Deck 5: The Greek Experience, 3500-30 Bce
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: The Greek Experience, 3500-30 Bce
1
How did the geography of Greece affect its development?
A) It had little impact on the development of Greek society.
B) It enabled a strong central government to dominate the political order.
C) It helped to unite the Greek city-states.
D) It was a divisive force in Greek life.
A) It had little impact on the development of Greek society.
B) It enabled a strong central government to dominate the political order.
C) It helped to unite the Greek city-states.
D) It was a divisive force in Greek life.
It was a divisive force in Greek life.
2
What two law-making bodies guided Athenian political life?
A) The boule and the ecclesia
B) The agora and the chora
C) The archon and the boule
D) The agora and the archon
A) The boule and the ecclesia
B) The agora and the chora
C) The archon and the boule
D) The agora and the archon
The boule and the ecclesia
3
What important position did Solon hold as he reformed Athens?
A) King
B) Archon
C) Emperor
D) Tyrant
A) King
B) Archon
C) Emperor
D) Tyrant
Archon
4
According to Map 5.3, "Alexander's Conquests, 336-324, B.C.E.," during his trek through Egypt, Alexander successfully overcame which obstacle that some historians suggest had long protected Egypt from invasion? 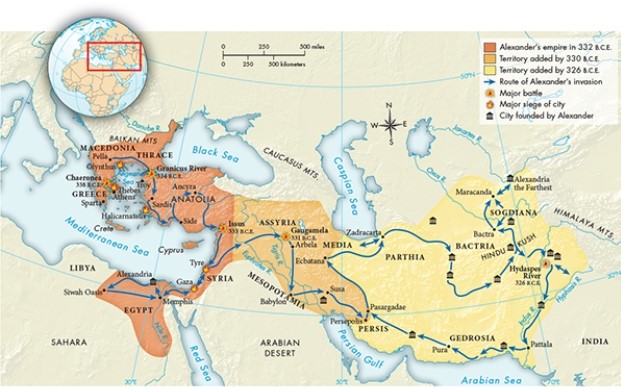
A) He gained access to the Nile River Valley.
B) He invaded the heart of Egyptian territory via the Red Sea
C) His army traversed the heart of the Arabian Desert. .
D) He crossed the Sahara Desert.

A) He gained access to the Nile River Valley.
B) He invaded the heart of Egyptian territory via the Red Sea
C) His army traversed the heart of the Arabian Desert. .
D) He crossed the Sahara Desert.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Athens and Persia began a series of wars over Greek cities in what region?
A) Peloponnesus
B) Macedonia
C) Ionia
D) Crete
A) Peloponnesus
B) Macedonia
C) Ionia
D) Crete

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following was one of the causes of Greek colonization and a particularly persistent problem for Sparta?
A) A lack of financial prosperity in the polis
B) Overpopulation and a limited food supply
C) The need to find new gods to worship
D) An overabundance of natural resources
A) A lack of financial prosperity in the polis
B) Overpopulation and a limited food supply
C) The need to find new gods to worship
D) An overabundance of natural resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
What did Solon accomplish through his reforms in Athens?
A) He established democracy.
B) He established social equality.
C) He gave common citizens a place in the assembly.
D) He eliminated the position of chief magistrate.
A) He established democracy.
B) He established social equality.
C) He gave common citizens a place in the assembly.
D) He eliminated the position of chief magistrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The crowning achievement of Pericles's rebuilding of the Acropolis was the Parthenon, a temple dedicated to which of the following?
A) Athena and the greatness of Athens
B) Zeus and the idea of a unified Greece
C) Poseidon and Athens's control of the seas
D) Aphrodite and the importance of love
A) Athena and the greatness of Athens
B) Zeus and the idea of a unified Greece
C) Poseidon and Athens's control of the seas
D) Aphrodite and the importance of love

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
How did the Lycurgan system in Sparta shape its political organization?
A) It led to the creation of a society ruled by an aristocratic, warrior elite.
B) It led to the start of a dictatorship controlled by the most powerful Spartan general.
C) It led to the development of a democratic state in which helot and Spartan ruled together.
D) It led to the erosion of Spartan military power in favor of the helots.
A) It led to the creation of a society ruled by an aristocratic, warrior elite.
B) It led to the start of a dictatorship controlled by the most powerful Spartan general.
C) It led to the development of a democratic state in which helot and Spartan ruled together.
D) It led to the erosion of Spartan military power in favor of the helots.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Which of the following refers to heavily armed Greek foot soldiers?
A) Hoplites
B) Acropolis
C) Chora
D) Legionaries
A) Hoplites
B) Acropolis
C) Chora
D) Legionaries

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which of the following contributed to the outbreak of the Peloponnesian War?
A) Spartan domination of the Aegean
B) Athenian imperialism
C) A Persian invasion of Asia Minor
D) A Spartan attempt to gain control of Ionia
A) Spartan domination of the Aegean
B) Athenian imperialism
C) A Persian invasion of Asia Minor
D) A Spartan attempt to gain control of Ionia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Which of the following was true of Spartan men?
A) They saw their wives as partners and equals.
B) They viewed military service as a necessary evil.
C) Their most meaningful relationships were same-sex ones.
D) They valued family above all else.
A) They saw their wives as partners and equals.
B) They viewed military service as a necessary evil.
C) Their most meaningful relationships were same-sex ones.
D) They valued family above all else.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
According to Map 5.1, "Classical Greece, ca. 450 B.C.E.," which geographic features lent themselves to the political fragmentation of Greece, but were not present in ancient civilizations such as Egypt or Mesopotamia? 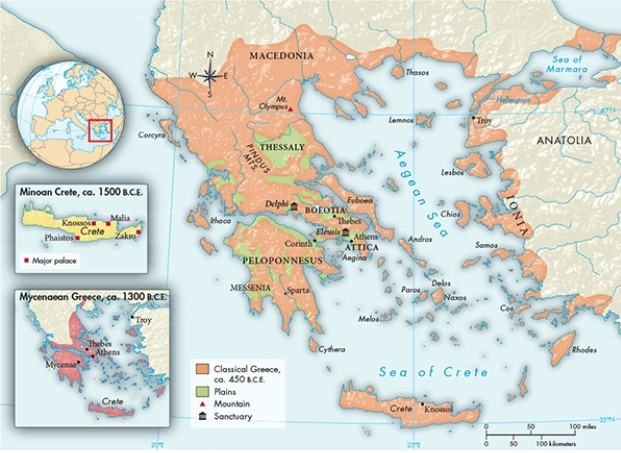
A) Rugged terrain and numerous island settlements
B) Internal waterways and key urban areas scattered over a major peninsula
C) Mountains and peninsular sanctuaries
D) Deserts and major inland waterways

A) Rugged terrain and numerous island settlements
B) Internal waterways and key urban areas scattered over a major peninsula
C) Mountains and peninsular sanctuaries
D) Deserts and major inland waterways

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
According to Map 5.2, "Greek Colonization, ca. 750-550 B.C.E.," how did Greek colonization routes mimic those of the Phoenicians? 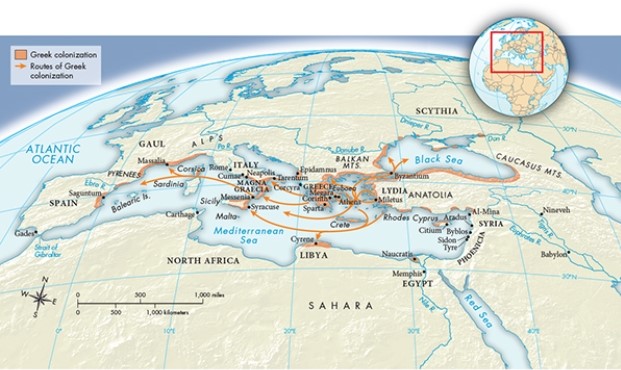
A) Their migratory route typically flowed in an easterly direction.
B) They built their most important settlements in the region of Syria.
C) They largely avoided contact with the coastline of North Africa.
D) Their primary route was along the coastlines of the Mediterranean Sea.

A) Their migratory route typically flowed in an easterly direction.
B) They built their most important settlements in the region of Syria.
C) They largely avoided contact with the coastline of North Africa.
D) Their primary route was along the coastlines of the Mediterranean Sea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What was an agora?
A) A temple complex
B) A fortified stronghold
C) A marketplace
D) A plot of arable land for farming
A) A temple complex
B) A fortified stronghold
C) A marketplace
D) A plot of arable land for farming

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
How was the Greek polis different from older models of city-states?
A) The polis was strictly a political institution.
B) The polis was a community of citizens.
C) The polis was unified by one shared religion.
D) The polis was seen as a kingdom under a divine ruler.
A) The polis was strictly a political institution.
B) The polis was a community of citizens.
C) The polis was unified by one shared religion.
D) The polis was seen as a kingdom under a divine ruler.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What does the term oligarchy mean?
A) "The rule of the few"
B) "The rule of the people"
C) "The rule of the excellent"
D) "The rule of the king"
A) "The rule of the few"
B) "The rule of the people"
C) "The rule of the excellent"
D) "The rule of the king"

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following is true of Spartan women?
A) They were expected to assist their husbands and travel with them on military campaigns.
B) They enjoyed a more active, public life than most other Greek women.
C) Their single responsibility was to have many children.
D) They were more restricted than most other Greek women.
A) They were expected to assist their husbands and travel with them on military campaigns.
B) They enjoyed a more active, public life than most other Greek women.
C) Their single responsibility was to have many children.
D) They were more restricted than most other Greek women.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Why was the growth of great empires (like those in Mesopotamia and Egypt) less likely to develop in ancient Greece?
A) The dominance of a middle class, not peasants, worked against empire building.
B) Its people were too ethnically and culturally diverse.
C) The rugged terrain discouraged expansion of any one center.
D) Greek military technology was slow to develop.
A) The dominance of a middle class, not peasants, worked against empire building.
B) Its people were too ethnically and culturally diverse.
C) The rugged terrain discouraged expansion of any one center.
D) Greek military technology was slow to develop.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following is true of the Minoans?
A) They formed a society that lived on the island of Crete.
B) They settled in Greece after they were driven from their homes in Persia.
C) They were a matriarchal society that lived on the island of Sicily.
D) They were the first peoples who formed a society on the Greek peninsula.
A) They formed a society that lived on the island of Crete.
B) They settled in Greece after they were driven from their homes in Persia.
C) They were a matriarchal society that lived on the island of Sicily.
D) They were the first peoples who formed a society on the Greek peninsula.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
What was the main function of women from citizen families in Athens?
A) To accompany their husbands in public settings
B) To run family estates and manage businesses while their husbands were at war
C) To perform manual labor in the fields or sell goods in the agora
D) To bear and raise children
A) To accompany their husbands in public settings
B) To run family estates and manage businesses while their husbands were at war
C) To perform manual labor in the fields or sell goods in the agora
D) To bear and raise children

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Philip II of Macedonia was able to conquer Greece because the Greek city-states were
A) still occupied fighting the Persians.
B) severely weakened by earthquakes.
C) unable to put aside their quarrels and unite to defend themselves.
D) unprepared for his surprise attack.
A) still occupied fighting the Persians.
B) severely weakened by earthquakes.
C) unable to put aside their quarrels and unite to defend themselves.
D) unprepared for his surprise attack.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What did Alexander the Great do after the Persian Empire fell?
A) Set out to conquer much of the rest of Asia
B) Returned home to Macedonia
C) Gave command of Persia to his favorite general
D) Turned west toward Italy
A) Set out to conquer much of the rest of Asia
B) Returned home to Macedonia
C) Gave command of Persia to his favorite general
D) Turned west toward Italy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following was a central component of the expansion of Alexander the Great's empire, but was absent from the process of Greek colonization as illustrated in Map 5.2, "Greek Colonization, ca. 750-550 B.C.E."? 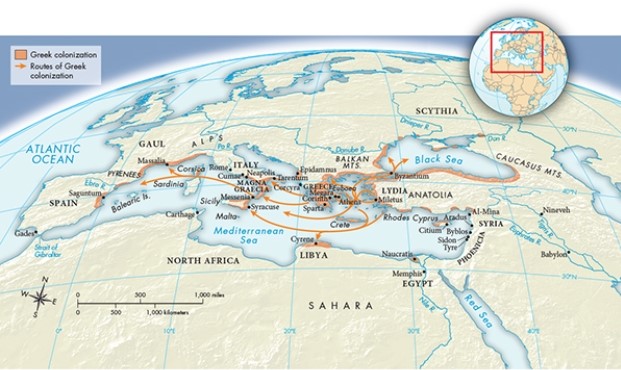
A) Predominantly westward-oriented migratory patterns
B) Contact with North Africa
C) Major military conflict
D) The founding of settlements in Southern Italy

A) Predominantly westward-oriented migratory patterns
B) Contact with North Africa
C) Major military conflict
D) The founding of settlements in Southern Italy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which student of Socrates developed the theory of "forms"?
A) Plato
B) Aristotle
C) Ptolemy
D) Zeno
A) Plato
B) Aristotle
C) Ptolemy
D) Zeno

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What did the Pre-Socratics conclude from their observations?
A) That the universe consisted of four substances--air, fire, earth, and water
B) That one god had created the entire world
C) That the universe was too complex to be understood
D) That humans had achieved physical perfection
A) That the universe consisted of four substances--air, fire, earth, and water
B) That one god had created the entire world
C) That the universe was too complex to be understood
D) That humans had achieved physical perfection

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
What happened to Alexander's empire following his death?
A) His empire was torn apart by more than forty years of civil war.
B) His son ruled briefly as emperor until he was assassinated.
C) Athens declared its independence from Macedonia.
D) His empire was peacefully partitioned by a trio of powerful generals.
A) His empire was torn apart by more than forty years of civil war.
B) His son ruled briefly as emperor until he was assassinated.
C) Athens declared its independence from Macedonia.
D) His empire was peacefully partitioned by a trio of powerful generals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How did the Hellenistic city differ from the polis?
A) It perceived itself as a community of citizens.
B) It was united by religious rituals.
C) It tolerated same-sex relations.
D) It was not autonomous and had to follow royal orders.
A) It perceived itself as a community of citizens.
B) It was united by religious rituals.
C) It tolerated same-sex relations.
D) It was not autonomous and had to follow royal orders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What did Hippocrates think was the best way to treat illnesses?
A) Pray that the evil spirits would leave
B) Use bloodletting and other invasive techniques to remove evil spirits from the body
C) Use natural means to address imbalances in the four basic humors
D) Offer more sacrifices to the gods
A) Pray that the evil spirits would leave
B) Use bloodletting and other invasive techniques to remove evil spirits from the body
C) Use natural means to address imbalances in the four basic humors
D) Offer more sacrifices to the gods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The spread of Hellenistic culture was bolstered by Alexander's tradition of doing what in his newly conquered territories?
A) Forcibly resettling conquered peoples in Greece
B) Founding new cities with mixed populations
C) Placing Macedonian kings in charge
D) Censoring art and culture that criticized him
A) Forcibly resettling conquered peoples in Greece
B) Founding new cities with mixed populations
C) Placing Macedonian kings in charge
D) Censoring art and culture that criticized him

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What crime was Socrates tried and executed for in 399 B.C.E.?
A) Giving information to a Persian intelligence agent
B) Undermining the authority of the government
C) Denying the divinity of Zeus
D) Corrupting the youth of Athens
A) Giving information to a Persian intelligence agent
B) Undermining the authority of the government
C) Denying the divinity of Zeus
D) Corrupting the youth of Athens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What was unusual about slaves in Athens?
A) All slaves were captured and imported from the wars in North Africa.
B) Slaves were legally forbidden to read.
C) Slaves could vote as a result of democratic reforms.
D) Slaves were paid for their work.
A) All slaves were captured and imported from the wars in North Africa.
B) Slaves were legally forbidden to read.
C) Slaves could vote as a result of democratic reforms.
D) Slaves were paid for their work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
After Philip II of Macedonia unified Greece, he called upon Greeks and Macedonians to do which of the following?
A) Promise five years of peace to allow for recovery from the war
B) Work together to liberate the Ionian colonies from Persian control
C) Move the royal court to Athens and build him a new palace
D) Form a naval alliance with Persia and invade India
A) Promise five years of peace to allow for recovery from the war
B) Work together to liberate the Ionian colonies from Persian control
C) Move the royal court to Athens and build him a new palace
D) Form a naval alliance with Persia and invade India

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
By the classical era, Greek religion focused on which of the following?
A) Worship of a group of gods understood to live on Mount Olympus
B) Monotheistic worship of Zeus as the one true god
C) Worship of only male deities, as female deities came to be seen as too powerless
D) Individual worship of a polis's chosen deity and abandonment of all Pan-Hellenic rituals
A) Worship of a group of gods understood to live on Mount Olympus
B) Monotheistic worship of Zeus as the one true god
C) Worship of only male deities, as female deities came to be seen as too powerless
D) Individual worship of a polis's chosen deity and abandonment of all Pan-Hellenic rituals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
How was the daily life of Greek elites similar to the lives of more ordinary people?
A) All people in Athens were relatively affluent and could afford a "good life."
B) Everyone paid heavy annual taxes regardless of social class.
C) They had a relatively modest material standard of living.
D) All families depended almost entirely on slave labor.
A) All people in Athens were relatively affluent and could afford a "good life."
B) Everyone paid heavy annual taxes regardless of social class.
C) They had a relatively modest material standard of living.
D) All families depended almost entirely on slave labor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
According to Aristotle, true knowledge could be discerned from which of the following?
A) Contemplation of perfect possibilities
B) Observations of the real world
C) Prayer or divine intervention
D) Specialized religious ritual
A) Contemplation of perfect possibilities
B) Observations of the real world
C) Prayer or divine intervention
D) Specialized religious ritual

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
After defeating Athens in the Peloponnesian War, Sparta was defeated in 371 B.C.E. by what city-state?
A) Alexandria
B) Corinth
C) Delos
D) Thebes
A) Alexandria
B) Corinth
C) Delos
D) Thebes

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is true of the Hellenistic city?
A) It had homogeneous populations.
B) It was hampered by an inefficient bureaucracy that proved difficult to maintain.
C) It was overseen by kings with limited authority.
D) It resembled modern cities and served as both a cultural and an economic center.
A) It had homogeneous populations.
B) It was hampered by an inefficient bureaucracy that proved difficult to maintain.
C) It was overseen by kings with limited authority.
D) It resembled modern cities and served as both a cultural and an economic center.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Why did Alexander's eastward expansion of his empire stop at the Hyphasis River?
A) His Macedonian army refused to continue fighting.
B) The powerful Indian army defeated the Macedonians.
C) The Persian army attacked him from the west.
D) His spiritual advisers warned of unfavorable omens.
A) His Macedonian army refused to continue fighting.
B) The powerful Indian army defeated the Macedonians.
C) The Persian army attacked him from the west.
D) His spiritual advisers warned of unfavorable omens.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The plays of Sophocles emphasized the precedence of which of the following over human law and customs?
A) Family needs
B) Personal happiness
C) Military success
D) Divine law
A) Family needs
B) Personal happiness
C) Military success
D) Divine law

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Describe the complex of Knossos on Crete and what it indicates about Minoan culture.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which early scientist dissected corpses to learn more about anatomy and physiology?
A) Euclid
B) Archimedes
C) Hippocrates
D) Herophilus
A) Euclid
B) Archimedes
C) Hippocrates
D) Herophilus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Describe the various commodities that were the basis of the commercial trading network of the Hellenistic world. Consider material and nonmaterial trade. How did this commercial network enhance the unification of the Mediterranean world and beyond?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following were major exports from Greek cities during the classical and Hellenistic periods?
A) Gold and precious stones
B) Olive oil and wine
C) Feta cheese and lamb
D) Silks and pearls
A) Gold and precious stones
B) Olive oil and wine
C) Feta cheese and lamb
D) Silks and pearls

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
How do the democratic and oligarchic styles of government in the Greek polis compare? At what point might a tyrant be called for?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Discuss how Athenian playwrights used their forum to address issues and attempt to understand or resolve life's basic conflicts.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Describe the cultural diversity of Alexander's empire. What happened (politically and culturally) to his empire after his death?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The extensive coastline illustrated in Map 5.1, "Classical Greece, ca. 450 B.C.E.," played an important role in the development of 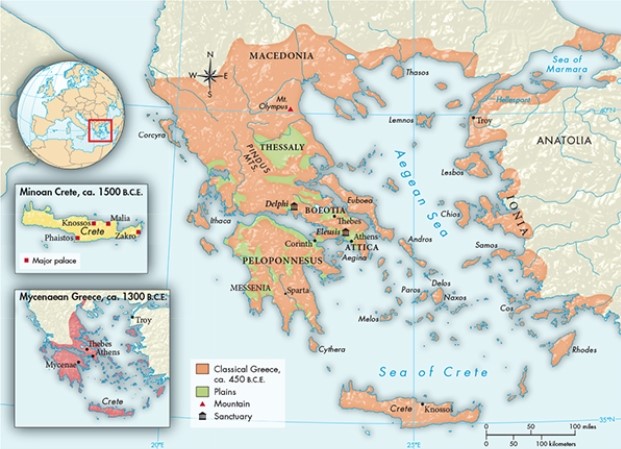
A) major settlements in the interior of Anatolia.
B) a wide variety of agricultural products.
C) that region's numerous land-based trade routes.
D) the Greeks as a seafaring people.

A) major settlements in the interior of Anatolia.
B) a wide variety of agricultural products.
C) that region's numerous land-based trade routes.
D) the Greeks as a seafaring people.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Why were slaves in high demand throughout the Hellenistic world?
A) Slaves were traded for goods from China and India.
B) Large-scale agriculture was dependent on slaves.
C) Monarchs equated their power with how many slaves they owned.
D) Manual labor continued to produce most goods.
A) Slaves were traded for goods from China and India.
B) Large-scale agriculture was dependent on slaves.
C) Monarchs equated their power with how many slaves they owned.
D) Manual labor continued to produce most goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Mystery religions featured which of the following?
A) The promise of reincarnation
B) The worship of a wide range of spirits and deities, both known and unknown
C) A belief in the mysterious and sometimes malevolent force of Tyche
D) A body of rituals and beliefs not divulged to anyone not initiated into them
A) The promise of reincarnation
B) The worship of a wide range of spirits and deities, both known and unknown
C) A belief in the mysterious and sometimes malevolent force of Tyche
D) A body of rituals and beliefs not divulged to anyone not initiated into them

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What did the philosophy of Stoicism strongly emphasize?
A) Personal achievement
B) The acceptance of Tyche or chance
C) The ability to endure suffering
D) Living a virtuous life
A) Personal achievement
B) The acceptance of Tyche or chance
C) The ability to endure suffering
D) Living a virtuous life

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Describe the geography of the areas inhabited by the Greeks. How did it affect the development of Greek civilization?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How do the mystery religions of the Hellenistic world represent a merging of Western (Greek) and Eastern cultures?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Archimedes's many contributions to Hellenistic science include his theories about which of the following?
A) Hydrostatics
B) Heliocentrism
C) Physics
D) Astronomy
A) Hydrostatics
B) Heliocentrism
C) Physics
D) Astronomy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What were some of the problems that led to Solon's reforms in Athens?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
We know that Mycenaean civilization was particularly prone to warfare because of what evidence?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
How was Hellenistic trading made easier?
A) Most traders spoke a variety of languages.
B) Slaves working as pirates moved goods all over the Hellenistic world.
C) Coinage was developed to facilitate convenient, standard payments.
D) Traders began using camels to move goods in Europe.
A) Most traders spoke a variety of languages.
B) Slaves working as pirates moved goods all over the Hellenistic world.
C) Coinage was developed to facilitate convenient, standard payments.
D) Traders began using camels to move goods in Europe.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How did the Peloponnesian War grow out of the Persian Wars?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What was Aristarchus's most important contribution to astronomy?
A) He argued that Earth is far larger than the sun.
B) He theorized that the stars are close to Earth and to one another.
C) He believed that Earth and the planets revolve around the sun.
D) He asserted that telescopes are necessary for all astronomical work.
A) He argued that Earth is far larger than the sun.
B) He theorized that the stars are close to Earth and to one another.
C) He believed that Earth and the planets revolve around the sun.
D) He asserted that telescopes are necessary for all astronomical work.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
What did Epicurus believe was the principal good of human life?
A) Individual contribution to the civic life of the polis
B) Pleasure, which he defined as the absence of pain
C) The accumulation of power and wealth
D) Helping others
A) Individual contribution to the civic life of the polis
B) Pleasure, which he defined as the absence of pain
C) The accumulation of power and wealth
D) Helping others

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Use the following to answer questions
oligarchy
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.
oligarchy
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the following to answer questions
Hellenization
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.
Hellenization
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Describe Greece in what historians have called the Dark Age. How did the development of the polis help Greece avoid some of the weaknesses of this period?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following to answer questions
Epicureanism
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.
Epicureanism
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The Hellenistic civilization saw the spread of cities founded by Alexander and his successors. What were the role and impact of these new cities?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the following to answer questions
polis
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.
polis
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following to answer questions
Stoicism
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.
Stoicism
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following to answer questions
hoplites
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.
hoplites
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the following to answer questions
Platonic ideals
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.
Platonic ideals
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the following to answer questions
mystery religions
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.
mystery religions
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Like Mesopotamian society, Greek civilization lacked political unity. Why? How did disunity affect the development of Greek society in general? What, if any, were the factors that fostered homogeneity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use the following to answer questions
Hellenistic
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.
Hellenistic
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
How did trade in the Hellenistic period provide the most enduring legacy of Alexander's empire? What long-distance trade patterns and relationships were established?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Trace the development of philosophy and science from the Pre-Socratic origins through Aristotle. What were the most significant developments? What was the general principle that guided Greek philosophers? How did this change in the Hellenistic period?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following to answer questions
democracy
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.
democracy
A)Generally translated as "city-state," it was the basic political and institutional unit of ancient Greece.
B)Heavily armed citizens who served as infantrymen and fought to defend the polis.
C)A type of Greek government in which all citizens administered the workings of government.
D)A type of Greek government in which citizens who owned a certain amount of property ruled.
E)Belief systems that were characterized by secret doctrines, rituals of initiation, and sometimes the promise of rebirth or an afterlife.
F)In Plato's thought, the eternal unchanging ideal forms that are the essence of true reality.
G)Literally means "like the Greek"; describes the period from the death of Alexander the Great in 323 B.C.E. to the Roman conquest of Egypt in 30 B.C.E., when Greek culture spread.
H)The spread of Greek ideas, culture, and traditions to non-Greek groups across a wide area.
I)A system of philosophy based on the teachings of Epicurus, who viewed a life of contentment, free from fear and suffering, as the greatest good.
J)A philosophy, based on the ideas of Zeno, that held that people could be happy only when living in accordance with nature and accepting whatever happened.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



