Deck 11: Input Markets and the Allocation of Resources
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/98
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Input Markets and the Allocation of Resources
1
An increase in the wage rate:
A)rotates outward the income- leisure budget constraint.
B)rotates outward the income budget constraint.
C)rotates outward the time constraint.
D)does not affect the income- leisure budget constraint.
A)rotates outward the income- leisure budget constraint.
B)rotates outward the income budget constraint.
C)rotates outward the time constraint.
D)does not affect the income- leisure budget constraint.
rotates outward the income- leisure budget constraint.
2
In a competitive market, firms value inputs:
A)the same as consumers.
B)at a lower level than consumers.
C)independently of consumers.
D)at a higher level than consumers.
A)the same as consumers.
B)at a lower level than consumers.
C)independently of consumers.
D)at a higher level than consumers.
the same as consumers.
3
If the marginal products of all inputs are identical, for the firm to be in long- run equilibrium:
A)input prices cannot be identical.
B)the output market must be perfectly competitive.
C)the firm must use just two inputs.
D)all input prices must be identical.
A)input prices cannot be identical.
B)the output market must be perfectly competitive.
C)the firm must use just two inputs.
D)all input prices must be identical.
all input prices must be identical.
4
If an input market is monopsonistic, and the firm's output market is monopolistic, then in equilibrium:
A)w < MFC = MRP < VMP.
B)w = MFC = MRP = VMP.
C)w < MFC = MRP = VMP.
D)w = MFC = MRP < VMP.
A)w < MFC = MRP < VMP.
B)w = MFC = MRP = VMP.
C)w < MFC = MRP = VMP.
D)w = MFC = MRP < VMP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A firm which is a competitor in its output market and a monopsonist in an input market is:
A)efficient.
B)inefficient because VMP > MRP and MFC > w.
C)inefficient because VMP > MRP.
D)inefficient because MFC > w.
A)efficient.
B)inefficient because VMP > MRP and MFC > w.
C)inefficient because VMP > MRP.
D)inefficient because MFC > w.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Consider a firm which is initially in long- run equilibrium and is faced with an increase in the price of a variable input, z. In that case, the:
A)firm will demand more if the input is inferior.
B)input quantity demanded will be reduced more in the long run.
C)firm's demand for that input will shift down.
D)input quantity demanded will be reduced more in the short run.
A)firm will demand more if the input is inferior.
B)input quantity demanded will be reduced more in the long run.
C)firm's demand for that input will shift down.
D)input quantity demanded will be reduced more in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In long- run equilibrium, for a firm which is a perfect competitor in its input and its output markets:
A)w = MRP = VMP for all inputs.
B)MP/p is identical for all inputs.
C)w = MRP < VMP.
D)VMP is identical for all inputs.
A)w = MRP = VMP for all inputs.
B)MP/p is identical for all inputs.
C)w = MRP < VMP.
D)VMP is identical for all inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In long- run equilibrium a firm that is a perfect competitor in its input and output markets will choose an input bundle such that for each input:
A)input price is equal to MRP.
B)MRP is greater than the VMP.
C)the marginal products of all inputs are identical.
D)MRP is less than VMP.
A)input price is equal to MRP.
B)MRP is greater than the VMP.
C)the marginal products of all inputs are identical.
D)MRP is less than VMP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The value of an input to a firm depends in part on the:
A)quantity of the input the firm uses.
B)quantity of output the firm produces.
C)price it can charge for its output.
D)price of the input in the resource market.
A)quantity of the input the firm uses.
B)quantity of output the firm produces.
C)price it can charge for its output.
D)price of the input in the resource market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
As a response to a change in the wage rate, the substitution effect will:
A)produce an direct relationship between the quantity demanded of an input and its price.
B)produce an direct relationship between the quantity demanded of an input and the price of the other input.
C)produce an inverse relationship between the quantity demanded of an input and the price of the other input.
D)produce an inverse relationship between the quantity demanded of an input and its price.
A)produce an direct relationship between the quantity demanded of an input and its price.
B)produce an direct relationship between the quantity demanded of an input and the price of the other input.
C)produce an inverse relationship between the quantity demanded of an input and the price of the other input.
D)produce an inverse relationship between the quantity demanded of an input and its price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Input z is the only variable input for Joe's manna factory. The supply function of the input is 10 + 2z and the MRP function is 110 - z. Then:
A)w* = 60.
B)w* = 90, z* = 20.
C)w* = 50, z* = 20.
D)w* = 100/3.
A)w* = 60.
B)w* = 90, z* = 20.
C)w* = 50, z* = 20.
D)w* = 100/3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Consider the following production function for a firm using two inputs x and y,
Q=20x+14y- 2x2+2xy- y2 where q denotes the quantity of output that is produced. An increase in the quantity of y:
A)is ambiguous in terms of the effect it has on the marginal product of x.
B)does nothing to the marginal product of x.
C)increases the marginal product of x.
D)decreases the marginal product of x.
Q=20x+14y- 2x2+2xy- y2 where q denotes the quantity of output that is produced. An increase in the quantity of y:
A)is ambiguous in terms of the effect it has on the marginal product of x.
B)does nothing to the marginal product of x.
C)increases the marginal product of x.
D)decreases the marginal product of x.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
In general, the demand functions for primary inputs reflect the:
A)provisions of union contracts.
B)utility- maximizing decisions of individuals.
C)demand for finished goods.
D)profit- maximizing decisions of firms.
A)provisions of union contracts.
B)utility- maximizing decisions of individuals.
C)demand for finished goods.
D)profit- maximizing decisions of firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
In perfectly competitive input markets
A)all units of the same input command the same price
B)there may be cases when there's only one seller
C)not all information is known by all parties
D)some units of input might be slightly different from others
A)all units of the same input command the same price
B)there may be cases when there's only one seller
C)not all information is known by all parties
D)some units of input might be slightly different from others

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If a resource is nonexhaustible, its supply curve in a single period is:
A)upward sloping.
B)perfectly elastic.
C)perfectly inelastic.
D)downward sloping.
A)upward sloping.
B)perfectly elastic.
C)perfectly inelastic.
D)downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
In the labour market, utility maximizing individuals:
A)divide their time between work and leisure.
B)choose the goods and services they consume.
C)maximize their wealth.
D)minimize time spent working.
A)divide their time between work and leisure.
B)choose the goods and services they consume.
C)maximize their wealth.
D)minimize time spent working.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The supply of labour:
A)is always backward bending.
B)is the result of a maximization process.
C)is independent of non- wage income.
D)is the inverse of the supply of capital.
A)is always backward bending.
B)is the result of a maximization process.
C)is independent of non- wage income.
D)is the inverse of the supply of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The firm's labour demand curve is given by:
A)its marginal cost function for any wage higher than the maximum value of average product.
B)its marginal product function for any wage lower than the maximum value of average product.
C)its marginal product function for any wage higher than the maximum value of average product.
D)its marginal cost function for any wage lower than the maximum value of average product.
A)its marginal cost function for any wage higher than the maximum value of average product.
B)its marginal product function for any wage lower than the maximum value of average product.
C)its marginal product function for any wage higher than the maximum value of average product.
D)its marginal cost function for any wage lower than the maximum value of average product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Figure 11A
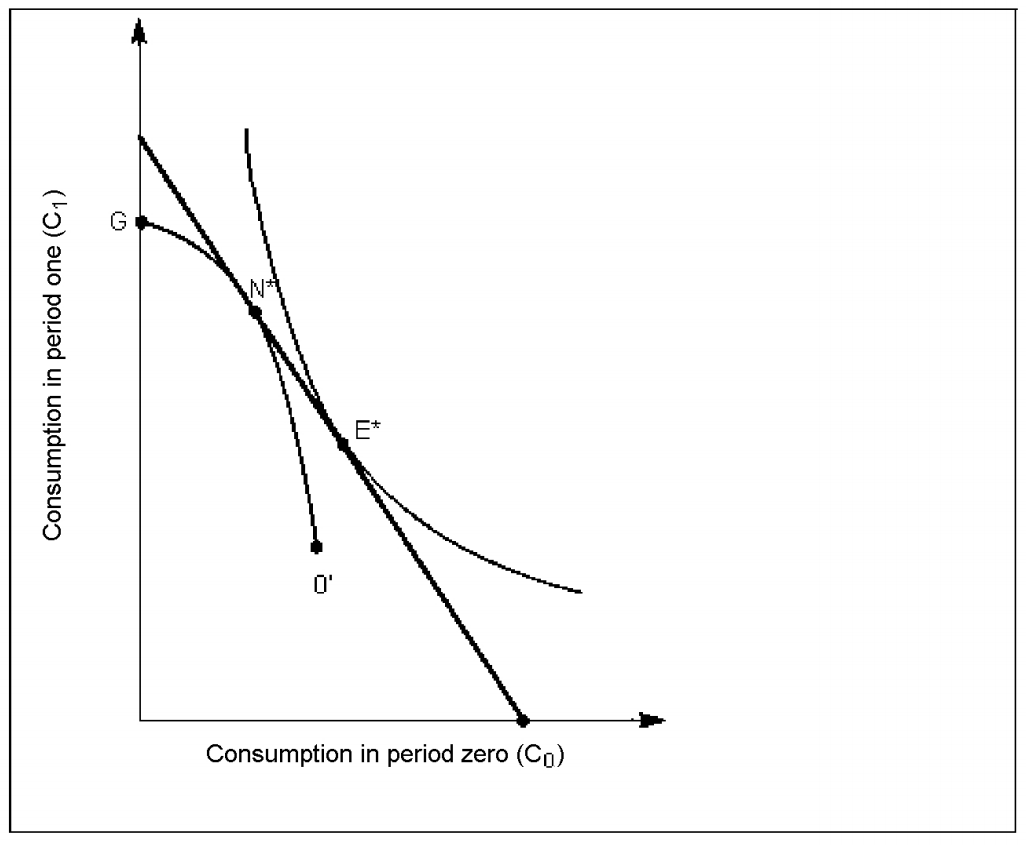
In Figure 11A, the individual's Intertemporal budget line is:
A)the line including the points G, N* and E*.
B)the line including the points N* and E*.
C)the line including the point E* only.
D)the line including the points G, N*, and 0'.

In Figure 11A, the individual's Intertemporal budget line is:
A)the line including the points G, N* and E*.
B)the line including the points N* and E*.
C)the line including the point E* only.
D)the line including the points G, N*, and 0'.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A firm which is a monopolist in an output market and a competitor in an input market is:
A)inefficient because MFC > w.
B)inefficient because VMP > MRP and MFC > w.
C)inefficient because VMP > MRP.
D)efficient.
A)inefficient because MFC > w.
B)inefficient because VMP > MRP and MFC > w.
C)inefficient because VMP > MRP.
D)efficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In the labour market, the optimal number of work hours is determined when:
A)the MRS of income for leisure is the wage.
B)the MRS of income for consumption is the wage.
C)the MRS of leisure for consumption is the wage.
D)total utility is maximized.
A)the MRS of income for leisure is the wage.
B)the MRS of income for consumption is the wage.
C)the MRS of leisure for consumption is the wage.
D)total utility is maximized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
In general, the supply functions of primary inputs reflect the:
A)demand for finished goods.
B)profit- maximizing decisions of firms.
C)provisions of union contracts.
D)utility- maximizing decisions of individuals.
A)demand for finished goods.
B)profit- maximizing decisions of firms.
C)provisions of union contracts.
D)utility- maximizing decisions of individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
In long- run equilibrium a firm that is a perfect competitor in its input markets but a monopolist in its output market will choose an input bundle such that for each input:
A)MRP is greater than the VMP.
B)input price is equal to VMP.
C)MRP is equal to the VMP.
D)MRP is less than the VMP.
A)MRP is greater than the VMP.
B)input price is equal to VMP.
C)MRP is equal to the VMP.
D)MRP is less than the VMP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The labour supply curve facing a monopsonist is positively sloped because:
A)the monopsonist must pay a higher wage if it wishes to attract more labour.
B)these workers are scarce and drive up the wage rate.
C)government intervenes in the labour market.
D)the monopsonist only hires skilled labour.
A)the monopsonist must pay a higher wage if it wishes to attract more labour.
B)these workers are scarce and drive up the wage rate.
C)government intervenes in the labour market.
D)the monopsonist only hires skilled labour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The most general profit maximization rule is to choose quantity such that the quantity of an input employed makes:
A)w = VMP.
B)MFC = MRP.
C)MFC = VMP.
D)w = MRP.
A)w = VMP.
B)MFC = MRP.
C)MFC = VMP.
D)w = MRP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If a firm is a monopsonist, it will hire an input when:
A)MRP does not equal w.
B)MRP > w.
C)MRP = w.
D)MRP < w.
A)MRP does not equal w.
B)MRP > w.
C)MRP = w.
D)MRP < w.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a firm is a competitor in its output market and a competitor in an input market, its input bundle will be chosen so that:
A)VMP < MRP for that input.
B)VMP > MRP for that input.
C)VMP is not equal MRP for that input.
D)VMP = MRP for that input.
A)VMP < MRP for that input.
B)VMP > MRP for that input.
C)VMP is not equal MRP for that input.
D)VMP = MRP for that input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
When the average product for labour exceeds the marginal product for labour:
A)average product is decreasing and marginal product is increasing.
B)average product is increasing and marginal product is increasing.
C)average product is increasing and marginal product is decreasing.
D)average product is decreasing and marginal product is decreasing.
A)average product is decreasing and marginal product is increasing.
B)average product is increasing and marginal product is increasing.
C)average product is increasing and marginal product is decreasing.
D)average product is decreasing and marginal product is decreasing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
If a firm is a monopolist in its output market and a competitor in an input market, its input bundle will be chosen so that:
A)VMP is not equal MRP for that input.
B)VMP = MRP for that input.
C)VMP > MRP for that input.
D)VMP < MRP for that input.
A)VMP is not equal MRP for that input.
B)VMP = MRP for that input.
C)VMP > MRP for that input.
D)VMP < MRP for that input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
the own price elasticity of demand for imports is not dependent upon which of the following?
A)the price elasticity of demand for other inputs
B)the price elasticity of demand for the final product
C)the price elasticity of supply for other inputs
D)the substitution effect between inputs
A)the price elasticity of demand for other inputs
B)the price elasticity of demand for the final product
C)the price elasticity of supply for other inputs
D)the substitution effect between inputs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the input market is competitive and the output market is monopolistic:
A)MFC>MRP.
B)MFCC)MFC=MRP.
D)MRP=VMP.
A)MFC>MRP.
B)MFC
D)MRP=VMP.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Investment in training is called:
A)human capital.
B)foregone income.
C)current consumption.
D)future consumption.
A)human capital.
B)foregone income.
C)current consumption.
D)future consumption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
When dealing with the demand for inputs
A)substitution and output effects work in opposite directions for substitutes
B)substitution and output effects always work in the same direction
C)substitution output effects work in opposite directions for compliments
D)substitution output effects work in opposite directions for inferior goods
A)substitution and output effects work in opposite directions for substitutes
B)substitution and output effects always work in the same direction
C)substitution output effects work in opposite directions for compliments
D)substitution output effects work in opposite directions for inferior goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The dead weight loss of a monopsonist is caused by
A)the average revenue product exceeding input price
B)the marginal revenue product exceeding input price
C)input price exceeding average revenue product
D)input price exceeding marginal revenue product
A)the average revenue product exceeding input price
B)the marginal revenue product exceeding input price
C)input price exceeding average revenue product
D)input price exceeding marginal revenue product

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A firm's downward sloping demand for an input is determined by the:
A)Marginal Revenue of output and the price of the input.
B)Marginal Revenue of output and the marginal product of the input.
C)demand for output.
D)Marginal Revenue of output and the average product of the input.
A)Marginal Revenue of output and the price of the input.
B)Marginal Revenue of output and the marginal product of the input.
C)demand for output.
D)Marginal Revenue of output and the average product of the input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The demand for labour:
A)is not the result of a maximization process.
B)is related to the demand for leisure.
C)is identical to the value of the marginal product when there is one input.
D)is identical to the value of the marginal product when there are two inputs.
A)is not the result of a maximization process.
B)is related to the demand for leisure.
C)is identical to the value of the marginal product when there is one input.
D)is identical to the value of the marginal product when there are two inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Firms will hire labor up to the point where
A)the marginal product is equal to the nominal wage
B)the average product is equal to the real wage
C)the average product is equal to the nominal wage
D)the marginal product is equal to the real wage
A)the marginal product is equal to the nominal wage
B)the average product is equal to the real wage
C)the average product is equal to the nominal wage
D)the marginal product is equal to the real wage

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
In general, the supply functions of intermediate inputs reflect the:
A)provisions of union contracts.
B)demand for finished goods.
C)profit- maximizing decisions of firms.
D)utility- maximizing decisions of individuals.
A)provisions of union contracts.
B)demand for finished goods.
C)profit- maximizing decisions of firms.
D)utility- maximizing decisions of individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An increase in the interest rate will:
A)shift the MRP curve to the right.
B)shift the MRP curve to the left.
C)not affect the MRP curve.
D)rotate the MRP curve.
A)shift the MRP curve to the right.
B)shift the MRP curve to the left.
C)not affect the MRP curve.
D)rotate the MRP curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The marginal revenue product is:
A)equal to the marginal revenue times the marginal product.
B)equal to the price of the input times the marginal product.
C)equal to the price of the output times the marginal product.
D)equal to the marginal revenue times the value of the marginal product.
A)equal to the marginal revenue times the marginal product.
B)equal to the price of the input times the marginal product.
C)equal to the price of the output times the marginal product.
D)equal to the marginal revenue times the value of the marginal product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The price of leisure:
A)depends on the number of hours worked.
B)is the wage rate.
C)cannot be measured.
D)depends on the price of capital.
A)depends on the number of hours worked.
B)is the wage rate.
C)cannot be measured.
D)depends on the price of capital.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following is not a potential source of monopsony power?
A)many firms competing for the same input
B)strong attachments of individuals to their home towns
C)costs of transporting bulky material inputs
D)immobility of inputs
A)many firms competing for the same input
B)strong attachments of individuals to their home towns
C)costs of transporting bulky material inputs
D)immobility of inputs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
If the VMP of an input for a competitive firm is downward sloping, then:
A)there are diminishing returns to the input.
B)the aggregate input demand (AID)is upward sloping.
C)the average revenue product curve is horizontal.
D)the input is a variable input.
A)there are diminishing returns to the input.
B)the aggregate input demand (AID)is upward sloping.
C)the average revenue product curve is horizontal.
D)the input is a variable input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The demand for labour can be expressed as Q = 10,000 - w and the supply of labour is Q = 5,000 + w where Q is total person- hours of work during the week and w is the weekly salary. What is the equilibrium weekly wage rate?
A)2,500
B)1,500
C)3,000
D)2,000
A)2,500
B)1,500
C)3,000
D)2,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A firm which is a competitor in its output market and a competitor in an input market is:
A)inefficient because VMP > MRP and MFC > w.
B)inefficient because VMP > MRP.
C)efficient.
D)inefficient because MFC > w.
A)inefficient because VMP > MRP and MFC > w.
B)inefficient because VMP > MRP.
C)efficient.
D)inefficient because MFC > w.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The marginal revenue product of labour in the local saw mill is MRPL = 20 - .5L, where L = the number of workers. If the wage of saw mill workers is $10 per hour, then how many workers will the mill hire?
A)20
B)30
C)10
D)25
A)20
B)30
C)10
D)25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Unlike a competitive buyer:
A)a monopsonist pays a different price for each unit purchased.
B)the price that a monopsonist pays depends on the number of units purchased.
C)a monopsonist sets marginal value equal to marginal expenditure.
D)a monopsonist faces an upward- sloping industry supply curve.
A)a monopsonist pays a different price for each unit purchased.
B)the price that a monopsonist pays depends on the number of units purchased.
C)a monopsonist sets marginal value equal to marginal expenditure.
D)a monopsonist faces an upward- sloping industry supply curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The firm's labour demand curve is given by:
A)its marginal revenue product function for any wage higher than the maximum value of average revenue product.
B)its marginal cost function for any wage lower than the maximum value of average product.
C)its marginal revenue product function for any wage lower than the maximum value of average revenue product.
D)its marginal cost function for any wage higher than the maximum value of average product.
A)its marginal revenue product function for any wage higher than the maximum value of average revenue product.
B)its marginal cost function for any wage lower than the maximum value of average product.
C)its marginal revenue product function for any wage lower than the maximum value of average revenue product.
D)its marginal cost function for any wage higher than the maximum value of average product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If leisure is a normal good and the wage increases:
A)labour supply may be upward sloping.
B)labour supply may decrease if substitution effect for leisure outweighs the income effect.
C)labour supply will shift to the right.
D)labour supply must increase if substitution effect for leisure outweighs the income effect.
A)labour supply may be upward sloping.
B)labour supply may decrease if substitution effect for leisure outweighs the income effect.
C)labour supply will shift to the right.
D)labour supply must increase if substitution effect for leisure outweighs the income effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Suppose MP = 10/L. If the firm sells its output in a competitive market at a price of $8, how much labour will the firm hire if the wage rate is $5 per unit of labour?
A)4
B)6
C)2
D)10
A)4
B)6
C)2
D)10

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If a resource is exhaustible, its supply curve in a single period is:
A)downward sloping.
B)perfectly elastic.
C)upward sloping.
D)perfectly inelastic.
A)downward sloping.
B)perfectly elastic.
C)upward sloping.
D)perfectly inelastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
An increase in one's non- labour income:
A)shifts the income- leisure budget constraint up in a parallel fashion.
B)shifts the income budget constraint up in a parallel fashion.
C)does not affect he income- leisure budget constraint.
D)shifts the time constraint up in a parallel fashion.
A)shifts the income- leisure budget constraint up in a parallel fashion.
B)shifts the income budget constraint up in a parallel fashion.
C)does not affect he income- leisure budget constraint.
D)shifts the time constraint up in a parallel fashion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Monopsony in an input market is a source of inefficiency in the allocation of resources because:
A)monopsony always entails discrimination.
B)the monopsonist hires too little of the input.
C)MR is necessarily less than price in the output market.
D)in equilibrium MRP < w.
A)monopsony always entails discrimination.
B)the monopsonist hires too little of the input.
C)MR is necessarily less than price in the output market.
D)in equilibrium MRP < w.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Figure 11A

In Figure 11A, the individual's human capital production function is:
A)the line including the point E* only.
B)the line including the points G, N* and E*.
C)the line including the points N* and E*.
D)the line including the points G, N*, and 0'.

In Figure 11A, the individual's human capital production function is:
A)the line including the point E* only.
B)the line including the points G, N* and E*.
C)the line including the points N* and E*.
D)the line including the points G, N*, and 0'.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A perfectly competitive input market:
A)assumes there are no intermediate goods.
B)has all firms as price takers and all inputs as price takers.
C)has all firms as price searchers, but all inputs as price takers.
D)is where the input price equals the output price.
A)assumes there are no intermediate goods.
B)has all firms as price takers and all inputs as price takers.
C)has all firms as price searchers, but all inputs as price takers.
D)is where the input price equals the output price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
For a monopsony buyer, the marginal expenditure per unit of an input:
A)equals the average expenditure per unit.
B)is less than the average expenditure per unit.
C)exceeds the average expenditure per unit.
D)is equal to the price.
A)equals the average expenditure per unit.
B)is less than the average expenditure per unit.
C)exceeds the average expenditure per unit.
D)is equal to the price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Donna's schmoo firm uses one input, z, and she sells her output at $10 per unit. The marginal product of z is 10 - z and the price of z is $20 per unit. The profit maximizing quantity of z is:
A)5.0.
B)5.5.
C)8.0.
D)10.0.
A)5.0.
B)5.5.
C)8.0.
D)10.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
A perfectly competitive firm's downward sloping demand for an input is determined by the:
A)price of output and the average product of the input.
B)demand for output.
C)price of output and the marginal product of the input.
D)price of output and the price of the input.
A)price of output and the average product of the input.
B)demand for output.
C)price of output and the marginal product of the input.
D)price of output and the price of the input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If a firm is perfectly competitive in its input markets, then, in short- run equilibrium:
A)MC = p.
B)MRP is the same for all inputs.
C)w = VMP, for all variable inputs.
D)w = MRP, for all variable inputs.
A)MC = p.
B)MRP is the same for all inputs.
C)w = VMP, for all variable inputs.
D)w = MRP, for all variable inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The marginal revenue product of labour in the local saw mill is MRPL = 20 - .5L, where L = the number of workers. If the mill hires 20 workers, what is the wage rate?
A)12
B)10
C)8
D)5
A)12
B)10
C)8
D)5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In the long run, a firm's demand curve for a resource is:
A)more elastic than it is in the short run.
B)less elastic than it is in the short run.
C)perfectly elastic.
D)as elastic as it is in the short run.
A)more elastic than it is in the short run.
B)less elastic than it is in the short run.
C)perfectly elastic.
D)as elastic as it is in the short run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Which of the following is not an assumption of perfectly competitive input markets?
A)increasing costs
B)perfect information
C)input homogeneity
D)large numbers
A)increasing costs
B)perfect information
C)input homogeneity
D)large numbers

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Figure 11A

In Figure 11A, the individual's Indifference curve is:
A)the line including the points G, N*, and 0'.
B)the line including the points G, N* and E*.
C)the line including the points N* and E*.
D)the line including the point E* only.

In Figure 11A, the individual's Indifference curve is:
A)the line including the points G, N*, and 0'.
B)the line including the points G, N* and E*.
C)the line including the points N* and E*.
D)the line including the point E* only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Average revenue product of an input is:
A)equal to output price times average product of the input.
B)equal to output price times marginal product of the input.
C)the firm's demand function for that input.
D)below MRP if MRP is always downward sloping.
A)equal to output price times average product of the input.
B)equal to output price times marginal product of the input.
C)the firm's demand function for that input.
D)below MRP if MRP is always downward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Consider the following production function for a firm using two inputs x and y,
Q=20x+14y- 2x2+2xy- y2 where q denotes the quantity of output that is produced. The marginal (physical)product of x is:
A)20+14y- 2x+2y.
B)20+14y- 2x2+2xy.
C)20- 4x+2y.
D)20- 2x+2xy.
Q=20x+14y- 2x2+2xy- y2 where q denotes the quantity of output that is produced. The marginal (physical)product of x is:
A)20+14y- 2x+2y.
B)20+14y- 2x2+2xy.
C)20- 4x+2y.
D)20- 2x+2xy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A firm which is a monopolist in its output market and a monopsonist in an input market is:
A)inefficient because VMP > MRP and MFC > w.
B)inefficient because VMP > MRP.
C)efficient.
D)inefficient because MFC > w.
A)inefficient because VMP > MRP and MFC > w.
B)inefficient because VMP > MRP.
C)efficient.
D)inefficient because MFC > w.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Holding quantities of all other inputs constant, a firm's MRP curve is:
A)its demand curve for the input regardless of market structure.
B)below its VMP curve if it is a monopolist in its output market.
C)its VMP curve if it is a monopolist in its output market.
D)above its VMP curve if it is a monopolist in its output market.
A)its demand curve for the input regardless of market structure.
B)below its VMP curve if it is a monopolist in its output market.
C)its VMP curve if it is a monopolist in its output market.
D)above its VMP curve if it is a monopolist in its output market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
If a wage change makes the wage greater than an input's maximum Average Revenue Product, a firm will:
A)hire more of the input.
B)hire the same amount of the input.
C)shut down.
D)hire less of the input.
A)hire more of the input.
B)hire the same amount of the input.
C)shut down.
D)hire less of the input.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
For a firm which is a perfect competitor in its input markets, in long- run equilibrium:
A)p = LRMC.
B)MRP/w is identical for all inputs.
C)MR = w for all inputs.
D)all input prices are identical.
A)p = LRMC.
B)MRP/w is identical for all inputs.
C)MR = w for all inputs.
D)all input prices are identical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
If the supply function of input z to some monopsonist is 10 + 2z:
A)MFC = 10.
B)MFC = 4z.
C)MFC = 10 + 4z.
D)MFC = 10 + 2z.
A)MFC = 10.
B)MFC = 4z.
C)MFC = 10 + 4z.
D)MFC = 10 + 2z.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The assumption of perfect mobility of resources in perfectly competitive input markets implies that
A)all units of the same input will sell for the same price
B)the resources will be identical in all markets
C)unemployment rates may differ in different parts of the country
D)there will always be enough firms to purchase all available resources
A)all units of the same input will sell for the same price
B)the resources will be identical in all markets
C)unemployment rates may differ in different parts of the country
D)there will always be enough firms to purchase all available resources

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A firm will not employ an input if its wage is greater than its maximum:
A)Average Revenue Product.
B)Average Product.
C)Marginal Revenue Product.
D)Marginal Product.
A)Average Revenue Product.
B)Average Product.
C)Marginal Revenue Product.
D)Marginal Product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The demand for labor will increase in response to:
A)increased labour productivity.
B)a decrease in the supply of labor.
C)a decrease in the price of capital that can be used in place of the labor.
D)lower product prices.
A)increased labour productivity.
B)a decrease in the supply of labor.
C)a decrease in the price of capital that can be used in place of the labor.
D)lower product prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A firm is likely to be a monopsonist if:
A)the supply of an input to it slopes downward.
B)the supply of an input to it is horizontal.
C)the supply of an input to it slopes upward.
D)the supply of an input to it is vertical.
A)the supply of an input to it slopes downward.
B)the supply of an input to it is horizontal.
C)the supply of an input to it slopes upward.
D)the supply of an input to it is vertical.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A firm's short- run demand function for some input will shift up if:
A)the competitive equilibrium price of the input decreases.
B)a new process makes the input more productive.
C)the prices of the fixed inputs decrease.
D)the price of the firm's product increases.
A)the competitive equilibrium price of the input decreases.
B)a new process makes the input more productive.
C)the prices of the fixed inputs decrease.
D)the price of the firm's product increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In long- run equilibrium, for a firm which is a monopolist in its output market and a perfect competitor in its input markets:
A)w = VMP for all inputs.
B)w = MRP > VMP for all inputs.
C)p = LRMC.
D)w = MRP < VMP for all inputs.
A)w = VMP for all inputs.
B)w = MRP > VMP for all inputs.
C)p = LRMC.
D)w = MRP < VMP for all inputs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Figure 11A

In Figure 11A, the individual's Production possibility frontier is:
A)the line including the points G, N* and E*.
B)the line including the points N* and E*.
C)the line including the points G, N*, and 0'.
D)the line including the point E* only.

In Figure 11A, the individual's Production possibility frontier is:
A)the line including the points G, N* and E*.
B)the line including the points N* and E*.
C)the line including the points G, N*, and 0'.
D)the line including the point E* only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
If leisure is a normal good:
A)then the supply of leisure is downward sloping.
B)then the supply of labour might be downward sloping.
C)then the demand for leisure is upward sloping.
D)then the demand for labour is upward sloping.
A)then the supply of leisure is downward sloping.
B)then the supply of labour might be downward sloping.
C)then the demand for leisure is upward sloping.
D)then the demand for labour is upward sloping.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The demand for labour can be expressed as Q = 10,000 - w and the supply of labour is Q = 5,000 + w where Q is total person- hours of work during the week and w is the weekly salary. How much compensation do the workers receive weekly?
A)28,125,000
B)43,750,000
C)15,625,000
D)18,750,000
A)28,125,000
B)43,750,000
C)15,625,000
D)18,750,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A perfectly competitive firm is producing at a positive level of output using two resources in the price of one of those resources rises
A)the firm will raise its output price
B)the average product of that resource will fall
C)the firm's average costs will fall
D)the quantity demanded of that resource will fall
A)the firm will raise its output price
B)the average product of that resource will fall
C)the firm's average costs will fall
D)the quantity demanded of that resource will fall

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



