Deck 3: Descriptive Statistics: Numerical Measures
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/173
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 3: Descriptive Statistics: Numerical Measures
1
The mean of the sample
A)is always smaller than the mean of the population from which the sample was taken
B)can never be zero
C)can never be negative
D)None of these alternatives is correct.
A)is always smaller than the mean of the population from which the sample was taken
B)can never be zero
C)can never be negative
D)None of these alternatives is correct.
None of these alternatives is correct.
2
Since the population is always larger than the sample, the value of the sample mean
A)is always smaller than the true value of the population mean
B)is always larger than the true value of the population mean
C)is always equal to the true value of the population mean
D)could be larger, equal to, or smaller than the true value of the population mean
A)is always smaller than the true value of the population mean
B)is always larger than the true value of the population mean
C)is always equal to the true value of the population mean
D)could be larger, equal to, or smaller than the true value of the population mean
could be larger, equal to, or smaller than the true value of the population mean
3
Growth factors for the population of Atlanta in the past five years have been 1, 2, 3, 4 , and 5. The geometric mean is
A)15
B)square root of 15
C)120
D)fifth root of 120
A)15
B)square root of 15
C)120
D)fifth root of 120
fifth root of 120
4
Growth factors for the population of Chattanoonga in the past two years has been 8 and 12. The geometric mean has a value of
A)20
B)square root of 20
C)square root of 96
D)96
A)20
B)square root of 20
C)square root of 96
D)96

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Which of the following provides a measure of central location for the data?
A)standard deviation
B)mean
C)variance
D)range
A)standard deviation
B)mean
C)variance
D)range

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If two groups of numbers have the same mean, then
A)their standard deviations must also be equal
B)their medians must also be equal
C)their modes must also be equal
D)None of these alternatives is correct.
A)their standard deviations must also be equal
B)their medians must also be equal
C)their modes must also be equal
D)None of these alternatives is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Geometric mean is a measure of
A)location
B)dispersion
C)variability
D)weight of items, when arranged in descending order
A)location
B)dispersion
C)variability
D)weight of items, when arranged in descending order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When computing the mean of a set of values xi, the value of xi
A)can never be zero
B)can never be negative
C)must always be positive
D)can be any value
A)can never be zero
B)can never be negative
C)must always be positive
D)can be any value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When the smallest and largest percentage of items are removed from a data set and the mean is computed, the mean of the remaining data is
A)the median
B)the mode
C)the trimmed mean
D)any of the above
A)the median
B)the mode
C)the trimmed mean
D)any of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
is an example of a
A)population parameter
B)sample statistic
C)population variance
D)mode
A)population parameter
B)sample statistic
C)population variance
D)mode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
In computing the mean of a sample, the value of xi is divided by
A)n
B)n - 1
C)n + 1
D)n - 2
A)n
B)n - 1
C)n + 1
D)n - 2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The measure of location which is the most likely to be influenced by extreme values in the data set is the
A)range
B)median
C)mode
D)mean
A)range
B)median
C)mode
D)mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A numerical value used as a summary measure for a sample, such as sample mean, is known as a
A)population parameter
B)sample parameter
C)sample statistic
D)population mean
A)population parameter
B)sample parameter
C)sample statistic
D)population mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The measure of location which is the most likely to be influenced by extreme values in the data set is the
A)range
B)median
C)mode
D)mean
A)range
B)median
C)mode
D)mean

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Geometric mean of five observations is
A)the same as weighted mean
B)the same as mean
C)square root of the product of the 5 observations
D)fifth root of the product of the 5 observations
A)the same as weighted mean
B)the same as mean
C)square root of the product of the 5 observations
D)fifth root of the product of the 5 observations

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The nth root of the product of the n observations is
A)weighted mean
B)geometric mean
C)product deviation
D)the sum of squares
A)weighted mean
B)geometric mean
C)product deviation
D)the sum of squares

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The hourly wages of a sample of 130 system analysts are given below. mean = 60
Range = 20
Mode = 73
Variance = 324
Median = 74
The coefficient of variation equals
A)0.30%
B)30%
C)5.4%
D)54%
Range = 20
Mode = 73
Variance = 324
Median = 74
The coefficient of variation equals
A)0.30%
B)30%
C)5.4%
D)54%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Since the population size is always larger than the sample size, then the sample statistic
A)can never be larger than the population parameter
B)can never be equal to the population parameter
C)can be smaller, larger, or equal to the population parameter
D)can never be smaller than the population parameter
A)can never be larger than the population parameter
B)can never be equal to the population parameter
C)can be smaller, larger, or equal to the population parameter
D)can never be smaller than the population parameter

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The mean of a sample
A)is always equal to the mean of the population
B)is always smaller than the mean of the population
C)is computed by summing the data values and dividing the sum by (n - 1)
D)is computed by summing all the data values and dividing the sum by the number of items
A)is always equal to the mean of the population
B)is always smaller than the mean of the population
C)is computed by summing the data values and dividing the sum by (n - 1)
D)is computed by summing all the data values and dividing the sum by the number of items

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The most important statistical descriptive measure of the location of a data set is the
A)mean
B)median
C)mode
D)variance
A)mean
B)median
C)mode
D)variance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The 50th percentile is the
A)mode
B)median
C)mean
D)third quartile
A)mode
B)median
C)mean
D)third quartile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The first quartile
A)contains at least one third of the data elements
B)is the same as the 25th percentile
C)is the same as the 50th percentile
D)is the same as the 75th percentile
A)contains at least one third of the data elements
B)is the same as the 25th percentile
C)is the same as the 50th percentile
D)is the same as the 75th percentile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
When computing the mean, the smallest value
A)can never be negative
B)can never be zero
C)can never be less than the mean
D)can be any value
A)can never be negative
B)can never be zero
C)can never be less than the mean
D)can be any value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The variance of a sample of 169 observations equals 576. The standard deviation of the sample equals
A)13
B)24
C)576
D)28,461
A)13
B)24
C)576
D)28,461

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The difference between the largest and the smallest data values is the
A)variance
B)interquartile range
C)range
D)coefficient of variation
A)variance
B)interquartile range
C)range
D)coefficient of variation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The variance of a sample of 81 observations equals 64. The standard deviation of the sample equals
A)9
B)4096
C)8
D)6561
A)9
B)4096
C)8
D)6561

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The value which has half of the observations above it and half the observations below it is called the
A)range
B)median
C)mean
D)mode
A)range
B)median
C)mean
D)mode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The pth percentile is a value such that at least p percent of the observations are
A)less than or equal to this value
B)less than this value
C)more than or equal to this value
D)more than this value
A)less than or equal to this value
B)less than this value
C)more than or equal to this value
D)more than this value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The standard deviation of a sample of 100 observations equals 64. The variance of the sample equals
A)8
B)10
C)6400
D)4,096
A)8
B)10
C)6400
D)4,096

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The median is a measure of
A)relative dispersion
B)absolute dispersion
C)central location
D)relative location
A)relative dispersion
B)absolute dispersion
C)central location
D)relative location

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The 75th percentile is referred to as the
A)first quartile
B)second quartile
C)third quartile
D)fourth quartile
A)first quartile
B)second quartile
C)third quartile
D)fourth quartile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If a data set has an even number of observations, the median
A)cannot be determined
B)is the average value of the two middle items
C)must be equal to the mean
D)is the average value of the two middle items when all items are arranged in ascending order
A)cannot be determined
B)is the average value of the two middle items
C)must be equal to the mean
D)is the average value of the two middle items when all items are arranged in ascending order

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The interquartile range is
A)the 50th percentile
B)another name for the variance
C)the difference between the largest and smallest values
D)the difference between the third quartile and the first quartile
A)the 50th percentile
B)another name for the variance
C)the difference between the largest and smallest values
D)the difference between the third quartile and the first quartile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The heights (in inches) of 25 individuals were recorded and the following statistics were calculated mean = 70
Range = 20
Mode = 73
Variance = 784
Median = 74
The coefficient of variation equals
A)11.2%
B)1120%
C)0.4%
D)40%
Range = 20
Mode = 73
Variance = 784
Median = 74
The coefficient of variation equals
A)11.2%
B)1120%
C)0.4%
D)40%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The weights (in pounds) of a sample of 36 individuals were recorded and the following statistics were calculated.mean = 160 range = 60
Mode = 165
Variance = 324
Median = 170
The coefficient of variation equals
A)0.1125%
B)11.25%
C)203.12%
D)0.20312%
Mode = 165
Variance = 324
Median = 170
The coefficient of variation equals
A)0.1125%
B)11.25%
C)203.12%
D)0.20312%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The median of a sample will always equal the
A)mode
B)mean
C)50th percentile
D)all of the above answers are correct
A)mode
B)mean
C)50th percentile
D)all of the above answers are correct

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If index i (which is used to determine the location of the pth percentile) is not an integer, its value should be
A)squared
B)divided by (n - 1)
C)rounded down
D)rounded up
A)squared
B)divided by (n - 1)
C)rounded down
D)rounded up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is a measure of dispersion?
A)percentiles
B)quartiles
C)interquartile range
D)all of the above are measures of dispersion
A)percentiles
B)quartiles
C)interquartile range
D)all of the above are measures of dispersion

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The most frequently occurring value of a data set is called the
A)range
B)mode
C)mean
D)median
A)range
B)mode
C)mean
D)median

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is not a measure of central location?
A)mean
B)median
C)variance
D)mode
A)mean
B)median
C)variance
D)mode

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Which of the following is not a measure of dispersion?
A)the range
B)the 50th percentile
C)the standard deviation
D)the interquartile range
A)the range
B)the 50th percentile
C)the standard deviation
D)the interquartile range

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Which of the following symbols represents the size of the sample
A) 2
B)
C)N
D)n
A) 2
B)
C)N
D)n

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When should measures of location and dispersion be computed from grouped data rather than from individual data values?
A)as much as possible since computations are easier
B)only when individual data values are unavailable
C)whenever computer packages for descriptive statistics are unavailable
D)only when the data are from a population
A)as much as possible since computations are easier
B)only when individual data values are unavailable
C)whenever computer packages for descriptive statistics are unavailable
D)only when the data are from a population

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
The sum of deviations of the individual data elements from their mean is
A)always greater than zero
B)always less than zero
C)sometimes greater than and sometimes less than zero, depending on the data elements
D)always equal to zero
A)always greater than zero
B)always less than zero
C)sometimes greater than and sometimes less than zero, depending on the data elements
D)always equal to zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The measure of dispersion that is influenced most by extreme values is
A)the variance
B)the standard deviation
C)the range
D)the interquartile range
A)the variance
B)the standard deviation
C)the range
D)the interquartile range

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The numerical value of the standard deviation can never be
A)larger than the variance
B)zero
C)negative
D)smaller than the variance
A)larger than the variance
B)zero
C)negative
D)smaller than the variance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following symbols represents the size of the population?
A) 2
B)
C)
D)N
A) 2
B)
C)
D)N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When data are positively skewed, the mean will usually be
A)greater than the median
B)smaller than the median
C)equal to the median
D)positive
A)greater than the median
B)smaller than the median
C)equal to the median
D)positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The variance can never be
A)zero
B)larger than the standard deviation
C)negative
D)smaller than the standard deviation
A)zero
B)larger than the standard deviation
C)negative
D)smaller than the standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Which of the following symbols represents the standard deviation of the population?
A) 2
B)
C)
D)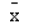
A) 2
B)
C)
D)
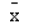

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The descriptive measure of dispersion that is based on the concept of a deviation about the mean is
A)the range
B)the interquartile range
C)the absolute value of the range
D)the standard deviation
A)the range
B)the interquartile range
C)the absolute value of the range
D)the standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following symbols represents the mean of the population?
A) 2
B)
C)
D)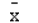
A) 2
B)
C)
D)
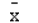

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Which of the following symbols represents the variance of the population?
A) 2
B)
C)
D)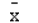
A) 2
B)
C)
D)
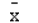

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In computing descriptive statistics from grouped data,
A)data values are treated as if they occur at the midpoint of a class
B)the grouped data result is more accurate than the ungrouped result
C)the grouped data computations are used only when a population is being analyzed
D)None of these alternatives is correct.
A)data values are treated as if they occur at the midpoint of a class
B)the grouped data result is more accurate than the ungrouped result
C)the grouped data computations are used only when a population is being analyzed
D)None of these alternatives is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
If the variance of a data set is correctly computed with the formula using n - 1 in the denominator, which of the following is true?
A)the data set is a sample
B)the data set is a population
C)the data set could be either a sample or a population
D)the data set is from a census
A)the data set is a sample
B)the data set is a population
C)the data set could be either a sample or a population
D)the data set is from a census

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When the data are skewed to the right, the measure of Skewness will be
A)negative
B)zero
C)positive
D)one
A)negative
B)zero
C)positive
D)one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The sample variance
A)is always smaller than the true value of the population variance
B)is always larger than the true value of the population variance
C)could be smaller, equal to, or larger than the true value of the population variance
D)can never be zero
A)is always smaller than the true value of the population variance
B)is always larger than the true value of the population variance
C)could be smaller, equal to, or larger than the true value of the population variance
D)can never be zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following symbols represents the mean of the sample?
A) 2
B)
C)
D)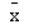
A) 2
B)
C)
D)
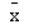

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The coefficient of variation is
A)the same as the variance
B)the standard deviation divided by the mean times 100
C)the square of the standard deviation
D)the mean divided by the standard deviation
A)the same as the variance
B)the standard deviation divided by the mean times 100
C)the square of the standard deviation
D)the mean divided by the standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The interquartile range is used as a measure of variability to overcome what difficulty of the range?
A)the sum of the range variances is zero
B)the range is difficult to compute
C)the range is influenced too much by extreme values
D)the range is negative
A)the sum of the range variances is zero
B)the range is difficult to compute
C)the range is influenced too much by extreme values
D)the range is negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The relative frequency of a class is computed by
A)dividing the midpoint of the class by the sample size
B)dividing the frequency of the class by the midpoint
C)dividing the sample size by the frequency of the class
D)dividing the frequency of the class by the sample size
A)dividing the midpoint of the class by the sample size
B)dividing the frequency of the class by the midpoint
C)dividing the sample size by the frequency of the class
D)dividing the frequency of the class by the sample size

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The value of the sum of the deviations from the mean, i.e., 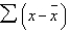 must always be
must always be
A)less than the zero
B)negative
C)either positive or negative depending on whether the mean is negative or positive
D)zero
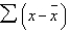 must always be
must always beA)less than the zero
B)negative
C)either positive or negative depending on whether the mean is negative or positive
D)zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the
A)variance
B)coefficient of variation
C)correlation coefficient
D)standard deviation
A)variance
B)coefficient of variation
C)correlation coefficient
D)standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Positive values of covariance indicate
A)a positive variance of the x values
B)a positive variance of the y values
C)the standard deviation is positive
D)positive relation between the independent and the dependent variables
A)a positive variance of the x values
B)a positive variance of the y values
C)the standard deviation is positive
D)positive relation between the independent and the dependent variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The coefficient of correlation ranges between
A)0 and 1
B)-1 and +1
C)minus infinity and plus infinity
D)1 and 100
A)0 and 1
B)-1 and +1
C)minus infinity and plus infinity
D)1 and 100

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Since the mode is the most frequently occurring data value, it
A)can never be larger than the mean
B)is always larger than the median
C)is always larger than the mean
D)None of these alternatives is correct.
A)can never be larger than the mean
B)is always larger than the median
C)is always larger than the mean
D)None of these alternatives is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Which of the following is not a measure of dispersion?
A)mode
B)standard deviation
C)range
D)interquartile range
A)mode
B)standard deviation
C)range
D)interquartile range

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
In a five number summary, which of the following is not used for data summarization?
A)the smallest value
B)the largest value
C)the mean
D)the 25th percentile
A)the smallest value
B)the largest value
C)the mean
D)the 25th percentile

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The numerical value of the variance
A)is always larger than the numerical value of the standard deviation
B)is always smaller than the numerical value of the standard deviation
C)is negative if the mean is negative
D)can be larger or smaller than the numerical value of the standard deviation
A)is always larger than the numerical value of the standard deviation
B)is always smaller than the numerical value of the standard deviation
C)is negative if the mean is negative
D)can be larger or smaller than the numerical value of the standard deviation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The symbol is used to represent
A)the variance of the population
B)the standard deviation of the sample
C)the standard deviation of the population
D)the variance of the sample
A)the variance of the population
B)the standard deviation of the sample
C)the standard deviation of the population
D)the variance of the sample

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A group of students had dinner at a local restaurant. The total bill for the dinner was $414.70. Each student paid his/her equal share of the bill, which was $18.85. How many student's were at the dinner?
A)4
B)415
C)19
D)22
A)4
B)415
C)19
D)22

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
The coefficient of correlation
A)is the same as the coefficient of determination
B)can be larger than 1
C)cannot be larger than 1
D)cannot be negative
A)is the same as the coefficient of determination
B)can be larger than 1
C)cannot be larger than 1
D)cannot be negative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
If the coefficient of variation is 40% and the mean is 70, then the variance is
A)28
B)2800
C)1.75
D)784
A)28
B)2800
C)1.75
D)784

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The symbol 2 is used to represent
A)the variance of the population
B)the standard deviation of the sample
C)the standard deviation of the population
D)the variance of the sample
A)the variance of the population
B)the standard deviation of the sample
C)the standard deviation of the population
D)the variance of the sample

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Given the following information: Standard deviation = 8
Coefficient of variation = 64%
The mean would then be
A)12.5
B)8
C)0.64
D)1.25
Coefficient of variation = 64%
The mean would then be
A)12.5
B)8
C)0.64
D)1.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
The measure of dispersion which is not measured in the same units as the original data is the
A)median
B)standard deviation
C)coefficient of determination
D)variance
A)median
B)standard deviation
C)coefficient of determination
D)variance

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
During a cold winter, the temperature stayed below zero for ten days (ranging from -20 to -5). The variance of the temperatures of the ten-day period
A)is negative since all the numbers are negative
B)must be at least zero
C)cannot be computed since all the numbers are negative
D)can be either negative or positive
A)is negative since all the numbers are negative
B)must be at least zero
C)cannot be computed since all the numbers are negative
D)can be either negative or positive

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A numerical measure of linear association between two variables is the
A)variance
B)covariance
C)standard deviation
D)coefficient of variation
A)variance
B)covariance
C)standard deviation
D)coefficient of variation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Since the median is the middle value of a data set it
A)must always be smaller than the mode
B)must always be larger than the mode
C)must always be smaller than the mean
D)None of these alternatives is correct.
A)must always be smaller than the mode
B)must always be larger than the mode
C)must always be smaller than the mean
D)None of these alternatives is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The variance of the sample
A)can never be negative
B)can be negative
C)cannot be zero
D)cannot be less than one
A)can never be negative
B)can be negative
C)cannot be zero
D)cannot be less than one

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 173 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



