Deck 7: East Asia and the Spread of Buddhism, 221 Bce-845 Ce
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/77
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: East Asia and the Spread of Buddhism, 221 Bce-845 Ce
1
What evidence is there in the illustration "Ban Zhao, Han Dynasty writer" that Zhao disagreed in some ways with accepted Chinese norms for the role of women in Han society? 
A) Her manner of dress is not reflective of the humility females were expected to display.
B) As an advocate of education for girls, she is reading a book.
C) In choosing to become educated, she is not displaying the filial piety expected in Han culture.
D) Reading a book as a female indicated that she would make a good wife.

A) Her manner of dress is not reflective of the humility females were expected to display.
B) As an advocate of education for girls, she is reading a book.
C) In choosing to become educated, she is not displaying the filial piety expected in Han culture.
D) Reading a book as a female indicated that she would make a good wife.
As an advocate of education for girls, she is reading a book.
2
What was the key to the Han tributary system?
A) The exchange of gifts via envoys
B) Sending royal children as hostages
C) Frequently sending armies to invade
D) Sending Confucian scholars as teachers
A) The exchange of gifts via envoys
B) Sending royal children as hostages
C) Frequently sending armies to invade
D) Sending Confucian scholars as teachers
The exchange of gifts via envoys
3
Which group of people did the First Emperor order to move to the capital?
A) Nobility
B) Merchants
C) Military generals
D) Foreigners
A) Nobility
B) Merchants
C) Military generals
D) Foreigners
Nobility
4
How did Gaozu change the centralized government created by the Qin?
A) He disbanded the army.
B) He gave most imperial powers back to local rulers.
C) He reduced taxes.
D) He abandoned its bureaucratic structure.
A) He disbanded the army.
B) He gave most imperial powers back to local rulers.
C) He reduced taxes.
D) He abandoned its bureaucratic structure.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What defensive barrier was built by the Qin emperor using conscripted labor?
A) The Grand Canal
B) The First Wall
C) The Silk Road
D) The Great Wall
A) The Grand Canal
B) The First Wall
C) The Silk Road
D) The Great Wall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which year marked the beginning of a unified China under the Qin state?
A) 206 C.E.
B) 581 B.C.E.
C) 221 B.C.E.
D) 764 C.E.
A) 206 C.E.
B) 581 B.C.E.
C) 221 B.C.E.
D) 764 C.E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Who became China's main military threat in the fifth to fourth centuries B.C.E.?
A) Koreans from the Silla kingdom
B) Nomadic horsemen of the north
C) Internal rebels trying to take control of trade
D) Bactrian merchants on the Silk Road
A) Koreans from the Silla kingdom
B) Nomadic horsemen of the north
C) Internal rebels trying to take control of trade
D) Bactrian merchants on the Silk Road

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How did Confucian scholars seek to make the Confucian classics more useful?
A) Made them freely available to all
B) Published them in inexpensive editions
C) Revised them
D) Wrote commentaries on them
A) Made them freely available to all
B) Published them in inexpensive editions
C) Revised them
D) Wrote commentaries on them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Which of the following was invented in China around 105 C.E.?
A) Writing
B) Bronze technology
C) Wet-field rice cultivation
D) Paper
A) Writing
B) Bronze technology
C) Wet-field rice cultivation
D) Paper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The early Han policy for dealing with the Xiongnu was to
A) invade and destroy their camps.
B) make peace with gifts and brides.
C) send them sons of the emperors.
D) capture as many of their horses as they could.
A) invade and destroy their camps.
B) make peace with gifts and brides.
C) send them sons of the emperors.
D) capture as many of their horses as they could.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which statement is true about the Confucian classics?
A) They were the texts written by Confucius in the sixth and fifth centuries B.C.E.
B) They rejected the ideas of yin and yang and instead promoted piety.
C) They were written by the disciples of Confucius after his death.
D) They were the ancient books recovered after the book burning of the third century B.C.E.
A) They were the texts written by Confucius in the sixth and fifth centuries B.C.E.
B) They rejected the ideas of yin and yang and instead promoted piety.
C) They were written by the disciples of Confucius after his death.
D) They were the ancient books recovered after the book burning of the third century B.C.E.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Who formed the first great confederation of nomadic tribes, known as the Huns in the West?
A) The Xiongnu
B) The Chengdu
C) The Qin
D) The Chang'an
A) The Xiongnu
B) The Chengdu
C) The Qin
D) The Chang'an

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Within the city of Chang'an, pictured here, the size and position of the Imperial City along with the well-planned layout of the surrounding areas are indicative of the 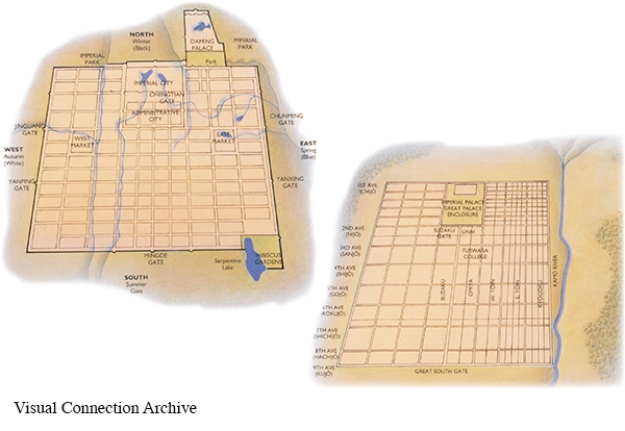
A) control that the Tang Dynasty exercised over society.
B) ever-present concern of protecting the city from outside influences.
C) influence of the city of Heian upon those who planned Chang'an.
D) acceptance of commonplace urban design standards in China by the Tang.

A) control that the Tang Dynasty exercised over society.
B) ever-present concern of protecting the city from outside influences.
C) influence of the city of Heian upon those who planned Chang'an.
D) acceptance of commonplace urban design standards in China by the Tang.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What happened to the Qin Dynasty after the death of the First Emperor?
A) Legalists gained power.
B) The Qin state collapsed.
C) The position of emperor became a weak figurehead.
D) His heir established popular reforms.
A) Legalists gained power.
B) The Qin state collapsed.
C) The position of emperor became a weak figurehead.
D) His heir established popular reforms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What did the first Qin emperor standardize, enabling China to operate more efficiently?
A) The prices for rice and wheat were set by the government so that no one paid more than others.
B) The Chinese script, weights, measures, and coinage were standardized to facilitate trade.
C) Scholars were put to work on an official volume of Confucian theories so that religious rituals could be standardized.
D) Ritual celebrations were set to a calendar so that they could be observed everywhere at the same time.
A) The prices for rice and wheat were set by the government so that no one paid more than others.
B) The Chinese script, weights, measures, and coinage were standardized to facilitate trade.
C) Scholars were put to work on an official volume of Confucian theories so that religious rituals could be standardized.
D) Ritual celebrations were set to a calendar so that they could be observed everywhere at the same time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The Confucian scholar-official system began during the
A) Han Dynasty.
B) Qin Dynasty.
C) Age of Division.
D) Zhou period.
A) Han Dynasty.
B) Qin Dynasty.
C) Age of Division.
D) Zhou period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What was significant about Sima Qian's writings?
A) They told the history of the eunuchs who served the Han emperors.
B) They were the first collection of Daoist ideas on government.
C) They included a comprehensive history of China and set a standard for historical writing.
D) They represented the first time a Han official had written in support of Legalism.
A) They told the history of the eunuchs who served the Han emperors.
B) They were the first collection of Daoist ideas on government.
C) They included a comprehensive history of China and set a standard for historical writing.
D) They represented the first time a Han official had written in support of Legalism.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
What did the Han emperor Gaozu do to reestablish stability after the fall of the Qin Dynasty?
A) He resurrected Legalism as the guiding philosophy of government.
B) He enacted harsh laws and high taxes in order to quell uprisings.
C) He outlawed Confucian philosophy.
D) He retained the centralized government created by the Qin.
A) He resurrected Legalism as the guiding philosophy of government.
B) He enacted harsh laws and high taxes in order to quell uprisings.
C) He outlawed Confucian philosophy.
D) He retained the centralized government created by the Qin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which of the following was true of metalworking in Han China?
A) It was less sophisticated than Roman metalworking.
B) It led to bronze replacing iron in tools.
C) It involved the use of liquefied iron poured into molds.
D) It resulted in bronze being phased out of all products.
A) It was less sophisticated than Roman metalworking.
B) It led to bronze replacing iron in tools.
C) It involved the use of liquefied iron poured into molds.
D) It resulted in bronze being phased out of all products.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
By taking over city-states in Central Asia, the Han under Emperor Wu were taking control of what transregional route?
A) Grand Canal
B) Silk Road
C) Incense Route
D) Khyber Pass
A) Grand Canal
B) Silk Road
C) Incense Route
D) Khyber Pass

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Why did Han officials encourage peasants to be independent and productive?
A) Peasants made up the bulk of the population and contributed vital taxes and labor services to the state.
B) All peasants had high social ambitions and were easily coerced into doing difficult jobs for the possibility of advancement.
C) China's peasants were well known for their military skills and were required to serve in the emperor's army.
D) Most peasants also had secondary skills such as metalworking and weaving and were vital to keeping the economy strong.
A) Peasants made up the bulk of the population and contributed vital taxes and labor services to the state.
B) All peasants had high social ambitions and were easily coerced into doing difficult jobs for the possibility of advancement.
C) China's peasants were well known for their military skills and were required to serve in the emperor's army.
D) Most peasants also had secondary skills such as metalworking and weaving and were vital to keeping the economy strong.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Ban Zhao's Admonitions for Women promoted the ideal virtues for Han women, particularly the virtue of
A) pride.
B) humility.
C) physical strength.
D) piety.
A) pride.
B) humility.
C) physical strength.
D) piety.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
During what dynasty did the great age of Chinese poetry occur?
A) Han
B) Qin
C) Sui
D) Tang
A) Han
B) Qin
C) Sui
D) Tang

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Han coins and jewelry were usually made of what metal?
A) Bronze
B) Iron
C) Gold
D) Silver
A) Bronze
B) Iron
C) Gold
D) Silver

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
How did the inheritance system in Han China usually work?
A) All land and property were passed to the eldest son.
B) All children inherited equally.
C) Land was divided equally among the sons in a family.
D) Land and money were divided between the spouse and the oldest child.
A) All land and property were passed to the eldest son.
B) All children inherited equally.
C) Land was divided equally among the sons in a family.
D) Land and money were divided between the spouse and the oldest child.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How did the Sui Dynasty contribute to China's infrastructure?
A) A well-planned government complex was established in Beijing.
B) Protective walls were built around cities for the first time.
C) The Yellow and Yangzi Rivers were connected by a canal.
D) China's first roads were built between Beijing and Chang'an.
A) A well-planned government complex was established in Beijing.
B) Protective walls were built around cities for the first time.
C) The Yellow and Yangzi Rivers were connected by a canal.
D) China's first roads were built between Beijing and Chang'an.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Who arranged marriages in a typical Han family?
A) Buddhist monks
B) The nearest noble
C) The groom
D) Parents
A) Buddhist monks
B) The nearest noble
C) The groom
D) Parents

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What was the form of Buddhism that spread from Central Asia to China, Japan, and Korea?
A) Mahayana
B) Little Vehicle
C) Zen
D) Shingon
A) Mahayana
B) Little Vehicle
C) Zen
D) Shingon

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What Chinese dynasty was founded in 581?
A) Qin
B) Sui
C) Ming
D) Han
A) Qin
B) Sui
C) Ming
D) Han

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What attracted Chinese women to Buddhism?
A) It encouraged women to pursue salvation and serve the faith on terms nearly equal to men.
B) It guaranteed every woman status as a bodhisattva.
C) It taught that being born female was higher than being born male.
D) It accepted the idea of female rulers and female independence.
A) It encouraged women to pursue salvation and serve the faith on terms nearly equal to men.
B) It guaranteed every woman status as a bodhisattva.
C) It taught that being born female was higher than being born male.
D) It accepted the idea of female rulers and female independence.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which Buddhist school of thought appealed to laypeople during the Tang era?
A) Theravada school
B) Chan school
C) Zen school
D) Pure Land school
A) Theravada school
B) Chan school
C) Zen school
D) Pure Land school

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What title did Taizong of the Tang Dynasty gain when he defeated the Turks in 630 C.E.?
A) Second Emperor
B) Son of Heaven
C) Sultan
D) Great Khan
A) Second Emperor
B) Son of Heaven
C) Sultan
D) Great Khan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The Mahayana Buddhism that spread to Central Asia was influenced by Iranian religions to become more
A) sacrificial.
B) devotional.
C) ritualistic.
D) monastic.
A) sacrificial.
B) devotional.
C) ritualistic.
D) monastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The location of the Great Wall in Map 7.1, "The Han Empire, 206 B.C.E-220 C.E.," indicates that its purpose was to protect 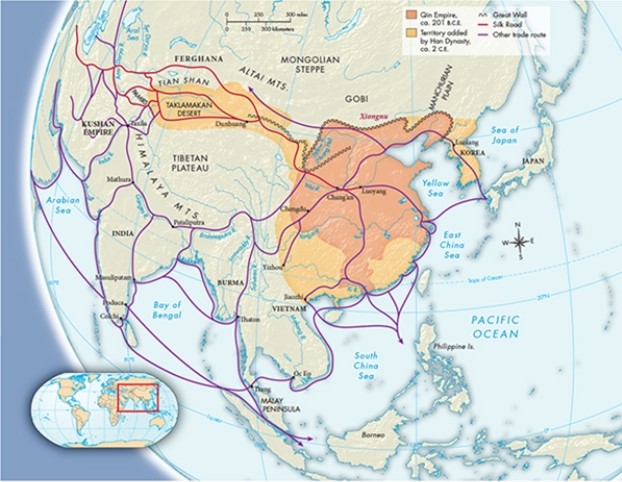
A) merchants traveling the Silk Road.
B) migrants seeking access to the Manchurian Plain.
C) Northern China from the nomadic Xiongnu.
D) trade routes into Korea.

A) merchants traveling the Silk Road.
B) migrants seeking access to the Manchurian Plain.
C) Northern China from the nomadic Xiongnu.
D) trade routes into Korea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What was the most glorified virtue in Han times?
A) Filial piety
B) Bureaucratic honesty
C) Honoring the emperor
D) Gentlemanly conduct
A) Filial piety
B) Bureaucratic honesty
C) Honoring the emperor
D) Gentlemanly conduct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Who led a rebellion against the Tang government in 755 C.E.?
A) Yang Guifei
B) Emperor Gaozong
C) Empress Wu
D) An Lushan
A) Yang Guifei
B) Emperor Gaozong
C) Empress Wu
D) An Lushan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Which of the following took place during the Age of Division?
A) A eunuch ruled China through child emperors.
B) The Han Dynasty only maintained control of northern China.
C) Buddhism was widely suppressed by most local rulers.
D) Nanjing became the capital of southern China.
A) A eunuch ruled China through child emperors.
B) The Han Dynasty only maintained control of northern China.
C) Buddhism was widely suppressed by most local rulers.
D) Nanjing became the capital of southern China.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What new method for choosing government officials was introduced in 605 C.E. under the Sui Dynasty?
A) Written examinations
B) Military challenges
C) Monastic training
D) Oral examinations
A) Written examinations
B) Military challenges
C) Monastic training
D) Oral examinations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
How did Empress Wu of the Tang seize power for herself?
A) She waged a coup d'état against her husband.
B) She took advantage of the illness of Emperor Gaozong.
C) She murdered her two sons.
D) She claimed she was pregnant with the dead emperor's son.
A) She waged a coup d'état against her husband.
B) She took advantage of the illness of Emperor Gaozong.
C) She murdered her two sons.
D) She claimed she was pregnant with the dead emperor's son.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
What was one of the objections to Buddhism in China?
A) Buddhists sought to build monasteries on land that was sacred to Confucians.
B) Buddhists wanted to provide education for everyone, not just sons of the nobility.
C) Buddhist monks established missionaries to convert all people, including members of the imperial family.
D) Buddhist monasteries and temples were built on untaxed land, and monks did not perform labor service.
A) Buddhists sought to build monasteries on land that was sacred to Confucians.
B) Buddhists wanted to provide education for everyone, not just sons of the nobility.
C) Buddhist monks established missionaries to convert all people, including members of the imperial family.
D) Buddhist monasteries and temples were built on untaxed land, and monks did not perform labor service.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following was a result of increased Japanese contact with the Asian mainland in the eighth century C.E.?
A) The introduction of Buddhism
B) A general decline in prices due to competition
C) A smallpox epidemic
D) The disappearance of the Japanese language
A) The introduction of Buddhism
B) A general decline in prices due to competition
C) A smallpox epidemic
D) The disappearance of the Japanese language

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The Tang Dynasty is said to have been one of the high points of Chinese civilization. What were the accomplishments of this period in Chinese history?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Why were the Yamato rulers of Japan able to come to power?
A) They had a strong military and claimed to be descended from the sun-goddess.
B) They claimed they had been chosen by the Tang and the Silla.
C) They claimed they possessed special powers that would ensure an overthrow of the Han Dynasty.
D) They promised material wealth for all followers and to never allow women to rule.
A) They had a strong military and claimed to be descended from the sun-goddess.
B) They claimed they had been chosen by the Tang and the Silla.
C) They claimed they possessed special powers that would ensure an overthrow of the Han Dynasty.
D) They promised material wealth for all followers and to never allow women to rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which area of East Asia was the least affected by Chinese cultural influences?
A) Japan
B) Tibet
C) Korea
D) Vietnam
A) Japan
B) Tibet
C) Korea
D) Vietnam

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What was the native religion of Japan?
A) Zen
B) Shinto
C) Yamato
D) Mahayana
A) Zen
B) Shinto
C) Yamato
D) Mahayana

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Prince Shōtoku's reforms of Japan included adopting what administrative ideas from China?
A) Using Legalism to organize a society
B) Instituting a ladder of ranks and using Confucianism as a guiding principle
C) Administering the country through a Daoist hands-off approach
D) Establishing an official policy of "family comes first"
A) Using Legalism to organize a society
B) Instituting a ladder of ranks and using Confucianism as a guiding principle
C) Administering the country through a Daoist hands-off approach
D) Establishing an official policy of "family comes first"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What was the extent of the expansion of Chinese territory and trade during the Han empire? What regions were added to the empire?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Who established the Nam Viet kingdom in the third century B.C.E.?
A) A Buddhist monk
B) A Confucian scholar
C) A former Qin general
D) A Viet prince
A) A Buddhist monk
B) A Confucian scholar
C) A former Qin general
D) A Viet prince

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What were the reasons for suspicion of, and sometime persecution of, Buddhism in China?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
How did the Han promote Confucianism, and did the philosophy aid the government?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Explain the difference between Pure Land and Chan Buddhism under the Tang.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
As evidenced by Map 7.3, "The Spread of Buddhism, ca. 500 B.C.E.-800 C.E.," which of the following is true? 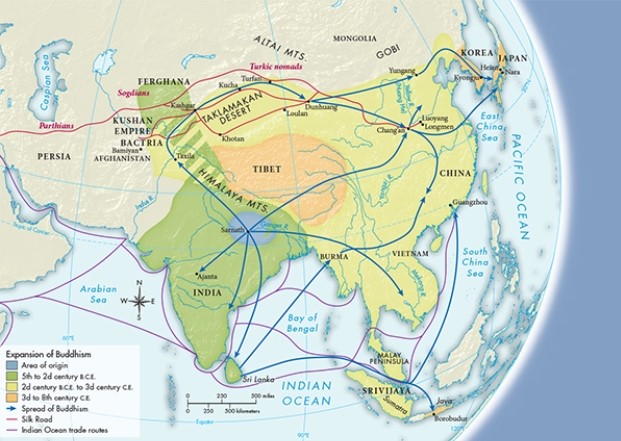
A) Buddhism typically spread in a pattern that mimicked major trade routes.
B) Buddhism took longer to spread in the east than in the west.
C) Buddhism would have never reached Tibet if not for the access granted by the Indus River,
D) Buddhism was introduced in the Kushan empire later than in most other regions.

A) Buddhism typically spread in a pattern that mimicked major trade routes.
B) Buddhism took longer to spread in the east than in the west.
C) Buddhism would have never reached Tibet if not for the access granted by the Indus River,
D) Buddhism was introduced in the Kushan empire later than in most other regions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Describe the Tang city. Who lived in it, and what kinds of goods were traded there?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Why was Buddhism so appealing to the people of China?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Who did the Vietnamese Trung sisters lead an uprising against in 39 C.E.?
A) Han rulers
B) Trieu Da
C) Nam Viet
D) Qin officials
A) Han rulers
B) Trieu Da
C) Nam Viet
D) Qin officials

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Explain what the Silk Road was and how China prospered from it beginning with the Han Dynasty onward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How do the Han and Roman empires compare in terms of how they handled peoples on their borders?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
According to Map 7.2, "The Silk Trade in the Seventh Century C.E.," the western end of the Silk Road terminated in the middle of territory that was once a part of which ancient civilization? 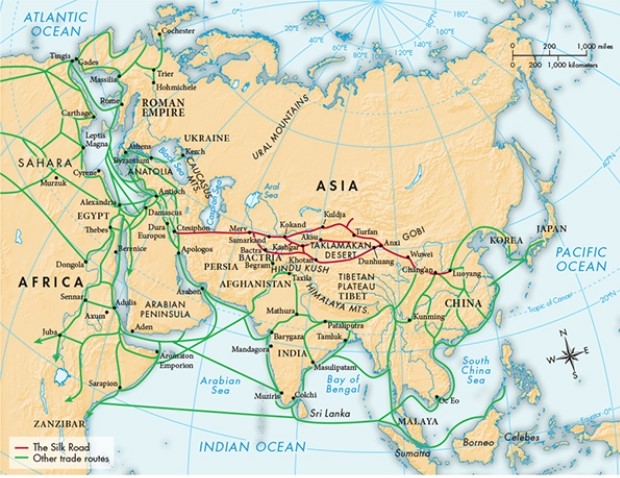
A) Egypt
B) Greece
C) Persia
D) Mesopotamia

A) Egypt
B) Greece
C) Persia
D) Mesopotamia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the three kingdoms of Korea was able to unify the entire peninsula under its control?
A) Paekche
B) Choson
C) Koguryŏ
D) Silla
A) Paekche
B) Choson
C) Koguryŏ
D) Silla

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Describe the relationship between Korea and Japan from the fourth and sixth centuries. What was exchanged between the two?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Use the following to answer questions :
Nara
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.
Nara
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
What different solutions did Chinese statesmen from the Qin era through the Tang use to address the problem of aggressive nomads to the north and west?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the following to answer questions :
eunuchs
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.
eunuchs
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following to answer questions :
Pure Land
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.
Pure Land
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following to answer questions :
Confucian classics
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.
Confucian classics
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
What did the Qin emperor standardize, and how did that standardization help him organize and rule his realm?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following to answer questions :
Grand Canal
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.
Grand Canal
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following to answer questions :
Silk Road
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.
Silk Road
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the following to answer questions :
Records of the Grand Historian
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.
Records of the Grand Historian
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the following to answer questions :
Chan
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.
Chan
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following to answer questions :
Great Wall
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.
Great Wall
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use the following to answer questions :
Shinto
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.
Shinto
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What were the distinctive features of the Han period, and how did the Han Dynasty build on its predecessor, the Qin Dynasty?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Use the following to answer questions :
tributary system
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.
tributary system
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
What was life like for peasants during the Han Dynasty? Include a description of the role of women and children.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the following to answer questions :
Age of Division
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.
Age of Division
A)A rammed-earth fortification built along the northern border of China during the reign of the First Emperor.
B)The ancient texts recovered during the Han Dynasty that Confucian scholars treated as sacred scriptures.
C)A comprehensive history of China written by Sima Qian.
D)The trade routes across Central Asia linking China to western Eurasia.
E)An arrangement first established during the Han Dynasty to regulate contact with foreign powers. States and tribes beyond its borders sent envoys bearing gifts and received gifts in return.
F)Castrated males who played an important role as palace servants.
G)The period after the fall of the Han Dynasty, when China was politically divided.
H)A waterway, built during the Sui Dynasty, that connected the Yellow and Yangzi Rivers. It was notable for strengthening China's internal cohesion and economic development.
I)A school of Buddhism that taught that by calling on the Buddha Amitabha, one could achieve rebirth in Amitabha's paradise.
J)A school of Buddhism (known in Japan as Zen) that rejected the authority of the sutras and claimed the superiority of mind-to-mind transmission of Buddhist truths.
K)The Way of the Gods, Japan's native religion.
L)Japan's capital and first true city; it was established in 710 and modeled on the Tang capital of Chang'an.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Describe the impact of Chinese civilization on Vietnam and Korea. What aspects of Vietnamese culture were most affected by China, and how were those elements spread from Chinese civilizations? How did non-Chinese accommodate themselves (or not) to these influences from China?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 77 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



