Deck 22: Corporations: Bonds
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/98
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Corporations: Bonds
1
A debenture bond is a common type of secured bond.
False
2
Bonds secured by a mortgage on corporate property are called guaranteed bonds.
False
3
Bonds issued in a series so that a specified amount of principal matures each year are called term bonds.
False
4
Usually, there is either a gain or a loss involved in the redemption of bonds before their maturity date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A bond is an obligation of the shareholders.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Bonds issued that mature at regular intervals are called serial bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
While bonds and notes are both formal written promises to pay an amount of money at a specified date, notes generally tend to be for much smaller amounts and for a shorter period of time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Premium on Bonds Payable should be classified as a contra-liability account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Bonds Sinking Fund is reported as a liability on the corporation's balance sheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Bondholders are the owners of the corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A discount amortization effects a gradual reduction of the bonds payable account to zero over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If the stated interest rate on bonds is less than the current market rate, the bonds will sell at a discount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Loss on Redemption generally is reported as other expense near the bottom of the income statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The straight-line method of amortizing a bond premium or discount provides for amortizing an equal amount each time period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Bonds payable less the discount on bonds payable is called the carrying value of the bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Gain on Redemption is reported as a component of other income on the corporation's income statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The process of adjusting the bond interest expense account for any premium or discount is called amortization of the premium or discount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
When bonds are issued at a discount, both bonds payable on the balance sheet and interest expense on the income statement are affected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A discount amortization does not affect the amount of cash paid for bond interest.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The Discount on Bonds Payable balance is subtracted from Bonds Payable on the income statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When bonds are redeemed at a loss, the journal entry would require a credit to Extraordinary Loss on Early Extinguishment of Debt.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
If the interest rate on bonds is lower than the current market rate, the bonds will sell at a premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Convertible bonds give the issuing corporation the option of calling for redemption at a stated price before maturity date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The interest rate specified in a bond contract is known as the market rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If bonds that originally were sold at a premium are redeemed, the calculation of the gain or loss must take into account the unamortized premium through the date of redemption.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If the interest rate on bonds is the same as the current market rate, the bonds will sell for their face value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Bonds issued with a provision that they may be called for redemption before the date of maturity are called convertible bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If a corporation issues term bonds, each bond will have the same maturity date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Convertible bonds are
A) bonds that all have the same maturity date.
B) bonds issued in a series so that a specified amount of the bonds matures each year.
C) bonds that give the issuing corporation the option of calling the bonds for redemption before the maturity date.
D) bonds that give the holder the option of exchanging the bonds for capital stock of the corporation.
A) bonds that all have the same maturity date.
B) bonds issued in a series so that a specified amount of the bonds matures each year.
C) bonds that give the issuing corporation the option of calling the bonds for redemption before the maturity date.
D) bonds that give the holder the option of exchanging the bonds for capital stock of the corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
An entry to record the sale and issuance of bonds at a discount will include a credit to Discount on Bonds Payable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Names and addresses of owners of coupon bonds are recorded and kept current in the corporate records.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
If bonds that originally were sold at face value are redeemed for less than face value, a gain results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The sum of bonds payable and premium on bonds payable is called the carrying value of the bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The accumulation and investment of money over a period of years that provides the amount necessary for the redemption of a bond issued at its maturity is called a sinking fund.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A $100,000 bond issue sold at 103 has a market price of $100,300.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Debenture bonds are backed by specific assets of the corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If cash is paid to a trustee who administers a sinking fund, the corporation would credit the Bond Sinking Fund for the amount of cash paid.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
To determine whether a bond will sell at a price equal to, greater than, or less than face value, compare the stated and market interest rates.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Premium on Bonds Payable should be classified as an adjunct-liability account.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Bonds Payable is reported as a long-term liability on the corporation's balance sheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Bonds that are backed solely by specific secured assets are called
A) mortgage bonds.
B) guaranteed bonds.
C) collateral bonds.
D) debenture bonds.
A) mortgage bonds.
B) guaranteed bonds.
C) collateral bonds.
D) debenture bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Bonds issued at the same time so that they all have the same maturity date are called
A) term bonds.
B) serial bonds.
C) convertible bonds.
D) callable bonds.
A) term bonds.
B) serial bonds.
C) convertible bonds.
D) callable bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Usually, there is a gain or loss involved when bonds are redeemed before maturity. The gain or loss is the difference between
A) the amount paid to redeem the bonds and the carrying value of the bonds.
B) the maturity value of the bonds and the market value of the bonds.
C) the carrying value of the bonds and the face value of the bonds.
D) the maturity value of the bonds and the carrying value of the bonds.
A) the amount paid to redeem the bonds and the carrying value of the bonds.
B) the maturity value of the bonds and the market value of the bonds.
C) the carrying value of the bonds and the face value of the bonds.
D) the maturity value of the bonds and the carrying value of the bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
If the rate of interest on bonds is lower that the current market rate, the bonds will sell at
A) a discount.
B) a premium.
C) face value.
D) maturity value.
A) a discount.
B) a premium.
C) face value.
D) maturity value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Bonds issued giving the holder the option of exchanging the bonds for capital stock of the corporation are called
A) term bonds.
B) convertible bonds.
C) capital stock bonds.
D) callable bonds.
A) term bonds.
B) convertible bonds.
C) capital stock bonds.
D) callable bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
If the interest rate on bonds is higher than the current market rate, they will sell at
A) a discount.
B) a premium.
C) face value.
D) maturity value.
A) a discount.
B) a premium.
C) face value.
D) maturity value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Bond Interest Payable is reported as a(n)
A) current liability on the income statement.
B) current liability on the balance sheet.
C) adjunct-liability on the balance sheet.
D) contra-liability on the income statement.
A) current liability on the income statement.
B) current liability on the balance sheet.
C) adjunct-liability on the balance sheet.
D) contra-liability on the income statement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
When selling bonds at a premium, the premium received effectively
A) reduces the cost of borrowing.
B) increases the cost of borrowing.
C) does not affect the cost of borrowing.
D) reduces the amount of cash received when bonds are sold.
A) reduces the cost of borrowing.
B) increases the cost of borrowing.
C) does not affect the cost of borrowing.
D) reduces the amount of cash received when bonds are sold.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If bonds were originally sold at face value and the corporation pays more than the face amount when the bonds are redeemed, there is a
A) loss.
B) gain.
C) premium.
D) discount.
A) loss.
B) gain.
C) premium.
D) discount.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The sale and issuance of $400,000, 8% bonds with a market rate of 8% would involve debiting Cash for
A) $32,000.
B) $368,000.
C) $400,000.
D) $432,000.
A) $32,000.
B) $368,000.
C) $400,000.
D) $432,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If bonds were being issued with a stated rate of 8% and the market rate is 9%, the bonds would most likely sell at which of the following?
A) 108
B) 100
C) 95
D) 80
A) 108
B) 100
C) 95
D) 80

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
The premium on bonds payable account would be classified as a(n)
A) current liability.
B) adjunct-liability.
C) contra-liability.
D) noncurrent liability.
A) current liability.
B) adjunct-liability.
C) contra-liability.
D) noncurrent liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Bondholders have which of the following relationships with a corporation?
A) They are creditors.
B) They are owners.
C) They become members of the board.
D) They are silent managers.
A) They are creditors.
B) They are owners.
C) They become members of the board.
D) They are silent managers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The discount on bonds payable account would be classified as a(n)
A) current liability.
B) adjunct-liability.
C) contra-liability.
D) noncurrent liability.
A) current liability.
B) adjunct-liability.
C) contra-liability.
D) noncurrent liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Bonds secured by a mortgage on corporate property are called
A) mortgage bonds.
B) property bonds.
C) investment bonds.
D) adjustment bonds.
A) mortgage bonds.
B) property bonds.
C) investment bonds.
D) adjustment bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When the selling price of a bond is stated at 100, it means that the bonds are selling
A) at a premium.
B) at a discount.
C) below par value.
D) at face value.
A) at a premium.
B) at a discount.
C) below par value.
D) at face value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Two of the main factors in determining the price at which bonds will sell are
A) the contract rate and the coupon rate.
B) the contract rate and the stated rate.
C) the market rate and the discount rate.
D) the stated rate and the market rate.
A) the contract rate and the coupon rate.
B) the contract rate and the stated rate.
C) the market rate and the discount rate.
D) the stated rate and the market rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Bonds issued in a series so that a specified amount of the bond matures each year are called
A) term bonds.
B) serial bonds.
C) convertible bonds.
D) callable bonds.
A) term bonds.
B) serial bonds.
C) convertible bonds.
D) callable bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
The bonds payable account would be classified as a(n)
A) current liability.
B) adjunct-liability.
C) contra-liability.
D) long-term liability.
A) current liability.
B) adjunct-liability.
C) contra-liability.
D) long-term liability.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Bonds issued with a provision that they may be called for redemption before the date of maturity are known as
A) convertible bonds.
B) term bonds.
C) debenture bonds.
D) callable bonds.
A) convertible bonds.
B) term bonds.
C) debenture bonds.
D) callable bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
A ten-year bond issue of $400,000, interest rate of 9% paid semiannually, is sold for $440,000 when the market rate is 8%. The bonds were not sold between interest dates and the straight-line amortization method is used. The entry to record the first interest payment would include
A) a debit to Cash of $18,000.
B) a debit to Bond Interest Payable of $18,000.
C) a debit to Premium on Bonds Payable of $2,000.
D) a credit to Bond Interest Expense of $16,000.
A) a debit to Cash of $18,000.
B) a debit to Bond Interest Payable of $18,000.
C) a debit to Premium on Bonds Payable of $2,000.
D) a credit to Bond Interest Expense of $16,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Gia Company had the following bond issue:
Date of issue/sale: April 1, 20-A
Face value: $200,000
Sale price of bonds: 99
Life of bonds: 10 years
Stated interest rate: 6% a year payable semiannually on September 30 and March 31
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on April 1, 20-A.
b.
The interest payment and premium amortization for first six months.
c.
The redemption of $50,000 worth of bonds on April 1, 20-E, at 102.
Date of issue/sale: April 1, 20-A
Face value: $200,000
Sale price of bonds: 99
Life of bonds: 10 years
Stated interest rate: 6% a year payable semiannually on September 30 and March 31
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on April 1, 20-A.
b.
The interest payment and premium amortization for first six months.
c.
The redemption of $50,000 worth of bonds on April 1, 20-E, at 102.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Fireside, Inc. had the following bond issue: 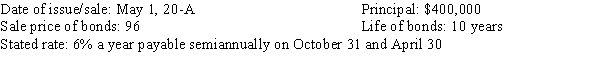
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on May 1, 20-A.
b.
The first interest payment for 20-A.
c.
The adjusting entry for December 31, 20-A.
d.
The reversing entry for January 1, 20-B.
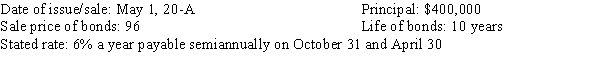
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on May 1, 20-A.
b.
The first interest payment for 20-A.
c.
The adjusting entry for December 31, 20-A.
d.
The reversing entry for January 1, 20-B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Baradzi Corporation had the following bond issue: 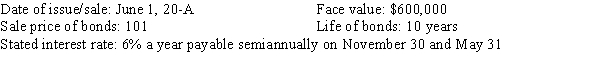
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on June 1, 20-A.
b.
The interest payment and premium amortization on the bonds for November 30, 20-A.
c.
The year-end adjusting entry for interest expense and premium amortization, 20-A.
d.
The reversing entry for January 1, 20-B.
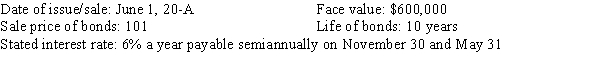
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on June 1, 20-A.
b.
The interest payment and premium amortization on the bonds for November 30, 20-A.
c.
The year-end adjusting entry for interest expense and premium amortization, 20-A.
d.
The reversing entry for January 1, 20-B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A $200,000, 8% bond issue was sold at face value and later redeemed at 104% of face value. The corporation would have a
A) loss of $8,000.
B) gain of $8,000.
C) loss of $20,000.
D) gain of $20,000.
A) loss of $8,000.
B) gain of $8,000.
C) loss of $20,000.
D) gain of $20,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Omni Video Corporation had the following bond issue: 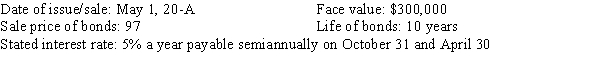
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on May 1, 20-A.
b.
The interest payment and discount amortization on the bonds for October 31, 20-A.
c.
The redemption of $100,000 worth of bonds on November 1, 20-F, at 98.
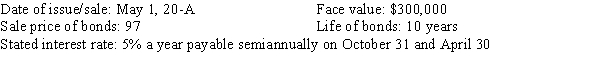
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on May 1, 20-A.
b.
The interest payment and discount amortization on the bonds for October 31, 20-A.
c.
The redemption of $100,000 worth of bonds on November 1, 20-F, at 98.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Roof Top Corporation had the following bond issue:
Date of issue/sale: May 1, 20-A
Principal: $400,000
Sale price of bonds: 98
Life of bonds: 10 years
Stated rate: 6% a year payable semiannually on October 31 and April 30
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on May 1, 20-A.
b.
The first interest payment.
c.
The redemption of $100,000 worth of bonds on May 1, 20-D, at 99.
Date of issue/sale: May 1, 20-A
Principal: $400,000
Sale price of bonds: 98
Life of bonds: 10 years
Stated rate: 6% a year payable semiannually on October 31 and April 30
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on May 1, 20-A.
b.
The first interest payment.
c.
The redemption of $100,000 worth of bonds on May 1, 20-D, at 99.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A ten-year bond issue of $400,000, interest rate of 9% paid semiannually, is sold for $440,000 when the market rate is 8%. The bonds were not sold between interest dates and the straight-line amortization method is used. The bond interest expense for the first interest payment would be
A) $2,000.
B) $16,000.
C) $18,000.
D) $32,000.
A) $2,000.
B) $16,000.
C) $18,000.
D) $32,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Match the terms with the definitions.a.amortization
b.bond
c.bond indenture
d.bond sinking fund
e.callable bonds
f.carrying value
g.convertible bonds
h.coupon bonds
i.debenture bonds
j.discount
k.face value
l.market rate
m.mortgage bonds
n.premium
o.principal
p.registered bonds
q.secured bonds
r.serial bonds
s.stated rate
t.term bonds
The difference between the face value and the price of a bond when the current market interest rate is less than the stated rate of that bond.
b.bond
c.bond indenture
d.bond sinking fund
e.callable bonds
f.carrying value
g.convertible bonds
h.coupon bonds
i.debenture bonds
j.discount
k.face value
l.market rate
m.mortgage bonds
n.premium
o.principal
p.registered bonds
q.secured bonds
r.serial bonds
s.stated rate
t.term bonds
The difference between the face value and the price of a bond when the current market interest rate is less than the stated rate of that bond.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Clearview Corporation had the following bond issue:
Date of issue/sale: March 1, 20-A
Face value: $700,000
Sale price of bonds: 103
Life of bonds: 10 years
Stated rate: 6% a year payable semiannually on August 31 and February 28
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on March 1, 20-A.
b.
The interest payment and premium amortization on the bonds for the first six months.
c.
The year-end adjusting entry for interest and premium amortization.
d.
The reversing entry for January 1, 20-B.
Date of issue/sale: March 1, 20-A
Face value: $700,000
Sale price of bonds: 103
Life of bonds: 10 years
Stated rate: 6% a year payable semiannually on August 31 and February 28
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on March 1, 20-A.
b.
The interest payment and premium amortization on the bonds for the first six months.
c.
The year-end adjusting entry for interest and premium amortization.
d.
The reversing entry for January 1, 20-B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Perez Corporation pays $47,000 into a bond sinking fund each year for the future redemption of bonds. During the first year, the fund earns $3,825. When the bonds mature, there is a balance in the sinking fund of $417,000, of which $400,000 is used to redeem the bonds.
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The initial sinking fund deposit.
b.
The first year's interest for the sinking fund.
c.
The redemption of the bonds.
d.
The return of excess cash to the corporation.
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The initial sinking fund deposit.
b.
The first year's interest for the sinking fund.
c.
The redemption of the bonds.
d.
The return of excess cash to the corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
City Slicker Corporation pays $55,000 into a bond sinking fund each year for the future redemption of bonds. During the first year, the fund earns $1,475. When the bonds mature, there is a sinking fund balance of $612,000, and $600,000 is needed to redeem the bonds.
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The initial sinking fund deposit.
b.
The first year's earnings.
c.
The redemption of the bonds.
d.
The return of excess cash to the corporation.
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The initial sinking fund deposit.
b.
The first year's earnings.
c.
The redemption of the bonds.
d.
The return of excess cash to the corporation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Match the terms with the definitions.a.amortization
b.bond
c.bond indenture
d.bond sinking fund
e.callable bonds
f.carrying value
g.convertible bonds
h.coupon bonds
i.debenture bonds
j.discount
k.face value
l.market rate
m.mortgage bonds
n.premium
o.principal
p.registered bonds
q.secured bonds
r.serial bonds
s.stated rate
t.term bonds
A written promise to pay a specific sum of money at a specific future date.
b.bond
c.bond indenture
d.bond sinking fund
e.callable bonds
f.carrying value
g.convertible bonds
h.coupon bonds
i.debenture bonds
j.discount
k.face value
l.market rate
m.mortgage bonds
n.premium
o.principal
p.registered bonds
q.secured bonds
r.serial bonds
s.stated rate
t.term bonds
A written promise to pay a specific sum of money at a specific future date.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The year-end adjusting entry required for bonds issued at a discount would require
A) a debit to Bond Interest Expense, a debit to Discount on Bonds Payable, and a credit to Cash.
B) a debit to Bond Interest Expense, a debit to Discount on Bonds Payable, and a credit to Bond Interest Payable.
C) a debit to Bond Interest Expense, a credit to Discount on Bonds Payable, and a credit to Cash.
D) a debit to Bond Interest Expense, a credit to Discount on Bonds Payable, and a credit to Bond Interest Payable.
A) a debit to Bond Interest Expense, a debit to Discount on Bonds Payable, and a credit to Cash.
B) a debit to Bond Interest Expense, a debit to Discount on Bonds Payable, and a credit to Bond Interest Payable.
C) a debit to Bond Interest Expense, a credit to Discount on Bonds Payable, and a credit to Cash.
D) a debit to Bond Interest Expense, a credit to Discount on Bonds Payable, and a credit to Bond Interest Payable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The carrying value of bonds is calculated by
A) subtracting the premium on bonds payable account balance from the bonds payable account balance.
B) adding the premium on bonds payable account balance to the bonds payable account balance.
C) adding the discount on bonds payable account balance to the bonds payable account balance.
D) adding the bonds payable account balance to the bond interest payable account balance.
A) subtracting the premium on bonds payable account balance from the bonds payable account balance.
B) adding the premium on bonds payable account balance to the bonds payable account balance.
C) adding the discount on bonds payable account balance to the bonds payable account balance.
D) adding the bonds payable account balance to the bond interest payable account balance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A bond issue of $500,000 selling at 100, would require a journal entry including a
A) credit to Cash of $500,000.
B) credit to Premium on Bonds Payable for $500,000.
C) credit to Bonds Payable of $500,000.
D) debit to Bonds Payable of $500,000.
A) credit to Cash of $500,000.
B) credit to Premium on Bonds Payable for $500,000.
C) credit to Bonds Payable of $500,000.
D) debit to Bonds Payable of $500,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A bond issue of $100,000 selling at 98, would require a journal entry including a
A) debit to Bonds Payable for $98,000.
B) credit to Cash for $98,000.
C) credit to Premium of Bonds Payable for $2,000.
D) debit to Discount on Bonds Payable for $2,000.
A) debit to Bonds Payable for $98,000.
B) credit to Cash for $98,000.
C) credit to Premium of Bonds Payable for $2,000.
D) debit to Discount on Bonds Payable for $2,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Bonds classified as to the timing of principal payments include all of the following EXCEPT
A) term bonds.
B) serial bonds.
C) debenture bonds.
D) callable bonds.
A) term bonds.
B) serial bonds.
C) debenture bonds.
D) callable bonds.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Island Cove Corporation had the following bond issue:
Date of issue/sale: May 1, 20-A
Principal: $500,000
Sale price of bonds: 104
Life of bonds: 10 years
Stated rate: 6% a year payable semiannually on October 31 and April 30
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on May 1, 20-A.
b.
The first interest payment for 20-A.
c.
The adjusting entry for December 31, 20-A.
d.
The reversing entry for January 1, 20-B.
Date of issue/sale: May 1, 20-A
Principal: $500,000
Sale price of bonds: 104
Life of bonds: 10 years
Stated rate: 6% a year payable semiannually on October 31 and April 30
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on May 1, 20-A.
b.
The first interest payment for 20-A.
c.
The adjusting entry for December 31, 20-A.
d.
The reversing entry for January 1, 20-B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
HiLi Corporation had the following bond issue:
Date of issue/sale: May 1, 20-A
Principal: $500,000
Sale price of bonds: 100
Life of bonds: 10 years
Stated rate: 6% a year payable semiannually on October 31 and April 30
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on May 1, 20-A.
b.
The first interest payment for 20-A.
c.
The adjusting entry for December 31, 20-A.
d.
The reversing entry for January 1, 20-B.
Date of issue/sale: May 1, 20-A
Principal: $500,000
Sale price of bonds: 100
Life of bonds: 10 years
Stated rate: 6% a year payable semiannually on October 31 and April 30
Required:
Prepare the following general journal entries.
a.
The issuance of the bonds on May 1, 20-A.
b.
The first interest payment for 20-A.
c.
The adjusting entry for December 31, 20-A.
d.
The reversing entry for January 1, 20-B.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 98 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



