Deck 5: Intertemporal Decision Making and Capital Values
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/94
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Intertemporal Decision Making and Capital Values
1
An increase in income in period 0 will:
A)parallel shift the budget line up.
B)rotate the budget line clockwise around the endowment point.
C)parallel shift the budget line down.
D)rotate the budget line counter- clockwise around the endowment point.
A)parallel shift the budget line up.
B)rotate the budget line clockwise around the endowment point.
C)parallel shift the budget line down.
D)rotate the budget line counter- clockwise around the endowment point.
parallel shift the budget line up.
2
The key to intertemporal decision making is:
A)the interest rate.
B)central bank actions.
C)commercial banking regulations.
D)individual risk preference.
A)the interest rate.
B)central bank actions.
C)commercial banking regulations.
D)individual risk preference.
the interest rate.
3
A decrease in income in period 1 will:
A)rotate the budget line clockwise around the endowment point.
B)rotate the budget line counter- clockwise around the endowment point.
C)parallel shift the budget line up.
D)parallel shift the budget line down.
A)rotate the budget line clockwise around the endowment point.
B)rotate the budget line counter- clockwise around the endowment point.
C)parallel shift the budget line up.
D)parallel shift the budget line down.
parallel shift the budget line down.
4
A decrease in interest rate will:
A)rotate the budget line clockwise around the endowment point.
B)parallel shift the budget line up.
C)parallel shift the budget line down.
D)rotate the budget line counter- clockwise around the endowment point.
A)rotate the budget line clockwise around the endowment point.
B)parallel shift the budget line up.
C)parallel shift the budget line down.
D)rotate the budget line counter- clockwise around the endowment point.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
If a person's marginal rate of time preference for equal amounts of consumption in the present and next periods is less than one, she is said to be:
A)elastic.
B)patient.
C)normal.
D)impatient.
A)elastic.
B)patient.
C)normal.
D)impatient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Figure 5A
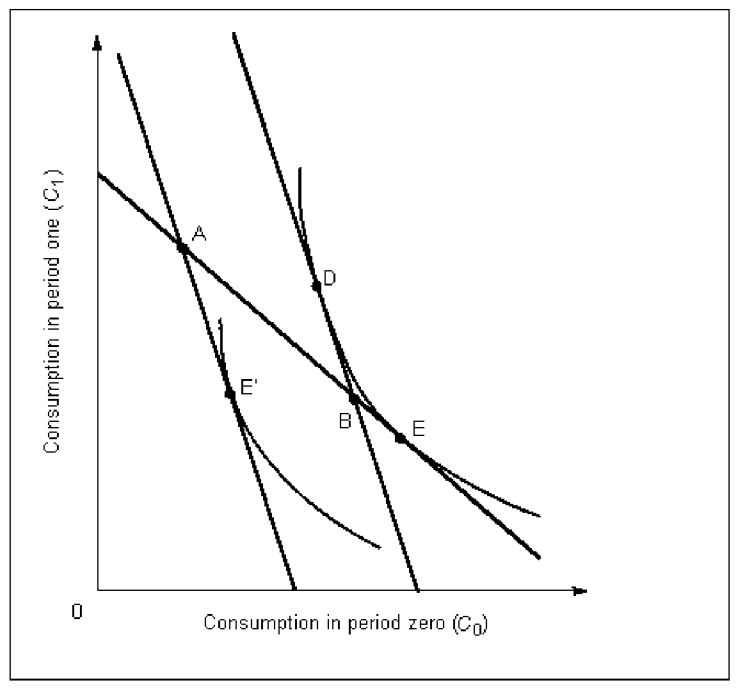
In Figure 5A, an individual who was compensated for an increase in interest rates would find her intertemporal equilibrium at point:
A)E.
B)A.
C)D.
D)E'.

In Figure 5A, an individual who was compensated for an increase in interest rates would find her intertemporal equilibrium at point:
A)E.
B)A.
C)D.
D)E'.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Consumer capital includes goods which are:
A)financed in the long term.
B)passed between generations.
C)consumed with complementary goods.
D)valuable in one time period only.
A)financed in the long term.
B)passed between generations.
C)consumed with complementary goods.
D)valuable in one time period only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the life cycle model, total amount available for consumption in period 0 is:
A)C0 = M0 + present value of(M1 - C1).
B)C0 = M0 + M1.
C)C0 = M0 + future value of (M1 - C1).
D)C0 = M0 + M1 - C1.
A)C0 = M0 + present value of(M1 - C1).
B)C0 = M0 + M1.
C)C0 = M0 + future value of (M1 - C1).
D)C0 = M0 + M1 - C1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Investment in training is called:
A)current consumption.
B)human capital.
C)future consumption.
D)foregone income.
A)current consumption.
B)human capital.
C)future consumption.
D)foregone income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The present value of $1000 payable in two years from today is:
A)$1000/(1 + 2r).
B)$1000/(1 + r)2.
C)$1000/(1 - 2r).
D)$1000.
A)$1000/(1 + 2r).
B)$1000/(1 + r)2.
C)$1000/(1 - 2r).
D)$1000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Intertemporal choice requires knowledge of:
A)prices and interest rates in all future time periods.
B)the present value of future receipts and expenditures.
C)the consumer's expected lifetime income.
D)prices and interest rates in selected future time periods.
A)prices and interest rates in all future time periods.
B)the present value of future receipts and expenditures.
C)the consumer's expected lifetime income.
D)prices and interest rates in selected future time periods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If the increase income from sale of a nonrenewable resource in the current period is less than the present value of income sale of the resource in the next period, the owner should:
A)wait to see what will happen in the future.
B)sell all of the resource in the next period.
C)sell some of the resource now and some in the next period.
D)sell all of the resource now.
A)wait to see what will happen in the future.
B)sell all of the resource in the next period.
C)sell some of the resource now and some in the next period.
D)sell all of the resource now.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If a person's marginal rate of time preference for equal amounts of consumption in the present and next periods is greater than one, she is said to be:
A)elastic.
B)normal.
C)impatient.
D)patient.
A)elastic.
B)normal.
C)impatient.
D)patient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
According to Hotelling's Law, the price of a nonrenewable resource changes from one period to the next at the:
A)real growth rate of national production.
B)nominal growth rate of national production.
C)rate of interest.
D)whim of its owner.
A)real growth rate of national production.
B)nominal growth rate of national production.
C)rate of interest.
D)whim of its owner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The present value of a perpetuity is:
A)M(1 + i).
B)Mi.
C)M/(1 + i).
D)M/i.
A)M(1 + i).
B)Mi.
C)M/(1 + i).
D)M/i.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
An individual that deposits $1,000 in the bank today and receives $1,368 in three years is earning an annual interest rate of approximately
A)9.2%
B)36.8%
C)12.3%
D)11%
A)9.2%
B)36.8%
C)12.3%
D)11%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
When the interest rate i rises, C0:
A)decreases because of the income effect.
B)increases because of the substitution effect.
C)increases because of a total effect.
D)decreases because of a total effect.
A)decreases because of the income effect.
B)increases because of the substitution effect.
C)increases because of a total effect.
D)decreases because of a total effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Consumers borrow money from commercial institutions by:
A)demonstrating the present value of their life- cycle income stream.
B)turning legal control of their future activities over to the lender.
C)providing a legally enforceable conditional claim against assets.
D)appealing to the lender's good will.
A)demonstrating the present value of their life- cycle income stream.
B)turning legal control of their future activities over to the lender.
C)providing a legally enforceable conditional claim against assets.
D)appealing to the lender's good will.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A 25- year- old individual is choosing between three occupations - an entertainer with large earnings when young but those earnings will decline with age; a teacher with constant income over time; and a physician with very low initial earnings but earnings that will continue to rise over time. Other than income the occupations are equally preferable. If the annual earnings of each occupation are added, the total is highest for the career as a physician, second as an entertainer, and lowest as a teacher. Which of the following is true?
A)It makes economic sense to add the annual earnings of an occupation only if the interest rate is positive.
B)Being a doctor is preferable for a low enough interest rate.
C)Being an entertainer is preferable for a low enough interest rate
D)Being a teacher is preferable for a certain value of the interest rate.
A)It makes economic sense to add the annual earnings of an occupation only if the interest rate is positive.
B)Being a doctor is preferable for a low enough interest rate.
C)Being an entertainer is preferable for a low enough interest rate
D)Being a teacher is preferable for a certain value of the interest rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An individual's intertemporal budget for current consumption includes her:
A)current income only.
B)current income and the present value of future income.
C)current income and the future value of future income.
D)present value of future income only.
A)current income only.
B)current income and the present value of future income.
C)current income and the future value of future income.
D)present value of future income only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An increase in interest rate will:
A)parallel shift the budget line down.
B)rotate the budget line clockwise around the intercept with the vertical axis.
C)rotate the budget line clockwise around the endowment point.
D)parallel shift the budget line up.
A)parallel shift the budget line down.
B)rotate the budget line clockwise around the intercept with the vertical axis.
C)rotate the budget line clockwise around the endowment point.
D)parallel shift the budget line up.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If C0 and C1 are both normal goods, for a person who saves in the initial equilibrium, when i rises:
A)C0 and C1 both increase.
B)C1 declines.
C)C1 increases.
D)C0 and C1 both decline.
A)C0 and C1 both increase.
B)C1 declines.
C)C1 increases.
D)C0 and C1 both decline.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If someone receives $24 from a pawnbroker for a watch and redeems it one month later for $30, he has:
A)paid about 150% interest at an annual rate to borrow $24 for one month.
B)paid about 25% interest at an annual rate to borrow $24 for one month.
C)borrowed money without paying interest.
D)paid about 300% interest at an annual rate to borrow $24 for one month.
E)paid about 72% interest at an annual rate to borrow $24 for one month.
A)paid about 150% interest at an annual rate to borrow $24 for one month.
B)paid about 25% interest at an annual rate to borrow $24 for one month.
C)borrowed money without paying interest.
D)paid about 300% interest at an annual rate to borrow $24 for one month.
E)paid about 72% interest at an annual rate to borrow $24 for one month.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
It is conventional to use the present value criterion rather than the future value criterion:
A)although they are equivalent.
B)because it gives smaller results.
C)because it gives better results.
D)because it gives larger results.
A)although they are equivalent.
B)because it gives smaller results.
C)because it gives better results.
D)because it gives larger results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If C0 and C1 are both normal goods, for someone who borrows in the initial equilibrium, when i
Rises:
A)C0 declines.
B)C0 increases.
C)C0 and C1 both increase.
D)C1 increases.
Rises:
A)C0 declines.
B)C0 increases.
C)C0 and C1 both increase.
D)C1 increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
In periods 0 and 1, Ralph consumed two goods, x1 and x2, and his utility functions in the two periods were identical. In period 0 the prices of x1 and x2 were $2 and $1 respectively, and Ralph consumed 10 units of x1 and 80 units of x2. In period 1 the prices of x1 and x2 were identical, and equal to $1. If Ralph consumed 40 units of x1 and 40 units of x2 in period 1, then the Paasche price index is:
A)3/2.
B)10/9.
C)2/3.
D)9/10.
A)3/2.
B)10/9.
C)2/3.
D)9/10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The rate of interest that people will be willing to pay:
A)is independent of their personal rate of time preference (impatience).
B)will increase as they come to assign more importance to distant events relative to events in the near future.
C)depends primarily upon their present plans for consumption.
D)will be higher the more attractive are the current opportunities they perceive relative to future opportunities.
A)is independent of their personal rate of time preference (impatience).
B)will increase as they come to assign more importance to distant events relative to events in the near future.
C)depends primarily upon their present plans for consumption.
D)will be higher the more attractive are the current opportunities they perceive relative to future opportunities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
In the life cycle model, total amount available for consumption in period 1 is:
A)C1 = M1 + (1 + i)/(M0 - C0).
B)C1 = M1 + (M0 - C0)/(1 + i).
C)C1 = M1 + M0 - C0.
D)C1 = M1 + (1 + i)(M0 - C0).
A)C1 = M1 + (1 + i)/(M0 - C0).
B)C1 = M1 + (M0 - C0)/(1 + i).
C)C1 = M1 + M0 - C0.
D)C1 = M1 + (1 + i)(M0 - C0).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The present value of income to be received in period t is given by:
A)$It*(1 + i)t.
B)$It/(1 + i)t.
C)$It.
D)$It/(1 + t)i.
A)$It*(1 + i)t.
B)$It/(1 + i)t.
C)$It.
D)$It/(1 + t)i.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The Separation Theorem:
A)implies that consumers maximize utility over time subject to a wealth constraint.
B)means that individuals choose occupations independent of their consumption streams.
C)requires that the present value of consumption expenditure exceeds the present value of income.
D)means that firms maximize profits as a function of the preferences of consumers.
A)implies that consumers maximize utility over time subject to a wealth constraint.
B)means that individuals choose occupations independent of their consumption streams.
C)requires that the present value of consumption expenditure exceeds the present value of income.
D)means that firms maximize profits as a function of the preferences of consumers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
You own two stocks, one whose value depreciated drastically in the last week, and one whose value increased by 80% last week. If you are forced to sell one, which one would you pick?
A)The one that increased in value, to take advantage of the capital gain.
B)You are indifferent because you invest in the market for fun, not income.
C)The past performance is irrelevant for this decision.
D)The one that has fallen in value, to salvage at least a part of its value.
A)The one that increased in value, to take advantage of the capital gain.
B)You are indifferent because you invest in the market for fun, not income.
C)The past performance is irrelevant for this decision.
D)The one that has fallen in value, to salvage at least a part of its value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the movie Wall Street, starring Michael Douglas and Charlie Sheen as stock brokers, the latter learns a valuable lesson about successful investing:
A)Illegal activity is the only way to above- average returns.
B)Mimicking star investors will always yield higher returns.
C)Tracking past stock performance is key to high returns.
D)Labourious analysis of stocks is the key to sound investment.
A)Illegal activity is the only way to above- average returns.
B)Mimicking star investors will always yield higher returns.
C)Tracking past stock performance is key to high returns.
D)Labourious analysis of stocks is the key to sound investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The rate of interest you receive for the use of money is called the:
A)deposit rate.
B)discount rate.
C)borrowing rate.
D)prime rate.
A)deposit rate.
B)discount rate.
C)borrowing rate.
D)prime rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
In the life cycle model, total amount available for consumption in period 0 is:
A)C0 = M0 + M1 - C1.
B)C0 = M0 + (M1 - C1)/(1 + i).
C)C0 = M0 + (1 + i)(M1 - C1).
D)C0 = M0 + (1 + i)/(M1 - C1).
A)C0 = M0 + M1 - C1.
B)C0 = M0 + (M1 - C1)/(1 + i).
C)C0 = M0 + (1 + i)(M1 - C1).
D)C0 = M0 + (1 + i)/(M1 - C1).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
In equilibrium:
A)everyone with a high rate of time preference borrows.
B)everyone with a low rate of time preference borrows.
C)everyone has the same marginal value of current consumption.
D)everyone has the same rate of time preference.
A)everyone with a high rate of time preference borrows.
B)everyone with a low rate of time preference borrows.
C)everyone has the same marginal value of current consumption.
D)everyone has the same rate of time preference.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The optimal time to harvest is:
A)when the value of the crop is maximized.
B)when the rate of growth of the crop is maximized.
C)when the present value of the crop is maximized.
D)when the rate of growth of the crop is zero.
A)when the value of the crop is maximized.
B)when the rate of growth of the crop is maximized.
C)when the present value of the crop is maximized.
D)when the rate of growth of the crop is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In equilibrium, the marginal rate of time preference is equal to:
A)1/(1 + i).
B)1/i.
C)1 + i.
D)i.
A)1/(1 + i).
B)1/i.
C)1 + i.
D)i.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The future value two years from today of $1000 received today is:
A)$1000(1 + 2r).
B)$1000(1 - 2r).
C)$1000(1 + r)2.
D)$1000.
A)$1000(1 + 2r).
B)$1000(1 - 2r).
C)$1000(1 + r)2.
D)$1000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A perpetuity is:
A)an annuity that lasts for one year.
B)an annuity that lasts for ten years.
C)an annuity that lasts for a long time.
D)an annuity that lasts forever.
A)an annuity that lasts for one year.
B)an annuity that lasts for ten years.
C)an annuity that lasts for a long time.
D)an annuity that lasts forever.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Assets that generate no utility directly:
A)can be expected to grow in value at a rate greater than the rate of interest.
B)should grow in value at a rate equal to the rate of interest.
C)should not be expected to grow in value.
D)can be expected to grow in value at a rate lower than the rate of interest.
A)can be expected to grow in value at a rate greater than the rate of interest.
B)should grow in value at a rate equal to the rate of interest.
C)should not be expected to grow in value.
D)can be expected to grow in value at a rate lower than the rate of interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A lottery offers the winner a choice between a 20 year annuity of $50,000 starting a year from now and a lump sum of half a million dollars payable today. If the current interest rate is 10%, the winner is better off to take:
A)the annuity, because it has a larger future value.
B)the annuity, because it has a larger present value.
C)the lump sum, because it has a larger future value.
D)the lump sum, because it has a larger present value.
A)the annuity, because it has a larger future value.
B)the annuity, because it has a larger present value.
C)the lump sum, because it has a larger future value.
D)the lump sum, because it has a larger present value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Consumer capital goods that last longer typically sell for higher prices because
A)consumers' reservation prices are higher
B)asymmetric information leads consumers to believe they are better
C)they have higher production costs
D)they provide consumers with greater utility
A)consumers' reservation prices are higher
B)asymmetric information leads consumers to believe they are better
C)they have higher production costs
D)they provide consumers with greater utility

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
From an individual consumer's point of view, mortgages and bonds are:
A)abstract commodities without practical value.
B)identical.
C)largely speculative.
D)dependent on present value calculations.
A)abstract commodities without practical value.
B)identical.
C)largely speculative.
D)dependent on present value calculations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Dick will receive $5,000 on December 25, 2013, and $15,000 on December 25, 2014. If the yearly rate of interest is 5.0%, then the present value of these payments on December 25, 2012, is:
A)$18,367.
B)$11,666.
C)$6,250.
D)$20,000.
A)$18,367.
B)$11,666.
C)$6,250.
D)$20,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The rate of interest you pay to use money is called the:
A)prime rate.
B)borrowing rate.
C)discount rate.
D)deposit rate.
A)prime rate.
B)borrowing rate.
C)discount rate.
D)deposit rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Brett's reservation price for a 1957 Plymouth Fury in mint condition is $2,500. Which of the following is false?
A)If the price of gasoline were to drop by $.50 per gallon, it is likely that Brett's reservation price would increase.
B)The price Brett pays would include storage costs.
C)If Brett paid $2,500 for such a car, he would be on the same indifference curve as he would have been if he had not bought the car.
D)Brett would buy such a car for $2,000.
A)If the price of gasoline were to drop by $.50 per gallon, it is likely that Brett's reservation price would increase.
B)The price Brett pays would include storage costs.
C)If Brett paid $2,500 for such a car, he would be on the same indifference curve as he would have been if he had not bought the car.
D)Brett would buy such a car for $2,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
When the market for loanable funds is perfect, the borrowing rate is:
A)independent of the deposit rate.
B)less than the deposit rate.
C)greater than the deposit rate.
D)equal to the deposit rate.
A)independent of the deposit rate.
B)less than the deposit rate.
C)greater than the deposit rate.
D)equal to the deposit rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In periods 0 and 1, Ralph consumed two goods, x1 and x2, and his utility functions in the two periods were identical. In period 0 the prices of x1 and x2 were $2 and $1 respectively, and Ralph consumed 10 units of x1 and 80 units of x2. In period 1 the prices of x1 and x2 were identical, and equal to $1. If Ralph consumed 40 units of x1 and 40 units of x2 in period 1:
A)he was better off in period 0.
B)we cannot say whether he was better off in one of the periods.
C)he was equally well off in both periods.
D)he was better off in period 1.
A)he was better off in period 0.
B)we cannot say whether he was better off in one of the periods.
C)he was equally well off in both periods.
D)he was better off in period 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A person who defers consumption to another day is concerned with the:
A)net present value of money.
B)net future value of money.
C)future value of money.
D)present value of money.
A)net present value of money.
B)net future value of money.
C)future value of money.
D)present value of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
It has been documented that an accounting degree offers a higher financial rate of return than an history degree. Why would any student enroll in a history program?
A)For logistics reasons, the accounting programs are capped.
B)Calculating these returns are always subject to error.
C)A utility return makes up the difference.
D)Prospective history students are not good with numbers.
A)For logistics reasons, the accounting programs are capped.
B)Calculating these returns are always subject to error.
C)A utility return makes up the difference.
D)Prospective history students are not good with numbers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The present value of $1 payable in the future decreases:
A)the longer time it is to be paid and the lower r is.
B)the longer time it is to be paid and the higher r is.
C)the sooner it is to be paid and the lower r is.
D)the sooner it is to be paid and the higher r is.
A)the longer time it is to be paid and the lower r is.
B)the longer time it is to be paid and the higher r is.
C)the sooner it is to be paid and the lower r is.
D)the sooner it is to be paid and the higher r is.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In periods 0 and 1, Ralph consumed two goods, x1 and x2, and his utility functions in the two periods were identical. In period 0 the prices of x1 and x2 were $2 and $1 respectively, and Ralph consumed 10 units of x1 and 80 units of x2. In period 1 the prices of x1 and x2 were identical, and equal to $1. If Ralph consumed 40 units of x1 and 40 units of x2 in period 1, then the Laspeyres price index is:
A)10/9.
B)2/3.
C)3/2.
D)9/10.
A)10/9.
B)2/3.
C)3/2.
D)9/10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Investing in art usually yields less than the market rate of return:
A)because art pieces are inferior goods.
B)because economics cannot explain the functioning of art markets.
C)because art collectors get to enjoy the items while in their possession.
D)because art collectors do not generally care about financially rates of return.
A)because art pieces are inferior goods.
B)because economics cannot explain the functioning of art markets.
C)because art collectors get to enjoy the items while in their possession.
D)because art collectors do not generally care about financially rates of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In periods 0 and 1, Ralph consumed two goods, x1 and x2, and his utility functions in the two periods were identical. In period 0 the prices of x1 and x2 were $2 and $1 respectively, and Ralph consumed 10 units of x1 and 80 units of x2. In period 1 the prices of x1 and x2 were identical, and equal to $1. If Ralph consumed 15 units of x1 and 65 units of x2 in period 1, then:
A)he may have been equally well off in both periods.
B)we cannot say whether he was better off in one of the periods.
C)he was better off in period 1.
D)he was better off in period 0.
A)he may have been equally well off in both periods.
B)we cannot say whether he was better off in one of the periods.
C)he was better off in period 1.
D)he was better off in period 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the increase income from sale of a nonrenewable resource in the current period is equal to the present value of income sale of the resource in the next period, the owner should:
A)sell all of the resource in the next period.
B)sell some of the resource now and some in the next period.
C)sell all of the resource now.
D)wait to see what will happen in the future.
A)sell all of the resource in the next period.
B)sell some of the resource now and some in the next period.
C)sell all of the resource now.
D)wait to see what will happen in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Future values are:
A)the inverse of present values.
B)amounts that can be borrowed today in exchange for future payment.
C)the negative of present values.
D)are the annuity values divided by the number of years.
A)the inverse of present values.
B)amounts that can be borrowed today in exchange for future payment.
C)the negative of present values.
D)are the annuity values divided by the number of years.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Phil owns a vacation cottage, and is considering the option of bringing electricity to the cottage. If he does, he can buy electricity for $.10 per kilowatt hour. The Public Utilities Company wants to charge Phil $2,000 for the electrical hook- up, but Phil's reservation price is only $1,500. This question concerns the measurement of the benefit to Phil for the privilege of buying electricity at
$.10 per kilowatt hour. Which of the following is true?
A)EV = $1,500
B)CV = $2,000
C)CS = $2,000
D)CV = $1,500
$.10 per kilowatt hour. Which of the following is true?
A)EV = $1,500
B)CV = $2,000
C)CS = $2,000
D)CV = $1,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Firms which sell consumer capital goods are likely to sell the consumable good:
A)at its reservation price and the capital good at cost.
B)and the consumable good at their reservation prices.
C)and the capital good at cost.
D)at cost and the capital good at its reservation price.
A)at its reservation price and the capital good at cost.
B)and the consumable good at their reservation prices.
C)and the capital good at cost.
D)at cost and the capital good at its reservation price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Using old capital goods, such as machinery and computers:
A)is not a good idea since firms have to use the newest technology if they are to compete successfully in the market place.
B)may work if accompanied with the necessary skills in terms of labour.
C)is a valid strategy if their prices are low enough for the rate of return to rival the one for newer capital goods.
D)is not an option in today's world given the tremendous value built in the newer machines.
A)is not a good idea since firms have to use the newest technology if they are to compete successfully in the market place.
B)may work if accompanied with the necessary skills in terms of labour.
C)is a valid strategy if their prices are low enough for the rate of return to rival the one for newer capital goods.
D)is not an option in today's world given the tremendous value built in the newer machines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Firms that sell both consumer capital goods and the complementary good
A)capture all the consumer surplus of the consumer capital good
B)sell the capital good at marginal cost
C)maximize profit on both goods individually
D)capture all the consumer surplus of the complementary good
A)capture all the consumer surplus of the consumer capital good
B)sell the capital good at marginal cost
C)maximize profit on both goods individually
D)capture all the consumer surplus of the complementary good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
If the increase income from sale of a nonrenewable resource in the current period is greater than the present value of income sale of the resource in the next period, the owner should:
A)sell all of the resource now.
B)wait to see what will happen in the future.
C)sell all of the resource in the next period.
D)sell some of the resource now and some in the next period.
A)sell all of the resource now.
B)wait to see what will happen in the future.
C)sell all of the resource in the next period.
D)sell some of the resource now and some in the next period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is not an example of intertemporal resource allocation?
A)locating a business in one locality or another
B)getting a job or starting a business
C)buying a car or a corporate stock
D)getting a job today or going to school
A)locating a business in one locality or another
B)getting a job or starting a business
C)buying a car or a corporate stock
D)getting a job today or going to school

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
In present value calculations, the assumption of a common interest rate is:
A)convenient.
B)essential.
C)redundant.
D)arbitrary.
A)convenient.
B)essential.
C)redundant.
D)arbitrary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A person who borrows money is concerned with the:
A)future value of money.
B)net present value of money.
C)net future value of money.
D)present value of money.
A)future value of money.
B)net present value of money.
C)net future value of money.
D)present value of money.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In periods 0 and 1, Ralph consumed two goods, x1 and x2, and his utility functions in the two periods were identical. In period 0 the prices of x1 and x2 were $2 and $1 respectively, and Ralph consumed 10 units of x1 and 80 units of x2. In period 1 the prices of x1 and x2 were identical, and equal to $1. If Ralph consumed 15 units of x1 and 65 units of x2 in period 1, then the Paasche quantity index is equal to:
A)95/100.
B)9/8.
C)8/9.
D)100/95.
A)95/100.
B)9/8.
C)8/9.
D)100/95.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The difference in present value between a perpetuity that promised $1 per year starting today and one that promised $1 per year starting next year is:
A)$1/(1 + i).
B)$1.
C)0.
D)$i/(1 + i).
A)$1/(1 + i).
B)$1.
C)0.
D)$i/(1 + i).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The life cycle model hypothesizes that:
A)older people are less risk averse.
B)younger people spend more than they earn.
C)older people spend more than they earn.
D)younger people earn more than they spend.
A)older people are less risk averse.
B)younger people spend more than they earn.
C)older people spend more than they earn.
D)younger people earn more than they spend.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The best time to log a forest is
A)when the trees have reached their maximum value
B)when the growth rate of the trees equals the interest rate
C)when the cost of cutting is minimized
D)when the trees have reached their maximum height
A)when the trees have reached their maximum value
B)when the growth rate of the trees equals the interest rate
C)when the cost of cutting is minimized
D)when the trees have reached their maximum height

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
In periods 0 and 1, Ralph consumed two goods, x1 and x2, and his utility functions in the two periods were identical. In period 0 the prices of x1 and x2 were $2 and $1 respectively, and Ralph consumed 10 units of x1 and 80 units of x2. In period 1 the prices of x1 and x2 were identical, and equal to $1. If Ralph consumed 40 units of x1 and 40 units of x2 in period 1, then the Laspeyres quantity index is:
A)9/8.
B)6/5.
C)8/9.
D)5/6.
A)9/8.
B)6/5.
C)8/9.
D)5/6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The reservation price for consumer capital good depends on
A)the present value of the EV from the complementary good
B)the marginal utility derived from the capital good
C)the present value of the CV from the capital good
D)consumer preferences and the price of the complementary good
A)the present value of the EV from the complementary good
B)the marginal utility derived from the capital good
C)the present value of the CV from the capital good
D)consumer preferences and the price of the complementary good

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Figure 5A

In Figure 5A, the equilibrium before an interest rate increase is at point:
A)E'.
B)E.
C)D.
D)A.

In Figure 5A, the equilibrium before an interest rate increase is at point:
A)E'.
B)E.
C)D.
D)A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
When making intertemporal resource allocations, substitution of consumption in the next period for consumption in the current period is called:
A)the marginal rate of time preference.
B)the borrowing rate.
C)risk preference.
D)the marginal rate of substitution.
A)the marginal rate of time preference.
B)the borrowing rate.
C)risk preference.
D)the marginal rate of substitution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Figure 5A

In Figure 5A, changes in the interest rate cause the intertemporal budget:
A)the intertemporal budget lines pivot around point B.
B)line to shift from the line AE' to DB.
C)line to shift from the line DB to AE'.
D)lines to pivot around point A.

In Figure 5A, changes in the interest rate cause the intertemporal budget:
A)the intertemporal budget lines pivot around point B.
B)line to shift from the line AE' to DB.
C)line to shift from the line DB to AE'.
D)lines to pivot around point A.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Figure 5A

In Figure 5A, the equilibrium after an interest rate increase is at point:
A)D.
B)A.
C)E.
D)E'.

In Figure 5A, the equilibrium after an interest rate increase is at point:
A)D.
B)A.
C)E.
D)E'.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Students that currently have a low level of income:
A)are not able to optimize with respect to intertemporal consumption.
B)cannot consume as a wealthy person.
C)cannot incur large levels of debt.
D)may still be wealthy because they expect higher income in the future.
A)are not able to optimize with respect to intertemporal consumption.
B)cannot consume as a wealthy person.
C)cannot incur large levels of debt.
D)may still be wealthy because they expect higher income in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Which of the following is an example of consumer capital?
A)education
B)bank account balance
C)refrigerator
D)shares of Procter and Gamble
A)education
B)bank account balance
C)refrigerator
D)shares of Procter and Gamble

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
According to the separation theorem, individuals choose among different income streams by choosing the one with the largest:
A)future value.
B)unconstrained utility.
C)constrained utility.
D)present value.
A)future value.
B)unconstrained utility.
C)constrained utility.
D)present value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
According to the separation theorem, individuals choose consumption expenditures over time by choosing the one with the largest:
A)unconstrained utility.
B)constrained utility.
C)future value.
D)present value.
A)unconstrained utility.
B)constrained utility.
C)future value.
D)present value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Powerful multinational firms:
A)care more about the numbers of items sold, not about quality products.
B)suppress innovation because consumers are not willing to pay for very high quality goods.
C)would never suppress quality that increases the value of the firm.
D)suppress innovation, especially concerning built- in quality, because it would cannibalize into its own sales.
A)care more about the numbers of items sold, not about quality products.
B)suppress innovation because consumers are not willing to pay for very high quality goods.
C)would never suppress quality that increases the value of the firm.
D)suppress innovation, especially concerning built- in quality, because it would cannibalize into its own sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Hotelling's Law applies to which of the following resources?
A)fresh water
B)mineral deposits
C)forests
D)fish
A)fresh water
B)mineral deposits
C)forests
D)fish

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 94 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



