Deck 20: Africa and the World, 1400-1800
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 20: Africa and the World, 1400-1800
1
In the fifteenth century, Kano and Katsina in Hausaland became centers for which of the following?
A) Transatlantic slave trade
B) African-style feudalism
C) Islamic scholarship
D) Artistic creativity
A) Transatlantic slave trade
B) African-style feudalism
C) Islamic scholarship
D) Artistic creativity
Islamic scholarship
2
How would a typical Senegambian community be described?
A) As a highly organized mercantile center
B) As nothing more than a nomadic band of related families
C) As organized entirely around the slave trade
D) As organized in a small, self-supporting agricultural village
A) As a highly organized mercantile center
B) As nothing more than a nomadic band of related families
C) As organized entirely around the slave trade
D) As organized in a small, self-supporting agricultural village
As organized in a small, self-supporting agricultural village
3
In the stateless societies of Senegambia, which of the following contributed to community loyalty and law enforcement?
A) Age-grade systems
B) Strong, patriarchal clans
C) Gender-specific roles
D) Communitywide assemblies
A) Age-grade systems
B) Strong, patriarchal clans
C) Gender-specific roles
D) Communitywide assemblies
Age-grade systems
4
What characteristic distinguished most West African marriages?
A) They were almost always monogamous.
B) They were often forced after war with a neighboring tribe.
C) They were virtually all love matches.
D) They were almost universally polygynous.
A) They were almost always monogamous.
B) They were often forced after war with a neighboring tribe.
C) They were virtually all love matches.
D) They were almost universally polygynous.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of these was the greatest killer in West Africa?
A) Typhoid
B) Hookworm
C) Malaria
D) Yellow fever
A) Typhoid
B) Hookworm
C) Malaria
D) Yellow fever

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
How were chattel slaves viewed?
A) Most were considered to be members of the owner's family.
B) Usually, they were slaves who had status and power.
C) They had the right to inherit land and wealth.
D) They were commodities that were considered subhuman property.
A) Most were considered to be members of the owner's family.
B) Usually, they were slaves who had status and power.
C) They had the right to inherit land and wealth.
D) They were commodities that were considered subhuman property.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Who supplied the labor on the royal farms of Songhai?
A) Slaves
B) Indentured servants
C) Tax debtors
D) War captives
A) Slaves
B) Indentured servants
C) Tax debtors
D) War captives

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In addition to famine, what was the greatest obstacle to population growth in West Africa?
A) Warfare and slave trading
B) The small population of women
C) The lack of available arable land
D) Diseases such as malaria
A) Warfare and slave trading
B) The small population of women
C) The lack of available arable land
D) Diseases such as malaria

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In the trans-Saharan trade, Kanem-Bornu traded slaves to North Africa for what?
A) Salt
B) Gold
C) Horses
D) Cattle
A) Salt
B) Gold
C) Horses
D) Cattle

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What brought Senegambia into frequent contact with Europeans?
A) European explorers
B) Christian missionaries
C) The slave trade
D) The ivory trade
A) European explorers
B) Christian missionaries
C) The slave trade
D) The ivory trade

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Why was the city of Timbuktu well known?
A) It was a major port for transatlantic trade.
B) It was the capital and major trade center of Benin.
C) It possessed a thriving urban culture.
D) It was dominated by Muslims and persecuted Jews.
A) It was a major port for transatlantic trade.
B) It was the capital and major trade center of Benin.
C) It possessed a thriving urban culture.
D) It was dominated by Muslims and persecuted Jews.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Based on Map 20.1, "West African Societies, ca. 1500-1800," which of the following played a major role in the Portuguese slave trade, due largely to its geographic location? 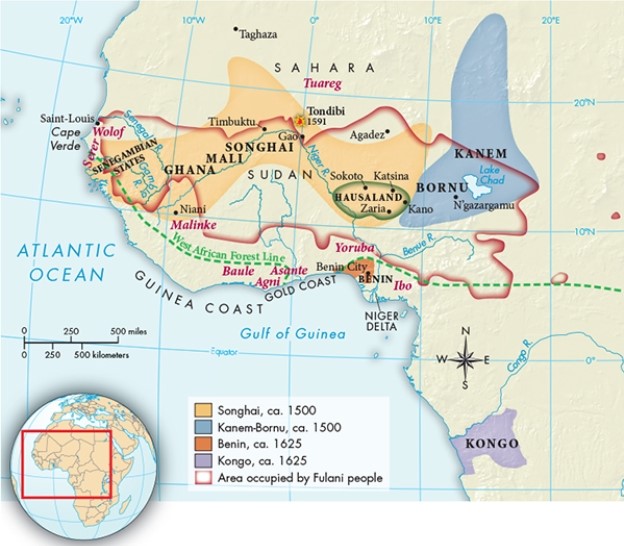
A) Zaria
B) Timbuktu
C) Agadez
D) Benin

A) Zaria
B) Timbuktu
C) Agadez
D) Benin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
What army ultimately destroyed the Songhai Empire?
A) A largely slave army from the sultanate of Morocco
B) Armies from the kingdom of Ethiopia
C) Prince Henry's army from the kingdom of Portugal
D) The army of the kingdom of Benin
A) A largely slave army from the sultanate of Morocco
B) Armies from the kingdom of Ethiopia
C) Prince Henry's army from the kingdom of Portugal
D) The army of the kingdom of Benin

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Benin City was known for artistic work in iron, ivory, and what other product?
A) Gold filigree jewelry
B) Decorative copper containers
C) Woven baskets
D) Bronze portrait busts
A) Gold filigree jewelry
B) Decorative copper containers
C) Woven baskets
D) Bronze portrait busts

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What was the oba in Benin?
A) Priest
B) Chief merchant
C) King
D) Sage
A) Priest
B) Chief merchant
C) King
D) Sage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
For what is Leo Africanus best known?
A) The further expansion of Songhai
B) His descriptions of African society
C) The expulsion of the Jesuits from Ethiopia
D) The establishment of mosques throughout West Africa
A) The further expansion of Songhai
B) His descriptions of African society
C) The expulsion of the Jesuits from Ethiopia
D) The establishment of mosques throughout West Africa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the fifteenth century, what state became the successor to Ghana and Mali in the Niger region?
A) Songhai
B) Benin
C) Senegambia
D) Hausa
A) Songhai
B) Benin
C) Senegambia
D) Hausa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
How did slavery in Senegambia compare to slavery in the Americas?
A) In Senegambia, slaves were treated harshly, while they were treated more kindly in the Americas.
B) In both places, slave status passed from one generation to the next, and the descendants of slaves were never free.
C) In the Americas, slave status passed from one generation to the next, while in Senegambia descendants of slaves were sometimes free.
D) In both places, slaves could be bought and sold.
A) In Senegambia, slaves were treated harshly, while they were treated more kindly in the Americas.
B) In both places, slave status passed from one generation to the next, and the descendants of slaves were never free.
C) In the Americas, slave status passed from one generation to the next, while in Senegambia descendants of slaves were sometimes free.
D) In both places, slaves could be bought and sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What ruler completed the expansion and consolidation of Songhai?
A) Muhammad Ali
B) Muhammad Toure
C) Ewuare
D) Leo Africanus
A) Muhammad Ali
B) Muhammad Toure
C) Ewuare
D) Leo Africanus

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Which of the following statements is true regarding the negotiation taking place in this illustration? 
A) Given the expense involved in conducting slave raids, the African male with whom the European trader is negotiating was likely a wealthy entrepreneur.
B) Other than being taken captive, the African people played little, if any, role in the African slave trade.
C) The African male engaged in negotiation was likely a poor merchant.
D) Based on his style of dress, the African trader most likely lived in the region of Benin.

A) Given the expense involved in conducting slave raids, the African male with whom the European trader is negotiating was likely a wealthy entrepreneur.
B) Other than being taken captive, the African people played little, if any, role in the African slave trade.
C) The African male engaged in negotiation was likely a poor merchant.
D) Based on his style of dress, the African trader most likely lived in the region of Benin.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Which of these was true of the great majority of slaves in the Islamic world?
A) They were black.
B) They were white.
C) They were Muslims.
D) They were Jews.
A) They were black.
B) They were white.
C) They were Muslims.
D) They were Jews.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Swahili independence ended with the arrival in 1498 of which Portuguese explorer?
A) Prince Henry the Navigator
B) Vasco da Gama
C) Giovanni da Verrazzano
D) Ferdinand Magellan
A) Prince Henry the Navigator
B) Vasco da Gama
C) Giovanni da Verrazzano
D) Ferdinand Magellan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
What West African industry had the greatest level of specialization?
A) Textiles
B) Salt mining
C) Gold working
D) Iron working
A) Textiles
B) Salt mining
C) Gold working
D) Iron working

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which European nation monopolized the slave trade until about 1600?
A) Venice
B) England
C) Spain
D) Portugal
A) Venice
B) England
C) Spain
D) Portugal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
What was the chief means of transport for the West African salt trade?
A) Donkey caravans
B) Camels
C) Horse-drawn carts
D) Slaves
A) Donkey caravans
B) Camels
C) Horse-drawn carts
D) Slaves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
What was the justification for slavery adopted by African rulers that originated from Islamic societies?
A) They argued that Africans were an inferior race who were better off as slaves.
B) They rationalized it by saying slaves lacked immortal souls.
C) They believed slavery was necessary for economic development.
D) They argued that prisoners of war could be sold and that captured people were chattel.
A) They argued that Africans were an inferior race who were better off as slaves.
B) They rationalized it by saying slaves lacked immortal souls.
C) They believed slavery was necessary for economic development.
D) They argued that prisoners of war could be sold and that captured people were chattel.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Defeated by General Ahmad ibn-Ghazi in 1529, the Ethiopian emperor Lebna Dengel sought aid from which of the following?
A) The Ottomans
B) Portugal
C) The Dutch Republic
D) India
A) The Ottomans
B) Portugal
C) The Dutch Republic
D) India

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Between 1690 and 1807, which European nation was the leading participant in the transatlantic slave trade?
A) England
B) Portugal
C) Spain
D) France
A) England
B) Portugal
C) Spain
D) France

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
By the eleventh century, what important change had the Swahili peoples made?
A) The majority had become full-time farmers.
B) They converted to Islam.
C) They established a large inland empire.
D) They developed trade with Portugal.
A) The majority had become full-time farmers.
B) They converted to Islam.
C) They established a large inland empire.
D) They developed trade with Portugal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
What missionary group attempted to introduce Roman Catholicism into Ethiopia in the sixteenth century?
A) Franciscans
B) Dominicans
C) Jesuits
D) Benedictines
A) Franciscans
B) Dominicans
C) Jesuits
D) Benedictines

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
What evidence in this illustration shows European influence on the African slave trade?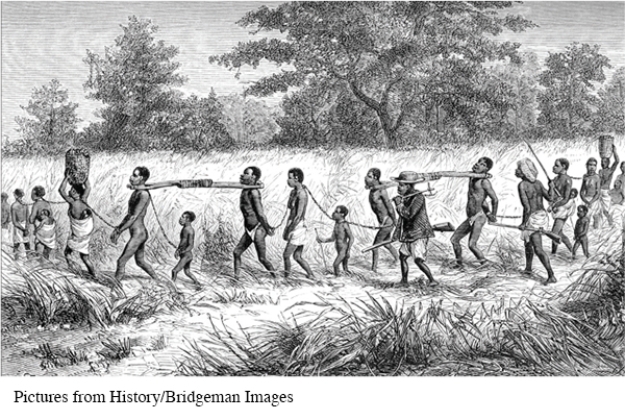 
A) The restraints are of European design.
B) The guards are carrying European-style firearms.
C) The large number of captives suggests traders are attempting to meet high European demand.
D) Europeans preferred younger slaves, as they typically sold for a higher price.

A) The restraints are of European design.
B) The guards are carrying European-style firearms.
C) The large number of captives suggests traders are attempting to meet high European demand.
D) Europeans preferred younger slaves, as they typically sold for a higher price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Cowrie shells were used for currency in North Africa and originated in the Maldives, which are islands located in what body of water?
A) South China Sea
B) Pacific Ocean
C) Philippine Sea
D) Indian Ocean
A) South China Sea
B) Pacific Ocean
C) Philippine Sea
D) Indian Ocean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
What was the chief trade good in the trans-Saharan trade routes?
A) Salt
B) Silver
C) Amber
D) Iron ore
A) Salt
B) Silver
C) Amber
D) Iron ore

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of these was true of the black population of eighteenth-century London?
A) Most black Londoners were agricultural laborers.
B) Most black Londoners were merchants and traders.
C) Most black Londoners were well-educated freemen.
D) Most black Londoners were sailors or personal servants.
A) Most black Londoners were agricultural laborers.
B) Most black Londoners were merchants and traders.
C) Most black Londoners were well-educated freemen.
D) Most black Londoners were sailors or personal servants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
What New World country received the largest numbers of slaves from the transatlantic trade during the late eighteenth and early nineteenth centuries?
A) Mexico
B) British North America
C) French Canada
D) Brazil
A) Mexico
B) British North America
C) French Canada
D) Brazil

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
What important role did the Portuguese forts and markets at Kilwa, Zanzibar, and Sofala have?
A) They became the foundation of Portuguese economic power on the Swahili coast.
B) They continued to provide the independent Swahili city-states with money.
C) They represented the merging of Portuguese and Swahili trade powers.
D) They benefited the inland gold mines of Sofala by opening new markets.
A) They became the foundation of Portuguese economic power on the Swahili coast.
B) They continued to provide the independent Swahili city-states with money.
C) They represented the merging of Portuguese and Swahili trade powers.
D) They benefited the inland gold mines of Sofala by opening new markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In the fourteenth and fifteenth centuries, who did the elite of Mali and Benin import to be slaves?
A) Songhai warriors
B) Berber women
C) Slavic women
D) Yoruba children
A) Songhai warriors
B) Berber women
C) Slavic women
D) Yoruba children

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
What was the primary religion of Ethiopia?
A) Byzantine Christianity
B) Islam
C) Coptic Christianity
D) Judaism
A) Byzantine Christianity
B) Islam
C) Coptic Christianity
D) Judaism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Roughly 75 percent of the slaves imported into the Dutch Cape Colony were from where?
A) West Africa and Angola
B) The Balkans and Anatolia
C) India, Southeast Asia, and Madagascar
D) Swahili-speaking areas
A) West Africa and Angola
B) The Balkans and Anatolia
C) India, Southeast Asia, and Madagascar
D) Swahili-speaking areas

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Roughly 35 percent of Swahili words come from which of the following languages?
A) Arabic
B) Coptic
C) Yoruba
D) Egyptian
A) Arabic
B) Coptic
C) Yoruba
D) Egyptian

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
What was the nature of trade and commerce in the Swahili city-states? What kinds of goods were traded?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Most slaves exported by the Portuguese to Brazil came from
A) Angola.
B) Madagascar.
C) Ethiopia.
D) Swahili.
A) Angola.
B) Madagascar.
C) Ethiopia.
D) Swahili.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How is disease related to African enslavement in the Americas?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
What was the Middle Passage?
A) The transfer of slaves from inland locations to coastal cities
B) The voyage of African slaves to the Americas
C) The transfer of slaves from ship to market
D) The shipping lane from the American colonies to Europe
A) The transfer of slaves from inland locations to coastal cities
B) The voyage of African slaves to the Americas
C) The transfer of slaves from ship to market
D) The shipping lane from the American colonies to Europe

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What kinds of external threats did Ethiopia face in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries? How did Ethiopians deal with these threats?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Scholars have determined that the transatlantic slave trade had what effect on African societies?
A) It led to wars that destabilized the political structure of many states.
B) It led to technological development because of population decline.
C) It laid the foundation for European colonies.
D) It hastened the Christianization of the sub-Sahara.
A) It led to wars that destabilized the political structure of many states.
B) It led to technological development because of population decline.
C) It laid the foundation for European colonies.
D) It hastened the Christianization of the sub-Sahara.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
How did the transatlantic slave trade influence the economy of the European colonies of the Americas and beyond?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
How is the insatiable demand for coffee and sugar reflected in this chart depicting slave imports by destination? 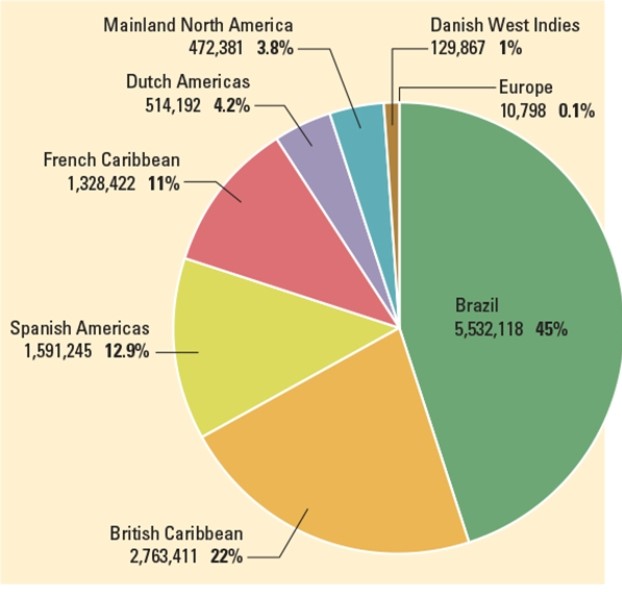
A) The largest numbers by far were sent to Brazil and the Caribbean, where these crops were produced.
B) The Spanish, who consumed massive amounts of both products, imported nearly 13% of slaves overall to their American colonies.
C) A relatively sizable number were sent to the West Indies.
D) Less than 1% were sent to Europe, where neither product was produced.

A) The largest numbers by far were sent to Brazil and the Caribbean, where these crops were produced.
B) The Spanish, who consumed massive amounts of both products, imported nearly 13% of slaves overall to their American colonies.
C) A relatively sizable number were sent to the West Indies.
D) Less than 1% were sent to Europe, where neither product was produced.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In the eighteenth century, what city was the world's greatest slave-trading port?
A) Bristol
B) London
C) Liverpool
D) Edinburgh
A) Bristol
B) London
C) Liverpool
D) Edinburgh

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Compare and contrast the economy of kingdoms in West Africa with those in East Africa during the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Male slaves were more highly desired in the Americas. Why? Was there a market in which female slaves were more highly desired? If so, where was this market, and why were women more highly prized?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
What goods were African slaves traded for in the American colonies?
A) Horses
B) Raw materials
C) Textiles
D) Firearms
A) Horses
B) Raw materials
C) Textiles
D) Firearms

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The great majority of the slaves sent to the Americas were to be employed in which of the following?
A) Tobacco plantations of British North America
B) Cotton plantations of British North America
C) Gold and silver mines in Central and South America
D) Coffee and sugar plantations in the Caribbean and South America
A) Tobacco plantations of British North America
B) Cotton plantations of British North America
C) Gold and silver mines in Central and South America
D) Coffee and sugar plantations in the Caribbean and South America

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Who were the nhara?
A) People of mixed African and European heritage
B) Female slaves taken as concubines by their owners
C) Dahomey slave raiders
D) Women slave merchants in Guinea
A) People of mixed African and European heritage
B) Female slaves taken as concubines by their owners
C) Dahomey slave raiders
D) Women slave merchants in Guinea

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the English slave trade, a "sorting" referred to which of the following?
A) An assortment of slaves presented for inspection by English purchasers
B) The throwing overboard of sick or weak slaves during the Middle Passage
C) A selection of goods traded in one lot for a slave or slaves
D) The division of Africans by age, gender, and perceived strength for a slave sale
A) An assortment of slaves presented for inspection by English purchasers
B) The throwing overboard of sick or weak slaves during the Middle Passage
C) A selection of goods traded in one lot for a slave or slaves
D) The division of Africans by age, gender, and perceived strength for a slave sale

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Describe the typical West African diet prior to the sixteenth century. How did contact with Europe alter that diet?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
What factors led to low population growth in West Africa? How did the low population growth affect gender relations?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In addition to the slave trade, what other economic impact did European powers have on West Africa?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
How did the Portuguese take control of the trade between the Swahili city-states and the Indian Ocean trade networks? How long did that dominance last?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The massive increase in the slave trade, as illustrated , "The Transatlantic Slave Trade, 1501-1866" can be attributed, in part, to which of the following? 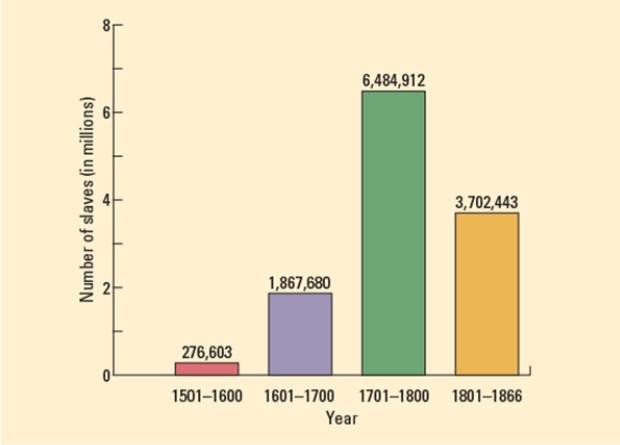
A) European demand for precious metals increased sharply.
B) A significant number of slaves being transported for sale died.
C) Slavery grew in the United States.
D) An increasing number of nations engaged in the trade.

A) European demand for precious metals increased sharply.
B) A significant number of slaves being transported for sale died.
C) Slavery grew in the United States.
D) An increasing number of nations engaged in the trade.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Use the following to answer questions :
cowrie shells
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.
cowrie shells
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Use the following to answer questions :
age-grade systems
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.
age-grade systems
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the following to answer questions :
Taghaza
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.
Taghaza
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following to answer questions :
chattel
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.
chattel
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following to answer questions :
oba
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.
oba
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
How was the transatlantic slave trade organized? Who participated, and who profited?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
What are the various theories as to why black Africans were enslaved in the sixteenth to eighteenth centuries more than other races? What are some of the problems with these theories?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following to answer questions :
Coptic Christianity
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.
Coptic Christianity
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the following to answer questions :
sorting
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.
sorting
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
How did contact with Islam and the later Portuguese intrusion influence the history of East Africa, particularly Ethiopia and the Swahili city-states?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following to answer questions :
Swahili
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.
Swahili
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Use the following to answer questions :
Tuareg
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.
Tuareg
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Islam played a significant role in sub-Saharan West Africa. Describe the impact of Islam in this region. How did Islam affect European expansion in Africa? Overall, was the impact of Islam on sub-Saharan African society positive or negative?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Use the following to answer questions :
Middle Passage
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.
Middle Passage
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following to answer questions :
shore trading
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.
shore trading
A)An item of personal property; a term used in reference to enslaved people that conveys the idea that they are subhuman, like animals, and therefore may be treated like animals.
B)Among the societies of Senegambia, groups of teenage males and females whom the society initiated into adulthood at the same time.
C)The title of the king of Benin.
D)A settlement in the western Sahara, the site of the main salt-mining center.
E)Major branch of the nomadic Berber peoples who controlled the north-south trans-Saharan trade in salt.
F)Imported from the Maldives, they served as the medium of exchange in West Africa.
G)Orthodox form of Christianity from Egypt practiced in Ethiopia.
H)Meaning "People of the Coast," the term used for the people living along the East African coast and on nearby islands.
I)Enslaved Africans' horrific voyage across the Atlantic to the Americas under appalling and often deadly conditions.
J)A collection or batch of British goods that would be traded for a slave or for a quantity of gold, ivory, or dyewood.
K)A process for exchanging goods in which European ships sent boats ashore or invited African dealers to bring traders and slaves out to the ships.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Courtship, marriage, and family patterns in West Africa displayed rather striking characteristics. Describe these patterns, and offer an explanation for their development.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



