Deck 7: Merger and Acquisition Cash Flow Valuation Basics
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/114
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 7: Merger and Acquisition Cash Flow Valuation Basics
1
Under what circumstances is it important to adjust the Capital Asset Pricing Model for firm size? Why?
Small firms tend to be subject to higher default risk and are often less liquid than larger firms. Studies show that the size of a firm is a good proxy for such factors. Since the CAPM reflects only non-diversifiable or market-related risk, it should be adjusted to reflect these factors.
2
Ergo Unlimited's current year's free cash flow is $10 million. It is projected to grow at 20% per year for the next five years. It is expected to grow at a more modest 5% beyond the fifth year. The firm estimates that its cost of capital is 12% during the next five years and then will drop to 10% beyond the fifth year as the business matures. Estimate the firm's current market value.
$358.30
PV1-5 = 10(1.2)/1.12 + 10(1.2)2/1.122 + 10(1.2)3/1.123 + 10(1.2)4/1.124 + 10(1.2)5/1.125
= 10.71 + 11.48 + 12.30 + 13.18 + 14.12 = 61.79
PVtv = 10(1.20)5x1.05/(.10-.05) = 522.55 = 296.51
PV1-5 = 10(1.2)/1.12 + 10(1.2)2/1.122 + 10(1.2)3/1.123 + 10(1.2)4/1.124 + 10(1.2)5/1.125
= 10.71 + 11.48 + 12.30 + 13.18 + 14.12 = 61.79
PVtv = 10(1.20)5x1.05/(.10-.05) = 522.55 = 296.51
3
Which of the following is true about the variable growth model?
A) Present value equals the discounted sum of the annual forecasts of cash flow
B) Present value equals the discounted sum of the annual forecasts of cash flow plus the discounted value of the terminal value
C) Present value equals the discounted value of the next year's cash flow grown at a constant rate in perpetuity
D) Present value equals the current year's free cash flow discounted in perpetuity
E) None of the above
A) Present value equals the discounted sum of the annual forecasts of cash flow
B) Present value equals the discounted sum of the annual forecasts of cash flow plus the discounted value of the terminal value
C) Present value equals the discounted value of the next year's cash flow grown at a constant rate in perpetuity
D) Present value equals the current year's free cash flow discounted in perpetuity
E) None of the above
B
4
Explain how you would value a patent under the following situations: a patent without any current
application, a patent linked to an existing product, and a patent portfolio.
application, a patent linked to an existing product, and a patent portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The following information is available for two different common stocks: company A and Company B.
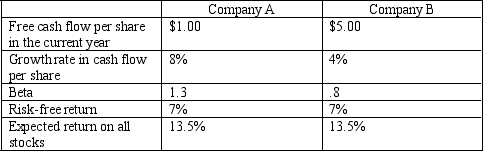
a. Estimate the cost of equity for each firm.
b. Assume that the companies' growth rates will continue at the same rate indefinitely. Estimate the per share value of each companies common stock.

a. Estimate the cost of equity for each firm.
b. Assume that the companies' growth rates will continue at the same rate indefinitely. Estimate the per share value of each companies common stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
What does a firm's measure? What is the difference between an unlevered and levered ? Why is this distinction significant?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
In the year in which it intends to go public, a firm has revenues of $20 million and net income after taxes of $2 million. The firm has no debt, and revenue is expected to grow at 20% annually for the next five years and 5% annually thereafter. Net profit margins are expected remain constant throughout. Capital expenditures are expected to grow in line with depreciation and working capital requirements are minimal. The average beta of a publicly traded company in this industry is 1.50 and the average debt/equity ratio is 20%. The firm is managed very conservatively and does not intend to borrow through the foreseeable future. The Treasury bond rate is 6% and the tax rate is 40%. The normal spread between the return on stocks and the risk free rate of return is believed to be 5.5%. Reflecting the slower growth rate in the sixth year and beyond, the firm's discount rate is expected to decline to the industry average cost of capital of 10.4%. Estimate the value of the firm's equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
How would you estimate the equity value of a firm if you knew its enterprise value and the present value of
all non-operating assets, non-operating liabilities, and long-term debt?
all non-operating assets, non-operating liabilities, and long-term debt?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Abbreviated financial statements are given for Fletcher Corporation in the following table:
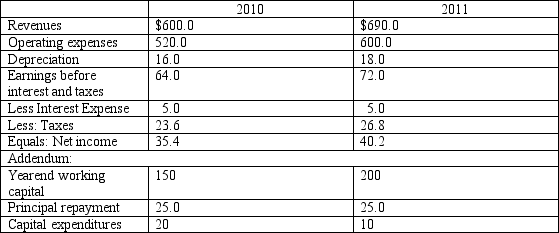 Yearend working capital in 2009 was $160 million and the firm's marginal tax rate is 40% in both 2010 and 2011. Estimate the following for 2010 and 2011:
Yearend working capital in 2009 was $160 million and the firm's marginal tax rate is 40% in both 2010 and 2011. Estimate the following for 2010 and 2011:
a. Free cash flow to equity.
b. Free cash flow to the firm.
 Yearend working capital in 2009 was $160 million and the firm's marginal tax rate is 40% in both 2010 and 2011. Estimate the following for 2010 and 2011:
Yearend working capital in 2009 was $160 million and the firm's marginal tax rate is 40% in both 2010 and 2011. Estimate the following for 2010 and 2011: a. Free cash flow to equity.
b. Free cash flow to the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
No Growth Incorporated had operating income before interest and taxes in 2011 of $220 million. The firm was expected to generate this level of operating income indefinitely. The firm had depreciation expense of $10 million that same year. Capital spending totaled $20 million during 2011. At the end of 2010 and 2011, working capital totaled $70 and $80 million, respectively. The firm's combined marginal state, local, and federal tax rate was 40% and its debt outstanding had a market value of $1.2 billion. The 10-year Treasury bond rate is 5% and the borrowing rate for companies exhibiting levels of creditworthiness similar to No Growth is 7%. The historical risk premium for stocks over the risk free rate of return is 5.5%. No Growth's beta was estimated to be 1.0. The firm had 2,500,000 common shares outstanding at the end of 2011. No Growth's target debt to total capital ratio is 30%.
a. Estimate free cash flow to the firm in 2011.
b. Estimate the firm's cost of capital.
c. Estimate the value of the firm (i.e., includes the value of equity and debt) at the end of 2011, assuming that it will generate the value of free cash flow estimated in (a) indefinitely.
d. Estimate the value of the equity of the firm at the end of 2011.
e. Estimate the value per share at the end of 2011.
a. Estimate free cash flow to the firm in 2011.
b. Estimate the firm's cost of capital.
c. Estimate the value of the firm (i.e., includes the value of equity and debt) at the end of 2011, assuming that it will generate the value of free cash flow estimated in (a) indefinitely.
d. Estimate the value of the equity of the firm at the end of 2011.
e. Estimate the value per share at the end of 2011.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Carlisle Enterprises, a specialty pharmaceutical manufacturer, has been losing market share for three years since several key patents have expired. The free cash flow to the firm in 2002 was $10 million. This figure is expected to decline rapidly as more competitive generic drugs enter the market. Projected cash flows for the next five years are $8.5 million, $7.0 million, $5 million, $2.0 million, and $.5 million. Cash flow after the fifth year is expected to be negligible. The firm's board has decided to sell the firm to a larger pharmaceutical company interested in using Carlisle's product offering to fill gaps in its own product offering until it can develop similar drugs. Carlisle's cost of capital is 15%. What purchase price must Carlisle obtain to earn its cost of capital?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
ABC Incorporated shares are currently trading for $32 per share. The firm has 1.13 billion shares outstanding. In addition, the market value of the firm's outstanding debt is $2 billion. The 10-year Treasury bond rate is 6.25%. ABC has an outstanding credit record and has earned an AAA rating from the major credit rating agencies. The current interest rate on AAA corporate bonds is 6.45%. The historical risk premium for stocks over the risk-free rate of return is 5.5 percentage points. The firm's beta is estimated to be 1.1 and its marginal tax rate, including federal, state, and local taxes is 40%.
a. What is the cost of equity?
b. What is the after-tax cost of debt?
c. What is the cost of capital?
a. What is the cost of equity?
b. What is the after-tax cost of debt?
c. What is the cost of capital?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Which discounted cash flow valuation methods require the estimation of a terminal value? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
You have been asked to estimate the beta of a high-technology firm, which has three divisions with the following characteristics.

a. What is the beta of the equity of the firm?
b. If the risk free return is 5% and the spread between the return on all stocks is 5.5%, estimate the
cost of equity for the software division?
c. What is the cost of equity for the entire firm?
d. Free cash flow to equity investors in the current year (FCFE) for the entire firm is $7.4 million
and for the software division is $3.1 million. If the total firm and the software division are
expected to grow at the same 8% rate into the foreseeable future, estimate the market value of the
firm and of the software division.

a. What is the beta of the equity of the firm?
b. If the risk free return is 5% and the spread between the return on all stocks is 5.5%, estimate the
cost of equity for the software division?
c. What is the cost of equity for the entire firm?
d. Free cash flow to equity investors in the current year (FCFE) for the entire firm is $7.4 million
and for the software division is $3.1 million. If the total firm and the software division are
expected to grow at the same 8% rate into the foreseeable future, estimate the market value of the
firm and of the software division.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Why is it important to distinguish between operating and on-operating assets and liabilities when valuing a firm? Be specific.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
What are the primary differences between FCFE and FCFF?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Do small changes in the assumptions pertaining to the estimation of the terminal value have a significant impact on the calculation of the total value of the target firm? If so, why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
HiFlyer Corporation does not currently have any debt. Its tax rate is .4 and its unlevered beta is estimated by examining comparable companies to be 2.0. The 10-year Treasury bond rate is 6.25% and the historical risk premium over the risk free rate is 5.5%. Next year, HiFlyer expects to borrow up to 75% of its equity value to fund future growth.
a. Calculate the firm's current cost of equity.
b. Estimate the firm's cost of equity after it increases its leverage to 75% of equity?
a. Calculate the firm's current cost of equity.
b. Estimate the firm's cost of equity after it increases its leverage to 75% of equity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
What is the significance of the weighted average cost of capital? How is it calculated? Do the weights reflect the firm's actual or target debt to total capital ratio? Why?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Explain the conditions under which it makes most sense to use the zero growth and constant growth DCF models. Be specific.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Free cash flow to the firm is also called enterprise cash flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A firm's beta is affected by the amount of debt a firm maintains relative to its equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
constant growth valuation model is primarily applicable to firms in mature markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
portion of the purchase price can be financed by 3PAR's nonoperating assets?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
discounted cash flow method for valuing a firm adjusts for differences in the magnitude and timing of cash flows and for risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
is it appropriate to utilize at least a 10-year annual time horizon before estimating a terminal value in valuing firm's such as 3PAR?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
cash flow to equity is calculated using operating income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Interest payments are tax deductible to firms in the U.S.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Estimate 3PAR's equity value per share based on the assumptions and selected 3PAR data provided in Table 7.12?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
cash flow to the firm is calculated before debt and taxes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
calculating the weighted average cost of capital, the weights should be estimated using the market value of the target firm's debt and equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
is possible to determine the equity value of the firm if you know the present value of free cash flow to the firm and the book value of the firm's outstanding shares.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The cost of equity is the minimum financial return required by investors to invest in stocks of comparable risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
the deal still make sense to HP if the terminal period growth rate is 3 percent rather than 5 percent? Explain your answer.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Financial Corporation wants to acquire Great Western Inc. Financial has estimated the enterprise value of Great Western at $104 million. The market value of Great Western's long-term debt is $15 million, and cash balances in excess of the firm's normal working capital requirements are $3 million. Financial estimates the present value of certain licenses that Great Western is not currently using to be $4 million. Great Western is the defendant in several outstanding lawsuits. Financial Corporation's legal department estimates the potential future cost of this litigation to be $3 million, with an estimated present value of $2.5 million. Great Western has 2 million common shares outstanding. What is the value of Great Western per common share?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
beta coefficient is a measure of a firm's diversifiable risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The capital asset pricing model is commonly used to estimate the cost of equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
estimation of present value using the constant growth model involves the calculation of a terminal value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
free cash flow to the firm is expected to remain at $10 million indefinitely and the firm's cost of equity is .10, the present value of the firm is $100 million.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
the absence of debt, the unlevered beta measures the volatility of the firm's financial return to changes in the general stock market's overall return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The enterprise or free cash flow to the firm approach to valuation discounts the after-tax free cash flow available to the firm from operations at the weighted average cost of capital to obtain the enterprise value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The after-tax cost of borrowed funds to the firm is estimated by multiplying the pretax interest rate, i, by (1 -
t), where t is the marginal tax rate for the firm.
t), where t is the marginal tax rate for the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Beta is a measure of non-diversifiable risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Free cash flow to the firm is often called enterprise cash flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When the firm increases its debt in direct proportion to the market value of its equity, the level of the debt is
perfectly correlated with the firm's market value.
perfectly correlated with the firm's market value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the absence of debt, measures the volatility of a firm's financial return to changes in the general market's overall financial return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Net debt is defined as all of the firm's interest bearing debt less the value of cash and marketable securities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Both public and private firms are subject to non-diversifiable risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Preferred stock exhibits some of the characteristics of long-term debt in that its dividend is generally constant
and preferred stockholders are paid before common shareholders in the event the firm is liquidated. True or
False
and preferred stockholders are paid before common shareholders in the event the firm is liquidated. True or
False

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Viewing preferred dividends as paid in perpetuity, the cost of preferred stock can be calculated as dividends
per share of preferred stock divided by the market value of the preferred stock.
per share of preferred stock divided by the market value of the preferred stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The cost of capital formula can be generalized to include hybrid sources of funds available to firms such as
convertible preferred and debt.
convertible preferred and debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The size factor used to adjust the capital asset pricing model serves as a proxy for factors such as smaller firms
being subject to higher default risk and generally being less liquid than large capitalization firms. True or
False
being subject to higher default risk and generally being less liquid than large capitalization firms. True or
False

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Studies show that it is generally unnecessary to adjust the capital asset pricing model for the size of the firm
.
.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The weighted average cost of capital consists only of debt and equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
The constant growth model is most applicable to firms in mature markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The weights used to calculate the weighted average cost of capital for a firm with common equity and debt
only represent the book value of equity and debt.
only represent the book value of equity and debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The variable growth model would be most appropriate for valuing firms in the growth phase of their product life cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
If an investor anticipates a future cash flow stream of five or ten years, she needs to use either a five- or ten-
year Treasury bond rate as the risk-free rate.
year Treasury bond rate as the risk-free rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
According to the capital asset pricing model, risk consists of both diversifiable and non-diversifiable
components.
components.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A risk-free rate of return is one for which the expected return is certain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
For a return to be considered risk-free over some future time period it must be free of default risk and there must not be any uncertainty about the reinvestment rate (i.e., the rate of return that can be earned at the end of the investor's holding period).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A three-month Treasury bill rate is not free of risk for a five- or ten-year period, since interest and principal received at maturity must be reinvested at three month intervals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The projected cash flow of firms in highly cyclical industries can be distorted depending on where the firm is in the business cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Whether an analyst should use a short or long-term interest rate for the risk free rate in calculating the
CAPM depends on when the investor receives their future cash flows.
CAPM depends on when the investor receives their future cash flows.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The market risk or equity premium refers to the additional rate of return in excess of the weighted average cost of capital that investors require to purchase a firm's equity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A firm's credit rating is a poor measure of a firm's default risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Growth rates can be calculated based on the historical experience of the firm or industry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The cost of equity can also be viewed as an opportunity cost.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
When cash flow is temporarily depressed due to strikes, litigation, warranty claims, or other one-time events, it is generally safe to assume that cash flow will recover in the near term.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Investors require a minimum rate of return on an investment to compensate them for the level of perceived risk associated with that investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Preferred dividends are tax deductible to U.S. corporations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Intuition suggests that the length of the high-growth period when applying the variable growth model should be shorter the greater the current growth rate of the firm's cash flow.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Betas do not vary over time and are quite insensitive to the time period and methodology employed in their estimation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Discounted cash flow and the asset-oriented valuation methods necessarily provide identical results. True
or False
or False

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The constant growth model may be used to estimate the risk premium component of the cost of equity as an alternative to relying on historical information as is done in the capital asset pricing model.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Assume the firm size premium for a firm with a market value of $20 million is 7.2%. Also, assume the risk-free rate of return, equity premium, and are 5.0%, 5.5%, and 1.75 respectively. The firm's cost of equity using the CAPM method adjusted for firm size is 21.8%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Studies show that the market risk premium is unstable, lower during periods of prosperity and higher during periods of economic slowdowns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The weighted average cost of capital (WACC) is the broadest measure of the firm's cost of funds and represents the return that a firm must earn to induce investors to buy its common stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
For non-rated firms, the analyst may estimate the pretax cost of debt for an individual firm by comparing debt-to-equity or total capital ratios, interest coverage ratios, and operating margins with those of similar rated firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
For firms whose market value is less than $50 million, the adjustment to the CAPM in estimating the cost of equity can be as large as 2 percentage points.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 114 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



