____ in wages and prices could block adjustments to full employment.
A) Adam Smith; British; flexibility
B) Milton Friedman; U.S.; inflexibility
C) John Maynard Keynes; British; stickiness
D) Robert Lucas; U.S.; stickiness
A) Adam Smith; British; flexibility
B) Milton Friedman; U.S.; inflexibility
C) John Maynard Keynes; British; stickiness
D) Robert Lucas; U.S.; stickiness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The groundbreaking book The General Theory of Employment, Money, and Interest was written by famed economist:
A) Ronald Reagan.
B) John Maynard Keynes.
C) Adam Smith.
D) Barack Obama.
A) Ronald Reagan.
B) John Maynard Keynes.
C) Adam Smith.
D) Barack Obama.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The consensus is that the Great Depression was ended by:
A) imposing fiscal discipline and reducing budget deficits.
B) following Keynes's analysis regarding the "animal spirits."
C) increasing the money supply and lowering the interest rate.
D) applying expansionary fiscal policy on a large scale.
A) imposing fiscal discipline and reducing budget deficits.
B) following Keynes's analysis regarding the "animal spirits."
C) increasing the money supply and lowering the interest rate.
D) applying expansionary fiscal policy on a large scale.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the following to answer questions: 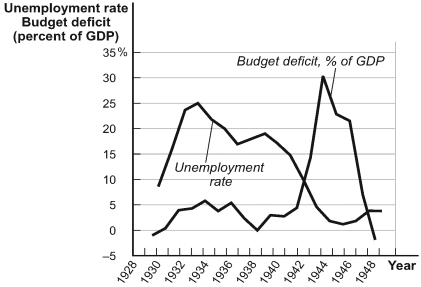
(Figure: Fiscal Policy and the End of the Great Depression) Refer to Figure: Fiscal Policy and the End of the Great Depression. The period from 1933 through 1936 would seem to indicate that in the short run a moderate level of government deficit spending can _____ the unemployment rate.
A) reduce
B) increase
C) not affect
D) eliminate

(Figure: Fiscal Policy and the End of the Great Depression) Refer to Figure: Fiscal Policy and the End of the Great Depression. The period from 1933 through 1936 would seem to indicate that in the short run a moderate level of government deficit spending can _____ the unemployment rate.
A) reduce
B) increase
C) not affect
D) eliminate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Because Keynes's theory recognized the problem of interest rates being at the zero bound (the liquidity trap), it:
A) perceived the economy as being mostly self-adjusting.
B) favored the use of monetary policy over fiscal policy.
C) considered technological progress the answer to any economic slump.
D) favored the use of fiscal policy over monetary policy.
A) perceived the economy as being mostly self-adjusting.
B) favored the use of monetary policy over fiscal policy.
C) considered technological progress the answer to any economic slump.
D) favored the use of fiscal policy over monetary policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Christina believes that shifts in aggregate demand cause a change in both real output and the price level. She believes that an economic recession will not necessarily self-correct in the long run, and therefore she believes that active fiscal and monetary policy is justified to smooth out the business cycle. Christina is BEST described as a:
A) classical economist.
B) Keynesian.
C) supply-sider.
D) monetarist.
A) classical economist.
B) Keynesian.
C) supply-sider.
D) monetarist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The historical validation of Keynes's theory came through the:
A) expansion in aggregate demand resulting from drastic interest rate cuts in the early 1940s.
B) successful application of his theories in the United States during the Great Depression in the early 1930s.
C) expansion in aggregate demand resulting from massive military spending in the early 1940s.
D) successful application of his theories in the United Kingdom during the mid 1930s.
A) expansion in aggregate demand resulting from drastic interest rate cuts in the early 1940s.
B) successful application of his theories in the United States during the Great Depression in the early 1930s.
C) expansion in aggregate demand resulting from massive military spending in the early 1940s.
D) successful application of his theories in the United Kingdom during the mid 1930s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the following to answer questions: 
(Figure: Fiscal Policy and the End of the Great Depression) Refer to Figure: Fiscal Policy and the End of the Great Depression. The period from 1936 to 1938 would seem to indicate that in the short run a decrease in government deficit spending can _____ the unemployment rate.
A) reduce
B) increase
C) not affect
D) eliminate

(Figure: Fiscal Policy and the End of the Great Depression) Refer to Figure: Fiscal Policy and the End of the Great Depression. The period from 1936 to 1938 would seem to indicate that in the short run a decrease in government deficit spending can _____ the unemployment rate.
A) reduce
B) increase
C) not affect
D) eliminate

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Friedman and Schwartz's work A Monetary History of the United States, 1867-1960 showed that the business cycle historically was associated with fluctuations in:
A) prices.
B) interest rates.
C) the money supply.
D) business investment.
A) prices.
B) interest rates.
C) the money supply.
D) business investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The main idea behind monetarism is that:
A) the aggregate output will be even greater than potential output if the money supply grows at a constant rate.
B) the aggregate price level will increase proportionally if the money supply grows at a constant rate.
C) the government budget will have a deficit if the government spending grows at a constant rate.
D) the aggregate output will grow steadily at a constant rate if the money supply also grows at a constant rate.
A) the aggregate output will be even greater than potential output if the money supply grows at a constant rate.
B) the aggregate price level will increase proportionally if the money supply grows at a constant rate.
C) the government budget will have a deficit if the government spending grows at a constant rate.
D) the aggregate output will grow steadily at a constant rate if the money supply also grows at a constant rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Keynesians argued that monetary policy would NOT be effective if:
A) there was a liquidity trap.
B) the Fed was independent of political pressure.
C) other countries did not follow monetary policy similar to that of the United States.
D) no one bought bonds when the Fed conducted open-market operations.
A) there was a liquidity trap.
B) the Fed was independent of political pressure.
C) other countries did not follow monetary policy similar to that of the United States.
D) no one bought bonds when the Fed conducted open-market operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Keynes's theory did not endorse the use of monetary policy during the Great Depression because:
A) at the time, the nominal interest rate was very close to zero.
B) during WWII, the convertibility of the pound sterling into gold was suspended.
C) under the gold standard, the zero bound on nominal interest rates did not exist.
D) monetary expansions were impossible under a gold standard.
A) at the time, the nominal interest rate was very close to zero.
B) during WWII, the convertibility of the pound sterling into gold was suspended.
C) under the gold standard, the zero bound on nominal interest rates did not exist.
D) monetary expansions were impossible under a gold standard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The Great Depression was ended in the United States by:
A) the government running budget surpluses throughout the 1930s.
B) the government increasing the money supply throughout the 1930s.
C) central planning of the economy by the government.
D) the huge amounts of government spending required to fight WWII during the early 1940s.
A) the government running budget surpluses throughout the 1930s.
B) the government increasing the money supply throughout the 1930s.
C) central planning of the economy by the government.
D) the huge amounts of government spending required to fight WWII during the early 1940s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Milton Friedman and Anna Schwartz wrote:
A) The Great Depression.
B) The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money.
C) The Wealth of Nations.
D) A Monetary History of the United States, 1867-1960.
A) The Great Depression.
B) The General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money.
C) The Wealth of Nations.
D) A Monetary History of the United States, 1867-1960.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The main consequence of Keynesian economics is:
A) the development of economic policy rules.
B) the rationale for macroeconomic policy activism.
C) a consensus that fiscal policy is ineffective.
D) a consensus that monetary policy is always effective.
A) the development of economic policy rules.
B) the rationale for macroeconomic policy activism.
C) a consensus that fiscal policy is ineffective.
D) a consensus that monetary policy is always effective.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Keynes's ideas were:
A) quickly adopted in the 1930s to end the Great Depression.
B) slowly but consistently used in 2008 to end the Great Recession.
C) used somewhat to help reduce the Great Depression.
D) ignored in the Great Depression.
A) quickly adopted in the 1930s to end the Great Depression.
B) slowly but consistently used in 2008 to end the Great Recession.
C) used somewhat to help reduce the Great Depression.
D) ignored in the Great Depression.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following to answer questions: 
(Figure: Fiscal Policy and the End of the Great Depression) Refer to Figure: Fiscal Policy and the End of the Great Depression. The period from 1939 through 1943 would seem to indicate that in the short run a large increase in government deficit spending can _____ the unemployment rate.
A) reduce
B) increase
C) not affect
D) reduce or increase

(Figure: Fiscal Policy and the End of the Great Depression) Refer to Figure: Fiscal Policy and the End of the Great Depression. The period from 1939 through 1943 would seem to indicate that in the short run a large increase in government deficit spending can _____ the unemployment rate.
A) reduce
B) increase
C) not affect
D) reduce or increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The main reason that the Great Depression ended was:
A) effective monetary policy by the Fed under the leadership of Paul Volcker.
B) the defeat of Adolf Hitler in Germany in the 1930s.
C) Winston Churchill's foreign policy.
D) deficit spending in the United States to finance World War II.
A) effective monetary policy by the Fed under the leadership of Paul Volcker.
B) the defeat of Adolf Hitler in Germany in the 1930s.
C) Winston Churchill's foreign policy.
D) deficit spending in the United States to finance World War II.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In a liquidity trap:
A) fiscal policy becomes ineffective because of the high budget deficit.
B) monetary policy becomes ineffective because the nominal interest rate is close to the zero bound.
C) the aggregate price level becomes downwardly sticky.
D) any increase in government spending drives out planned investment spending.
A) fiscal policy becomes ineffective because of the high budget deficit.
B) monetary policy becomes ineffective because the nominal interest rate is close to the zero bound.
C) the aggregate price level becomes downwardly sticky.
D) any increase in government spending drives out planned investment spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Scenario: The Velocity Equation Suppose that real GDP equals $10 trillion, nominal GDP equals $20 trillion, and the aggregate price level equals 2. If the velocity of money is 2, the money supply is:
A) $20 trillion.
B) $10 trillion.
C) $5 trillion.
D) $40 trillion.
A) $20 trillion.
B) $10 trillion.
C) $5 trillion.
D) $40 trillion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
In A Monetary History of the United States, 1867-1960, Milton Friedman and Anna Schwartz argued that:
A) only fiscal policy could be effective in managing the economy.
B) the Depression was caused by irresponsible government spending.
C) monetary policy should play a key role in stabilizing the economy.
D) the Federal Reserve should be abolished.
A) only fiscal policy could be effective in managing the economy.
B) the Depression was caused by irresponsible government spending.
C) monetary policy should play a key role in stabilizing the economy.
D) the Federal Reserve should be abolished.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Which statement is FALSE? Keynesian economics:
A) emphasizes that factors other than the money supply can affect aggregate demand.
B) provides the rationale for macroeconomic policy activism.
C) emphasizes short-run economic fluctuations.
D) emphasizes long-run fluctuations.
A) emphasizes that factors other than the money supply can affect aggregate demand.
B) provides the rationale for macroeconomic policy activism.
C) emphasizes short-run economic fluctuations.
D) emphasizes long-run fluctuations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 283 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



