Deck 13: Accounting for Merchandise Inventory
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/87
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 13: Accounting for Merchandise Inventory
1
A method of allocating merchandise cost that is based on the average cost of identical units is known as weighted-average cost or average cost.
True
2
The term "FIFO" relates to the merchandise in inventory at the end of the accounting period, not to the merchandise sold during the period.
False
3
A method of assigning merchandise cost that requires that each item sold and each item remaining in inventory be separately identified with respect to its purchase cost is called last-in, first-out.
False
4
The "FIFO" and "LIFO" inventory costing methods are based on assumed cost flows that are not required to reflect the actual physical movement of merchandise within the company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Under the perpetual system of accounting for inventory, the merchandise inventory account is debited for the cost of all merchandise bought.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The specific identification method of inventory is generally practical only for businesses in which sales volume is relatively low and inventory unit value is relatively high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A method of allocating merchandise costs that assumes the sales in the period were made from the most recently purchased merchandise and the earliest merchandise bought remain in inventory is called the last-in, first-out method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
When cost is greater than market value, it is considered a loss due to holding inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Accurate inventory amounts are not necessary for accounting purposes because an error in inventory will "wash out" over a two-year period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Last-in, first-out costing matches the most current cost of items purchased against the current sales revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The principle of conservatism states that gains should not be anticipated but that all potential losses should be recognized.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Last-in, first-out costing assigns the most recent purchase cost to the ending inventory shown on the balance sheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A widely used method of allocating merchandise cost that assumes the first merchandise bought is the first merchandise sold is called the first-in, first-out method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Errors in the ending inventory have a direct effect on net income for the period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
When prices are rising, net income calculated by using the last-in, first-out method is smaller than the amount determined from using either the first-in, first-out or the weighted-average method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If market value is less than cost, the difference between the cost and market value of inventory is considered a loss due to holding inventory and should be reported on the income statement as an expense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Overstating the ending inventory causes the cost of goods sold to be overstated and net income to be understated.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The loss due to write-down of inventory should be reported on the income statement as an expense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The natural business year is a fiscal year that starts and ends at the time the stock of merchandise is normally at its lowest level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If merchandise is shipped FOB destination, the merchandise is the property of the selling company until it is received by the buying company.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Under the perpetual inventory system, the balance in the merchandise inventory account is merely a record of the most recent physical inventory account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When merchandise is acquired on account and the perpetual system of inventory is used, the journal entry for the purchase would include
A) debiting Purchases and crediting Accounts Payable.
B) debiting Accounts Payable and crediting Merchandise Inventory.
C) debiting Merchandise Inventory and crediting Accounts Payable.
D) debiting Accounts Payable and crediting Purchases.
A) debiting Purchases and crediting Accounts Payable.
B) debiting Accounts Payable and crediting Merchandise Inventory.
C) debiting Merchandise Inventory and crediting Accounts Payable.
D) debiting Accounts Payable and crediting Purchases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Under the periodic inventory system, no entries are made to the merchandise inventory or cost of goods sold accounts during the year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
When perpetual inventory records are kept, the merchandise inventory account in the general ledger is usually a control account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The gross profit (inventory valuation) method requires keeping records of the selling prices of merchandise purchased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Under conditions of rising prices, the FIFO inventory method provides the highest gross profit because the most recent purchase costs are matched against sales revenue.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
If a difference is found between the physical count and the amount in the perpetual inventory records, the records must be corrected by an appropriate adjusting entry.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The term "LIFO" relates to the merchandise in inventory at the end of the accounting period, not to the merchandise sold during the period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Under the periodic system of accounting for inventory, the purchases account is debited for the cost of all merchandise purchased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In the perpetual inventory system, no year-end adjusting entry is necessary, as long as the physical inventory agrees with the amount reported in the merchandise inventory account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The increasing use of computers and optical scanning devices at the point-of-sale probably will cause more businesses to switch from periodic to perpetual inventories.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The gross profit (inventory valuation) method is appropriate if a firm's normal gross profit on sales has been relatively stable over time and for estimating the cost of inventory that was destroyed by casualty.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Under the periodic inventory system, the merchandise inventory and the cost of goods sold for the current periods are determined
A) when a physical inventory is taken.
B) on a daily basis.
C) on a quarterly basis.
D) once a year.
A) when a physical inventory is taken.
B) on a daily basis.
C) on a quarterly basis.
D) once a year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Under the retail (inventory valuation) method, the amount of sales during the period is reduced by the normal profit percentage to determine the estimated cost of merchandise sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Costs of goods sold may include all of the following EXCEPT
A) insurance.
B) shipping costs.
C) manufacturing costs.
D) management salaries.
A) insurance.
B) shipping costs.
C) manufacturing costs.
D) management salaries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The retail method of inventory is preferred by businesses such as department and clothing stores because they compute inventory values at wholesale prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The gross profit method estimates the ending inventory and cost of goods sold by using the firm's normal gross profit as a percentage of net sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The amount by which cost exceeds market value is considered a loss due to holding inventory and normally is charged to an account such as Loss on Write-Down of Inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
When each unit of inventory can be specifically identified, the specific identification method can be used.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Firms should report a loss due to write-down of inventory in the cost of goods sold account on the income statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The inventory system that uses the merchandise inventory account as an active account is called
A) perpetual.
B) LIFO.
C) FIFO.
D) periodic.
A) perpetual.
B) LIFO.
C) FIFO.
D) periodic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The merchandise costing method that matches the most current cost of items purchased against the current sales revenue is called the
A) last-in, first-out method.
B) first-in, first-out method.
C) specific identification method.
D) weighted-average method.
A) last-in, first-out method.
B) first-in, first-out method.
C) specific identification method.
D) weighted-average method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
When a fiscal year that starts and ends at the time the stock of merchandise is normally at its lowest level is selected, it is known as a(n)
A) natural business year.
B) calendar year.
C) base year.
D) accounting cycle.
A) natural business year.
B) calendar year.
C) base year.
D) accounting cycle.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Lower-of-cost-or-market (for tax purposes) may be used with all of the following merchandise costing methods EXCEPT
A) the last-in, first-out method.
B) the first-in, first-out method.
C) the weighted-average method.
D) the specific identification method.
A) the last-in, first-out method.
B) the first-in, first-out method.
C) the weighted-average method.
D) the specific identification method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The following data applies to a particular item of merchandise: ? Of the 1,600 units sold during the period, 300 were from the beginning inventory; 500 from the first purchase; 600 from the second purchase; and 200 from the last purchase. Using the weighted-average costing method and rounding the average unit cost to the nearest whole cent, the cost of goods sold would be
A) $11,140.
B) $11,130.
C) $8,480.
D) $8,410.
A) $11,140.
B) $11,130.
C) $8,480.
D) $8,410.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The following data applies to a particular item of merchandise: ? Of the 1,600 units sold during the period, 300 were from the beginning inventory; 500 from the first purchase; 600 from the second purchase; and 200 from the last purchase. Using the last-in, first-out costing method, the value of the inventory on hand at the end of the period would be
A) $2,730.
B) $2,750.
C) $2,570.
D) $8,570.
A) $2,730.
B) $2,750.
C) $2,570.
D) $8,570.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A method of allocating merchandise cost requiring each item sold and each item remaining in inventory to be separately identified with respect to its purchase cost is called the
A) last-in, first-out method.
B) first-in, first-out method.
C) specific identification method.
D) weighted-average method.
A) last-in, first-out method.
B) first-in, first-out method.
C) specific identification method.
D) weighted-average method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When merchandise is sold and the perpetual system of inventory is used, the journal entry for a sale would include
A) debiting Accounts Receivable and crediting Sales.
B) debiting Accounts Receivable and crediting Merchandise Inventory.
C) debiting Accounts Receivable and crediting Cost of Goods Sold.
D) debiting Cost of Goods Sold and crediting Sales.
A) debiting Accounts Receivable and crediting Sales.
B) debiting Accounts Receivable and crediting Merchandise Inventory.
C) debiting Accounts Receivable and crediting Cost of Goods Sold.
D) debiting Cost of Goods Sold and crediting Sales.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The following data applies to a particular item of merchandise: ? Of the 1,600 units sold during the period, 300 were from the beginning inventory; 500 from the first purchase; 600 from the second purchase; and 200 from the last purchase. Using the first-in, first-out costing method, the value of the inventory on hand at the end of the period would be
A) $2,730.
B) $2,750.
C) $2,570.
D) $8,390.
A) $2,730.
B) $2,750.
C) $2,570.
D) $8,390.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A method of allocating merchandise cost that assigns the most recent purchased costs to the ending inventory shown on the balance sheet is called the
A) last-in, first-out method.
B) first-in, first-out method.
C) specific identification method.
D) weighted-average method.
A) last-in, first-out method.
B) first-in, first-out method.
C) specific identification method.
D) weighted-average method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A method of allocating merchandise cost that assumes the sales in the period were made from the recently purchased merchandise and its earliest merchandise bought remains in the inventory is called the
A) last-in, first-out method.
B) first-in, first-out method.
C) specific identification method.
D) weighted-average method.
A) last-in, first-out method.
B) first-in, first-out method.
C) specific identification method.
D) weighted-average method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A method of allocating merchandise cost that assumes the first merchandise bought was the first merchandise sold is called the
A) last-in, first-out method.
B) first-in, first-out method.
C) specific identification method.
D) average cost method.
A) last-in, first-out method.
B) first-in, first-out method.
C) specific identification method.
D) average cost method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
An error in the reported inventory will cause errors in all of the following EXCEPT
A) the balance sheet.
B) the statement of owner's equity.
C) the following year's financial statements.
D) the cash account.
A) the balance sheet.
B) the statement of owner's equity.
C) the following year's financial statements.
D) the cash account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The following data applies to a particular item of merchandise: ? Of the 1,600 units sold during the period, 300 were from the beginning inventory; 500 from the first purchase; 600 from the second purchase; and 200 from the last purchase. Using the specific identification costing method, the amount of the cost of goods sold would be
A) $2,730.
B) $8,410.
C) $11,140.
D) $13,870.
A) $2,730.
B) $8,410.
C) $11,140.
D) $13,870.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A method of allocating merchandise cost that is based on the average cost of identical units is called the
A) last-in, first-out method.
B) first-in, first-out method.
C) specific identification method.
D) weighted-average method.
A) last-in, first-out method.
B) first-in, first-out method.
C) specific identification method.
D) weighted-average method.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The following data applies to a particular item of merchandise: ? Of the 1,600 units sold during the period, 300 were from the beginning inventory; 500 from the first purchase; 600 from the second purchase; and 200 from the last purchase. Using the last-in, first-out costing method, the cost of goods sold would be
A) $8,390.
B) $8,410.
C) $2,530.
D) $8,570.
A) $8,390.
B) $8,410.
C) $2,530.
D) $8,570.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The inventory system whereby the merchandise inventory account balance is merely a record of the most recent physical inventory count is called
A) perpetual.
B) LIFO.
C) FIFO.
D) periodic.
A) perpetual.
B) LIFO.
C) FIFO.
D) periodic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
The following data applies to a particular item of merchandise: ? Of the 1,600 units sold during the period, 300 were from the beginning inventory; 500 from the first purchase; 600 from the second purchase; and 200 from the last purchase. Using the weighted-average costing method and rounding the average unit cost to the nearest whole cent, the value of the inventory on hand at the end of the period would be
A) $2,650.
B) $2,750.
C) $2,730.
D) $2,530.
A) $2,650.
B) $2,750.
C) $2,730.
D) $2,530.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The following data applies to a particular item of merchandise: ? Of the 1,600 units sold during the period, 300 were from the beginning inventory; 500 from the first purchase; 600 from the second purchase; and 200 from the last purchase. Using the specific identification costing method, the value of inventory on hand at the end of the period would be
A) $2,730.
B) $2,570.
C) $8,390.
D) $8,410.
A) $2,730.
B) $2,570.
C) $8,390.
D) $8,410.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The following data applies to a particular item of merchandise: ? Of the 1,600 units sold during the period, 300 were from the beginning inventory; 500 from the first purchase; 600 from the second purchase; and 200 from the last purchase. Using the first-in, first-out costing method, the cost of goods sold would be
A) $2,750.
B) $8,390.
C) $8,410.
D) $8,570.
A) $2,750.
B) $8,390.
C) $8,410.
D) $8,570.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
Refer to the following data:
Net sales, first month
$13,000
Normal gross profit as a percentage of sales
45%
Inventory, start of period
$8,000
Net purchases, first month
$7,000
Using the gross profit method of inventory estimation, the amount of normal gross profit would be
A) $5,850.
B) $3,600.
C) $6,750.
D) $15,000.
Net sales, first month
$13,000
Normal gross profit as a percentage of sales
45%
Inventory, start of period
$8,000
Net purchases, first month
$7,000
Using the gross profit method of inventory estimation, the amount of normal gross profit would be
A) $5,850.
B) $3,600.
C) $6,750.
D) $15,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Match the terms with the definitions.a.average cost
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
Under this system, cost of goods sold and the amount of merchandise inventory on hand are updated when merchandise is bought and sold.
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
Under this system, cost of goods sold and the amount of merchandise inventory on hand are updated when merchandise is bought and sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Match the terms with the definitions.a.average cost
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
The principle that states that a business should use the same accounting methods from period to period. This improves the comparability of the financial statements over time.
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
The principle that states that a business should use the same accounting methods from period to period. This improves the comparability of the financial statements over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Over the past several years, Landmark Supplies has averaged a gross profit of 34%. At the end of 20--, the income statement of the company included the information shown below: 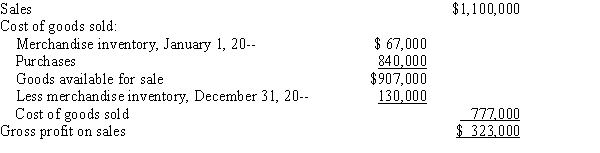
Investigation revealed that employees of the company had not taken an actual physical count of the inventory on December 31, 20--. Instead, they had merely estimated the inventory.
Required:
Under the gross profit method of inventory estimation, determine the following items to check the accuracy of the employees' estimates.
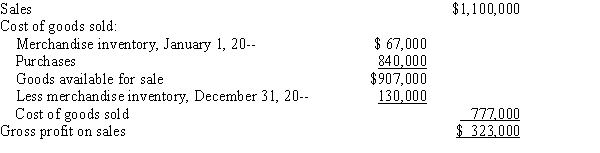
Investigation revealed that employees of the company had not taken an actual physical count of the inventory on December 31, 20--. Instead, they had merely estimated the inventory.
Required:
Under the gross profit method of inventory estimation, determine the following items to check the accuracy of the employees' estimates.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Smart Tech's beginning inventory and purchases for the month of August were as follows: 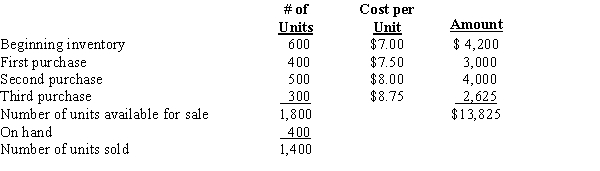
Required:
Calculate the total amount to be assigned to cost of goods sold and ending inventory for August 31, using each of the following methods.
a.
First-in, first-out (FIFO)
b.
Last-in, first-out (LIFO)
c.
Weighted-average cost (round the unit price)
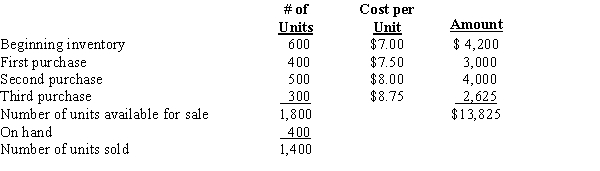
Required:
Calculate the total amount to be assigned to cost of goods sold and ending inventory for August 31, using each of the following methods.
a.
First-in, first-out (FIFO)
b.
Last-in, first-out (LIFO)
c.
Weighted-average cost (round the unit price)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The April 1 inventory of Inotech Inc. had a cost of $35,505 and had a retail value of $79,000. During April, merchandise was purchased for $125,000 and marked to sell for $262,500. April sales totaled $201,000.
Required:
Calculate the following items using the retail method of inventory estimation.
Required:
Calculate the following items using the retail method of inventory estimation.


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Refer to the following data: ? Using the gross profit method of inventory estimation, the cost of goods sold would be
A) $5,850.
B) $7,150
C) $7,850
D) $15,000.
A) $5,850.
B) $7,150
C) $7,850
D) $15,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Assume the beginning inventory as of January 1 consisted of 500 units that were purchased for $8.25 each. During the month, three new purchases were made. The first purchase consisted of 700 units costing $8.50 each, the second purchase had 800 units costing $9.00 each, and the third purchase had 600 units costing $9.50 each. At the end of the month, ending inventory shows 700 units. Compute the cost of goods sold and the ending inventory for the company using each of the following methods. Also determine the gross margin if the total sales revenue is $43,000.
a.
Specific identification: Of the units sold, 300 were from the beginning inventory, 600 from the first purchase, 700 from the second purchase, and 300 from the third purchase.
b.
First-in, first-out (FIFO)
c.
Weighted-average (round the unit price)
d.
Last-in, first-out (LIFO)
a.
Specific identification: Of the units sold, 300 were from the beginning inventory, 600 from the first purchase, 700 from the second purchase, and 300 from the third purchase.
b.
First-in, first-out (FIFO)
c.
Weighted-average (round the unit price)
d.
Last-in, first-out (LIFO)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Assume the market price per unit (cost to replace) of the R. &. K. Company's inventory on December 31, was $16. Calculate the total amount to be assigned to the ending inventory on December 31, under each of the following methods:
a.
FIFO lower-of-cost-or-market
b.
Weighted-average lower-of-cost-or-market
a.
FIFO lower-of-cost-or-market
b.
Weighted-average lower-of-cost-or-market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Match the terms with the definitions.a.average cost
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
A method of estimating inventory in which a business's normal gross profit percentage is used to estimate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory.
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
A method of estimating inventory in which a business's normal gross profit percentage is used to estimate the cost of goods sold and ending inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Match the terms with the definitions.a.average cost
b.weighted-average method
c.consignee
d.consigned goods
e.specific identification method
f.retail method
g.cost
h.physical inventory
i.periodic inventory system
j.in transit
k.inventory sheet
l.natural business year
m.lower-of-cost-or-market method
An inventory valuation method under which inventory is valued at cost or replacement cost, whichever is lower.
b.weighted-average method
c.consignee
d.consigned goods
e.specific identification method
f.retail method
g.cost
h.physical inventory
i.periodic inventory system
j.in transit
k.inventory sheet
l.natural business year
m.lower-of-cost-or-market method
An inventory valuation method under which inventory is valued at cost or replacement cost, whichever is lower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Match the terms with the definitions.a.average cost
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
The accounting practice that states that we should never anticipate gains, but always anticipate and account for losses.
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
The accounting practice that states that we should never anticipate gains, but always anticipate and account for losses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Match the terms with the definitions.a.average cost
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
The owner of the merchandise that is held by another business.
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
The owner of the merchandise that is held by another business.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Assigning of the lower-of-cost-or-market to the items that comprise the inventory of merchandise at the end of the account period is an application of which of the following concepts?
A) materiality
B) conservatism
C) reliability
D) full disclosure
A) materiality
B) conservatism
C) reliability
D) full disclosure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Match the terms with the definitions.a.average cost
b.weighted-average method
c.consignee
d.consigned goods
e.specific identification method
f.retail method
g.cost
h.physical inventory
i.periodic inventory system
j.in transit
k.inventory sheet
l.natural business year
m.lower-of-cost-or-market method
The company holding the merchandise of another business to be sold.
b.weighted-average method
c.consignee
d.consigned goods
e.specific identification method
f.retail method
g.cost
h.physical inventory
i.periodic inventory system
j.in transit
k.inventory sheet
l.natural business year
m.lower-of-cost-or-market method
The company holding the merchandise of another business to be sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Delmar Industries uses the perpetual inventory method in accounting for inventory. Prepare the necessary adjusting entry for each of the following independent cases using the cost of goods sold account. 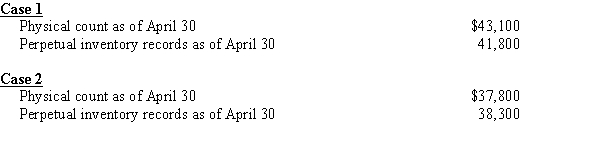

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Match the terms with the definitions.a.average cost
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
The cost to replace inventory at the prevailing purchase price.
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
The cost to replace inventory at the prevailing purchase price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Match the terms with the definitions.a.average cost
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
A method of allocating merchandise cost which assumes that the first goods purchased were the first goods sold and, therefore, that the latest goods purchased remain in inventory.
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
A method of allocating merchandise cost which assumes that the first goods purchased were the first goods sold and, therefore, that the latest goods purchased remain in inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Match the terms with the definitions.a.average cost
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
A method of allocating merchandise cost which assumes that the sales in the period were made from the most recently purchased goods. Therefore, the earliest goods purchased remain in inventory.
b.conservatism
c.perpetual inventory system
d.market value
e.consignor
f.consistency
g.cost
h.first-in, first-out method
i.gross profit method
j.last-in, first-out method
k.inventory sheet
A method of allocating merchandise cost which assumes that the sales in the period were made from the most recently purchased goods. Therefore, the earliest goods purchased remain in inventory.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Match the terms with the definitions.a.average cost
b.weighted-average method
c.consignee
d.consigned goods
e.specific identification method
f.retail method
g.cost
h.physical inventory
i.periodic inventory system
j.in transit
k.inventory sheet
l.natural business year
m.lower-of-cost-or-market method
A fiscal year that starts and ends at the time the stock of goods is normally at its lowest level.
b.weighted-average method
c.consignee
d.consigned goods
e.specific identification method
f.retail method
g.cost
h.physical inventory
i.periodic inventory system
j.in transit
k.inventory sheet
l.natural business year
m.lower-of-cost-or-market method
A fiscal year that starts and ends at the time the stock of goods is normally at its lowest level.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 87 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



