Deck 16: Monetary Policy
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/266
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 16: Monetary Policy
1
Monetary policy is used to stabilize the economy by changing factors that shift the:
A) AD curve.
B) SRAS curve.
C) LRAS curve.
D) aggregate demand, short-run aggregate supply, and LRAS curves.
A) AD curve.
B) SRAS curve.
C) LRAS curve.
D) aggregate demand, short-run aggregate supply, and LRAS curves.
AD curve.
2
In the case of a negative shock to aggregate demand, the central bank should:
A) decrease the rate of growth of the money supply to control inflation.
B) increase the rate of growth of the money supply to restore spending growth.
C) decrease the rate of growth of the price level to keep real growth high.
D) do nothing.
A) decrease the rate of growth of the money supply to control inflation.
B) increase the rate of growth of the money supply to restore spending growth.
C) decrease the rate of growth of the price level to keep real growth high.
D) do nothing.
increase the rate of growth of the money supply to restore spending growth.
3
Which is a limitation of monetary policy in stabilizing the economy?
A) Central banks have too much control over the money supply.
B) Most central bank policymakers are controlled by the government.
C) Monetary policy is subject to uncertain lags.
D) Central banks have no discretion over policy tools.
A) Central banks have too much control over the money supply.
B) Most central bank policymakers are controlled by the government.
C) Monetary policy is subject to uncertain lags.
D) Central banks have no discretion over policy tools.
Monetary policy is subject to uncertain lags.
4
If the Fed adheres to a strict "money growth rule" of 3% (that is, they keep at 3% no matter what), what happens if velocity growth (
) drops?
A) Inflation, real growth, and nominal wage growth all decrease.
B) Inflation increases, but real growth and nominal wage growth decrease.
C) Inflation and nominal wage growth decrease, but real growth increases.
D) Inflation, real growth, and nominal wage growth all increase.
) drops?
A) Inflation, real growth, and nominal wage growth all decrease.
B) Inflation increases, but real growth and nominal wage growth decrease.
C) Inflation and nominal wage growth decrease, but real growth increases.
D) Inflation, real growth, and nominal wage growth all increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
To offset the effect of negative growth in money velocity ( ), the central bank should:
A) decrease the growth rate of the money supply.
B) increase the growth rate of the money supply.
C) apply a policy that stabilizes the growth in money velocity.
D) apply a policy that reduces the growth in money velocity.
A) decrease the growth rate of the money supply.
B) increase the growth rate of the money supply.
C) apply a policy that stabilizes the growth in money velocity.
D) apply a policy that reduces the growth in money velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In the AD-AS diagram, a "tight" monetary policy shifts the:
A) AD curve to the left.
B) AD curve to the right.
C) LRAS curve to the left.
D) LRAS curve to the right.
A) AD curve to the left.
B) AD curve to the right.
C) LRAS curve to the left.
D) LRAS curve to the right.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Disinflation is:
A) a decrease in prices; that is, a negative inflation rate.
B) a reduction in the rate of inflation.
C) an increase in prices.
D) an increase in the rate of inflation.
A) a decrease in prices; that is, a negative inflation rate.
B) a reduction in the rate of inflation.
C) an increase in prices.
D) an increase in the rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
In the face of a negative shock to consumer confidence, politicians are on the fence about whether to implement policies based on the advice of economists or to make decisions on the basis of Tarot card readings. What would happen during the period in which they are making up their minds about which strategy to pursue?
A)
Would rise
B)
Would fall
C)
Would rise
D)
Would rise
A)
Would rise
B)
Would fall
C)
Would rise
D)
Would rise

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
When the Fed supplies "too much" monetary stimulus in the face of a negative aggregate demand shock:
A) inflation, real growth, and nominal wage growth all decrease.
B) inflation increases, but real growth and nominal wage growth decrease.
C) inflation and nominal wage growth decrease, but real growth increases.
D) inflation, real growth, and nominal wage growth all increase.
A) inflation, real growth, and nominal wage growth all decrease.
B) inflation increases, but real growth and nominal wage growth decrease.
C) inflation and nominal wage growth decrease, but real growth increases.
D) inflation, real growth, and nominal wage growth all increase.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Deflation is:
A) a decrease in prices; that is, a negative inflation rate.
B) a reduction in the rate of inflation.
C) an increase in prices.
D) an increase in the rate of inflation.
A) a decrease in prices; that is, a negative inflation rate.
B) a reduction in the rate of inflation.
C) an increase in prices.
D) an increase in the rate of inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Which shock can the Fed deal with most effectively?
A) a major oil shock
B) a shock to the LRAS curve
C) a shock that shifts the SRAS curve
D) a shock to AD
A) a major oil shock
B) a shock to the LRAS curve
C) a shock that shifts the SRAS curve
D) a shock to AD

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
If the Fed overreacts to a negative spending shock by increasing money growth too much:
A) both real GDP growth and inflation will decrease more than the Fed prefers.
B) both real GDP growth and inflation will increase more than the Fed prefers.
C) real GDP growth will increase more and inflation will increase less than the Fed prefers.
D) real GDP growth will increase less and inflation will increase more than the Fed prefers.
A) both real GDP growth and inflation will decrease more than the Fed prefers.
B) both real GDP growth and inflation will increase more than the Fed prefers.
C) real GDP growth will increase more and inflation will increase less than the Fed prefers.
D) real GDP growth will increase less and inflation will increase more than the Fed prefers.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The economy's AD curve is:
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
What is a reason it might be hard for the Fed to restore aggregate demand in the face of a negative demand shock?
A) The Fed might run out of money.
B) Banks usually don't do what the Fed demands of them.
C) The Fed must operate in real time, when a lot of the data about the state of the economy are unknown.
D) The economy responds to the Fed's actions with no lag.
A) The Fed might run out of money.
B) Banks usually don't do what the Fed demands of them.
C) The Fed must operate in real time, when a lot of the data about the state of the economy are unknown.
D) The economy responds to the Fed's actions with no lag.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
If initially, = 5%,
= 3%,
= 2%, and
= 6% and then because of economic uncertainty
Falls to 1%, what should the Fed do?
A) Quietly raise
To 8% to offset the decrease in
.
B) Publicly lower
To 3% so that
-
Stays constant at 2%.
C) Publicly demonstrate a commitment to keep
+
At 8% by raising
.
D) Quietly raise
Without telling anyone, as only unexpected inflation is expansionary.
= 3%,
= 2%, and
= 6% and then because of economic uncertainty
Falls to 1%, what should the Fed do?
A) Quietly raise
To 8% to offset the decrease in
.
B) Publicly lower
To 3% so that
-
Stays constant at 2%.
C) Publicly demonstrate a commitment to keep
+
At 8% by raising
.
D) Quietly raise
Without telling anyone, as only unexpected inflation is expansionary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The economy's SRAS curve is:
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
In the absence of monetary intervention following a negative shock to aggregate demand:
A) inflation, real growth, and nominal wage growth will all decrease.
B) inflation will decrease, but real growth and nominal wage growth will increase.
C) inflation will increase, real growth will decrease, and nominal wage growth will stay the same.
D) inflation and real growth will decrease, but nominal wage growth will stay the same.
A) inflation, real growth, and nominal wage growth will all decrease.
B) inflation will decrease, but real growth and nominal wage growth will increase.
C) inflation will increase, real growth will decrease, and nominal wage growth will stay the same.
D) inflation and real growth will decrease, but nominal wage growth will stay the same.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The economy's LRAS curve is:
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.
A) upward sloping.
B) downward sloping.
C) vertical.
D) horizontal.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Which is NOT a tool that the Federal Reserve can use to influence AD?
A) open-market operations
B) lending to banks and other financial institutions
C) changes in reserve requirements and the interest rate paid on reserves
D) printing money
A) open-market operations
B) lending to banks and other financial institutions
C) changes in reserve requirements and the interest rate paid on reserves
D) printing money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Disinflation is more painful when the central bank:
A) increases the rate of inflation.
B) runs out of money.
C) is credible.
D) is not credible.
A) increases the rate of inflation.
B) runs out of money.
C) is credible.
D) is not credible.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Although the Federal Reserve may increase the monetary base, the larger monetary aggregates (M1 and M2) and thus aggregate demand won't increase very much in response if:
A) the interest rate is too high.
B) the tax rate is too high.
C) banks are slow to lend.
D) the economy is in recession.
A) the interest rate is too high.
B) the tax rate is too high.
C) banks are slow to lend.
D) the economy is in recession.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
An increase in the money supply typically affects the economy with a lag that varies in time from:
A) 1 to 2 months.
B) 3 to 6 months.
C) 6 to 18 months.
D) 18 to 36 months.
A) 1 to 2 months.
B) 3 to 6 months.
C) 6 to 18 months.
D) 18 to 36 months.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Increased uncertainty will cause the economy's AD curve to:
A) shift inward.
B) shift outward.
C) become steeper.
D) become flatter.
A) shift inward.
B) shift outward.
C) become steeper.
D) become flatter.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
In the short run, a negative AD shock will cause the growth rate of output to:
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) become more volatile.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) become more volatile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The BEST type of negative shock for the Federal Reserve to respond to is a negative shock to:
A) AD.
B) SRAS.
C) LRAS.
D) inflation.
A) AD.
B) SRAS.
C) LRAS.
D) inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Which describes one of the difficulties that make it hard for the Fed to effectively implement monetary policy?
A) The Fed has too much data to sort through quickly.
B) All monetary policies must be approved by Congress before being implemented.
C) The Fed's control of the money supply is incomplete and subject to uncertain lags.
D) The effects of monetary policy always offset those of fiscal policy.
A) The Fed has too much data to sort through quickly.
B) All monetary policies must be approved by Congress before being implemented.
C) The Fed's control of the money supply is incomplete and subject to uncertain lags.
D) The effects of monetary policy always offset those of fiscal policy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Shortly after September 11, 2011, the Federal Reserve:
A) decreased its lending to banks.
B) increased its lending to banks.
C) decreased its lending to individuals.
D) increased its lending to individuals.
A) decreased its lending to banks.
B) increased its lending to banks.
C) decreased its lending to individuals.
D) increased its lending to individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
If the Federal Reserve offsets a negative shock to aggregate demand with increased money growth:
A) inflation will rise, but real GDP growth will remain unchanged.
B) inflation will fall, but real GDP growth will remain unchanged.
C) both inflation and real GDP growth will rise.
D) both inflation and real GDP growth will fall.
A) inflation will rise, but real GDP growth will remain unchanged.
B) inflation will fall, but real GDP growth will remain unchanged.
C) both inflation and real GDP growth will rise.
D) both inflation and real GDP growth will fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
In the short run, a monetary contraction leads to increased unemployment because:
A) wages and prices are sticky.
B) wages and prices are flexible.
C) wages are sticky, while prices are flexible.
D) wages are flexible, while prices are sticky.
A) wages and prices are sticky.
B) wages and prices are flexible.
C) wages are sticky, while prices are flexible.
D) wages are flexible, while prices are sticky.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A decrease in money supply growth will cause the:
A) AD curve to shift to the left.
B) SRAS curve to shift to the left.
C) LRAS curve to shift to the left.
D) price level to fall.
A) AD curve to shift to the left.
B) SRAS curve to shift to the left.
C) LRAS curve to shift to the left.
D) price level to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Use the following to answer questions: Figure: Monetary Policy 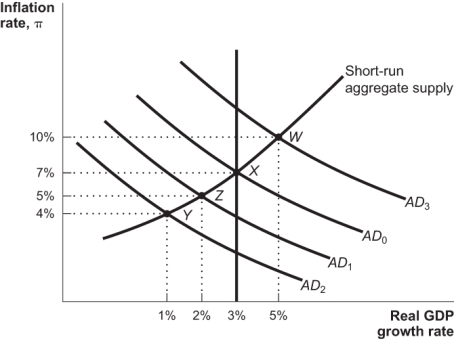
(Figure: Monetary Policy) Refer to the figure. Assume that the economy is initially at point Y in the graph. If the Fed takes the appropriate action with monetary policy, but banks are slow to lend, then:
A) the Fed action would be magnified and the economy would move to point X.
B) the Fed action would be nullified and the economy would remain at point Y.
C) the Fed action would be partially effective and the economy would move to point Z.
D) the LRAS curve would shift to the left.

(Figure: Monetary Policy) Refer to the figure. Assume that the economy is initially at point Y in the graph. If the Fed takes the appropriate action with monetary policy, but banks are slow to lend, then:
A) the Fed action would be magnified and the economy would move to point X.
B) the Fed action would be nullified and the economy would remain at point Y.
C) the Fed action would be partially effective and the economy would move to point Z.
D) the LRAS curve would shift to the left.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In the short run, a negative AD shock will cause the inflation rate to:
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) become more volatile.
A) increase.
B) decrease.
C) remain unchanged.
D) become more volatile.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
If the growth rate of the money supply slows, there will be a(n):
A) decrease in aggregate demand.
B) decrease in aggregate supply.
C) increase in aggregate demand.
D) increase in aggregate supply.
A) decrease in aggregate demand.
B) decrease in aggregate supply.
C) increase in aggregate demand.
D) increase in aggregate supply.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Use the following to answer questions: Figure: Monetary Policy 
(Figure: Monetary Policy) Refer to the figure. Assume that the economy is initially at point Y in the graph. In the best case scenario, the Fed will:
A) increase money supply to take the economy to point X.
B) decrease money supply to take the economy to point W.
C) increase money supply to take the economy to point W.
D) decrease money supply to take the economy to point X.

(Figure: Monetary Policy) Refer to the figure. Assume that the economy is initially at point Y in the graph. In the best case scenario, the Fed will:
A) increase money supply to take the economy to point X.
B) decrease money supply to take the economy to point W.
C) increase money supply to take the economy to point W.
D) decrease money supply to take the economy to point X.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The Fed's job in manipulating monetary policy is made harder by the fact that:
A) monetary authorities do not have a good understanding of how monetary policy works.
B) monetary policy is usually pulling the economy in the opposite direction from fiscal policy.
C) the Fed operates in real time and information on recessions becomes available with a lag.
D) monetary policy is hardly ever effective in influencing business fluctuations.
A) monetary authorities do not have a good understanding of how monetary policy works.
B) monetary policy is usually pulling the economy in the opposite direction from fiscal policy.
C) the Fed operates in real time and information on recessions becomes available with a lag.
D) monetary policy is hardly ever effective in influencing business fluctuations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
When aggregate demand decreases, the Fed will want to use its policy tools to:
A) keep aggregate demand lower until wages catch up.
B) quickly bring aggregate demand back to its original position.
C) push aggregate demand higher than it was originally to make up for lost growth potential.
D) shift aggregate supply to left to balance with lower demand.
A) keep aggregate demand lower until wages catch up.
B) quickly bring aggregate demand back to its original position.
C) push aggregate demand higher than it was originally to make up for lost growth potential.
D) shift aggregate supply to left to balance with lower demand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the Federal Reserve wishes to avoid short-run increases in the unemployment rate, the correct response to a negative AD shock would be:
A) an increase in government spending growth.
B) a tax cut.
C) an increase in money supply growth.
D) a lower goal for inflation.
A) an increase in government spending growth.
B) a tax cut.
C) an increase in money supply growth.
D) a lower goal for inflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
A significant decrease in the rate of inflation is called:
A) deflation.
B) credible inflation.
C) disinflation.
D) quantitative easing.
A) deflation.
B) credible inflation.
C) disinflation.
D) quantitative easing.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
If businesses react to a pessimistic outlook and decrease spending, the Fed can counteract this by:
A) decreasing money supply growth to spur the economy out of the recession.
B) increasing money supply growth, lowering real interest rates, and encouraging borrowing.
C) increasing government expenditures to spur the economy out of the recession.
D) decreasing corporate taxes to encourage firms to increase their spending.
A) decreasing money supply growth to spur the economy out of the recession.
B) increasing money supply growth, lowering real interest rates, and encouraging borrowing.
C) increasing government expenditures to spur the economy out of the recession.
D) decreasing corporate taxes to encourage firms to increase their spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Many economists worry about the Federal Reserve overstimulating the economy because such overstimulation will lead to rising:
A) unemployment.
B) inflation.
C) output growth.
D) Solow growth.
A) unemployment.
B) inflation.
C) output growth.
D) Solow growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
When a negative shock to aggregate demand occurs, the inflation rate will:
A) increase.
B) remain the same.
C) decrease.
D) be automatically adjusted by the Fed.
A) increase.
B) remain the same.
C) decrease.
D) be automatically adjusted by the Fed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Use the following to answer questions: Figure: Monetary Policy 
(Figure: Monetary Policy) Refer to the figure. Assume that the economy is initially at point Y in the graph. If the Fed takes the appropriate action with monetary policy, but overestimates how serious the recession is, then:
A) the LRAS curve would shift to the left.
B) the Fed would take the economy to point X.
C) the Fed would fail to stimulate the economy and it would remain at point Y.
D) the Fed would overshoot and the economy would move to point W.

(Figure: Monetary Policy) Refer to the figure. Assume that the economy is initially at point Y in the graph. If the Fed takes the appropriate action with monetary policy, but overestimates how serious the recession is, then:
A) the LRAS curve would shift to the left.
B) the Fed would take the economy to point X.
C) the Fed would fail to stimulate the economy and it would remain at point Y.
D) the Fed would overshoot and the economy would move to point W.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
What is a possible reason for the Fed's inability to prevent a recession?
A) The Fed has too much power over M1 and M2 and can flood the money supply.
B) Much of the information about the economy is unknown when the Fed is making policy.
C) Firms and individuals do not often understand the goals of the Fed.
D) The Fed often performs complex and conflicting maneuvers at the same time.
A) The Fed has too much power over M1 and M2 and can flood the money supply.
B) Much of the information about the economy is unknown when the Fed is making policy.
C) Firms and individuals do not often understand the goals of the Fed.
D) The Fed often performs complex and conflicting maneuvers at the same time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In the AD-AS model, an increase in money growth will cause the growth rate of real GDP to increase in:
A) the short run only.
B) the long run only.
C) both the short run and the long run.
D) neither the short run nor the long run.
A) the short run only.
B) the long run only.
C) both the short run and the long run.
D) neither the short run nor the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
In the AD-AS diagram, an increase in money supply growth causes:
A) a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the left.
B) a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right.
C) a downward movement along the aggregate demand curve.
D) an upward movement along the aggregate demand curve.
A) a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the left.
B) a shift of the aggregate demand curve to the right.
C) a downward movement along the aggregate demand curve.
D) an upward movement along the aggregate demand curve.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
An increase in money growth will cause the inflation rate to increase in:
A) the short run only.
B) the long run only.
C) both the short run and the long run.
D) neither the short run nor the long run.
A) the short run only.
B) the long run only.
C) both the short run and the long run.
D) neither the short run nor the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
A negative shock to AD will cause the growth rate of real GDP to increase in:
A) the short run only.
B) the long run only.
C) both the short run and the long run.
D) neither the short run nor the long run.
A) the short run only.
B) the long run only.
C) both the short run and the long run.
D) neither the short run nor the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Use the following to answer questions: Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks 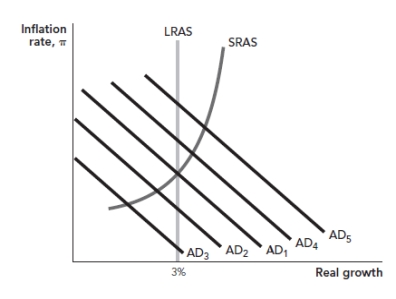
(Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks) Refer to the figure. In the figure, assume the initial real growth rate of the economy is 3% when a negative aggregate demand shock shifts the AD curve from AD1 to AD2. As a result of the Fed's policy response, the AD curve shifts to AD5 in the short run. Which of the following is TRUE about the Fed's policy response?
A) The Fed responded too little to the shock.
B) The Fed responded too much to the shock.
C) The Fed provided just the right amount of response to the shock.
D) The Fed was too fast in responding to the shock.

(Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks) Refer to the figure. In the figure, assume the initial real growth rate of the economy is 3% when a negative aggregate demand shock shifts the AD curve from AD1 to AD2. As a result of the Fed's policy response, the AD curve shifts to AD5 in the short run. Which of the following is TRUE about the Fed's policy response?
A) The Fed responded too little to the shock.
B) The Fed responded too much to the shock.
C) The Fed provided just the right amount of response to the shock.
D) The Fed was too fast in responding to the shock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Use the following to answer questions: Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks 
(Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks) Refer to the figure. In the figure, assume the initial real growth rate of the economy is 3% when a negative aggregate demand shock shifts the AD curve from AD1 to AD2. The correct monetary policy response is to:
A) reduce money supply growth, so that the AD curve shifts back to AD1.
B) reduce money supply growth, so that the AD curve remains at AD2.
C) increase money supply growth, so that the AD curve shifts to AD3.
D) increase money supply growth, so that the AD curve shifts to AD5.

(Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks) Refer to the figure. In the figure, assume the initial real growth rate of the economy is 3% when a negative aggregate demand shock shifts the AD curve from AD1 to AD2. The correct monetary policy response is to:
A) reduce money supply growth, so that the AD curve shifts back to AD1.
B) reduce money supply growth, so that the AD curve remains at AD2.
C) increase money supply growth, so that the AD curve shifts to AD3.
D) increase money supply growth, so that the AD curve shifts to AD5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
How can the Fed offset a positive shock to aggregate demand?
A) Increase the growth rate of the money supply.
B) Decrease the growth rate of the money supply.
C) Increase the growth rate of government spending.
D) Decrease the growth rate of government spending.
A) Increase the growth rate of the money supply.
B) Decrease the growth rate of the money supply.
C) Increase the growth rate of government spending.
D) Decrease the growth rate of government spending.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Use the following to answer questions: Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks 
(Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks) Refer to the figure. In the figure, assume the initial real growth rate of the economy is 3% when a positive aggregate demand shock shifts the AD curve from AD1 to AD4. As a result of the Fed's policy response, the AD curve shifts to AD3 in the short run. Which of the following is TRUE about the Fed's policy response?
A) The Fed responded too little to the shock.
B) The Fed responded too much to the shock.
C) The Fed provided just the right amount of response to the shock.
D) The Fed was too fast in responding to the shock.

(Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks) Refer to the figure. In the figure, assume the initial real growth rate of the economy is 3% when a positive aggregate demand shock shifts the AD curve from AD1 to AD4. As a result of the Fed's policy response, the AD curve shifts to AD3 in the short run. Which of the following is TRUE about the Fed's policy response?
A) The Fed responded too little to the shock.
B) The Fed responded too much to the shock.
C) The Fed provided just the right amount of response to the shock.
D) The Fed was too fast in responding to the shock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
In the best case scenario, the Federal Reserve is most successful at counteracting a negative:
A) AD shock.
B) SRAS shock.
C) LRAS shock.
D) real shock.
A) AD shock.
B) SRAS shock.
C) LRAS shock.
D) real shock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
The economy is growing at its long-run potential growth rate of 3% with an inflation rate of 4%. If a positive aggregate demand shock occurs and the Fed responds by decreasing money growth, but fails to offset the aggregate demand shock, then in the short run:
A) the real growth rate will be 3%, and the inflation rate will be 4%.
B) the real growth rate will be lower than 3%, and the inflation rate will be lower than 4%.
C) the real growth rate will be higher than 3% and the inflation rate will be lower than 4%.
D) the real growth rate will be higher than 3% and the inflation rate will be higher than 4%.
A) the real growth rate will be 3%, and the inflation rate will be 4%.
B) the real growth rate will be lower than 3%, and the inflation rate will be lower than 4%.
C) the real growth rate will be higher than 3% and the inflation rate will be lower than 4%.
D) the real growth rate will be higher than 3% and the inflation rate will be higher than 4%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
When an economy is adjusting to a recent reduction in the money supply, what is a likely consequence?
A) Inflation remains high.
B) Growth stays positive.
C) Interest rates continue to rise.
D) Unemployment is high.
A) Inflation remains high.
B) Growth stays positive.
C) Interest rates continue to rise.
D) Unemployment is high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Use the following to answer questions: Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks 
(Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks) Refer to the figure. In the figure, assume the initial real growth rate of the economy is 3% when a positive aggregate demand shock shifts the AD curve from AD1 to AD4. The correct monetary policy response is to:
A) reduce money supply growth, so that the AD curve shifts back to AD1.
B) reduce money supply growth, so that the AD curve remains at AD4.
C) increase money supply growth, so that the AD curve shifts to AD3.
D) increase money supply growth, so that the AD curve shifts to AD5.

(Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks) Refer to the figure. In the figure, assume the initial real growth rate of the economy is 3% when a positive aggregate demand shock shifts the AD curve from AD1 to AD4. The correct monetary policy response is to:
A) reduce money supply growth, so that the AD curve shifts back to AD1.
B) reduce money supply growth, so that the AD curve remains at AD4.
C) increase money supply growth, so that the AD curve shifts to AD3.
D) increase money supply growth, so that the AD curve shifts to AD5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
The first signs of trouble in the subprime mortgage market came in August of:
A)2006.
B)2007.
C)2008.
D) 2009.
A)2006.
B)2007.
C)2008.
D) 2009.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Suppose the Fed reacts to an economic shock and quickly restores the economy to its long-run potential growth rate. It is most likely that this shock was:
A) an aggregate demand shock.
B) a real shock.
C) a productivity shock.
D) a supply shock.
A) an aggregate demand shock.
B) a real shock.
C) a productivity shock.
D) a supply shock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Use the following to answer questions: Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks 
(Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks) Refer to the figure. In the figure, assume the initial real growth rate of the economy is 3% when a negative aggregate demand shock shifts the AD curve from AD1 to AD3. As a result of the Fed's policy response, the AD curve shifts to AD2 in the short run. Which of the following is TRUE about the Fed's policy response?
A) The Fed responded too little to the shock.
B) The Fed responded too much to the shock.
C) The Fed provided just the right amount of response to the shock.
D) The Fed was too fast in responding to the shock.

(Figure: Monetary Policy and Demand Shocks) Refer to the figure. In the figure, assume the initial real growth rate of the economy is 3% when a negative aggregate demand shock shifts the AD curve from AD1 to AD3. As a result of the Fed's policy response, the AD curve shifts to AD2 in the short run. Which of the following is TRUE about the Fed's policy response?
A) The Fed responded too little to the shock.
B) The Fed responded too much to the shock.
C) The Fed provided just the right amount of response to the shock.
D) The Fed was too fast in responding to the shock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
An increase in the money supply can typically affect the economy with a lag of:
A) 2 to 3 months.
B) 4 to 10 months.
C) 6 to 18 months.
D) 10 to 24 months.
A) 2 to 3 months.
B) 4 to 10 months.
C) 6 to 18 months.
D) 10 to 24 months.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A negative shock to AD will cause the inflation rate to increase in:
A) the short run only.
B) the long run only.
C) both the short run and the long run.
D) neither the short run nor the long run.
A) the short run only.
B) the long run only.
C) both the short run and the long run.
D) neither the short run nor the long run.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
When the price level actually falls, what is the economy experiencing?
A) deflation
B) disinflation
C) stagflation
D) devaluation
A) deflation
B) disinflation
C) stagflation
D) devaluation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The disinflation experiment reduced inflation in the United States, but at the cost of:
A) an increase in the long-run growth rate of the economy.
B) high unemployment.
C) high inflation.
D) deflation.
A) an increase in the long-run growth rate of the economy.
B) high unemployment.
C) high inflation.
D) deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An economy in which the central bank overstimulates aggregate demand will suffer from:
A) inflation.
B) unemployment.
C) increases in money supply.
D) deflation.
A) inflation.
B) unemployment.
C) increases in money supply.
D) deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
When the Fed reacts to a positive aggregate demand shock, which is likely to make the period of disinflation shorter?
A) credibility on the part of the Fed
B) higher uncertainty about investment returns
C) flexible wages and prices
D) an increase in the velocity of money
A) credibility on the part of the Fed
B) higher uncertainty about investment returns
C) flexible wages and prices
D) an increase in the velocity of money

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Under Paul Volcker, the Fed reduced the inflation rate in the early 1980s by more than10 percentage points, causing:
A) unemployment to decrease.
B) housing prices to soar and interest rates to remain high.
C) GDP growth rise to 6% and consumer confidence to grow.
D) a severe recession to take place.
A) unemployment to decrease.
B) housing prices to soar and interest rates to remain high.
C) GDP growth rise to 6% and consumer confidence to grow.
D) a severe recession to take place.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
If a country's central bank becomes more credible and announces a monetary contraction in advance, then:
A) more firms will invest now before the threat materializes.
B) slower wages will fall.
C) wages will rise in anticipation of the fall in incomes.
D) unemployment costs will be lower.
A) more firms will invest now before the threat materializes.
B) slower wages will fall.
C) wages will rise in anticipation of the fall in incomes.
D) unemployment costs will be lower.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
The problem associated with too much expansionary monetary policy is:
A) additional inflation.
B) additional unemployment.
C) higher interest rates.
D) reduced economic growth.
A) additional inflation.
B) additional unemployment.
C) higher interest rates.
D) reduced economic growth.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Use the following to answer questions: Table: Annual Inflation
-(Table: Annual Inflation) Refer to the figure. This table shows inflation data for an economy. During what period did this economy experience disinflation?
A) 2001 to 2002
B) 2003 to 2005
C) 2005 to 2006
D) 1998 to 2000
-(Table: Annual Inflation) Refer to the figure. This table shows inflation data for an economy. During what period did this economy experience disinflation?
A) 2001 to 2002
B) 2003 to 2005
C) 2005 to 2006
D) 1998 to 2000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The lags associated with monetary policy make its implementation more difficult during:
A) recessions only.
B) expansions only.
C) both expansions and recessions.
D) neither expansions nor recessions.
A) recessions only.
B) expansions only.
C) both expansions and recessions.
D) neither expansions nor recessions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
What reason do many people think explains why the Fed overstimulated the money supply in the 1970s?
A) because of a presidential dictate to do so
B) to induce a recession
C) because of the high unemployment associated with the oil crises
D) because it was trying to control inflation
A) because of a presidential dictate to do so
B) to induce a recession
C) because of the high unemployment associated with the oil crises
D) because it was trying to control inflation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
Disinflation occurs when the Fed:
A) raises the growth rate of the money supply.
B) reduces the growth rate of the money supply.
C) sets the money supply growth rate above the inflation rate.
D) does nothing when a shock occurs.
A) raises the growth rate of the money supply.
B) reduces the growth rate of the money supply.
C) sets the money supply growth rate above the inflation rate.
D) does nothing when a shock occurs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
What do many economists think contributed to the greater than 13% inflation rates experienced by the United States in the 1980s?
A) The Fed was inflexible in its rule of 3% growth.
B) The Fed did not do enough to increase money supply.
C) The Fed overstimulated the economy with too much money in the 1970s.
D) The Fed did not react to the oil shocks of the 1970s.
A) The Fed was inflexible in its rule of 3% growth.
B) The Fed did not do enough to increase money supply.
C) The Fed overstimulated the economy with too much money in the 1970s.
D) The Fed did not react to the oil shocks of the 1970s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
The Fed dealt with high inflation in the 1980s by:
A) reducing the money supply and causing aggregate demand to fall.
B) raising the money supply and causing aggregate demand to rise.
C) reducing the money supply and causing aggregate demand to rise.
D) raising the money supply and causing aggregate demand to fall.
A) reducing the money supply and causing aggregate demand to fall.
B) raising the money supply and causing aggregate demand to rise.
C) reducing the money supply and causing aggregate demand to rise.
D) raising the money supply and causing aggregate demand to fall.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
Which BEST describes U.S. economic conditions in the 1980s?
A) Deflation occurred because the Fed reacted too much to AD shocks.
B) High inflation occurred because the Fed reacted too little to AD shocks.
C) High real growth occurred because of the deliberate actions of the Fed.
D) Disinflation occurred because of the deliberate actions of the Fed.
A) Deflation occurred because the Fed reacted too much to AD shocks.
B) High inflation occurred because the Fed reacted too little to AD shocks.
C) High real growth occurred because of the deliberate actions of the Fed.
D) Disinflation occurred because of the deliberate actions of the Fed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
When people believe that a central bank will stick with its policy, monetary policy is likely to have:
A) high credibility.
B) low credibility.
C) a high bandwagon effect.
D) a low bandwagon effect.
A) high credibility.
B) low credibility.
C) a high bandwagon effect.
D) a low bandwagon effect.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A reduction in the rate of inflation is called:
A) deflation.
B) disinflation.
C) stagflation.
D) devaluation.
A) deflation.
B) disinflation.
C) stagflation.
D) devaluation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If a central bank wishes to reduce inflation, it should announce its intentions and follow through with them, thereby using _____ monetary policy.
A) visible
B) integral
C) credible
D) authoritative
A) visible
B) integral
C) credible
D) authoritative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
A potential problem with expansionary monetary policy is that banks can:
A) be loaned up prior to open-market operations.
B) be unwilling to lend.
C) decide that a recession is best for the economy.
D) choose not to hold any reserves.
A) be loaned up prior to open-market operations.
B) be unwilling to lend.
C) decide that a recession is best for the economy.
D) choose not to hold any reserves.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the difference between disinflation and deflation?
A) Disinflation is a slower increase in prices, whereas deflation is a decrease in prices.
B) Deflation is a slower increase in prices, whereas disinflation is a decrease in prices.
C) The Fed can engineer disinflation, but not deflation.
D) There is no difference between disinflation and deflation.
A) Disinflation is a slower increase in prices, whereas deflation is a decrease in prices.
B) Deflation is a slower increase in prices, whereas disinflation is a decrease in prices.
C) The Fed can engineer disinflation, but not deflation.
D) There is no difference between disinflation and deflation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Use the following to answer questions: Table: Annual Inflation
-(Table: Annual Inflation) Refer to the figure. This table shows inflation data for an economy. During what period did this economy experience deflation?
A) 2003 to 2005
B) 2005 to 2006
C) 1998 to 2000
D) 2000 to 2002
-(Table: Annual Inflation) Refer to the figure. This table shows inflation data for an economy. During what period did this economy experience deflation?
A) 2003 to 2005
B) 2005 to 2006
C) 1998 to 2000
D) 2000 to 2002

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 266 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



