Deck 3: Demand Theory
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Demand Theory
1
Hamburger University is losing $4 million dollars per year. The trustees of the university want to increase fees to cover the deficit. The president of the student body wants to decrease fees to cover the deficit. On the basis of this information, which of the following is true?
A)The trustees think demand is price elastic, and the president of the student body thinks it is price inelastic.
B)Both the trustee and president of the student body think the price elasticity of demand is one.
C)The trustees think demand is price inelastic, and the student body president thinks it is price elastic.
D)There is no disagreement with respect to elasticity.
A)The trustees think demand is price elastic, and the president of the student body thinks it is price inelastic.
B)Both the trustee and president of the student body think the price elasticity of demand is one.
C)The trustees think demand is price inelastic, and the student body president thinks it is price elastic.
D)There is no disagreement with respect to elasticity.
The trustees think demand is price inelastic, and the student body president thinks it is price elastic.
2
Joseph's utility function is given by xA + 2xB, where xA denotes his consumption of apples and xB his consumption of bananas. Suppose a banana cost 50 cents and an apple costs also 50 cents. If his income is $10, then his consumption bundle (xA,xB)is:
A)(20,40).
B)(20,20).
C)(0,20).
D)(20,0).
A)(20,40).
B)(20,20).
C)(0,20).
D)(20,0).
(0,20).
3
Figure 3A
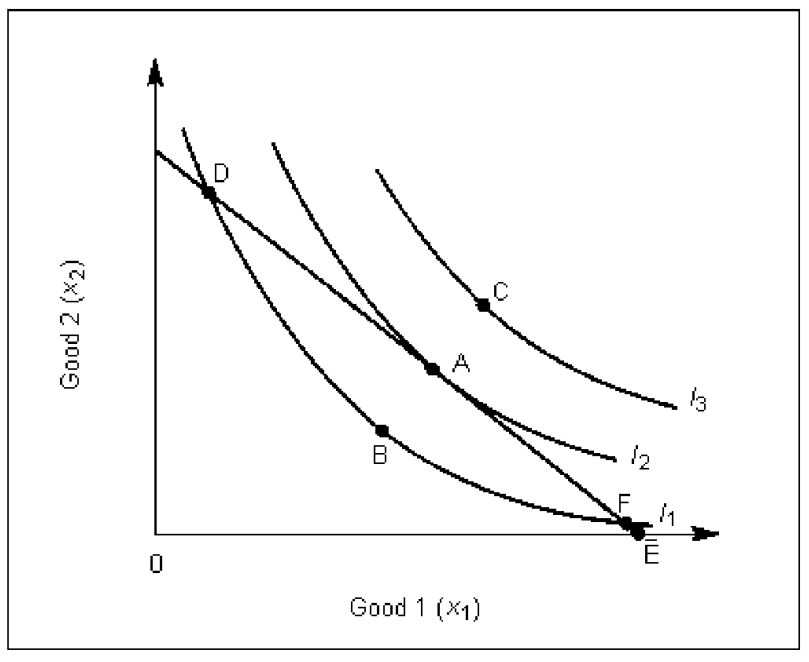
This consumer's utility maximizing consumption bundle is what point in Figure 3A?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

This consumer's utility maximizing consumption bundle is what point in Figure 3A?
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D
A
4
If two linear demand functions intersect the quantity axis at the same point, then:
A)when prices are equal, so are the elasticities.
B)when quantities are equal, so are the price elasticities.
C)when prices are equal, so are the quantities.
D)at the point of intersection the two elasticities are equal to one.
A)when prices are equal, so are the elasticities.
B)when quantities are equal, so are the price elasticities.
C)when prices are equal, so are the quantities.
D)at the point of intersection the two elasticities are equal to one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A negative sloped income consumption line indicates that:
A)one of the goods is a Giffen good
B)the two goods are substitutes
C)the two goods are complements
D)one of the goods is normal and the other is inferior.
A)one of the goods is a Giffen good
B)the two goods are substitutes
C)the two goods are complements
D)one of the goods is normal and the other is inferior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A budget constraint defines the:
A)odds of earning a particular income.
B)consumer's preference ordering.
C)funds allocated for a particular purpose.
D)attainable consumption bundles.
A)odds of earning a particular income.
B)consumer's preference ordering.
C)funds allocated for a particular purpose.
D)attainable consumption bundles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Along an individual demand curve for food, which one of the following is not held constant?
A)the consumer's utility function
B)the consumer's level of utility
C)the consumer's income
D)the price of all other goods
A)the consumer's utility function
B)the consumer's level of utility
C)the consumer's income
D)the price of all other goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If good x1 is a substitute for good x2, then the cross price elasticity of demand for x1 with respect to the price of x2 is:
A)zero.
B)negative.
C)positive.
D)undefined.
A)zero.
B)negative.
C)positive.
D)undefined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Beth consumes two goods, x1 and x2, and her income is $120. The price of x1 is $10, and the price of x2 is $5. If her indifference curves exhibit a diminishing marginal rate of substitution and if her marginal rate of substitution at bundle (7, 10)is 1, then her utility maximizing bundle is:
A)(7, 10).
B)(6, 12).
C)on the budget line to the left of (7, 10).
D)on the budget line to the right of (7, 10).
A)(7, 10).
B)(6, 12).
C)on the budget line to the left of (7, 10).
D)on the budget line to the right of (7, 10).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Figure 3B
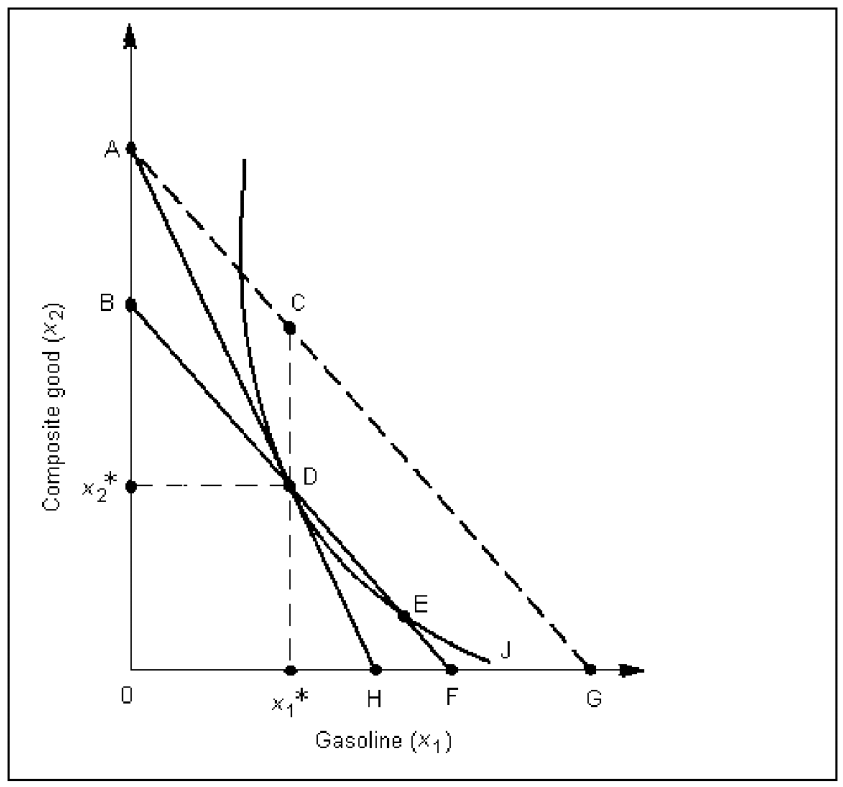
Which of the following is the excise budget line in Figure 3B?
A)BF
B)AG
C)AH
D)IJ

Which of the following is the excise budget line in Figure 3B?
A)BF
B)AG
C)AH
D)IJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Excise taxes are imposed when society's primary objective is to:
A)encourage behaviour.
B)change preferences.
C)raise revenue.
D)discourage behaviour.
A)encourage behaviour.
B)change preferences.
C)raise revenue.
D)discourage behaviour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Figure 3A

This consumer's utility maximizing consumption bundle is illustrated in Figure 3A. Which assumption about consumer preferences guarantees it is not point B?
A)continuity
B)transitivity
C)nonsatiation
D)completeness

This consumer's utility maximizing consumption bundle is illustrated in Figure 3A. Which assumption about consumer preferences guarantees it is not point B?
A)continuity
B)transitivity
C)nonsatiation
D)completeness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Mr. Inflexible's utility function is U(x1,x2)= min(x1,x2). The price of x1 is $1, the price of x2 is $2, and Mr. Inflexible's budget is $120. His utility maximizing consumption bundle is:
A)(20, 40).
B)(20, 50).
C)(40, 40).
D)(60, 30).
A)(20, 40).
B)(20, 50).
C)(40, 40).
D)(60, 30).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Figure 3A

Which of the following is true about the goods in Figure 3A?
A)x1 is an inferior and x2 is a normal good.
B)x1 is a normal and x2 is an inferior good.
C)Both x1 and x2 are normal goods.
D)Both x1 and x2 are inferior goods.

Which of the following is true about the goods in Figure 3A?
A)x1 is an inferior and x2 is a normal good.
B)x1 is a normal and x2 is an inferior good.
C)Both x1 and x2 are normal goods.
D)Both x1 and x2 are inferior goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Beth consumes two goods, x1 and x2, and her income is $120. The price of x1 is $10, and the price of
X2 is $5. Her budget line intersects the x2 axis at consumption bundle:
A)(0, 24).
B)(0, 12).
C)(24, 0).
D)(12, 0).
X2 is $5. Her budget line intersects the x2 axis at consumption bundle:
A)(0, 24).
B)(0, 12).
C)(24, 0).
D)(12, 0).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Price elasticity of demand for a product tends to be greater:
A)the lower its price.
B)the more broadly the product is defined.
C)the closer substitutes are for it.
D)the less close substitutes are for it.
A)the lower its price.
B)the more broadly the product is defined.
C)the closer substitutes are for it.
D)the less close substitutes are for it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Bonnie spends her entire income, $200 on 3 goods, x1, x2 and x3. When p1 = $1, p2 = $3, and p3 =
$5, she buys the following consumption bundle: (15, 20, 25). The price of x1 increases by 25%, and she now buys 15 units of x2 and 28 units of x3. Which of the following is not true?
A)the price elasticity of demand for x1 is one
B)x1 is a Giffen good
C)total revenue for x1 is maximized
D)total expenditure on x1 is unchanged
$5, she buys the following consumption bundle: (15, 20, 25). The price of x1 increases by 25%, and she now buys 15 units of x2 and 28 units of x3. Which of the following is not true?
A)the price elasticity of demand for x1 is one
B)x1 is a Giffen good
C)total revenue for x1 is maximized
D)total expenditure on x1 is unchanged

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Joseph's utility function is given by xA + 2xB, where xA denotes his consumption of apples and xB his consumption of bananas. If a banana cost 50 cents and an apple costs also 50 cents, how many apples will he buy if his income is $10?
A)20
B)10
C)0
D)5
A)20
B)10
C)0
D)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Richie's demand function for comic books is x = 30 - 10p where p is the price in dollars and x is the quantity he demands. If the price of comic books is $0.5, what is Richie's price elasticity of demand for comic books?
A)- 10
B)- 1/3
C)- 1/10
D)- 1/5
A)- 10
B)- 1/3
C)- 1/10
D)- 1/5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
In January a severe frost destroyed 1/3 of the American orange crop, and growers anticipated bankruptcy. By year's end, however, they realized that their profits were larger than ever. Which of the following could not explain this curious result?
A)There was a similar frost in exporting countries.
B)The demand for oranges shift to the left.
C)The demand for oranges shifted to the right.
D)The demand for oranges is price inelastic.
A)There was a similar frost in exporting countries.
B)The demand for oranges shift to the left.
C)The demand for oranges shifted to the right.
D)The demand for oranges is price inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If good x1 is a substitute for good x2, then an increase in the price of x2 causes the demand of x1 to:
A)be indeterminate.
B)increase.
C)decrease.
D)remain unchanged.
A)be indeterminate.
B)increase.
C)decrease.
D)remain unchanged.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When consumers join a club, or a cooperative pays for a project, the individuals involved:
A)move to a higher indifference curve.
B)move to a lower indifference curve.
C)may move or remain depending on the prices of other goods.
D)remain on the same indifference curve.
A)move to a higher indifference curve.
B)move to a lower indifference curve.
C)may move or remain depending on the prices of other goods.
D)remain on the same indifference curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If some constraint is relaxed or alleviated:
A)preferences likewise will be relaxed or alleviated.
B)a consumer will be worse off.
C)a consumer's behaviour will not change.
D)a consumer will have more options available.
A)preferences likewise will be relaxed or alleviated.
B)a consumer will be worse off.
C)a consumer's behaviour will not change.
D)a consumer will have more options available.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A negative sloped income consumption line indicates that:
A)both goods are normal.
B)both goods are inferior.
C)one of the goods is normal and the other is inferior.
D)the goods may be normal or inferior.
A)both goods are normal.
B)both goods are inferior.
C)one of the goods is normal and the other is inferior.
D)the goods may be normal or inferior.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
For an inessential good, which of the following is true?
A)Quantity demanded is always zero.
B)Quantity demanded is negative.
C)Quantity demanded is always positive.
D)Quantity demanded can be either positive or zero.
A)Quantity demanded is always zero.
B)Quantity demanded is negative.
C)Quantity demanded is always positive.
D)Quantity demanded can be either positive or zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Ron's utility function is given by U(x,y)= min[x,y]. If the price of x is 2 and the price of y is 1 and if Ron's preferred consumption bundle is [4,4], then his income is:
A)16.
B)10.
C)14.
D)12.
A)16.
B)10.
C)14.
D)12.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If goods A and B are complements:
A)the own price elasticity may be superior.
B)a decrease in the price of B causes the demand for A to increase.
C)they are also substitutes.
D)an increase in the price of A causes the demand for B to increase.
A)the own price elasticity may be superior.
B)a decrease in the price of B causes the demand for A to increase.
C)they are also substitutes.
D)an increase in the price of A causes the demand for B to increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Constraints in the theory of consumer behaviour:
A)have no bearing on choices individuals make.
B)are the only influence on consumer choices.
C)are measurable in principle.
D)restrict choices.
A)have no bearing on choices individuals make.
B)are the only influence on consumer choices.
C)are measurable in principle.
D)restrict choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Marc consumes apples (x)and oranges (y). If Marc's demand function for apples is given by: x =
Mpy/2px and Marc's demand for oranges is given by: x = Mpx/2py, then apples and oranges are:
A)inferior goods.
B)inessential goods.
C)complements.
D)substitutes.
Mpy/2px and Marc's demand for oranges is given by: x = Mpx/2py, then apples and oranges are:
A)inferior goods.
B)inessential goods.
C)complements.
D)substitutes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Beth consumes two goods, x1 and x2, and her income is $120. The price of x1 is $10, and the price of
X2 is $5. The consumption bundle (4, 18)is:
A)well defined.
B)an unattainable bundle.
C)an attainable bundle.
D)on the budget line.
X2 is $5. The consumption bundle (4, 18)is:
A)well defined.
B)an unattainable bundle.
C)an attainable bundle.
D)on the budget line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following is true?
A)Individuals prefer excise taxes.
B)Individuals prefer lump- sum taxes.
C)Lump- sum taxes give individuals fewer choices than excise taxes.
D)Excise taxes impose smaller individual costs than lump- sum taxes.
A)Individuals prefer excise taxes.
B)Individuals prefer lump- sum taxes.
C)Lump- sum taxes give individuals fewer choices than excise taxes.
D)Excise taxes impose smaller individual costs than lump- sum taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
When the price elasticity of demand for x is greater than one:
A)total revenue is negative.
B)the slope of the total revenue function is positive.
C)the slope of the total revenue function is negative.
D)the slope of the total revenue function is zero.
A)total revenue is negative.
B)the slope of the total revenue function is positive.
C)the slope of the total revenue function is negative.
D)the slope of the total revenue function is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Joe consumes just two goods, x1 and x2 and both are inessential. His indifference curves are convex. Joe will buy a positive quantity of x1 if:
A)MRS(0, M/p2)> p1/p2.
B)MRS(0, M/p2)= p1/p2.
C)MRS(0, M/p2)< p1/p2.
D)MRS(M/p1, 0)< p1/p2.
A)MRS(0, M/p2)> p1/p2.
B)MRS(0, M/p2)= p1/p2.
C)MRS(0, M/p2)< p1/p2.
D)MRS(M/p1, 0)< p1/p2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Suppose your income doubled and, at the same time, the prices of all goods doubled. Suppose you continue to purchase exactly the same bundle as before. What would the law of demand suggest about this behaviour?
A)Reasonable, because the relative price did not change.
B)Uncertain, because we don't know if the goods you purchase are normal or not.
C)Once you have a chance to adjust, you will purchase the low cost goods.
D)Not possible, because when the price goes up the quantity demanded always falls.
A)Reasonable, because the relative price did not change.
B)Uncertain, because we don't know if the goods you purchase are normal or not.
C)Once you have a chance to adjust, you will purchase the low cost goods.
D)Not possible, because when the price goes up the quantity demanded always falls.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Given that the government wishes to raise a certain amount of tax revenue, individuals prefer:
A)a 100% lump sum tax.
B)a combination of a 70% excise tax and a 30% lump sum tax.
C)a combination of a 30% excise tax and a 70% lump sum tax.
D)a 100% excise tax.
A)a 100% lump sum tax.
B)a combination of a 70% excise tax and a 30% lump sum tax.
C)a combination of a 30% excise tax and a 70% lump sum tax.
D)a 100% excise tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Beth consumes two goods, x1 and x2, and her income is $120. The price of x1 is $10, and the price of
X2 is $5. The opportunity cost of x2 is:
A)0.25 units of x1.
B)2 units of x1.
C)1 unit of x1.
D)0.5 units of x1.
X2 is $5. The opportunity cost of x2 is:
A)0.25 units of x1.
B)2 units of x1.
C)1 unit of x1.
D)0.5 units of x1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A price consumption path is derived by:
A)connecting all of the tangency points as the price of a good changes.
B)connecting all of the tangency points as the price of both goods change proportionately.
C)connecting all of the tangency points holding real income constant as the price of a good changes.
D)connecting all of the tangency points holding utility constant as the price of a good changes.
A)connecting all of the tangency points as the price of a good changes.
B)connecting all of the tangency points as the price of both goods change proportionately.
C)connecting all of the tangency points holding real income constant as the price of a good changes.
D)connecting all of the tangency points holding utility constant as the price of a good changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A temporal choice problem involves:
A)two goods.
B)given income and prices.
C)imperfect information.
D)intertemporal choices.
A)two goods.
B)given income and prices.
C)imperfect information.
D)intertemporal choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Mr. Inflexible's utility function is U(x1,x2)= min(x1,x2). The price of x1 is $1, the price of x2 is $2, and Mr. Inflexible's budget is $120. If an excise tax of $1 per unit is placed on x1, the utility maximizing bundle is:
A)(40, 20).
B)(50, 25).
C)(30, 30).
D)(20, 40).
A)(40, 20).
B)(50, 25).
C)(30, 30).
D)(20, 40).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Mr. Inflexible's utility function is U(x1,x2)= min(x1,x2). The price of x1 is $1, the price of x2 is $2, and Mr. Inflexible's budget is $120. If Mr. Inflexible were given the choice between a lump- sum tax and an excise tax which raised the same amount of tax revenue, then:
A)he would prefer the excise tax.
B)he would prefer the lump- sum tax.
C)he would be indifferent between them.
D)one cannot say which tax he would prefer.
A)he would prefer the excise tax.
B)he would prefer the lump- sum tax.
C)he would be indifferent between them.
D)one cannot say which tax he would prefer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is not a constraint on choice?
A)self- interest
B)time
C)income
D)endowed resources
A)self- interest
B)time
C)income
D)endowed resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Figure 3A

The Engel curves associated with the indifference map in Figure 3A are:
A)upward sloping.
B)downward sloping.
C)vertical.
D)horizontal.

The Engel curves associated with the indifference map in Figure 3A are:
A)upward sloping.
B)downward sloping.
C)vertical.
D)horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Imagine an excise tax and a lump- sum tax which would raise the same revenue from an individual Ms. Arbitrary who has convex preferences. If she was given a choice between the two taxes, then:
A)she would prefer the excise tax.
B)she would be indifferent between the two taxes.
C)we cannot know Ms. Arbitrary's preferences regarding the taxes.
D)she would prefer the lump- sum tax.
A)she would prefer the excise tax.
B)she would be indifferent between the two taxes.
C)we cannot know Ms. Arbitrary's preferences regarding the taxes.
D)she would prefer the lump- sum tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following assumptions about consumer behaviour implies that the utility maximizing choice will be on the budget constraint.
A)non- satiation
B)transitivity
C)continuity
D)completeness
A)non- satiation
B)transitivity
C)continuity
D)completeness

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Own price elasticity of demand is defined as:
A)the change in quantity demanded divided by the change in price.
B)the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
C)the change in price divided by the change in quantity demanded.
D)the percentage change in price divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded.
A)the change in quantity demanded divided by the change in price.
B)the percentage change in quantity demanded divided by the percentage change in price.
C)the change in price divided by the change in quantity demanded.
D)the percentage change in price divided by the percentage change in quantity demanded.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Given the choice between a lump- sum tax and an excise tax that raises the same revenue, a consumer:
A)will be hard- pressed to choose one option over the other.
B)will choose the the excise tax.
C)will choose the lump- sum tax.
D)is indifferent between the two.
A)will be hard- pressed to choose one option over the other.
B)will choose the the excise tax.
C)will choose the lump- sum tax.
D)is indifferent between the two.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Carol experiences a 4% increase in income this year. She is:
A)perhaps better or worse off.
B)unambiguously no better or worse off.
C)unambiguously worse off.
D)unambiguously better off.
A)perhaps better or worse off.
B)unambiguously no better or worse off.
C)unambiguously worse off.
D)unambiguously better off.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In order for a maker of cellophane not to be charged with monopolizing the market, the cross- price elasticity of cellophane and other packaging products has to be:
A)high.
B)low.
C)not defined.
D)zero.
A)high.
B)low.
C)not defined.
D)zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If goods A and B are complements
A)the price- consumption path is downward sloping
B)the price- consumption path is upward sloping
C)the income- consumption line is downward sloping
D)the income- consumption line is upward sloping
A)the price- consumption path is downward sloping
B)the price- consumption path is upward sloping
C)the income- consumption line is downward sloping
D)the income- consumption line is upward sloping

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Percy currently buys soup at $4 per bowl, and tea at $2 per cup. His marginal utility from soup is 12 and his marginal utility from tea is 8. The opportunity cost of purchasing one more cup of tea is:
A)1.5
B)2
C)0.66
D)0.5
A)1.5
B)2
C)0.66
D)0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Tammy spent all of the money in her purse to buy 5 plates of spaghetti and 6 burgers. Spaghetti costs $8 per plate and she had $82 in her purse. If s denotes the number of plates of spaghetti and b denotes the number of burgers purchased, which equation describes the budget line of Tammy?
A)5s+6b = 164
B)5s+6b = 82
C)6s+8b = 82
D)16s +14b = 164
A)5s+6b = 164
B)5s+6b = 82
C)6s+8b = 82
D)16s +14b = 164

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Mr. Inflexible's utility function is U(x1,x2)= min(x1,x2). The price of x1 is $2 including a $1 excise tax, the price of x2 is $2, and Mr. Inflexible's budget is $120. Imagine substituting a lump- sum tax for the excise tax. If both taxes leave Mr. Inflexible on the same indifference curve, then the
Lump- sum tax is:
A)$30.
B)$10.
C)$20.
D)$50.
Lump- sum tax is:
A)$30.
B)$10.
C)$20.
D)$50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Figure 3A

As the consumer's income changes (while prices remain constant), the consumer would be most likely to choose which points in Figure 3A?
A)A, B, and C
B)B, D, and E
C)A, D, and E
D)E, D, and F

As the consumer's income changes (while prices remain constant), the consumer would be most likely to choose which points in Figure 3A?
A)A, B, and C
B)B, D, and E
C)A, D, and E
D)E, D, and F

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Beth consumes two goods, x1 and x2, and her income is $120. The price of x1 is $10, and the price of
X2 is $5. If her utility function is U(x1,x2)= x1 + x2, her utility maximizing bundle is:
A)(12, 0).
B)(7, 10).
C)(0, 24).
D)(8, 8).
X2 is $5. If her utility function is U(x1,x2)= x1 + x2, her utility maximizing bundle is:
A)(12, 0).
B)(7, 10).
C)(0, 24).
D)(8, 8).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
By "real" price, an economist means:
A)what an individual seriously pays for a good.
B)not the artificial price.
C)the dollar amount of money required to buy the good.
D)the price in terms of other goods.
A)what an individual seriously pays for a good.
B)not the artificial price.
C)the dollar amount of money required to buy the good.
D)the price in terms of other goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If the price of the house you just bought went up:
A)you are worse off because you pay higher taxes for the same house.
B)you are better off because you can substitute among a wide variety of items in your consumption bundle.
C)you are better off because you made a quick capital gain.
D)you are worse off because you face higher prices in the economy.
A)you are worse off because you pay higher taxes for the same house.
B)you are better off because you can substitute among a wide variety of items in your consumption bundle.
C)you are better off because you made a quick capital gain.
D)you are worse off because you face higher prices in the economy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Joseph's utility function is given by xA + 2xB, where xA denotes his consumption of apples and xB his consumption of bananas. Suppose apples and bananas have the same price, 50 cents. If his income is $10, then Joseph will consume:
A)no apples.
B)twice as many bananas than apples.
C)twice as many apples than bananas.
D)same quantity of apples and bananas.
A)no apples.
B)twice as many bananas than apples.
C)twice as many apples than bananas.
D)same quantity of apples and bananas.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If an individual's Engel curve for a good is negatively sloped, then the good is:
A)a normal good.
B)an Engel good.
C)a Giffen good.
D)an inferior good.
A)a normal good.
B)an Engel good.
C)a Giffen good.
D)an inferior good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Fred's demand for beer is given by x = M/2px. For Fred, beer is a(n):
A)inessential good.
B)normal good.
C)inferior good.
D)Giffen good.
A)inessential good.
B)normal good.
C)inferior good.
D)Giffen good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If an excise tax on good x and a lump- sum tax put Ms. Arbitrary on the same indifference curve, she would:
A)have identical budget lines under the two taxes.
B)consume more of x given the excise tax than given the lump- sum tax.
C)prefer the lump- sum tax.
D)consume no more of x given the excise tax than given the lump- sum tax.
A)have identical budget lines under the two taxes.
B)consume more of x given the excise tax than given the lump- sum tax.
C)prefer the lump- sum tax.
D)consume no more of x given the excise tax than given the lump- sum tax.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Ron's utility function is given by U(x,y)= min[x,y]. If the price of x is 2 and the price of y is 1, Ron spends his $12 income on:
A)4 units of x and 2 units of y.
B)4 units of x and 4 units of y.
C)2 units of x and 4 units of y.
D)2 units of x and 2 units of y.
A)4 units of x and 2 units of y.
B)4 units of x and 4 units of y.
C)2 units of x and 4 units of y.
D)2 units of x and 2 units of y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Beth consumes two goods, x1 and x2, and her income is $120. The price of x1 is $10, and the price of
X2 is $5. If her utility function is U(x1,x2)= min(x1,x2), her utility maximizing bundle is:
A)(7, 10).
B)(12, 0).
C)(8, 8).
D)(0, 24).
X2 is $5. If her utility function is U(x1,x2)= min(x1,x2), her utility maximizing bundle is:
A)(7, 10).
B)(12, 0).
C)(8, 8).
D)(0, 24).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Ron's utility function is given by U(x,y)= min[2x,y]. If the price of x is 1 and the price of y is 1, Ron spends his $12 income on:
A)4 units of x and 4 units of y.
B)8 units of x and 8 units of y.
C)4 units of x and 8 units of y.
D)8 units of x and 4 units of y.
A)4 units of x and 4 units of y.
B)8 units of x and 8 units of y.
C)4 units of x and 8 units of y.
D)8 units of x and 4 units of y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Joseph's utility function is given by xA +2xB, where xA denotes his consumption of apples and xB his consumption of bananas. If a banana cost 50 cents and an apple costs also 50 cents, how many bananas will he buy if his income is $10?
A)0
B)10
C)20
D)5
A)0
B)10
C)20
D)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A utility maximizing bundle is:
A)the bundle which satiates the consumer's desires.
B)inside the budget line and on an indifference curve.
C)on a budget line tangent to an indifference curve.
D)at the origin of the indifference map.
A)the bundle which satiates the consumer's desires.
B)inside the budget line and on an indifference curve.
C)on a budget line tangent to an indifference curve.
D)at the origin of the indifference map.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The fact that most bundles of goods purchased at a given store are more expensive if bought elsewhere:
A)is a sign of deeply discounted prices.
B)can be interpreted in a wide variety of ways.
C)is a clear proof that this store is cheaper on average than other stores.
D)is an illustration of the maximization process.
A)is a sign of deeply discounted prices.
B)can be interpreted in a wide variety of ways.
C)is a clear proof that this store is cheaper on average than other stores.
D)is an illustration of the maximization process.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Figure 3B

Which of the following is the lump- sum budget line in Figure 3B?
A)AH
B)BF
C)IJ
D)AG

Which of the following is the lump- sum budget line in Figure 3B?
A)AH
B)BF
C)IJ
D)AG

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
When Netscape took Microsoft to court for using anti- competitive practices, the contention was that the Internet Explorer, a browser, and Windows, the operating system, were:
A)not working properly.
B)incompatible.
C)substitutes.
D)complements.
A)not working properly.
B)incompatible.
C)substitutes.
D)complements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If Mary always spends 10% of her income on records, regardless of the prices of records or other goods, then:
A)Mary could not be a utility maximizer.
B)records are inferior goods.
C)Mary's income elasticity of demand for records is one.
D)records are abnormal goods.
A)Mary could not be a utility maximizer.
B)records are inferior goods.
C)Mary's income elasticity of demand for records is one.
D)records are abnormal goods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following statements is false on theoretical grounds?
A)It is possible that all goods are normal.
B)It is possible that all goods are inferior.
C)It is possible that all goods are essential.
D)It is possible that all goods are inessential.
A)It is possible that all goods are normal.
B)It is possible that all goods are inferior.
C)It is possible that all goods are essential.
D)It is possible that all goods are inessential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Which of the following will not cause a change in the demand for butter?
A)a new disease strikes milk cows
B)the price of butter falls
C)a frost hits Florida
D)dairy workers get a wage increase
A)a new disease strikes milk cows
B)the price of butter falls
C)a frost hits Florida
D)dairy workers get a wage increase

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Which of the following statements accurately reflects the money illusion?
A)Consumers care only about relative prices, not money prices.
B)Pure inflation does not change the budget constraint.
C)A change in money prices changes the indifference curves.
D)Money has no intrinsic value and therefore is essentially worthless.
A)Consumers care only about relative prices, not money prices.
B)Pure inflation does not change the budget constraint.
C)A change in money prices changes the indifference curves.
D)Money has no intrinsic value and therefore is essentially worthless.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If the market demand for oranges is relatively inelastic with respect to price, orange consumers:
A)will buy fewer oranges at any higher price but will spend more money on oranges.
B)will buy fewer oranges at any higher price and will spend less money on oranges.
C)will buy more oranges at any higher price.
D)pay no attention to price in their purchasing decisions.
A)will buy fewer oranges at any higher price but will spend more money on oranges.
B)will buy fewer oranges at any higher price and will spend less money on oranges.
C)will buy more oranges at any higher price.
D)pay no attention to price in their purchasing decisions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A consumer's demand functions depend on:
A)her income and the prices of goods and services.
B)the supply of goods and services.
C)weakly convex indifference curves.
D)careful mathematical analysis.
A)her income and the prices of goods and services.
B)the supply of goods and services.
C)weakly convex indifference curves.
D)careful mathematical analysis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Income elasticity of demand for an inferior good is:
A)not properly defined.
B)negative.
C)positive.
D)zero.
A)not properly defined.
B)negative.
C)positive.
D)zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Quantity demanded of good x does not increase as the price of x increases if x is:
A)a Giffen good.
B)an inferior good whose income effect dominates its substitution effect.
C)a normal good.
D)an Engel good.
A)a Giffen good.
B)an inferior good whose income effect dominates its substitution effect.
C)a normal good.
D)an Engel good.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Elasticity is an attractive measure of comparative static responses for all of the following reasons except, elasticities:
A)relate changes in price to changes in total revenue.
B)are directly observable.
C)are units- free.
D)relate %- changes in one variable to %- changes in other variables.
A)relate changes in price to changes in total revenue.
B)are directly observable.
C)are units- free.
D)relate %- changes in one variable to %- changes in other variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Figure 3B

Which of the following is the pretax budget line in Figure 3B?
A)AG
B)BF
C)IJ
D)AH

Which of the following is the pretax budget line in Figure 3B?
A)AG
B)BF
C)IJ
D)AH

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Suppose that px = 2 and py = 5. Jane spends her $100 income on 25 units of x and 10 units of y. When the price of x doubled to $10 per unit, Jane's father gave her an extra $50 so that she could buy the same bundle that she did before the price change. Assuming convex indifference curves, which of the following statements is true?
A)No conclusions can be drawn regarding Jill's welfare unless we know her utility function
B)Jill is just as well off as before the price change
C)Jill is actually better off now than she was before
D)Jill is worse off now than she was before
A)No conclusions can be drawn regarding Jill's welfare unless we know her utility function
B)Jill is just as well off as before the price change
C)Jill is actually better off now than she was before
D)Jill is worse off now than she was before

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Mr. Inflexible's utility function is U(x1,x2)= min(x1,x2). The price of x1 is $2 including a $1 excise tax, the price of x2 is $2, and Mr. Inflexible's budget is $120. Imagine substituting a lump- sum tax for the excise tax. If both taxes raise the same amount of tax revenue, the lump- sum tax is:
A)$20.
B)$30.
C)$10.
D)$50.
A)$20.
B)$30.
C)$10.
D)$50.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



