Deck 6: The World of Rome, Ca 1000 Bce-400 Ce
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 6: The World of Rome, Ca 1000 Bce-400 Ce
1
One result of the Struggle of the Orders was the creation of a law code that made all
A) plebeians more powerful than patricians.
B) patricians more powerful than plebeians.
C) Roman-born citizens more important than foreigners.
D) citizens, plebeian and patrician, equal before the law.
A) plebeians more powerful than patricians.
B) patricians more powerful than plebeians.
C) Roman-born citizens more important than foreigners.
D) citizens, plebeian and patrician, equal before the law.
citizens, plebeian and patrician, equal before the law.
2
In the third century B.C.E., the main challenge to Roman control of the Mediterranean came from which of the following?
A) Ptolemaic Egypt
B) Carthage
C) Alexandria
D) Macedonia
A) Ptolemaic Egypt
B) Carthage
C) Alexandria
D) Macedonia
Carthage
3
What was an important difference between the political systems of the Romans and Greeks?
A) Some Greek city-states had monarchies, while Roman city-states never did.
B) Rome extended citizenship to its conquered peoples, while the Greeks did not.
C) Rome had written laws, while no Greek city-states did.
D) Greeks endured civil war, while Romans did not.
A) Some Greek city-states had monarchies, while Roman city-states never did.
B) Rome extended citizenship to its conquered peoples, while the Greeks did not.
C) Rome had written laws, while no Greek city-states did.
D) Greeks endured civil war, while Romans did not.
Rome extended citizenship to its conquered peoples, while the Greeks did not.
4
During the Struggle of the Orders, how did the plebeians force political concessions?
A) Plebian farmers refused to sell agricultural goods to the cities.
B) All plebeians declined to pay annual taxes and local fees.
C) Plebian men refused to serve in the military.
D) Plebian leaders ordered the assassination of several senators and consuls.
A) Plebian farmers refused to sell agricultural goods to the cities.
B) All plebeians declined to pay annual taxes and local fees.
C) Plebian men refused to serve in the military.
D) Plebian leaders ordered the assassination of several senators and consuls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following was true of Roman religion?
A) It was a deeply reflective religion emphasizing inner piety.
B) It was largely a matter of rites and ceremonies, not inner piety.
C) It was centered on ancestor worship.
D) It advocated human sacrifice.
A) It was a deeply reflective religion emphasizing inner piety.
B) It was largely a matter of rites and ceremonies, not inner piety.
C) It was centered on ancestor worship.
D) It advocated human sacrifice.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Why was the ius gentium important to Roman society?
A) It covered both Roman citizens and foreigners as a kind of universal law.
B) It was the first written law code in the Mediterranean world.
C) It limited the rights of patricians and elevated plebeians.
D) It provided for the impeachment of the consuls.
A) It covered both Roman citizens and foreigners as a kind of universal law.
B) It was the first written law code in the Mediterranean world.
C) It limited the rights of patricians and elevated plebeians.
D) It provided for the impeachment of the consuls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Why did the Carthaginians recall Hannibal from Italy?
A) He had disgraced himself there.
B) The Romans had attacked Carthage itself.
C) His father was dying.
D) He had served his full term as general.
A) He had disgraced himself there.
B) The Romans had attacked Carthage itself.
C) His father was dying.
D) He had served his full term as general.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
According to the most common Roman creation myth, who assisted Rome's first ruler, Romulus, with the rule of the city?
A) He was helped by a council of advisers called the Senate.
B) He was assisted by his brother Remus, a military commander.
C) He was only able to rule the city with help of the gods.
D) He relied heavily on his aristocratic wife and her family.
A) He was helped by a council of advisers called the Senate.
B) He was assisted by his brother Remus, a military commander.
C) He was only able to rule the city with help of the gods.
D) He relied heavily on his aristocratic wife and her family.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
During the republic, which of the following was true of the Roman Senate?
A) Its only function was to pass legislation.
B) It had little power and was advised by consuls.
C) Like the consuls, it changed its membership annually.
D) One of its chief responsibilities was to advise officials and consuls.
A) Its only function was to pass legislation.
B) It had little power and was advised by consuls.
C) Like the consuls, it changed its membership annually.
D) One of its chief responsibilities was to advise officials and consuls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the early republic, which group controlled political power and military leadership?
A) Plebeians
B) Etruscan nobles
C) Patricians
D) Merchants
A) Plebeians
B) Etruscan nobles
C) Patricians
D) Merchants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
According to legend, who founded Rome?
A) Latium
B) Romulus and Remus
C) Domitian
D) Silla and Gaulius
A) Latium
B) Romulus and Remus
C) Domitian
D) Silla and Gaulius

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Other than Greeks, who were the first people to build permanent settlements in Italy?
A) Etruscans
B) Egyptians
C) Hittites
D) Persians
A) Etruscans
B) Egyptians
C) Hittites
D) Persians

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
How was Roman society divided in the early republic?
A) Into two groups-the patricians and the plebeians
B) Between Roman citizens and non-Romans who were seen as subject peoples
C) Between urban and rural dwellers
D) Between Roman citizens and their slaves
A) Into two groups-the patricians and the plebeians
B) Between Roman citizens and non-Romans who were seen as subject peoples
C) Between urban and rural dwellers
D) Between Roman citizens and their slaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
How are Roman women portrayed in Rome's founding legends?
A) Dominant and superior
B) Meek and quiet
C) Virtuous and brave
D) Conniving and deceitful
A) Dominant and superior
B) Meek and quiet
C) Virtuous and brave
D) Conniving and deceitful

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
According to Map 6.1, "Roman Italy and the City of Rome, ca. 218 B.C.E.," what evidence is there to suggest that the Greeks had begun to colonize the peninsula prior to the emergence of Roman Italy? 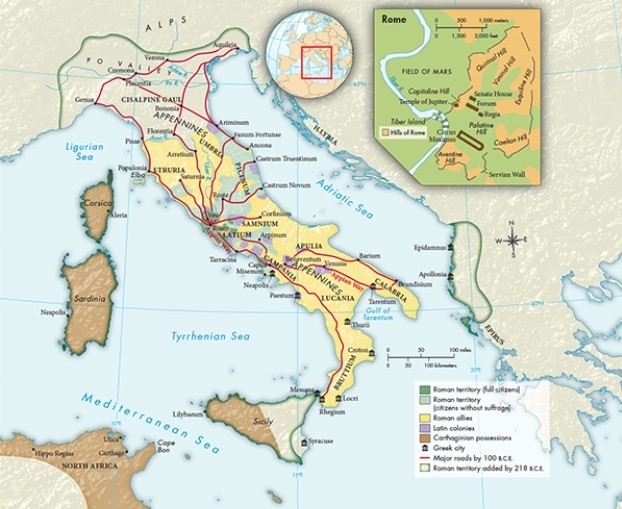
A) Greek cities existed on the southeastern shore of the Adriatic Sea.
B) Some Greek cities were connected by major roads to the city of Rome.
C) Several Greek cities existed on the southern part of the peninsula.
D) There are no Greek cities in the northern part of the peninsula.

A) Greek cities existed on the southeastern shore of the Adriatic Sea.
B) Some Greek cities were connected by major roads to the city of Rome.
C) Several Greek cities existed on the southern part of the peninsula.
D) There are no Greek cities in the northern part of the peninsula.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The villages that became Rome were located on what river?
A) Po
B) Tiber
C) Danube
D) Adige
A) Po
B) Tiber
C) Danube
D) Adige

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What was recorded on the Twelve Tables?
A) Myths
B) Prayers
C) Religious texts
D) Laws
A) Myths
B) Prayers
C) Religious texts
D) Laws

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What did Romans, like the Persians, do once they conquered an area?
A) They killed the men and took the women as slaves.
B) They built large temples to please the gods and ensure success.
C) They forced the men to serve in the Roman military.
D) They built roads to facilitate communication and trade.
A) They killed the men and took the women as slaves.
B) They built large temples to please the gods and ensure success.
C) They forced the men to serve in the Roman military.
D) They built roads to facilitate communication and trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The First Punic War ended with a Roman victory and the creation of Rome's first
A) monarchy.
B) diplomatic corps.
C) navy.
D) hospitals.
A) monarchy.
B) diplomatic corps.
C) navy.
D) hospitals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Who was the Carthaginian general who brought the Second Punic War to the gates of Rome?
A) Scipio Aemilianus
B) Pyrrhus
C) Tarquin the Proud
D) Hannibal
A) Scipio Aemilianus
B) Pyrrhus
C) Tarquin the Proud
D) Hannibal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
During the pax Romana, what regions became prime grain producers for the empire?
A) Gaul and Italy
B) Southern Spain and Italy
C) Egypt and Syria
D) Britain and Belgium
A) Gaul and Italy
B) Southern Spain and Italy
C) Egypt and Syria
D) Britain and Belgium

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
How did Rome solve the problem of feeding its growing population?
A) Emperors provided free bread, oil, and wine to the population.
B) Leaders started subsidizing the cost of basic commodities.
C) Emperors combined small tenant farms into huge agricultural operations.
D) The Senate forced thousands of residents out of the city to colonize the frontiers.
A) Emperors provided free bread, oil, and wine to the population.
B) Leaders started subsidizing the cost of basic commodities.
C) Emperors combined small tenant farms into huge agricultural operations.
D) The Senate forced thousands of residents out of the city to colonize the frontiers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What was one of Augustus's important military reforms?
A) He created an all-volunteer force.
B) He developed an all-mercenary force.
C) He assembled an all-plebeian army.
D) He began a permanent standing army.
A) He created an all-volunteer force.
B) He developed an all-mercenary force.
C) He assembled an all-plebeian army.
D) He began a permanent standing army.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
What important improvements in urban planning were made in Rome during the second century C.E.?
A) Separate districts were created for different ethnic groups in the cities.
B) A new domestic police force was developed in the city of Rome.
C) Hundreds of miles of aqueducts and sewers were built.
D) Streets were made straight, and all roads and streets were paved.
A) Separate districts were created for different ethnic groups in the cities.
B) A new domestic police force was developed in the city of Rome.
C) Hundreds of miles of aqueducts and sewers were built.
D) Streets were made straight, and all roads and streets were paved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How did Romans view slavery during the republic?
A) The only people who could be taken as slaves were North Africans.
B) It was viewed as a lifelong condition for the enslaved.
C) It was an unfortunate state but one from which a slave might become free.
D) It became less economically important over time as Rome grew to include more citizens.
A) The only people who could be taken as slaves were North Africans.
B) It was viewed as a lifelong condition for the enslaved.
C) It was an unfortunate state but one from which a slave might become free.
D) It became less economically important over time as Rome grew to include more citizens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which emperor transformed the principate into a hereditary monarchy?
A) Nero
B) Hadrian
C) Claudius
D) Vespasian
A) Nero
B) Hadrian
C) Claudius
D) Vespasian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
According to Map 6.2, "Roman Expansion, 262 B.C.E.-180 C.E.," which of the following was the northernmost Roman city during the period 262 B.C.E.-180 C.E.? 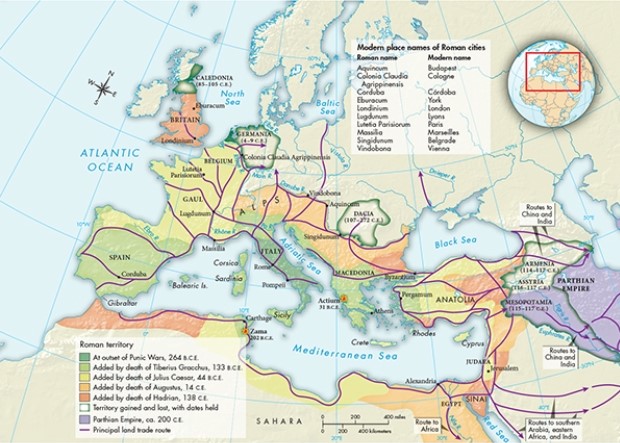
A) York
B) London
C) Lyons
D) Vienna

A) York
B) London
C) Lyons
D) Vienna

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Who was the author of the Aeneid?
A) Cicero
B) Virgil
C) Augustus
D) Julius Caesar
A) Cicero
B) Virgil
C) Augustus
D) Julius Caesar

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What was relatively unusual about women in Roman families?
A) They seldom ventured outside their homes.
B) They were not allowed to learn to read or write.
C) They had no role in raising their children.
D) They were able to inherit and own property.
A) They seldom ventured outside their homes.
B) They were not allowed to learn to read or write.
C) They had no role in raising their children.
D) They were able to inherit and own property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In Roman families, what was the paterfamilias?
A) The oldest dominant male in a family, who had near absolute power
B) A family council that was composed of all adult males
C) The marriage contract between husband and wife
D) The male family member who was entitled to vote for public office
A) The oldest dominant male in a family, who had near absolute power
B) A family council that was composed of all adult males
C) The marriage contract between husband and wife
D) The male family member who was entitled to vote for public office

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Based on Map 6.2, "Roman Expansion, 262 B.C.E.-180 C.E.," which of the following was likely attractive to the Romans due to its strategic importance as a harbor city? 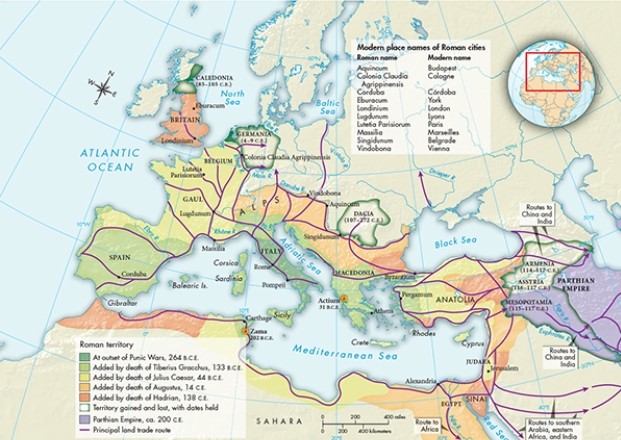
A) Carthage
B) Corduba
C) Jerusalem
D) Lugdunum

A) Carthage
B) Corduba
C) Jerusalem
D) Lugdunum

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
To whom did the term pagan originally refer?
A) Those who lived in the countryside
B) Those who lived in the city
C) Those who worshipped more than one god
D) Those who worshipped no god at all
A) Those who lived in the countryside
B) Those who lived in the city
C) Those who worshipped more than one god
D) Those who worshipped no god at all

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What was the main feature of the reform program proposed by Tiberius Gracchus?
A) To provide free bread to the poor of Rome
B) To redistribute public land to poor Romans
C) To abolish the class distinctions of patricians and plebeians
D) To establish colonies populated by ex-soldiers and their families
A) To provide free bread to the poor of Rome
B) To redistribute public land to poor Romans
C) To abolish the class distinctions of patricians and plebeians
D) To establish colonies populated by ex-soldiers and their families

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Under Augustus, women could be freed from male guardianship if they
A) had a certain number of children.
B) were related to Augustus.
C) had a son killed in a war.
D) bought their freedom from the state.
A) had a certain number of children.
B) were related to Augustus.
C) had a son killed in a war.
D) bought their freedom from the state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
At its height, what was the population of ancient Rome?
A) 100,000
B) 10,000
C) 1 million
D) 10 million
A) 100,000
B) 10,000
C) 1 million
D) 10 million

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
How did Gaius Marius recruit men to serve in an African campaign?
A) He promised them citizenship.
B) He recruited them by paying them gold coins.
C) He offered to pardon them if they had been criminals.
D) He promised land to landless men in return for their service.
A) He promised them citizenship.
B) He recruited them by paying them gold coins.
C) He offered to pardon them if they had been criminals.
D) He promised land to landless men in return for their service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
According to Map 6.2, "Roman Expansion, 262 B.C.E.-180 C.E.," which region was home to the largest number of land trade routes? 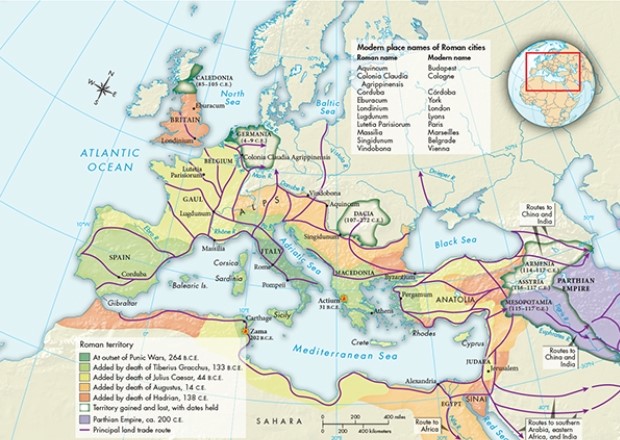
A) Germania
B) Britain
C) Spain
D) Gaul

A) Germania
B) Britain
C) Spain
D) Gaul

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What does the phrase Roma et Augustus mean?
A) It is the title of a historical account of Augustus's reign by Tacitus.
B) It is an epic poem of Augustus's deeds written by Virgil.
C) It means that the empire was divinely ordained.
D) It refers to the cult of the emperor and the state.
A) It is the title of a historical account of Augustus's reign by Tacitus.
B) It is an epic poem of Augustus's deeds written by Virgil.
C) It means that the empire was divinely ordained.
D) It refers to the cult of the emperor and the state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Who played the role of middlemen between the Romans and the Chinese in the trade along the Silk Road?
A) Indians
B) Goths
C) Parthians
D) Jews
A) Indians
B) Goths
C) Parthians
D) Jews

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
To what does the term latifundia refer?
A) All lands conquered by Roman armies
B) A new social class primarily created by imperial expansion
C) Huge agricultural estates created by warfare and absentee farmers
D) Lands given to returning soldiers as payment for their service
A) All lands conquered by Roman armies
B) A new social class primarily created by imperial expansion
C) Huge agricultural estates created by warfare and absentee farmers
D) Lands given to returning soldiers as payment for their service

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What did the mystery religions offer adherents in the Roman Empire?
A) Access to political power
B) The promise of eternal life
C) Independence from the state
D) Veneration of the state
A) Access to political power
B) The promise of eternal life
C) Independence from the state
D) Veneration of the state

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What was the significance of Augustus's rule? In the long run, did he help or hurt the Roman Empire?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What writings provide the historical documentation of the life of Jesus?
A) The sermons he wrote are the main source for his life story.
B) The biographies written by his contemporaries tell his life story.
C) The four Gospels of the Bible provide the principal evidence for his life and deeds.
D) Accounts written by Pontius Pilate provide the most comprehensive information.
A) The sermons he wrote are the main source for his life story.
B) The biographies written by his contemporaries tell his life story.
C) The four Gospels of the Bible provide the principal evidence for his life and deeds.
D) Accounts written by Pontius Pilate provide the most comprehensive information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What feature of Map 6.1, "Roman Italy and the City of Rome, ca. 218 B.C.E.," reflects Etruscan influence? 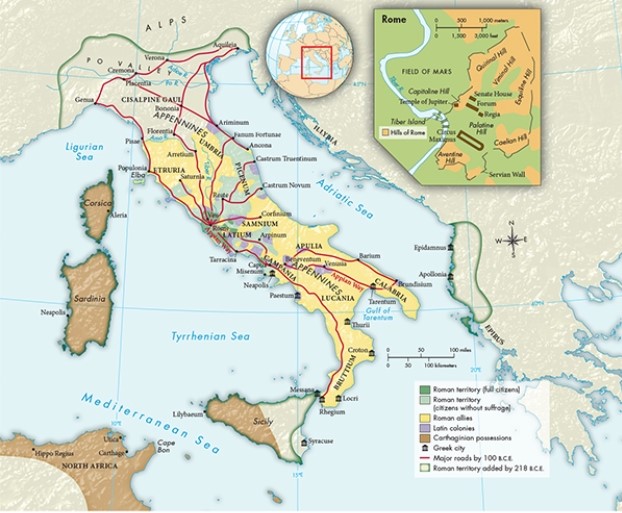
A) The existence of paved roads
B) The location of the Latin colonies
C) The division of Sicily into Carthaginian and Roman territory
D) The absence of roads in the northern part of the region of Apulia

A) The existence of paved roads
B) The location of the Latin colonies
C) The division of Sicily into Carthaginian and Roman territory
D) The absence of roads in the northern part of the region of Apulia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Discuss the aspects of Jesus's teaching and life that were Jewish in origin, and how he differed from Jewish orthodoxy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Explain why Rome and Carthage were natural rivals and why the Roman victory in the Punic Wars led to the establishment of Roman control of the Mediterranean world.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What did Paul of Tarsus advocate with regard to Christian ideals?
A) That Christ's teachings should be proclaimed to all
B) That Christianity should be used to defeat Rome
C) That Christ's message applied only to Jews
D) That Christians should avoid contact with pagans
A) That Christ's teachings should be proclaimed to all
B) That Christianity should be used to defeat Rome
C) That Christ's message applied only to Jews
D) That Christians should avoid contact with pagans

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When was Christianity made the official religion of the Roman Empire?
A) 337 C.E.
B) 380 C.E.
C) 405 C.E.
D) 418 C.E.
A) 337 C.E.
B) 380 C.E.
C) 405 C.E.
D) 418 C.E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Explain how the Roman Senate demonstrated Roman ideals related to shared government.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following was true of the emperor Constantine?
A) He supported Christianity.
B) He abdicated his power.
C) He raised taxes on clergy.
D) He was assassinated by the army.
A) He supported Christianity.
B) He abdicated his power.
C) He raised taxes on clergy.
D) He was assassinated by the army.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What developments in the Roman military during the early republic made it so effective and for such a long time?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Describe the Roman family structure. What role did women play?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How did the Roman Empire influence the development of Christianity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Why did Pontius Pilate condemn Jesus to death?
A) He believed Jesus was the Messiah.
B) He was an adherent of the mystery religions.
C) He was told to do it by the emperor Tiberius.
D) He was concerned with maintaining social order.
A) He believed Jesus was the Messiah.
B) He was an adherent of the mystery religions.
C) He was told to do it by the emperor Tiberius.
D) He was concerned with maintaining social order.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
How was the Roman road system used to create, expand, and maintain the empire?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What was one of the primary early rituals celebrated by Christians?
A) Re-creating the preaching of Jesus
B) Visiting the site of the crucifixion
C) Protest marches against the Romans
D) A commemorative meal
A) Re-creating the preaching of Jesus
B) Visiting the site of the crucifixion
C) Protest marches against the Romans
D) A commemorative meal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What were some of the economic hardships faced by the Roman Empire in the fourth century C.E. onward?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What was one of the advantages of the huge estates, or villas, created in the fourth century?
A) They were a way peasants could avoid paying taxes.
B) They offered protection in an unsettled world.
C) They provided the basis for agriculture, trade, and industry.
D) They facilitated a process of cultural exchange.
A) They were a way peasants could avoid paying taxes.
B) They offered protection in an unsettled world.
C) They provided the basis for agriculture, trade, and industry.
D) They facilitated a process of cultural exchange.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What significant political change did Diocletian enact?
A) He used the titles "Augustus" and "Caesar."
B) He adopted the court ceremonies of the Persian Empire.
C) He converted to Christianity and made it the state religion.
D) He divided the Roman Empire into two parts.
A) He used the titles "Augustus" and "Caesar."
B) He adopted the court ceremonies of the Persian Empire.
C) He converted to Christianity and made it the state religion.
D) He divided the Roman Empire into two parts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What do the terms princeps civitatis, principate, and Roma et Augustus tell us about Augustus's power?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Describe the different concepts of law in the Roman Republic and the Roman Empire. How did law change from republic to empire?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the following to answer questions
pagan
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
pagan
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the following to answer questions
bishop
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
bishop
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following to answer questions
Punic Wars
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
Punic Wars
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following to answer questions
patricians
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
patricians
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the following to answer questions
consuls
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
consuls
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following to answer questions
pax Romana
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
pax Romana
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following to answer questions
paterfamilias
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
paterfamilias
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
"The acquisition of empire spelled doom for the republic." Assess the validity of this quote, considering the problems resulting from the wars of conquest and the attempts to solve these serious problems.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the following to answer questions
plebeians
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
plebeians
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following to answer questions
Messiah
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
Messiah
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
One of the most important events during the time of the Roman Empire was the birth of Christianity. Describe the evolution of Christianity. How do historians explain the success of early Christianity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The Roman Republic underwent two great social upheavals: the Struggle of the Orders and the civil wars of the late republic. Compare these two upheavals in terms of causes, participants, and results. Was Rome better off after each upheaval? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Use the following to answer questions
Senate
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.
Senate
A)The assembly that was the main institution of power in the Roman Republic, originally composed only of aristocrats.
B)Primary executives in the Roman Republic, elected for one-year terms, who commanded the army in battle, administered state business, and supervised financial affairs.
C)The Roman hereditary aristocracy, who held most of the political power in the republic.
D)The common people of Rome, who were free but had few of the patricians' advantages.
E)A series of three wars between Rome and Carthage in which Rome emerged the victor.
F)The oldest dominant male of the family, who held great power over the lives of family members.
G)The "Roman peace," a period during the first and second centuries C.E. of political stability and relative peace.
H)In Jewish belief, a savior who would bring a period of peace and happiness for Jews; many Christians came to believe that Jesus was that savior.
I)Originally referring to those who lived in the countryside, the term came to mean those who practiced religions other than Judaism or Christianity.
J)A Christian Church official with jurisdiction over a certain area and the power to determine the correct interpretation of Christian teachings.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Describe some of the ways the Etruscans influenced Roman culture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



