Deck 31: Review
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/82
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 31: Review
1
In 1947, what happened when the United Nations proposed partitioning Palestine into separate Arab and Jewish states?
A) The proposal was accepted by both sides.
B) The proposal was accepted by the Jews but rejected by the Arabs.
C) The proposal was accepted by the Arabs but rejected by the Jews.
D) The proposal was rejected by both sides.
A) The proposal was accepted by both sides.
B) The proposal was accepted by the Jews but rejected by the Arabs.
C) The proposal was accepted by the Arabs but rejected by the Jews.
D) The proposal was rejected by both sides.
The proposal was accepted by the Jews but rejected by the Arabs.
2
What was the goal of the Truman Doctrine?
A) To contain communism to areas already occupied by the Soviet army
B) To rebuild the western European economies
C) To force the Communists out of eastern Europe
D) To destroy Communist parties in western Europe
A) To contain communism to areas already occupied by the Soviet army
B) To rebuild the western European economies
C) To force the Communists out of eastern Europe
D) To destroy Communist parties in western Europe
To contain communism to areas already occupied by the Soviet army
3
How was Korea divided in 1945?
A) Into four zones of influence
B) Into Soviet and American zones of occupation
C) Into Soviet and Japanese zones of occupation
D) Into United Nations mandate zones
A) Into four zones of influence
B) Into Soviet and American zones of occupation
C) Into Soviet and Japanese zones of occupation
D) Into United Nations mandate zones
Into Soviet and American zones of occupation
4
How can American military involvement in Vietnam be characterized?
A) It never had much support in the general population.
B) Intervention in Vietnam was based on U.S. imperialism.
C) It grew out of the ideology of containment.
D) It was part of a larger strategy to destroy the Soviet Union.
A) It never had much support in the general population.
B) Intervention in Vietnam was based on U.S. imperialism.
C) It grew out of the ideology of containment.
D) It was part of a larger strategy to destroy the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following resulted after Gamal Abdel Nasser ordered the Egyptian army to take control of the Suez Canal in 1956?
A) The Soviet Union joined forces with Britain and France to prevent Egyptian control of the canal.
B) A violent battle erupted, and the resulting treaty established joint control of the canal between Egypt, Britain, and France.
C) The United States, fearing a Soviet-Egyptian alliance, negotiated a cease-fire granting Egypt control of the canal.
D) The Soviet Union, fearing a U.S.-Egyptian alliance, negotiated a cease-fire granting Egypt control of the canal.
A) The Soviet Union joined forces with Britain and France to prevent Egyptian control of the canal.
B) A violent battle erupted, and the resulting treaty established joint control of the canal between Egypt, Britain, and France.
C) The United States, fearing a Soviet-Egyptian alliance, negotiated a cease-fire granting Egypt control of the canal.
D) The Soviet Union, fearing a U.S.-Egyptian alliance, negotiated a cease-fire granting Egypt control of the canal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What defined the rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union during the Cold War?
A) Both nations were determined to dominate NATO.
B) Both nations sought to spread their culture through imperialism and "civilize" other states.
C) Both nations engaged in a fierce commercial rivalry.
D) Both nations saw themselves as the defenders of important ideological principles.
A) Both nations were determined to dominate NATO.
B) Both nations sought to spread their culture through imperialism and "civilize" other states.
C) Both nations engaged in a fierce commercial rivalry.
D) Both nations saw themselves as the defenders of important ideological principles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Why was India split into two separate independent nations, India and Pakistan, in 1947?
A) Great Britain insisted that India be split into two nations as a condition of granting independence.
B) Muhammad Ali Jinnah and the Muslim League insisted on the creation of an independent Muslim state.
C) Mohandas Gandhi and the Indian National Congress Party insisted on the creation of an independent Hindu state.
D) A popular vote across India determined that the nation should be split into a Muslim state and a Hindu state.
A) Great Britain insisted that India be split into two nations as a condition of granting independence.
B) Muhammad Ali Jinnah and the Muslim League insisted on the creation of an independent Muslim state.
C) Mohandas Gandhi and the Indian National Congress Party insisted on the creation of an independent Hindu state.
D) A popular vote across India determined that the nation should be split into a Muslim state and a Hindu state.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
At the Potsdam Conference, why did Stalin reject free elections in eastern Europe?
A) He worried that the United States would manipulate the results.
B) He argued that they would not be impartial because the United States would try to control them.
C) He worried that the results would be anti-Soviet and destroy his plans of a buffer zone.
D) He worried they would obligate the Soviet Union to shoulder the cost of war refugees in the region.
A) He worried that the United States would manipulate the results.
B) He argued that they would not be impartial because the United States would try to control them.
C) He worried that the results would be anti-Soviet and destroy his plans of a buffer zone.
D) He worried they would obligate the Soviet Union to shoulder the cost of war refugees in the region.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What was the central premise of Raúl Prebisch's dependency theory?
A) That many countries remained borrowers of capital and technology and producers of primary commodities
B) That many countries were dependent on the military power of the United States
C) That newly independent countries were dependent on great leadership
D) That many nations depended on the generosity of the international community
A) That many countries remained borrowers of capital and technology and producers of primary commodities
B) That many countries were dependent on the military power of the United States
C) That newly independent countries were dependent on great leadership
D) That many nations depended on the generosity of the international community

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
After gaining independence from Pakistan in 1971, Bangladesh struggled to find political and economic stability as a result of
A) famines and flooding.
B) continued violent clashes with Pakistan even after the civil war, which depleted resources.
C) the introduction of communism and subsequent struggle to establish a stable government.
D) religious disputes within the country's population.
A) famines and flooding.
B) continued violent clashes with Pakistan even after the civil war, which depleted resources.
C) the introduction of communism and subsequent struggle to establish a stable government.
D) religious disputes within the country's population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Western allies began the Berlin airlift in response to which of the following?
A) The inability to adequately aid citizens because of the destruction caused by the war
B) The humanitarian crisis in Berlin that followed the collapse of the Third Reich
C) The outbreak of the Korean War
D) Stalin's blockade of all road traffic through the Soviet zone of Germany
A) The inability to adequately aid citizens because of the destruction caused by the war
B) The humanitarian crisis in Berlin that followed the collapse of the Third Reich
C) The outbreak of the Korean War
D) Stalin's blockade of all road traffic through the Soviet zone of Germany

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
How did the United Nations differ from the earlier League of Nations?
A) The United Nations was designed to mediate international conflicts.
B) The United Nations was envisioned as a smaller organization.
C) The League of Nations was not made up of nation-states.
D) The United Nations had a more ambitious role to play.
A) The United Nations was designed to mediate international conflicts.
B) The United Nations was envisioned as a smaller organization.
C) The League of Nations was not made up of nation-states.
D) The United Nations had a more ambitious role to play.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The United Nations Security Council
A) was made up of most of the smaller member states.
B) had the power to launch nuclear attacks.
C) included five main regional powers who held veto power.
D) supported the Soviet Union in the Cold War.
A) was made up of most of the smaller member states.
B) had the power to launch nuclear attacks.
C) included five main regional powers who held veto power.
D) supported the Soviet Union in the Cold War.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Article 9 of Japan's postwar constitution did which of the following?
A) It banned ultranationalists from holding office.
B) It established a command-and-control economy.
C) It gave women the right to vote.
D) It abolished all Japanese armed forces.
A) It banned ultranationalists from holding office.
B) It established a command-and-control economy.
C) It gave women the right to vote.
D) It abolished all Japanese armed forces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was originally formed as which of the following?
A) An anti-Soviet military alliance
B) A pan-European unity alliance
C) An economic alliance to promote peace
D) A union of American states
A) An anti-Soviet military alliance
B) A pan-European unity alliance
C) An economic alliance to promote peace
D) A union of American states

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Why did Jiang Jieshi and 2 million others flee to Taiwan in 1949?
A) They were fleeing the largest typhoon in Chinese history.
B) They were fleeing the Communist takeover of mainland China
C) They were fleeing yet another Soviet invasion.
D) They were fleeing American advances into North Korea.
A) They were fleeing the largest typhoon in Chinese history.
B) They were fleeing the Communist takeover of mainland China
C) They were fleeing yet another Soviet invasion.
D) They were fleeing American advances into North Korea.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What were the effects of the American occupation of Japan?
A) Japan remained politically divided.
B) Japanese people became increasingly anti-American.
C) Japanese culture became increasingly traditional as Japanese people resisted occupation.
D) Japan became an economic power and a strong American ally.
A) Japan remained politically divided.
B) Japanese people became increasingly anti-American.
C) Japanese culture became increasingly traditional as Japanese people resisted occupation.
D) Japan became an economic power and a strong American ally.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In 1946, real power in Japan was in the hands of
A) Japanese businessmen.
B) the emperor.
C) General Douglas MacArthur.
D) Japanese military officials.
A) Japanese businessmen.
B) the emperor.
C) General Douglas MacArthur.
D) Japanese military officials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The central feature of the Marshall Plan was
A) a formal military alliance.
B) food and economic aid.
C) the provision of nuclear armaments.
D) military aid to African states.
A) a formal military alliance.
B) food and economic aid.
C) the provision of nuclear armaments.
D) military aid to African states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Who took control of territory including the Sinai Peninsula and the Golan Heights after the Six-Day War in 1967?
A) Jordan
B) Israel
C) Egypt
D) Palestine
A) Jordan
B) Israel
C) Egypt
D) Palestine

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Based on Map 31.5, "Decolonization in Africa, 1947 to the Present," the former colonies of which European power appear to have been the most unstable? 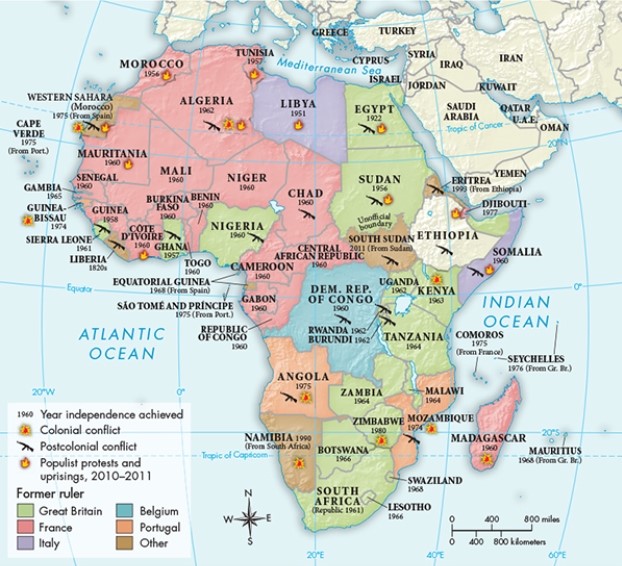
A) France
B) Britain
C) Portugal
D) Italy

A) France
B) Britain
C) Portugal
D) Italy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
What was Fidel Castro's main goal during the Cuban Revolution?
A) To make Cuba a communist country
B) To regain control of Cuba's economy and government from the United States
C) To gain wealth for himself and his allies
D) To create a fascist state
A) To make Cuba a communist country
B) To regain control of Cuba's economy and government from the United States
C) To gain wealth for himself and his allies
D) To create a fascist state

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What were the goals of economic nationalists in postwar Latin America?
A) They sought to return people to the land.
B) They sought economic domination of neighboring states.
C) They sought to end neocolonialism and develop industry.
D) They looked to expand their states politically by developing strong economies.
A) They sought to return people to the land.
B) They sought economic domination of neighboring states.
C) They sought to end neocolonialism and develop industry.
D) They looked to expand their states politically by developing strong economies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Juan Perón sought to transform the postwar Argentinian economy by
A) demanding that farmers switch to industrial production.
B) confiscating peasant agricultural production to resell it domestically.
C) encouraging the development of a domestic fashion industry.
D) arranging for government purchase and resale of all agricultural production.
A) demanding that farmers switch to industrial production.
B) confiscating peasant agricultural production to resell it domestically.
C) encouraging the development of a domestic fashion industry.
D) arranging for government purchase and resale of all agricultural production.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of these was an element of Richard Nixon's Vietnam strategy?
A) It transferred the burden of fighting the war to the Vietnamese.
B) It sought an immediate U.S. withdrawal from the conflict.
C) It insisted that the commanders of the war effort be Vietnamese generals.
D) It sought to broaden the conflict from Vietnam to other neighboring states.
A) It transferred the burden of fighting the war to the Vietnamese.
B) It sought an immediate U.S. withdrawal from the conflict.
C) It insisted that the commanders of the war effort be Vietnamese generals.
D) It sought to broaden the conflict from Vietnam to other neighboring states.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
How did white settlers in Africa respond to postwar independence movements?
A) They fought to preserve their privileged position.
B) They generally led the independence movements.
C) They attempted to unite in a white settlers union.
D) They gave away much of their land in exchange for the right to emigrate.
A) They fought to preserve their privileged position.
B) They generally led the independence movements.
C) They attempted to unite in a white settlers union.
D) They gave away much of their land in exchange for the right to emigrate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
How were post-World War II African leaders different from the interwar generation?
A) They were more willing to cooperate with colonial authorities.
B) They were less likely to be Western-educated.
C) They were typically of more humble origins.
D) They were mostly returned soldiers.
A) They were more willing to cooperate with colonial authorities.
B) They were less likely to be Western-educated.
C) They were typically of more humble origins.
D) They were mostly returned soldiers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What was the goal of Pan-Africanist thinkers?
A) They sought political revolutions in the West that might free Africa.
B) They sought to unite Africa under a single strong ruler.
C) They sought to spread African values into Europe and North America.
D) They sought black solidarity and self-government for Africans.
A) They sought political revolutions in the West that might free Africa.
B) They sought to unite Africa under a single strong ruler.
C) They sought to spread African values into Europe and North America.
D) They sought black solidarity and self-government for Africans.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What was the relationship of Fidel Castro and the Cuban Revolution to the Soviet Union and communism?
A) Castro was driven to seek the support of the Soviet Union after the United States opposed the revolution.
B) Castro was a Communist, but he allowed the revolution to proceed democratically.
C) Castro was not a Communist, but almost all of his supporters were.
D) Cuban Communists seized control of Castro's revolution shortly after he came to power.
A) Castro was driven to seek the support of the Soviet Union after the United States opposed the revolution.
B) Castro was a Communist, but he allowed the revolution to proceed democratically.
C) Castro was not a Communist, but almost all of his supporters were.
D) Cuban Communists seized control of Castro's revolution shortly after he came to power.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of these was a goal of the westernized African elite in the 1920s?
A) Increased support for traditional chiefs
B) Modest steps toward self-government
C) The end of colonial taxation
D) Immediate independence
A) Increased support for traditional chiefs
B) Modest steps toward self-government
C) The end of colonial taxation
D) Immediate independence

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The former African colonies of which European power constituted a majority of the member states in the United Nations' Afro-Asian bloc? 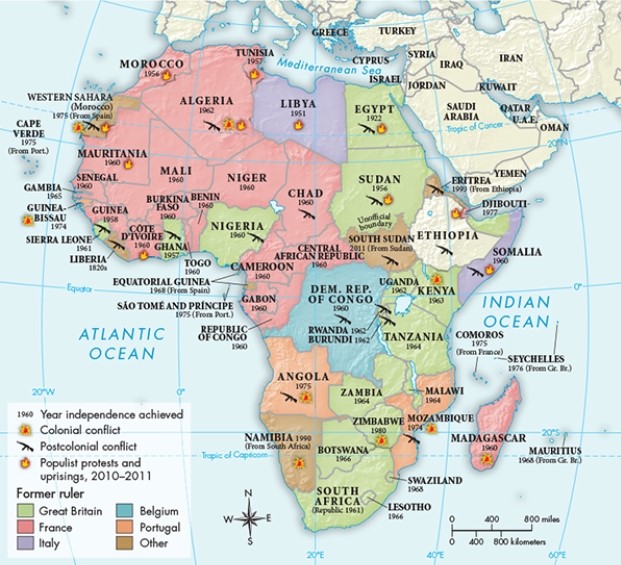
A) Great Britain
B) Belgium
C) France
D) Italy

A) Great Britain
B) Belgium
C) France
D) Italy

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
What contributed to the collapse of Juan Perón's government in 1955?
A) A small-scale American invasion
B) The death of his popular wife, Evita
C) The unwillingness of Perón to rule outside the law
D) An economic boom that provoked rivals
A) A small-scale American invasion
B) The death of his popular wife, Evita
C) The unwillingness of Perón to rule outside the law
D) An economic boom that provoked rivals

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What factor led Ghana to become the first sub-Saharan African colonial states to achieve independence?
A) As a former French colony, Ghana had a weak colonial connection.
B) Ghana had a long tradition of independent political power.
C) Ghana was home to especially violent and warlike tribes.
D) Revolution in Ghana was organized by a capable and charismatic leader.
A) As a former French colony, Ghana had a weak colonial connection.
B) Ghana had a long tradition of independent political power.
C) Ghana was home to especially violent and warlike tribes.
D) Revolution in Ghana was organized by a capable and charismatic leader.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How did Charles de Gaulle moderate calls for independence in French African colonies?
A) He threatened violent resistance to rebellions.
B) He insisted that all Africans leave France and return to strengthen African independence movements.
C) He forbade French settlers from returning from Africa.
D) He divided French colonies in Africa into thirteen separate governments.
A) He threatened violent resistance to rebellions.
B) He insisted that all Africans leave France and return to strengthen African independence movements.
C) He forbade French settlers from returning from Africa.
D) He divided French colonies in Africa into thirteen separate governments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What was Nikita Khrushchev's "secret speech" in 1956?
A) An endorsement of the capitalistic system of the West
B) A rejection of communism as theorized by Marx
C) A condemnation of the crimes of Stalin
D) A promise to undertake a war against NATO
A) An endorsement of the capitalistic system of the West
B) A rejection of communism as theorized by Marx
C) A condemnation of the crimes of Stalin
D) A promise to undertake a war against NATO

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
According to Map 31.4, "Decolonization in Asia," what is one way in which colonization in Asia differed from that of Africa? 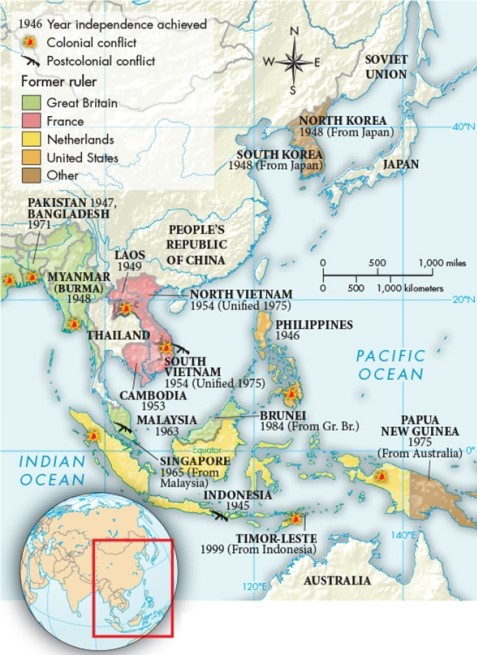
A) Australia and Great Britain held colonies in Asia.
B) The United States and the Netherlands held colonies in Asia.
C) Japan and France held colonies in Asia.
D) Malaysia and Great Britain held colonies in Asia.

A) Australia and Great Britain held colonies in Asia.
B) The United States and the Netherlands held colonies in Asia.
C) Japan and France held colonies in Asia.
D) Malaysia and Great Britain held colonies in Asia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Cuba was a virtual colony of what country until the 1930s?
A) Britain
B) Spain
C) France
D) The United States
A) Britain
B) Spain
C) France
D) The United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What political and social elements was Cuban leader Fulgencio Batista closely allied with?
A) Wealthy Cubans and multinational corporations
B) Expatriate elites and the Catholic Church
C) Liberal social reformers and journalists
D) Marxists and populist nationalists
A) Wealthy Cubans and multinational corporations
B) Expatriate elites and the Catholic Church
C) Liberal social reformers and journalists
D) Marxists and populist nationalists

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Workers who came to Europe after the war to fill low-paying jobs were known as what?
A) Migrants
B) Day laborers
C) Guest workers
D) Indentured servants
A) Migrants
B) Day laborers
C) Guest workers
D) Indentured servants

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following describes Konrad Adenauer's administration in postwar Germany?
A) It was propped up in power by the Soviet Union.
B) It was short-lived, as he was assassinated by Soviet agents for working with the United States.
C) It was led by a small, neofascist party of ultranationalists who resisted democratic reforms.
D) It brought Germany firmly into the Western capitalist camp.
A) It was propped up in power by the Soviet Union.
B) It was short-lived, as he was assassinated by Soviet agents for working with the United States.
C) It was led by a small, neofascist party of ultranationalists who resisted democratic reforms.
D) It brought Germany firmly into the Western capitalist camp.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Nikita Khrushchev believed which of the following was possible in the 1950s and 1960s?
A) The advent of Soviet-style capitalism
B) The global triumph of communism
C) Peaceful coexistence with capitalism
D) A communist revolution in the United States
A) The advent of Soviet-style capitalism
B) The global triumph of communism
C) Peaceful coexistence with capitalism
D) A communist revolution in the United States

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
What was the only European Communist country to resist Soviet domination after 1945?
A) Hungary
B) Yugoslavia
C) Czechoslovakia
D) Romania
A) Hungary
B) Yugoslavia
C) Czechoslovakia
D) Romania

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What factors contributed to the push in postwar Europe for political and economic unity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What evidence in this illustration indicates that the person portrayed was a member of the Red Guards? 
A) She is clutching a Little Red Book.
B) The button she is wearing indicates her position within the Red Guard.
C) Only members of the Red Guard were allowed to wear green uniforms.
D) The illustrations that decorate the background reflect all of the activities in which the Red Guard was involved.

A) She is clutching a Little Red Book.
B) The button she is wearing indicates her position within the Red Guard.
C) Only members of the Red Guard were allowed to wear green uniforms.
D) The illustrations that decorate the background reflect all of the activities in which the Red Guard was involved.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What was the effect on Japan of the postwar American occupation?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What allowed Yugoslavia to reject Soviet control?
A) Tito, the leader of Yugoslavia, was not a Communist.
B) Yugoslavia had rich oil reserves and a consumer economy.
C) There was no Russian army in Yugoslavia.
D) The United States sent aid to Yugoslavia to keep the country democratic.
A) Tito, the leader of Yugoslavia, was not a Communist.
B) Yugoslavia had rich oil reserves and a consumer economy.
C) There was no Russian army in Yugoslavia.
D) The United States sent aid to Yugoslavia to keep the country democratic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What role did students play in the political disruptions of 1968?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Khrushchev was removed from office in 1964, two years after his failed attempt to
A) build the Berlin Wall.
B) promote more private agriculture.
C) install a permanent cache of missiles in Cuba.
D) quell a rebellion in Poland.
A) build the Berlin Wall.
B) promote more private agriculture.
C) install a permanent cache of missiles in Cuba.
D) quell a rebellion in Poland.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
What factors led to the civil rights revolution in the United States?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What were the different opinions within the Soviet Communist Party about de-Stalinization and its effects?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
What European city was divided by a wall in 1961?
A) Berlin
B) Moscow
C) Budapest
D) Stalingrad
A) Berlin
B) Moscow
C) Budapest
D) Stalingrad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is one of the ways in which this poster seeks to glorify the Chinese Communist state?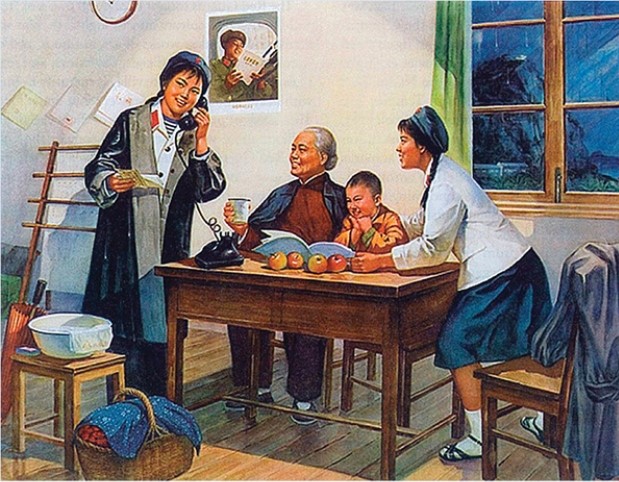 
A) It depicts a typical bourgeois Chinese family.
B) It includes examples of many of the material goods available in abundance in Communist China.
C) The landscape visible through the window represents the abundant land available to middle-class Chinese families under the Communist regime.
D) The females are wearing the Communist red star on their caps.

A) It depicts a typical bourgeois Chinese family.
B) It includes examples of many of the material goods available in abundance in Communist China.
C) The landscape visible through the window represents the abundant land available to middle-class Chinese families under the Communist regime.
D) The females are wearing the Communist red star on their caps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
How did the Middle East develop after World War II?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
To what extent was the revolution in Cuba a Communist takeover of a popular democratic state?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
What were the roots of the Cold War?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
What happened when the leaders of the Czechoslovakian reform movement of 1968 gained a majority and replaced a long-time Stalinist leader with Alexander Dubček, whose new government launched dramatic reforms?
A) Dubček abolished the Communist Party and instituted democratic elections.
B) The reform leaders removed Czechoslovakia from participation in the Warsaw Pact.
C) Capitalism and liberalism were reintroduced with great success.
D) Military troops from Russia and eastern Europe occupied Czechoslovakia.
A) Dubček abolished the Communist Party and instituted democratic elections.
B) The reform leaders removed Czechoslovakia from participation in the Warsaw Pact.
C) Capitalism and liberalism were reintroduced with great success.
D) Military troops from Russia and eastern Europe occupied Czechoslovakia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
After World War II, the Soviet Union presented itself as the global defender of the rights of
A) workers.
B) party members.
C) liberals.
D) capitalists.
A) workers.
B) party members.
C) liberals.
D) capitalists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
How did migrant labor reshape western European society?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Decolonization after World War II was a process of political decolonization combined with economic neocolonialism. Explain how that is possible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The first attempt at unifying Europe came from which industry?
A) Banking and finance
B) Coal and steel
C) Agriculture
D) Tourism
A) Banking and finance
B) Coal and steel
C) Agriculture
D) Tourism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Use the following to answer questions :
Pan-Africanists
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Pan-Africanists
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the following to answer questions :
Marshall Plan
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Marshall Plan
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the following to answer questions :
dependency theory
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
dependency theory
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What motivated the nations of Europe to seek unity in the postwar era? What were the successes and failures of these efforts? What factors explain the successes and failures?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following to answer questions :
Cold War
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Cold War
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Use the following to answer questions :
Muslim League
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Muslim League
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What was the dominant dynamic in the social and political upheavals of 1968?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following to answer questions :
import substitution industrialization (ISI)
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
import substitution industrialization (ISI)
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the following to answer questions :
Great Leap Forward
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Great Leap Forward
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the following to answer questions :
Common Market
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Common Market
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Describe the process of "de-Stalinization" that the Soviet Union underwent after Stalin's death. What was its impact domestically and internationally? Why did later Soviet leaders re-Stalinize?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use the following to answer questions :
liberation theology
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
liberation theology
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What were the key drivers of western Europe's economic recovery? Were these the same factors that drove Japan's recovery?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
How did African nationalism grow during the postwar era? What did it accomplish?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following to answer questions :
Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the following to answer questions :
Arab socialism
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Arab socialism
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following to answer questions :
NATO
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
NATO
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Use the following to answer questions :
modernization theory
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
modernization theory
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Use the following to answer questions :
cocoa holdups
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
cocoa holdups
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Use the following to answer questions :
National Liberation Front
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.
National Liberation Front
A)The belief, held in countries such as the United States in the mid-twentieth century, that all countries evolved in a linear progression from traditional to mature.
B)People who, through a movement beginning in 1919, sought black solidarity and envisioned a vast self-governing union of all African peoples.
C)A movement within the Catholic Church to support the poor in situations of exploitation that emerged with particular force in Latin America in the 1960s.
D)A 1948 American plan for providing economic aid to Europe to help it rebuild after World War II.
E)The 1945 American policy of preventing the spread of Communist rule.
F)Political party founded in 1906 in colonial India that advocated for a separate Muslim homeland after independence.
G)Mao Zedong's acceleration of Chinese development in which industrial growth was to be based on small-scale backyard workshops run by peasants living in gigantic self-contained communes.
H)An anti-Soviet military alliance of Western nations, formed in 1949.
I)Mass protests in Africa's Gold Coast in the 1930s by producers of cocoa who refused to sell their beans to British firms and instead sold them directly to European and American chocolate manufacturers.
J)The anticolonial movement in Algeria, which began a war against the French in 1954 and won independence in 1962.
K)A modernizing, secular, and nationalist project of nation building in the Middle East aimed at economic development and the development of a strong military.
L)A movement launched in 1965 by Mao Zedong that attempted to recapture the revolutionary fervor of his guerrilla struggle.
M)The use of trade barriers to keep certain products out of one's country so that domestic industry can emerge and produce the same goods.
N)The belief, formulated in Latin America in the mid-twentieth century, that development in some areas of the world locks other nations into underdevelopment.
O)The European Economic Community created in 1957.
P)Created in 1964, a loose union of Palestinian refugee groups opposed to Israel and united in the goal of establishing a Palestinian state.
Q)The post-World War II conflict between the United States and the Soviet Union.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 82 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



