Deck 12: Cultural Exchange in Central and Southern Asia, 300-1400
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/76
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 12: Cultural Exchange in Central and Southern Asia, 300-1400
1
In the mid-twelfth century, which of the following created a subsistence crisis in Central Asia?
A) A population boom put pressures on agricultural resources.
B) An outbreak of plague caused widespread death among agricultural workers.
C) A drop in the mean annual temperature led to agricultural problems.
D) A sustained drought led to crop failure and other hardships.
A) A population boom put pressures on agricultural resources.
B) An outbreak of plague caused widespread death among agricultural workers.
C) A drop in the mean annual temperature led to agricultural problems.
D) A sustained drought led to crop failure and other hardships.
A drop in the mean annual temperature led to agricultural problems.
2
Which of the following was an important activity of the Eastern Turks?
A) They controlled a united confederation.
B) They practiced settled agriculture.
C) They were Buddhists.
D) They frequently raided China.
A) They controlled a united confederation.
B) They practiced settled agriculture.
C) They were Buddhists.
D) They frequently raided China.
They frequently raided China.
3
The Turks first appeared as part of what empire on the Silk Road?
A) Rouruan
B) Byzantine
C) Mongol
D) Xiongnu
A) Rouruan
B) Byzantine
C) Mongol
D) Xiongnu
Rouruan
4
The Mongol script that Chinggis Khan ordered created was based on the script used by what other society?
A) Sanskrit
B) Uighur Turks
C) Urdu
D) Chinese
A) Sanskrit
B) Uighur Turks
C) Urdu
D) Chinese

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What important talent did Mongol women possess?
A) They were expert horseback riders.
B) They were trained to be skilled warriors.
C) They preserved Mongol culture by being masterful orators.
D) They were known for their beautiful pottery.
A) They were expert horseback riders.
B) They were trained to be skilled warriors.
C) They preserved Mongol culture by being masterful orators.
D) They were known for their beautiful pottery.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What is the first great nomad confederation that historians have clearly identified?
A) The Scythians
B) The Xiongnu (or Huns)
C) The Turks
D) The Uzbeks
A) The Scythians
B) The Xiongnu (or Huns)
C) The Turks
D) The Uzbeks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
According to Map 12.3, "The Spice Trade, ca. 100 B.C.E-1500 C.E.," which spice was sourced from the largest number of locations? 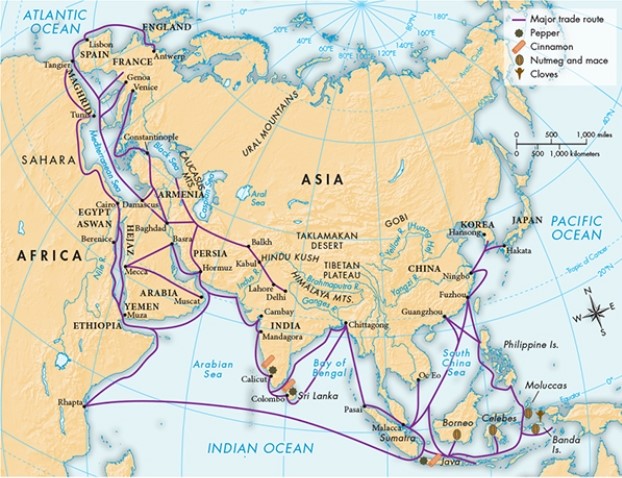
A) Pepper
B) Nutmeg
C) Cinnamon
D) Cloves

A) Pepper
B) Nutmeg
C) Cinnamon
D) Cloves

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What was one of the first things recorded in the new Mongol script?
A) A record of the Mongol laws and customs
B) The Secret History, a history of the Mongol people
C) Prayers to the Sky and Earth
D) A warfare manual to be distributed among the confederation
A) A record of the Mongol laws and customs
B) The Secret History, a history of the Mongol people
C) Prayers to the Sky and Earth
D) A warfare manual to be distributed among the confederation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
What happened to Chinggis Khan's empire at his death?
A) It was inherited by his grandson Khubilai Khan.
B) It was divided into four parts among his descendants.
C) It almost immediately fell into disarray.
D) It came entirely under the control of his eldest son.
A) It was inherited by his grandson Khubilai Khan.
B) It was divided into four parts among his descendants.
C) It almost immediately fell into disarray.
D) It came entirely under the control of his eldest son.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
In the seventh century, who ultimately defeated the Eastern Turks?
A) Xiongnu
B) Tang Dynasty
C) Byzantines
D) Western Turks
A) Xiongnu
B) Tang Dynasty
C) Byzantines
D) Western Turks

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Political organization among nomadic herding peoples was generally based on which of the following?
A) Clan ties
B) Buddhism
C) Economic arrangements
D) Language
A) Clan ties
B) Buddhism
C) Economic arrangements
D) Language

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
What was one of the few specialist professions among the Mongol people?
A) Mare milker
B) Cheese maker
C) Blacksmith
D) Wool felter
A) Mare milker
B) Cheese maker
C) Blacksmith
D) Wool felter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In what warfare skill did the steppe nomads excel?
A) They were particularly adept at sieges.
B) They were very skilled archers.
C) Their very large population gave them a large, talented infantry.
D) Their command of iron smelting gave them the weapons to excel at hand-to-hand combat.
A) They were particularly adept at sieges.
B) They were very skilled archers.
C) Their very large population gave them a large, talented infantry.
D) Their command of iron smelting gave them the weapons to excel at hand-to-hand combat.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What evidence in this illustration reflects Chinese influence on Mongol military tactics? 
A) The exploding projectile
B) The color variations of their clothing
C) The fighting isn't taking place on horseback
D) The grouping pattern of the soldiers

A) The exploding projectile
B) The color variations of their clothing
C) The fighting isn't taking place on horseback
D) The grouping pattern of the soldiers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Which of the following dominate Central Asian geography?
A) Tropical forests
B) Arid grasslands
C) High mountain ranges
D) Fertile plains
A) Tropical forests
B) Arid grasslands
C) High mountain ranges
D) Fertile plains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What conventions guided family decision making in Mongol society?
A) Women participated in family decisions.
B) As in most patriarchies, men made decisions.
C) Elders were responsible for decisions.
D) A democratically elected council made decisions.
A) Women participated in family decisions.
B) As in most patriarchies, men made decisions.
C) Elders were responsible for decisions.
D) A democratically elected council made decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What goods predominated in the trade of Central Asian nomads?
A) Textiles
B) Iron
C) Grain
D) Horses and fur
A) Textiles
B) Iron
C) Grain
D) Horses and fur

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In organizing his army, Chinggis Khan sought to do which of the following?
A) Incorporate women into the cavalry
B) Use exclusively Chinese units
C) Break traditional tribal loyalties
D) Mix infantry and cavalry in one unit
A) Incorporate women into the cavalry
B) Use exclusively Chinese units
C) Break traditional tribal loyalties
D) Mix infantry and cavalry in one unit

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is a yurt?
A) The castle of a Mongol war chief
B) The protective body covering worn by Mongol warriors
C) The small horse that Mongols rode
D) A round tent in which Mongol families lived
A) The castle of a Mongol war chief
B) The protective body covering worn by Mongol warriors
C) The small horse that Mongols rode
D) A round tent in which Mongol families lived

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
What happened to the father of Temujin (or Chinggis Khan)?
A) He was killed by his wife.
B) He was captured and enslaved by a rival.
C) No one knows because his story is lost.
D) He was poisoned by a rival.
A) He was killed by his wife.
B) He was captured and enslaved by a rival.
C) No one knows because his story is lost.
D) He was poisoned by a rival.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The Gupta modeled their empire on what earlier empire?
A) Alexander the Great's
B) The Tang Dynasty of China
C) Chinggis Khan's
D) The Mauryan
A) Alexander the Great's
B) The Tang Dynasty of China
C) Chinggis Khan's
D) The Mauryan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
By the middle of the thirteenth century, there were many
A) Muslims in power in China.
B) Mongol converts to Catholicism.
C) Chinese in positions of power in Mongolia.
D) Nestorian Christians in Central Asia.
A) Muslims in power in China.
B) Mongol converts to Catholicism.
C) Chinese in positions of power in Mongolia.
D) Nestorian Christians in Central Asia.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Mongols were aided in their conquest of Syria by exploiting the unrest of what part of Syria's population?
A) Muslims
B) Jews
C) Zoroastrians
D) Christians
A) Muslims
B) Jews
C) Zoroastrians
D) Christians

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Who benefited most from the Mongols' dissemination of technological and scientific ideas?
A) Europe
B) The Middle East
C) China
D) Japan
A) Europe
B) The Middle East
C) China
D) Japan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Why did the Mongol army return to Karakorum in 1241?
A) For the coronation ceremony of Khubilai
B) For the election of a new khan following the death of Ögödei
C) To provide needed staffing and monitoring of the China trade center
D) To gather more troops after being defeated in Baghdad
A) For the coronation ceremony of Khubilai
B) For the election of a new khan following the death of Ögödei
C) To provide needed staffing and monitoring of the China trade center
D) To gather more troops after being defeated in Baghdad

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which of the following is true of the Mongol conquest of southern China?
A) It took less than two years.
B) It drew on the skills of experts in naval and siege warfare.
C) It was successful, in large part, as a result of their expert use of horses.
D) It included the killing of the Chinese empress dowager.
A) It took less than two years.
B) It drew on the skills of experts in naval and siege warfare.
C) It was successful, in large part, as a result of their expert use of horses.
D) It included the killing of the Chinese empress dowager.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
During the rule of Khubilai in China, how did Mongols interact with the Chinese people and their culture?
A) Mongols adopted many Chinese cultural practices.
B) Chinese were treated as legally inferior to all non-Chinese.
C) Mongols adopted Chinese-style housing and gave up their use of yurts.
D) Mongol governors and other administrators were required to wear Chinese-style clothing.
A) Mongols adopted many Chinese cultural practices.
B) Chinese were treated as legally inferior to all non-Chinese.
C) Mongols adopted Chinese-style housing and gave up their use of yurts.
D) Mongol governors and other administrators were required to wear Chinese-style clothing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
How did the Mongols use conquest to improve their empire?
A) To further the Mongol social system, they imposed their traditional tribal groupings on subjugated peoples.
B) They treated all subjugated men as slaves who were used as soldiers and agricultural workers.
C) They improved their own capital city by importing skilled workers from conquered regions.
D) They often exploited the labor of women of conquered territories who were forced to work at Mongol military camps.
A) To further the Mongol social system, they imposed their traditional tribal groupings on subjugated peoples.
B) They treated all subjugated men as slaves who were used as soldiers and agricultural workers.
C) They improved their own capital city by importing skilled workers from conquered regions.
D) They often exploited the labor of women of conquered territories who were forced to work at Mongol military camps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
What was a consequence in Europe of Marco Polo's travels to China?
A) His writings inspired Europeans to try to conquer China.
B) He convinced the Pope to dispatch a mission to convert the Chinese.
C) He was jailed for serving Khubilai Khan.
D) His writings helped convince Europeans that Asia was a land of riches.
A) His writings inspired Europeans to try to conquer China.
B) He convinced the Pope to dispatch a mission to convert the Chinese.
C) He was jailed for serving Khubilai Khan.
D) His writings helped convince Europeans that Asia was a land of riches.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Khubilai discouraged the Mongols in China from doing what?
A) Marrying the Chinese
B) Learning to read Chinese
C) Returning to Mongolia
D) Harming Chinese citizens
A) Marrying the Chinese
B) Learning to read Chinese
C) Returning to Mongolia
D) Harming Chinese citizens

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
How is Chinese influence on Mongol military tactics reflected in this illustration of the Mongols conquering Baghdad?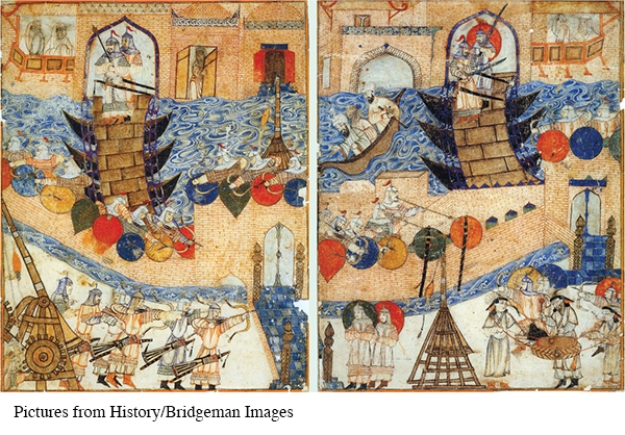 
A) It is reflected in the clothing they wear.
B) It depicts them utilizing a traditional Chinese battle formation.
C) It depicts them using a catapult and arrows.
D) It is reflected in their use of amphibious troops.

A) It is reflected in the clothing they wear.
B) It depicts them utilizing a traditional Chinese battle formation.
C) It depicts them using a catapult and arrows.
D) It is reflected in their use of amphibious troops.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
According to Map 12.3, "The Spice Trade, ca. 100 B.C.E.-1500 C.E.," which cities or countries were most likely to engage in the ever-increasing spice trade? 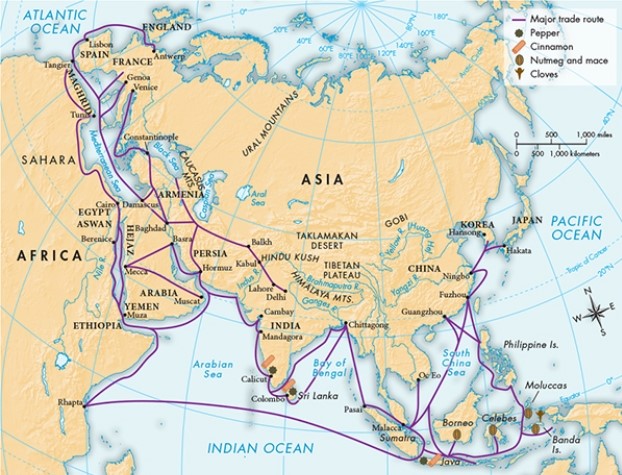
A) Those that were maritime powers
B) Those that were located along major inland waterways in southern and eastern Asia
C) Those that were located on or near the Caspian Sea
D) Those that were accessible to the trade routes that ran through the Tibetan Plateau

A) Those that were maritime powers
B) Those that were located along major inland waterways in southern and eastern Asia
C) Those that were located on or near the Caspian Sea
D) Those that were accessible to the trade routes that ran through the Tibetan Plateau

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Of all the religions the Mongols encountered, which expanded the most under their empire?
A) Catholicism
B) Orthodox Christianity
C) Islam
D) Buddhism
A) Catholicism
B) Orthodox Christianity
C) Islam
D) Buddhism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
How was Khubilai related to Chinggis?
A) Nephew
B) Father
C) Grandson
D) Brother
A) Nephew
B) Father
C) Grandson
D) Brother

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Many positions in the Mongol Empire's administration went to which ethnic group?
A) Uighur Turks
B) Persians
C) Turks
D) Chinese
A) Uighur Turks
B) Persians
C) Turks
D) Chinese

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Which of the following helped the Japanese to repeatedly repulse Mongol invasions?
A) Strong samurai armies and two fierce storms that destroyed the Mongol fleets
B) The expert military leadership of the Japanese emperor
C) The bravery and skill of the Japanese citizenry
D) The intervention of Korea on the side of Japan
A) Strong samurai armies and two fierce storms that destroyed the Mongol fleets
B) The expert military leadership of the Japanese emperor
C) The bravery and skill of the Japanese citizenry
D) The intervention of Korea on the side of Japan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The route taken by Marco Polo, illustrated in Map 12.1, "The Mongol Empire," mimicked very closely the route utilized by which of the following? 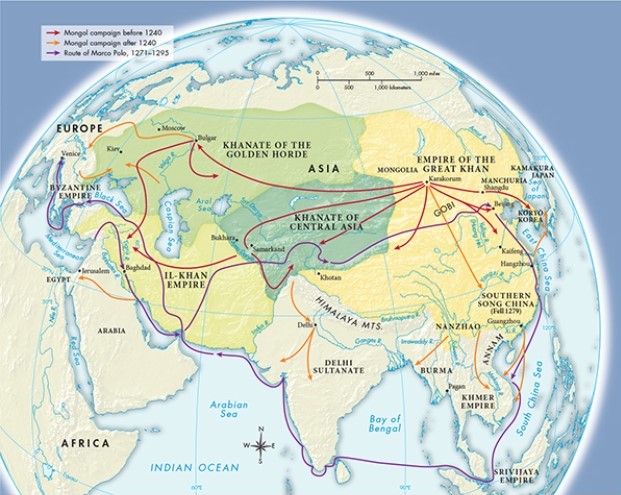
A) Mongol invaders on their way to Japan
B) Viking raiders attempting to establish supremacy in the Arabian Sea
C) Traders shipping precious metals from South America
D) Spice traders

A) Mongol invaders on their way to Japan
B) Viking raiders attempting to establish supremacy in the Arabian Sea
C) Traders shipping precious metals from South America
D) Spice traders

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The Black Death that struck Europe and the Middle East in the mid-fourteenth century probably came from where?
A) Africa
B) India
C) West Asia
D) Central Asia
A) Africa
B) India
C) West Asia
D) Central Asia

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Timur, who arose as a new conqueror as Mongol rule declined, began as which of the following?
A) A Mongolian nomad
B) A Persian scholar
C) A Uighur herdsman
D) A Turkish noble
A) A Mongolian nomad
B) A Persian scholar
C) A Uighur herdsman
D) A Turkish noble

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following was true of the Mongol system of tax-farming in China?
A) It helped establish social stability.
B) It was favored by ordinary Chinese over their traditional taxes.
C) It allotted farmland to the highest bidders.
D) It involved the sale of tax licenses to Central Asian Muslim merchants.
A) It helped establish social stability.
B) It was favored by ordinary Chinese over their traditional taxes.
C) It allotted farmland to the highest bidders.
D) It involved the sale of tax licenses to Central Asian Muslim merchants.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
How did Chinggis Khan reorder the Mongol army?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Describe the role of women in Mongol society.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
How did warfare make some nomadic tribes of Central Asia powerful and others less so?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
How was the Gupta Empire organized?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What group's attacks irreparably weakened the Gupta Empire?
A) Mongols
B) Muslims
C) Huns
D) Buddhism
A) Mongols
B) Muslims
C) Huns
D) Buddhism

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What was the name of the first state to appear in Southeast Asia, with its capital in southern Vietnam?
A) Funan
B) Khmer
C) Indonesia
D) Malay
A) Funan
B) Khmer
C) Indonesia
D) Malay

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
What was the religious policy of the Gupta emperors?
A) They were Hindu but tolerated all faiths.
B) They persecuted Buddhists.
C) They encouraged the adoption of Islam.
D) They demanded that their subjects be Hindus.
A) They were Hindu but tolerated all faiths.
B) They persecuted Buddhists.
C) They encouraged the adoption of Islam.
D) They demanded that their subjects be Hindus.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Why were Europeans considered the biggest beneficiaries of the spread of technology with the Mongol conquests?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The Khmer Empire was centered in what modern-day country?
A) Vietnam
B) Thailand
C) Cambodia
D) Laos
A) Vietnam
B) Thailand
C) Cambodia
D) Laos

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What was Kalidasa's profession in Gupta India?
A) Playwright and poet
B) Mathematician
C) Hindu Brahman
D) Ascetic monk
A) Playwright and poet
B) Mathematician
C) Hindu Brahman
D) Ascetic monk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Briefly describe the Uighur empire and subsequent kingdom to the thirteenth century. What kind of model did it present for later Central Asian empires?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Trace the extent of the Mongol conquests. What was the cultural and economic impact of the initial conquests?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
What led to the collapse of the Easter Island society?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
How did Muslim Turkic rulers generally treat Hindus in India?
A) They saw them as an inferior race subject to extermination.
B) They considered them exempt from taxation because of their holiness.
C) They considered them a "protected people" like the Christians and Jews.
D) They ignored the caste system, viewing all Hindus as untouchables.
A) They saw them as an inferior race subject to extermination.
B) They considered them exempt from taxation because of their holiness.
C) They considered them a "protected people" like the Christians and Jews.
D) They ignored the caste system, viewing all Hindus as untouchables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Who invaded and looted the Delhi sultanate in 1398?
A) Timur
B) Chinggis Khan
C) Ögödei
D) Khubilai Khan
A) Timur
B) Chinggis Khan
C) Ögödei
D) Khubilai Khan

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
How did Muslim rulers in northern India generally treat indigenous Hindus?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Where did "Arabic" numerals originate?
A) Mecca
B) Karakorum
C) Persia
D) India
A) Mecca
B) Karakorum
C) Persia
D) India

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
What led to the success of Chinggis and the Mongols as invaders?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
What did the Arab invaders of the Sind and the Turkish invaders of Khurasan have in common?
A) Interest in Buddhism
B) Ethnic background
C) Respect for Hinduism
D) Belief in Islam
A) Interest in Buddhism
B) Ethnic background
C) Respect for Hinduism
D) Belief in Islam

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
From where did the Srivijayan rulers of Sumatra draw their ideas on governing?
A) India
B) Vietnam/Funan
C) The Khmer Empire
D) China's Tang Dynasty
A) India
B) Vietnam/Funan
C) The Khmer Empire
D) China's Tang Dynasty

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Why were the Mongols unsuccessful in conquering Japan and the Delhi sultanate? What do these defeats tell us about the limitations of Mongol military skills?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The civilizations that arose in Southeast Asia featured both indigenous and foreign elements. Identify and describe those elements that were borrowed. How can we explain the adoption of these foreign elements?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Use the following to answer questions:
Sanskrit
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.
Sanskrit
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Use the following to answer questions:
steppe
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.
steppe
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Use the following to answer questions:
protected people
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.
protected people
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Describe the encounter between Muslim Turkic warriors and Hindu India. What cultural barriers separated Muslim from Hindu? What different tactics did Muslim rulers use to govern Hindu populations?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Use the following to answer questions:
yurts
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.
yurts
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
During the twelfth through fourteenth centuries, nomadic peoples from the Eurasian steppe conquered most of the continent, culminating in the Mongol conquest. How can we explain this shift in military power from the older urban civilizations to the nomadic steppe peoples?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Use the following to answer questions:
khanates
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.
khanates
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Use the following to answer questions:
Chinggis Khan
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.
Chinggis Khan
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Use the following to answer questions:
jati
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.
jati
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
How do you explain the fact that the various nomadic empires, particularly the Mongol, were relatively short-lived?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Use the following to answer questions:
tax-farming
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.
tax-farming
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Use the following to answer questions:
nomads
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.
nomads
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Use the following to answer questions:
Srivijaya
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.
Srivijaya
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Use the following to answer questions:
sati
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.
sati
A)Groups of people who move from place to place in search of food, water, and pasture for their animals, usually following the seasons.
B)Grasslands that are too dry for crops but support pasturing animals; they are common across much of the center of Eurasia.
C)Tents in which the pastoral nomads lived; they could be quickly dismantled and loaded onto animals or carts.
D)The title given to the Mongol ruler Temujin in 1206; it means Great Ruler.
E)The states ruled by a khan; the four units into which Chinggis divided the Mongol Empire.
F)Assigning the collection of taxes to whoever bids the most for the privilege.
G)The Muslim classification used for Hindus, Christians, and Jews; they were allowed to follow their religions but had to pay a special tax.
H)The thousands of Indian castes.
I)A practice whereby a high-caste Hindu woman would throw herself on her husband's funeral pyre.
J)India's classical literary language.
K)A maritime empire that held the Strait of Malacca and the waters around Sumatra and adjacent islands.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 76 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



