Deck 4: Numerical Descriptive Techniques
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/316
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Numerical Descriptive Techniques
1
Which of the following is correct about the shape of a distribution?
A)The shape can show you how many modes there are.
B)The shape can help you determine the approximate center of the distribution.
C)The shape can help you determine whether the data are close or spread out.
D)All of these choices are true.
A)The shape can show you how many modes there are.
B)The shape can help you determine the approximate center of the distribution.
C)The shape can help you determine whether the data are close or spread out.
D)All of these choices are true.
All of these choices are true.
2
Statisticians usually apply graphical techniques as a first step in analyzing data because we first need to know the ____________________ of the distribution.
shape
3
Statisticians typically apply graphical techniques as a first step in a data analysis because we first need to know the shape of the distribution.
True
4
If , , n = 12, and the slope equals 0.5, then the y-intercept of the least squares line is b0 = 276.08.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
What statistics and graphs can you use to answer the following question: Is the distribution symmetric? If not, is it skewed? If symmetric, is it bell shaped?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The coefficient of correlation and the least squares line both describe the relationship between two interval variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
If the covariance of x and y is 26.16, and the standard deviation of x is 32.7, then the slope of the least squares line is b1 =.80.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
What statistics and graphs can you use to answer the following questions: Is the distribution unimodal, bimodal, or multimodal? If there is more than one mode, where are the peaks, and where are the valleys?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A scatter diagram reveals a strong positive linear relationship between oil and gasoline prices. Which of the following numerical techniques will not give us more detailed information about this relationship?
A)Coefficient of determination
B)Coefficient of correlation
C)Coefficient of variation.
D)All of these choices help us describe this relationship.
A)Coefficient of determination
B)Coefficient of correlation
C)Coefficient of variation.
D)All of these choices help us describe this relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
What statistics and graphs can you use to look for a relationship between two interval variables?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
We can frequently make several inferences about the nature of the data from the ____________________ of its histogram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
The precision provided by the numerical techniques (mean, median, and standard deviation) provides more useful information than graphical techniques (histograms and box plots) alone.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Box plots and medians work well to describe ____________________ data, while histograms and means work well to describe ____________________ data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following characteristics does a histogram help you identify?
A)The shape of distribution.
B)The approximate center of a distribution.
C)The amount of spread in a distribution.
D)All of these choices are true.
A)The shape of distribution.
B)The approximate center of a distribution.
C)The amount of spread in a distribution.
D)All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
What statistics and graphs can you use to answer the following question: Are the observations close to one another, or are they widely dispersed?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Graphical and numerical techniques, such as histograms and least squares lines provide identical information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
What statistics and graphs can you use to answer the following question: Where is the approximate center of the distribution?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The shape of a distribution helps answer which question about the data?
A)Where is the approximate center of the distribution?
B)Are the observations close to one another, or are they widely dispersed?
C)Is the distribution symmetric?
D)All of these choices are true.
A)Where is the approximate center of the distribution?
B)Are the observations close to one another, or are they widely dispersed?
C)Is the distribution symmetric?
D)All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Scatter diagrams, covariance, and the coefficient of correlation are useful techniques for detecting relationships between two ____________________ variables.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
____________________ techniques give you the big picture of a distribution, and ____________________ techniques give you more precise details.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Three measures of the linear relationship between x and y are the coefficient of correlation, the coefficient of determination, and the coefficient of variation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the standard deviation of x is 18, the covariance of x and y is 120, the coefficient r = 0.90, then the standard deviation of y is 54.87.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If the standard deviations of x and y are 12.5 and 10.8, respectively, and the covariance is 118.8, then the coefficient of correlation r is 0.88.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The slope b1 of the least squares line represents the:
A)predicted value of Y when X = 0.
B)estimated average change in Y per unit change in X.
C)predicted value of Y.
D)variation around the regression line.
A)predicted value of Y when X = 0.
B)estimated average change in Y per unit change in X.
C)predicted value of Y.
D)variation around the regression line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If the correlation coefficient r = 1.00, then all the observations must fall exactly on:
A)a straight line with a slope that equals 1.00.
B)a straight line with a negative slope.
C)a straight line with a positive slope.
D)a horizontal straight line with a zero slope.
A)a straight line with a slope that equals 1.00.
B)a straight line with a negative slope.
C)a straight line with a positive slope.
D)a horizontal straight line with a zero slope.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A perfect straight line sloping downward would produce a correlation coefficient equal to:
A)+1.0
B)-1.0
C)0.0
D)Cannot tell from the information given.
A)+1.0
B)-1.0
C)0.0
D)Cannot tell from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If the coefficient of correlation r = 0, there can be no relationship whatsoever between the dependent variable y and the independent variable x.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The variance is a measure of the linear relationship between two variables

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
When the standard deviation is expressed as a percentage of the mean, the result is the coefficient of correlation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Assuming a linear relationship between X and Y, if the coefficient of correlation (r) equals -0.75, this means that:
A)there is very weak correlation
B)the slope b1 is = -0.75
C)the value of X is always greater than the value of Y
D)None of these choices are true
A)there is very weak correlation
B)the slope b1 is = -0.75
C)the value of X is always greater than the value of Y
D)None of these choices are true

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The Y-intercept, b0, of the least squares line represents the:
A)estimated average value of Y when X = 0.
B)estimated average change in Y per unit change in X.
C)predicted value of Y.
D)variation around the sample regression line.
A)estimated average value of Y when X = 0.
B)estimated average change in Y per unit change in X.
C)predicted value of Y.
D)variation around the sample regression line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Generally speaking, if two variables are unrelated (as one increases, the other shows no pattern), the covariance will be:
A)a large positive number.
B)a large negative number.
C)a positive or negative number close to zero.
D)None of these choices.
A)a large positive number.
B)a large negative number.
C)a positive or negative number close to zero.
D)None of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the coefficient of correlation r = -.81, the standard deviations of x and y are 20 and 25, respectively, then cov(x, y) must be -405.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
If the coefficient of correlation r = 0, there can be no linear relationship between the dependent variable y and the independent variable x.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If the coefficient of correlation r = 1, then the best-fit linear equation will actually include all of the observations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A perfect straight line sloping upward would produce a correlation coefficient value of 1.0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Generally speaking, if two variables are unrelated, the covariance will be a number close to zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is a property of r, the coefficient of correlation?
A)r always lies between 0 and 1.
B)r has no units.
C)If you switch the values of X and Y, the sign of r changes.
D)All of these choices are true.
A)r always lies between 0 and 1.
B)r has no units.
C)If you switch the values of X and Y, the sign of r changes.
D)All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The coefficient of correlation r is a number that indicates the direction and the strength of the linear relationship between the dependent variable y and the independent variable x.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The advantage that the coefficient of correlation has over the covariance is that the former has set lower and upper limits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The ____________________ measures the margin of relative change in the dependent variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The method used to find the best fitting line through the observations is called the ____________________ method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When two variables x and y are linearly related, it does not necessarily mean that x ____________________ y.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Given the following sample data:

a.Calculate the covariance and the correlation coefficient.
b.Comment on the relationship between x and y.
c.Determine the least squares line.
d.Draw the scatter diagram and plot the least squares line.

a.Calculate the covariance and the correlation coefficient.
b.Comment on the relationship between x and y.
c.Determine the least squares line.
d.Draw the scatter diagram and plot the least squares line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The strength of the linear relationship between two interval variables can be measured by the:
A)coefficient of variation.
B)coefficient of correlation.
C)slope of the regression line.
D)Y-intercept.
A)coefficient of variation.
B)coefficient of correlation.
C)slope of the regression line.
D)Y-intercept.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
NARRBEGIN: Experience and Salary
Longevity and Salary
A sample of eight observations of variables x (years of experience) and y (salary in $1,000s) is shown below:
 NARREND
NARREND
{Longevity and Salary Narrative}
a.Calculate the coefficient of correlation, and comment on the relationship between x and y.
b.Give a possible reason that the correlation is negative.
Longevity and Salary
A sample of eight observations of variables x (years of experience) and y (salary in $1,000s) is shown below:
 NARREND
NARREND{Longevity and Salary Narrative}
a.Calculate the coefficient of correlation, and comment on the relationship between x and y.
b.Give a possible reason that the correlation is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
NARRBEGIN: Experience and Salary
Longevity and Salary
A sample of eight observations of variables x (years of experience) and y (salary in $1,000s) is shown below:
 NARREND
NARREND
{Longevity and Salary Narrative} Draw the scatter diagram and plot the least squares line.
Longevity and Salary
A sample of eight observations of variables x (years of experience) and y (salary in $1,000s) is shown below:
 NARREND
NARREND{Longevity and Salary Narrative} Draw the scatter diagram and plot the least squares line.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The magnitude of the correlation measures the ____________________ of a linear relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Which of the following is a property of the slope, b1?
A)The slope equals one if X and Y have the same variance.
B)The slope has the same sign as r, the coefficient of correlation.
C)The slope equals one if r equals one.
D)All of these choices are true.
A)The slope equals one if X and Y have the same variance.
B)The slope has the same sign as r, the coefficient of correlation.
C)The slope equals one if r equals one.
D)All of these choices are true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The y-intercept of the least squares line is the point on the line where ________________ = 0.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The denominator in the calculation of the sample covariance, cov (x,y), is:
A)n - 2
B)n -1
C)n
D)2n - 1
A)n - 2
B)n -1
C)n
D)2n - 1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The ____________________ of the correlation indicates the direction of a linear relationship.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The coefficient of determination is the percentage of variation in the ____________________ variable that is explained by the variation in the ____________________ variable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
NARRBEGIN: Experience and Salary
Longevity and Salary
A sample of eight observations of variables x (years of experience) and y (salary in $1,000s) is shown below:
 NARREND
NARREND
{Longevity and Salary Narrative}
a.Calculate and interpret the covariance between x and y.
b.Give a possible reason that the covariance is negative.
Longevity and Salary
A sample of eight observations of variables x (years of experience) and y (salary in $1,000s) is shown below:
 NARREND
NARREND{Longevity and Salary Narrative}
a.Calculate and interpret the covariance between x and y.
b.Give a possible reason that the covariance is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
In the equation of the least squares line, 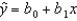 , b0 is the ____________________ and b1 is the ____________________.
, b0 is the ____________________ and b1 is the ____________________.
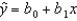 , b0 is the ____________________ and b1 is the ____________________.
, b0 is the ____________________ and b1 is the ____________________.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If cov(x, y) = 20, and then the sample coefficient of correlation r is:
A)1.400
B)0.026
C)0.710
D)None of these choices.
A)1.400
B)0.026
C)0.710
D)None of these choices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
NARRBEGIN: Experience and Salary
Longevity and Salary
A sample of eight observations of variables x (years of experience) and y (salary in $1,000s) is shown below:
 NARREND
NARREND
{Longevity and Salary Narrative} Determine the least squares line, and use it to estimate the value of y for x = 6.
Longevity and Salary
A sample of eight observations of variables x (years of experience) and y (salary in $1,000s) is shown below:
 NARREND
NARREND{Longevity and Salary Narrative} Determine the least squares line, and use it to estimate the value of y for x = 6.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following are measures of the linear relationship between two variables?
A)The covariance
B)The coefficient of correlation
C)The variance
D)Both a and b
A)The covariance
B)The coefficient of correlation
C)The variance
D)Both a and b

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
NARRBEGIN: Experience and Salary
Longevity and Salary
A sample of eight observations of variables x (years of experience) and y (salary in $1,000s) is shown below:
 NARREND
NARREND
How is the value of the correlation coefficient r affected in each of the following cases?
a.Each x value and y is multiplied by 4.
b.Each x value is switched with the corresponding y value.
c.Each x value is increased by 2.
Longevity and Salary
A sample of eight observations of variables x (years of experience) and y (salary in $1,000s) is shown below:
 NARREND
NARRENDHow is the value of the correlation coefficient r affected in each of the following cases?
a.Each x value and y is multiplied by 4.
b.Each x value is switched with the corresponding y value.
c.Each x value is increased by 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The ____________________ of a linear relationship is hard to interpret from the covariance, but it is easy to interpret from the correlation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The interquartile range is found by taking the difference between the 1st and 3rd quartiles and dividing that value by 2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The value for Q3 can never be smaller than the value for Q1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The first and second quartiles of a data set can never be equal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
The interquartile range is an interval of numbers starting at Q1 and ending at Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The line drawn within the box of a box plot always represents the mean.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The interquartile range will always exceed that of the range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A box plot is a graphical representation of the 5-number summary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Quartiles divide the observations in a data set into four parts with the same amount of data in each part.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
NARRBEGIN: Experience and Salary
Longevity and Salary
A sample of eight observations of variables x (years of experience) and y (salary in $1,000s) is shown below:
 NARREND
NARREND
Consider the following data:
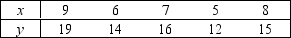
a.Calculate the covariance and the coefficient of correlation for the sample.
b.What do these statistics tell you about the relationship between x and y?
Longevity and Salary
A sample of eight observations of variables x (years of experience) and y (salary in $1,000s) is shown below:
 NARREND
NARRENDConsider the following data:

a.Calculate the covariance and the coefficient of correlation for the sample.
b.What do these statistics tell you about the relationship between x and y?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The line drawn within the box of a box plot always represents the median.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
The distance between the 25th percentile and the median is always the same as the distance between the median and the 75th percentile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
In a negatively skewed distribution, the distance from the smallest observation to Q1 exceeds the distance from Q3 to the largest observation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The 5-number summary consists of the smallest observation, the first quartile, the median, the third quartile, and the largest observation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The interquartile range is a measure of variability in a set of data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Expressed in percentiles, the interquartile range is the difference between the 25th and 75th percentiles.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In symmetric data, the value for Q2 is always halfway between Q1 and Q3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
In a positively skewed distribution, the percentage of data between the smallest observation and Q1 is less than the percentage of data between Q3 and the largest observation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Percentiles can be converted into quintiles and deciles, where quintiles divide the data into fifths and deciles divide the data into tenths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
If the distribution of a data set were perfectly symmetric, the distance from Q1 to the median would always equal the distance from Q3 to the median in a box plot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
The length of the box in a box plot portrays the interquartile range.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 316 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



