Deck 16: Trigonometric Models
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/67
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Trigonometric Models
1
Evaluate the integral.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
2
Recall that the average of a function on an interval is
Find the average of the given function.
over
A)Average =
B) Average =
C) Average =
D) Average =
E) Average =
Find the average of the given function.
over
A)Average =
B) Average =
C) Average =
D) Average =
E) Average =
Average =
3
Use geometry to compute the given integral.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) none of these
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) none of these
4
Evaluate the integral.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) none of these
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Evaluate the integral. ? ?
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Recall that the total income received from time to time from a continuous income stream of dollars per year is
Total value = TV =
Find the total value of the given income stream and also find its future value (at the end of the given interval) using the given interest rate.
, , at 9%
A)TV = $0, FV = $72,344.91
B) TV = $0, FV = $327,074.77
C) TV = $1,600,000, FV = $834,722.23
D) TV = $0, FV = $256,372.45
E) none of these
Total value = TV =
Find the total value of the given income stream and also find its future value (at the end of the given interval) using the given interest rate.
, , at 9%
A)TV = $0, FV = $72,344.91
B) TV = $0, FV = $327,074.77
C) TV = $1,600,000, FV = $834,722.23
D) TV = $0, FV = $256,372.45
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Evaluate the integral.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Evaluate the integral.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Evaluate the integral.
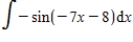
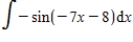

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Decide whether the integral converges. If the integral converges, compute its value.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) diverges
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) diverges

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Evaluate the integral.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) none of these
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Recall that the average of a function on an interval is
Calculate the 9-unit moving average of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
Calculate the 9-unit moving average of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Evaluate the integral.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Evaluate the integral.
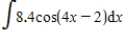
Use the symbol C to write the constant.
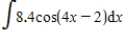
Use the symbol C to write the constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Evaluate the integral.
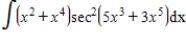
Use the symbol C to write the constant.
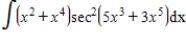
Use the symbol C to write the constant.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Evaluate the integral
A)9.5
B) 9
C) 31.5
D) 22.5
E) 13.5
A)9.5
B) 9
C) 31.5
D) 22.5
E) 13.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Evaluate the integral.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Evaluate the integral.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Evaluate the integral.
A)2
B) 10
C) 1
D) 6
E) 4
A)2
B) 10
C) 1
D) 6
E) 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use geometry to compute the given integral.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) none of these
A)
B)
C)
D)
E) none of these

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Calculate the derivative.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Calculate the derivative.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Calculate the derivative.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Calculate the derivative.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Decide whether each integral converges. If the integral converges, compute its value.
Choose the correct letter for each question.
-converges to
A)
B)
Choose the correct letter for each question.
-converges to
A)
B)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Decide whether each integral converges. If the integral converges, compute its value.
Choose the correct letter for each question.
-diverges
A)
B)
Choose the correct letter for each question.
-diverges
A)
B)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Find the derivative of the function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Model the curve with a cosine function. ![<strong>Model the curve with a cosine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = \frac { 1 } { 6 } and its range is [ - 1,1 ] . </strong> A) f ( x ) = \cos ( 12 x ) B) f ( x ) = \cos \left( \frac { \pi x } { 12 } \right) C) f ( x ) = \cos ( 12 \pi x ) D) f ( x ) = 12 \cos ( \pi x ) E) f ( x ) = \cos \left( \frac { x } { 12 } \right)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f5_c5c8_9431_6d16d29b564a_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is and its range is .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
![<strong>Model the curve with a cosine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = \frac { 1 } { 6 } and its range is [ - 1,1 ] . </strong> A) f ( x ) = \cos ( 12 x ) B) f ( x ) = \cos \left( \frac { \pi x } { 12 } \right) C) f ( x ) = \cos ( 12 \pi x ) D) f ( x ) = 12 \cos ( \pi x ) E) f ( x ) = \cos \left( \frac { x } { 12 } \right)](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f5_c5c8_9431_6d16d29b564a_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is and its range is .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The cost of Dig-It brand snow shovels is given by
Where t is time in years since January 1, 1997. How fast, in dollars per year, is the cost increasing on October 30, 1997
A)$21.85 per year
B) $18.85 per year
C) $9.42 per year
D) $20.85 per year
E) $6.00 per year
Where t is time in years since January 1, 1997. How fast, in dollars per year, is the cost increasing on October 30, 1997
A)$21.85 per year
B) $18.85 per year
C) $9.42 per year
D) $20.85 per year
E) $6.00 per year

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Starting with the identity , choose the right trigonometric identity.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Sketch the curves without any technological help. ;
A)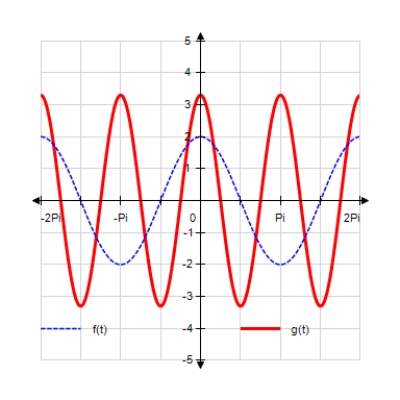
B)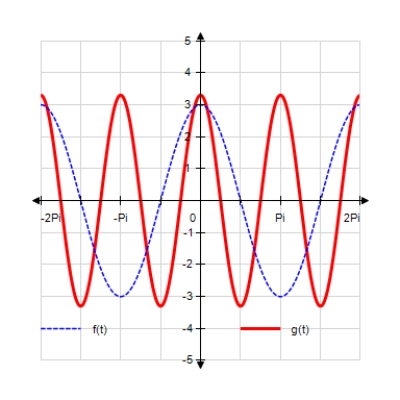
C)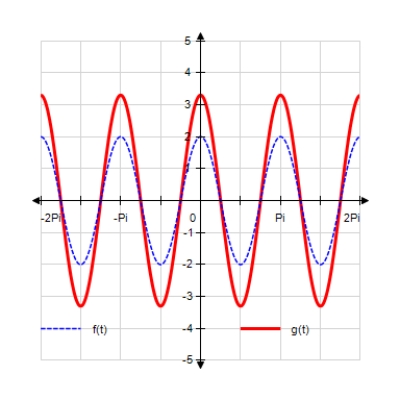
D)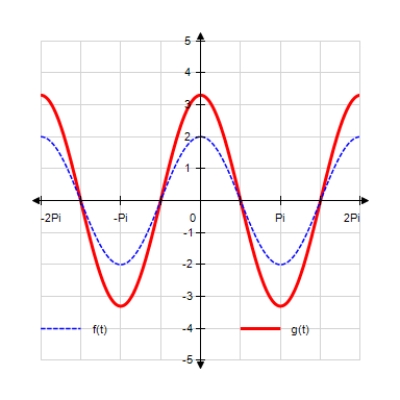
E)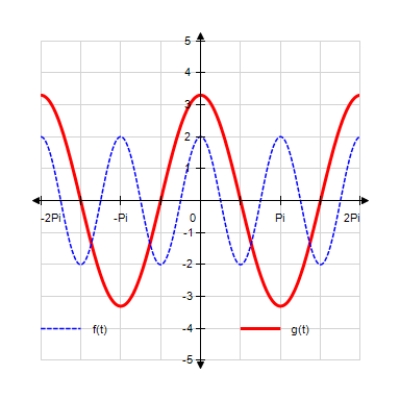
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Sketch the curves without any technological help. ;
A)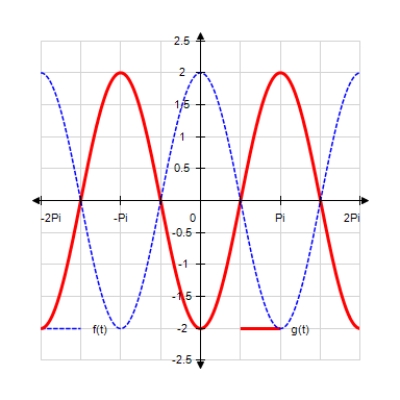
B)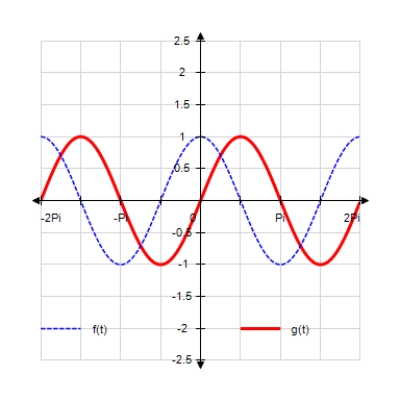
C)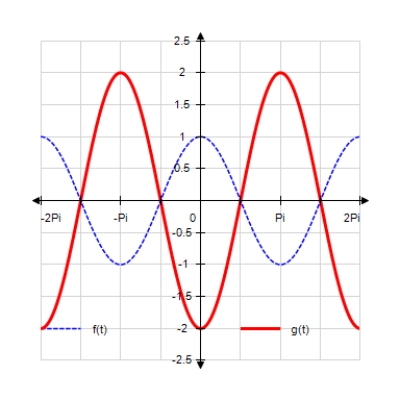
D)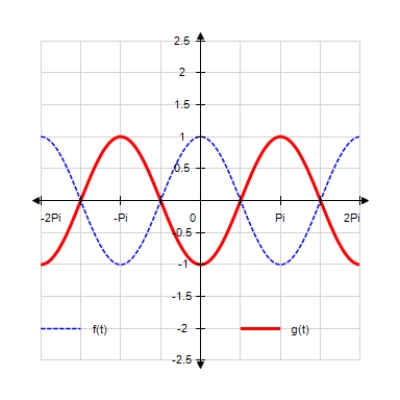
E)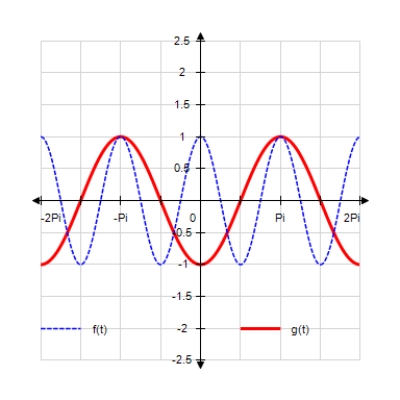
A)

B)

C)

D)

E)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Sales of computers are subject to seasonal fluctuations. Computer City's sales of computers in 1995 and 1996 can be approximated by the function
Where t is time in quarters ( represents the end of the first quarter of 1995) and is computer sales (quarterly revenue) in billions of dollars. Estimate Computer City's maximum and minimum quarterly revenue from computer sales.
A) ,
B) ,
C) ,
D) ,
E) ,
Where t is time in quarters ( represents the end of the first quarter of 1995) and is computer sales (quarterly revenue) in billions of dollars. Estimate Computer City's maximum and minimum quarterly revenue from computer sales.
A) ,
B) ,
C) ,
D) ,
E) ,

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Model the curve with a sine function. ![<strong>Model the curve with a sine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = 0.4 and its range is [ - 3 , - 1 ] . </strong> A) f ( x ) = 2 - \sin x B) f ( x ) = - 2 + 5 \sin x C) f ( x ) = - 2 + \sin ( 5 \pi x ) D) f ( x ) = 2 - \sin ( 5 \pi x ) E) f ( x ) = - 2 + \sin ( \pi x )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f5_2970_9431_5f0c106a54e7_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is and its range is .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
![<strong>Model the curve with a sine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = 0.4 and its range is [ - 3 , - 1 ] . </strong> A) f ( x ) = 2 - \sin x B) f ( x ) = - 2 + 5 \sin x C) f ( x ) = - 2 + \sin ( 5 \pi x ) D) f ( x ) = 2 - \sin ( 5 \pi x ) E) f ( x ) = - 2 + \sin ( \pi x )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f5_2970_9431_5f0c106a54e7_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is and its range is .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Use the addition formulas:
To express in terms of .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
To express in terms of .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Use the formula for to simplify the expression .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Use the addition formulas:
To calculate , given that and .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
To calculate , given that and .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the conversion formula to replace the expression
By a sine function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
By a sine function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Use the conversion formula to replace the expression
By a sine function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
By a sine function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Model the curve with a cosine function. ![<strong>Model the curve with a cosine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = 14 , its range is [ 0,120 ] the graph of the cosine function is shifted upward 60 units and shifted to the right 7 units. </strong> A) f ( x ) = 120 \cos \left( \frac { \pi ( x - 60 ) } { 60 } \right) + 7 B) f ( x ) = 120 \cos \left( \frac { \pi ( x - 60 ) } { 60 } \right) - 7 C) f ( x ) = 60 \cos \left( \frac { \pi ( x + 7 ) } { 7 } \right) + 60 D) f ( x ) = 7 \cos \left( \frac { \pi ( x - 60 ) } { 60 } \right) + 7 E) f ( x ) = 60 \cos \left( \frac { \pi ( x - 7 ) } { 7 } \right) + 60](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f6_6220_9431_732eab67604e_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is , its range is the graph of the cosine function is shifted upward 60 units and shifted to the right 7 units.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
![<strong>Model the curve with a cosine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = 14 , its range is [ 0,120 ] the graph of the cosine function is shifted upward 60 units and shifted to the right 7 units. </strong> A) f ( x ) = 120 \cos \left( \frac { \pi ( x - 60 ) } { 60 } \right) + 7 B) f ( x ) = 120 \cos \left( \frac { \pi ( x - 60 ) } { 60 } \right) - 7 C) f ( x ) = 60 \cos \left( \frac { \pi ( x + 7 ) } { 7 } \right) + 60 D) f ( x ) = 7 \cos \left( \frac { \pi ( x - 60 ) } { 60 } \right) + 7 E) f ( x ) = 60 \cos \left( \frac { \pi ( x - 7 ) } { 7 } \right) + 60](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f6_6220_9431_732eab67604e_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is , its range is the graph of the cosine function is shifted upward 60 units and shifted to the right 7 units.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Use the conversion formula to replace the expression
By a sine function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
By a sine function.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Model the curve with a sine function. ![<strong>Model the curve with a sine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = 32 and its range is [ - 40,0 ] , the graph of the sine function is shifted to the right 7 units. </strong> A) f ( x ) = 20 \sin \left( \frac { \pi ( x + 7 ) } { 16 } \right) + 20 B) f ( x ) = - 20 \sin \left( \frac { \pi ( x + 7 ) } { 16 } \right) + 20 C) f ( x ) = 40 \sin \left( \frac { \pi ( x - 7 ) } { 16 } \right) - 40 D) f ( x ) = 40 \sin \left( \frac { \pi ( x + 7 ) } { 16 } \right) - 40 E) f ( x ) = 20 \sin \left( \frac { \pi ( x - 7 ) } { 16 } \right) - 20](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f5_9eb0_9431_797781ccdfb4_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is and its range is , the graph of the sine function is shifted to the right 7 units.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
![<strong>Model the curve with a sine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = 32 and its range is [ - 40,0 ] , the graph of the sine function is shifted to the right 7 units. </strong> A) f ( x ) = 20 \sin \left( \frac { \pi ( x + 7 ) } { 16 } \right) + 20 B) f ( x ) = - 20 \sin \left( \frac { \pi ( x + 7 ) } { 16 } \right) + 20 C) f ( x ) = 40 \sin \left( \frac { \pi ( x - 7 ) } { 16 } \right) - 40 D) f ( x ) = 40 \sin \left( \frac { \pi ( x + 7 ) } { 16 } \right) - 40 E) f ( x ) = 20 \sin \left( \frac { \pi ( x - 7 ) } { 16 } \right) - 20](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f5_9eb0_9431_797781ccdfb4_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is and its range is , the graph of the sine function is shifted to the right 7 units.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
Model the curve with a sine function.
![<strong>Model the curve with a sine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = \frac { 1 } { 5 } and its range is [ - 2.2,2.2 ] and the graph of the sine function is shifted to the left 0.55 units. </strong> A) f ( x ) = 2.2 \sin ( 10 \pi ( x + 0.55 ) ) B) f ( x ) = 2.2 \sin ( 10 \pi ( x - 0.55 ) ) C) f ( x ) = 2.2 \sin ( 10 \pi x + 0.55 ) D) f ( x ) = 2.2 \sin ( 10 \pi ( 2 x + 0.55 ) ) E) f ( x ) = 4.4 \sin ( 5 \pi ( x + 0.55 ) )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f5_5088_9431_39a24a4c05a7_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is and its range is and the graph of the sine function is shifted to the left 0.55 units.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
![<strong>Model the curve with a sine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = \frac { 1 } { 5 } and its range is [ - 2.2,2.2 ] and the graph of the sine function is shifted to the left 0.55 units. </strong> A) f ( x ) = 2.2 \sin ( 10 \pi ( x + 0.55 ) ) B) f ( x ) = 2.2 \sin ( 10 \pi ( x - 0.55 ) ) C) f ( x ) = 2.2 \sin ( 10 \pi x + 0.55 ) D) f ( x ) = 2.2 \sin ( 10 \pi ( 2 x + 0.55 ) ) E) f ( x ) = 4.4 \sin ( 5 \pi ( x + 0.55 ) )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f5_5088_9431_39a24a4c05a7_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is and its range is and the graph of the sine function is shifted to the left 0.55 units.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Calculate the derivative.
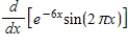
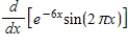

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The depth of water at my favorite surfing spot varies from 8 to 20 feet, depending on the time. Last Sunday high tide occurred at 5:00 A.M. and the next high tide occurred at 6:30 P.M. Use a sine function to model the depth of water as a function of time t in hours since midnight on Sunday morning.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Model the curve with a cosine function. ![<strong>Model the curve with a cosine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = \frac { 1 } { 5 } , its range is [ - 3.3,3.3 ] and the graph of the cosine function is shifted to the right 0.35 units. </strong> A) f ( x ) = 6.6 \cos ( 20 \pi ( 2 x - 0.35 ) ) B) f ( x ) = 3.3 \cos ( 10 ( x - 0.35 ) ) C) f ( x ) = 6.6 \cos ( 20 \pi ( 2 x + 0.35 ) ) D) f ( x ) = 3.3 \cos ( 10 \pi ( x - 0.35 ) ) E) f ( x ) = 3.3 \cos ( 10 \pi ( x + 0.35 ) )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f6_3b08_9431_1b8d47411eb8_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is , its range is and the graph of the cosine function is shifted to the right 0.35 units.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
![<strong>Model the curve with a cosine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = \frac { 1 } { 5 } , its range is [ - 3.3,3.3 ] and the graph of the cosine function is shifted to the right 0.35 units. </strong> A) f ( x ) = 6.6 \cos ( 20 \pi ( 2 x - 0.35 ) ) B) f ( x ) = 3.3 \cos ( 10 ( x - 0.35 ) ) C) f ( x ) = 6.6 \cos ( 20 \pi ( 2 x + 0.35 ) ) D) f ( x ) = 3.3 \cos ( 10 \pi ( x - 0.35 ) ) E) f ( x ) = 3.3 \cos ( 10 \pi ( x + 0.35 ) )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f6_3b08_9431_1b8d47411eb8_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is , its range is and the graph of the cosine function is shifted to the right 0.35 units.
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Model the curve with a cosine function. ![<strong>Model the curve with a cosine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = \frac { 1 } { 3 } and its range is [ - 1,1 ] . </strong> A) f ( x ) = \cos ( 6 x ) B) f ( x ) = \cos ( 6 \pi x ) C) f ( x ) = \cos \left( \frac { x } { 6 } \right) D) f ( x ) = \cos \left( \frac { \pi x } { 6 } \right) E) f ( x ) = 6 \cos ( \pi x )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f5_ece0_9431_cfca3daaba3b_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is and its range is .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
![<strong>Model the curve with a cosine function. Note that the period of the curve is P = \frac { 1 } { 3 } and its range is [ - 1,1 ] . </strong> A) f ( x ) = \cos ( 6 x ) B) f ( x ) = \cos ( 6 \pi x ) C) f ( x ) = \cos \left( \frac { x } { 6 } \right) D) f ( x ) = \cos \left( \frac { \pi x } { 6 } \right) E) f ( x ) = 6 \cos ( \pi x )](https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB6226/11eb0df5_e5f5_ece0_9431_cfca3daaba3b_TB6226_00.jpg)
Note that the period of the curve is and its range is .
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Starting with the identity  and then dividing both sides of the equation by a suitable trigonometric function, derive the trigonometric identity.
and then dividing both sides of the equation by a suitable trigonometric function, derive the trigonometric identity.
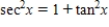
 and then dividing both sides of the equation by a suitable trigonometric function, derive the trigonometric identity.
and then dividing both sides of the equation by a suitable trigonometric function, derive the trigonometric identity.
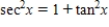

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The uninflated cost of Dugout brand snow shovels currently varies from a high of $30 on January 1 to a low of $6 on July 1 . Assuming this trend were to continue indefinitely, calculate the uninflated cost of Dugout snow shovels as a function of time t in years. (Use a sine function.)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)
A)
B)
C)
D)
E)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
The depth of water 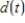 at my favorite surfing spot varies from 5 to 15 feet, depending on the time. Last Sunday high tide occurred at 5:00 A.M. and the next high tide occurred at 6:30 P.M. Use a sine function to model to the depth of water as a function of time t in hours since midnight in Sunday morning.
at my favorite surfing spot varies from 5 to 15 feet, depending on the time. Last Sunday high tide occurred at 5:00 A.M. and the next high tide occurred at 6:30 P.M. Use a sine function to model to the depth of water as a function of time t in hours since midnight in Sunday morning.
 at my favorite surfing spot varies from 5 to 15 feet, depending on the time. Last Sunday high tide occurred at 5:00 A.M. and the next high tide occurred at 6:30 P.M. Use a sine function to model to the depth of water as a function of time t in hours since midnight in Sunday morning.
at my favorite surfing spot varies from 5 to 15 feet, depending on the time. Last Sunday high tide occurred at 5:00 A.M. and the next high tide occurred at 6:30 P.M. Use a sine function to model to the depth of water as a function of time t in hours since midnight in Sunday morning.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Model the curve with a sine function.
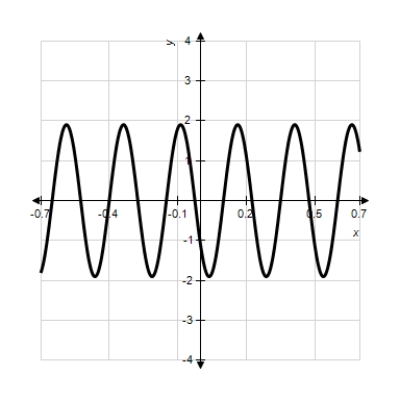
Note that the period of the curve is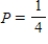 , its range is
, its range is 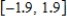 and the graph of the sine function is shifted to the left 0.9 units. Write the model function as a function of x and π.
and the graph of the sine function is shifted to the left 0.9 units. Write the model function as a function of x and π.

Note that the period of the curve is
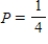 , its range is
, its range is 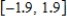 and the graph of the sine function is shifted to the left 0.9 units. Write the model function as a function of x and π.
and the graph of the sine function is shifted to the left 0.9 units. Write the model function as a function of x and π.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Model the curve with a cosine function.
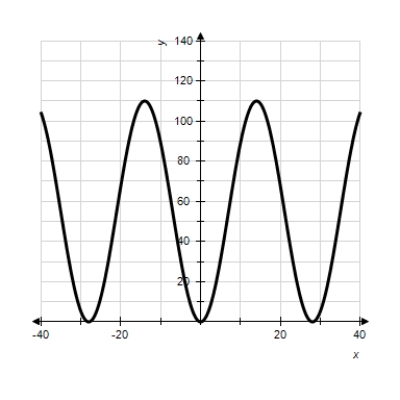
Note that the period of the curve is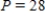 , its range is
, its range is 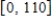 and the graph of the cosine function is shifted upward 55 units and shifted to the right 14 units. Write the model function as a function of x and π.
and the graph of the cosine function is shifted upward 55 units and shifted to the right 14 units. Write the model function as a function of x and π.

Note that the period of the curve is
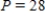 , its range is
, its range is 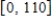 and the graph of the cosine function is shifted upward 55 units and shifted to the right 14 units. Write the model function as a function of x and π.
and the graph of the cosine function is shifted upward 55 units and shifted to the right 14 units. Write the model function as a function of x and π.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Model the curve with a sine function.
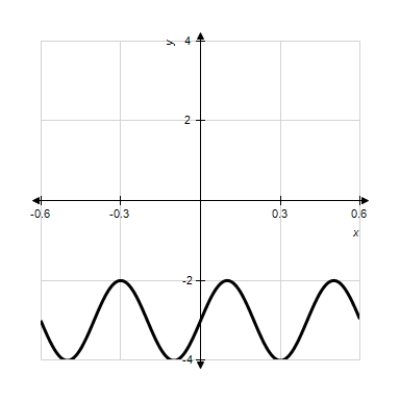
Note that the period of the curve is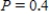 and its range is
and its range is 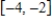 . Write the model function as a function of x and π.
. Write the model function as a function of x and π.

Note that the period of the curve is
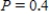 and its range is
and its range is 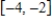 . Write the model function as a function of x and π.
. Write the model function as a function of x and π.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Sales of computers are subject to seasonal fluctuations. Computer City's sales of computers in 1995 and 1996 can be approximated by the function
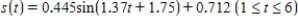
where t is time in quarters (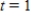 represents the end of the first quarter of 1995) and
represents the end of the first quarter of 1995) and 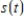 is computer sales (quarterly revenue) in billions of dollars. Estimate Computer City's maximum and minimum quarterly revenue from computer sales.
is computer sales (quarterly revenue) in billions of dollars. Estimate Computer City's maximum and minimum quarterly revenue from computer sales.
Maximum sales __________ billions of dollars
Minimum sales __________ billions of dollars
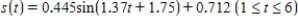
where t is time in quarters (
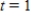 represents the end of the first quarter of 1995) and
represents the end of the first quarter of 1995) and 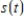 is computer sales (quarterly revenue) in billions of dollars. Estimate Computer City's maximum and minimum quarterly revenue from computer sales.
is computer sales (quarterly revenue) in billions of dollars. Estimate Computer City's maximum and minimum quarterly revenue from computer sales.
Maximum sales __________ billions of dollars
Minimum sales __________ billions of dollars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



