Deck 11: Imperfect Competition
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/99
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 11: Imperfect Competition
1
A Nash equilibrium occurs when:
A) each firm is doing the best it can in light of the actions taken by other firms.
B) each firm is doing the worst it can in light of the actions taken by other firms.
C) an oligopoly industry is characterized by excess demand despite a market-clearing price.
D) an oligopoly industry is characterized by excess supply despite a market-clearing price.
A) each firm is doing the best it can in light of the actions taken by other firms.
B) each firm is doing the worst it can in light of the actions taken by other firms.
C) an oligopoly industry is characterized by excess demand despite a market-clearing price.
D) an oligopoly industry is characterized by excess supply despite a market-clearing price.
A
2
Use the following to answer question:
Figure 11.2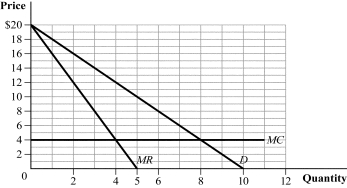
(Figure 11.2) The graph depicts the market demand curve for a two-firm industry with no fixed costs. Suppose that the two firms are colluding by acting like a monopolist, with each firm producing half the market output. If one of the firms cheats on the cartel agreement and produces an additional unit of output, its profits will rise from:
A) $16 to $18.
B) $32 to $36.
C) $24 to $32.
D) $8 to $12.
Figure 11.2

(Figure 11.2) The graph depicts the market demand curve for a two-firm industry with no fixed costs. Suppose that the two firms are colluding by acting like a monopolist, with each firm producing half the market output. If one of the firms cheats on the cartel agreement and produces an additional unit of output, its profits will rise from:
A) $16 to $18.
B) $32 to $36.
C) $24 to $32.
D) $8 to $12.
A
3
Use the following to answer question:
Table 11.2
Payoffs: University of Michigan's Football Revenue, Michigan State's Football Revenue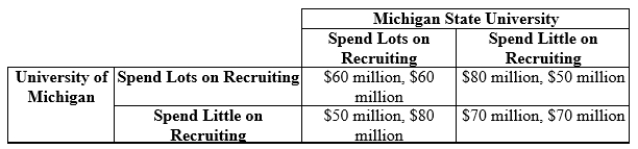
(Table 11.2) The table shows the payoffs associated with two levels of spending for recruitment of star football players. What is the Nash equilibrium?
A) Each school will spend a little money on recruiting.
B) Each school will spend lots of money on recruiting.
C) The University of Michigan will spend a little money on recruiting and Michigan State University will spend lots of money on recruiting.
D) There are two Nash equilibria: (1) both schools spend lots of money recruiting and (2) both schools spend little money recruiting.
Table 11.2
Payoffs: University of Michigan's Football Revenue, Michigan State's Football Revenue

(Table 11.2) The table shows the payoffs associated with two levels of spending for recruitment of star football players. What is the Nash equilibrium?
A) Each school will spend a little money on recruiting.
B) Each school will spend lots of money on recruiting.
C) The University of Michigan will spend a little money on recruiting and Michigan State University will spend lots of money on recruiting.
D) There are two Nash equilibria: (1) both schools spend lots of money recruiting and (2) both schools spend little money recruiting.
B
4
The market inverse demand curve is P = 60 - Q. The three firms in this industry are acting like a monopolist, evenly splitting output. The marginal cost is $6. Suppose one of the firms produces an additional unit of output. The cheating firm's profit will change from:
A) $50 to $40.
B) $34 to $67.
C) $230 to $252.
D) $243 to $260.
A) $50 to $40.
B) $34 to $67.
C) $230 to $252.
D) $243 to $260.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The inverse market demand curve is P = 170 - 4Q. Two firms in this market are evenly splitting the output. Each firm produces the product at a constant marginal cost of $10. Which of the following statements is TRUE? 
A) I and III
B) II and III
C) I and II
D) I, II, and III

A) I and III
B) II and III
C) I and II
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Which of the following statements is TRUE? 
A) I, II, and III
B) II
C) I and III
D) III

A) I, II, and III
B) II
C) I and III
D) III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Use the following to answer questions 3-4:
Table 11.1
Payoffs: Henry's Monthly Profit, Nancy's Monthly Profit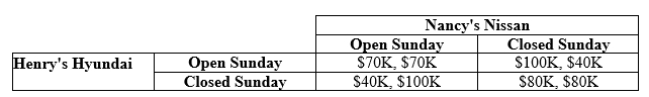
(Table 11.1) If car dealerships are allowed to be open on Sunday, what is the Nash equilibrium?
A) Henry earns $70K and Nancy earns $70K.
B) Henry earns $100K and Nancy earns $100K.
C) Henry earns $80K and Nancy earns $80K.
D) There is no Nash equilibrium in this market.
Table 11.1
Payoffs: Henry's Monthly Profit, Nancy's Monthly Profit

(Table 11.1) If car dealerships are allowed to be open on Sunday, what is the Nash equilibrium?
A) Henry earns $70K and Nancy earns $70K.
B) Henry earns $100K and Nancy earns $100K.
C) Henry earns $80K and Nancy earns $80K.
D) There is no Nash equilibrium in this market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Which of the following are model assumptions of Bertrand competition with identical goods? 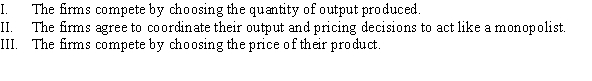
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I, II, and III
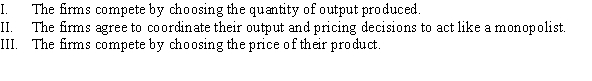
A) I
B) II
C) III
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The Nash equilibrium in Bertrand competition with identical goods:
A) occurs when each firm produces where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B) occurs when each firm sets price equal to marginal cost.
C) occurs when each firm sets price equal to average total cost.
D) does not exist.
A) occurs when each firm produces where marginal revenue equals marginal cost.
B) occurs when each firm sets price equal to marginal cost.
C) occurs when each firm sets price equal to average total cost.
D) does not exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Crush and Frenzy both produce motorized bicycles, which are identical in all aspects. The total demand in this market is for Q motorized bicycles. The price of Crush's bicycle is PC and the price of Frenzy's bicycle is PF. If the firms are engaged in Bertrand competition, which of the following statements is TRUE? 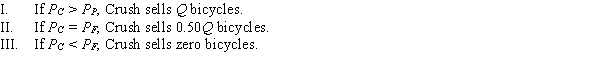
A) I and III
B) I, II, and III
C) II
D) II and III
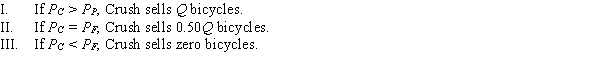
A) I and III
B) I, II, and III
C) II
D) II and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Use the following to answer question:
Figure 11.3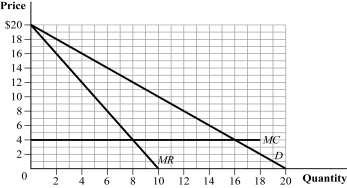
(Figure 11.3) The graph depicts a four-firm industry with no fixed costs. Suppose that the four firms are colluding by acting like a monopolist, with each firm producing one-fourth of the market output. If one of the firms cheats on the cartel agreement and produces an additional unit of output, the profits of each of the compliant firms go from:
A) $36 to $40.
B) $16 to $14.
C) $8 to $12.
D) $18 to $12.
Figure 11.3

(Figure 11.3) The graph depicts a four-firm industry with no fixed costs. Suppose that the four firms are colluding by acting like a monopolist, with each firm producing one-fourth of the market output. If one of the firms cheats on the cartel agreement and produces an additional unit of output, the profits of each of the compliant firms go from:
A) $36 to $40.
B) $16 to $14.
C) $8 to $12.
D) $18 to $12.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Use the following to answer question:
Figure 11.1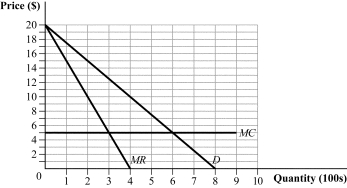
(Figure 11.1) The graph depicts the market demand curve for a two-firm industry. If the two firms collude and evenly split the market output, how much output will each firm produce?
A) 400 units
B) 200 units
C) 150 units
D) 300 units
Figure 11.1

(Figure 11.1) The graph depicts the market demand curve for a two-firm industry. If the two firms collude and evenly split the market output, how much output will each firm produce?
A) 400 units
B) 200 units
C) 150 units
D) 300 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
An industry faces the demand curve Q = 200 - P, where each firm produces an identical good at a constant marginal cost of $8. What are the Bertrand equilibrium price and quantity?
A) Q = 96; P = $8
B) Q = 96; P = $104
C) Q = 192; P = $8
D) Q = 192; P = $104
A) Q = 96; P = $8
B) Q = 96; P = $104
C) Q = 192; P = $8
D) Q = 192; P = $104

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A two-firm cartel that produces at a constant marginal cost of $20 faces a market inverse demand curve of P = 100 - 0.50Q. Initially, both firms agree to act like a monopolist, each producing 40 units of output. If one of the firms cheats on the agreement (assuming the other firm is compliant and continues to produce at 40 units), how much output should the cheating firm produce to maximize profits?
A) 41 units
B) 60 units
C) 80 units
D) 44 units
A) 41 units
B) 60 units
C) 80 units
D) 44 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A market is characterized with the inverse demand curve P = 130 - 1.5Q, and marginal cost of production is constant at $10. If this market is served by a two-firm cartel that evenly splits the market output, how much output does each firm produce?
A) 20 units
B) 80 units
C) 40 units
D) 65 units
A) 20 units
B) 80 units
C) 40 units
D) 65 units

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements is TRUE? 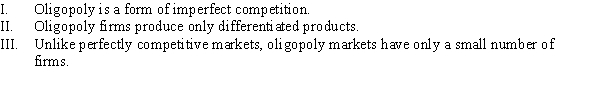
A) I
B) II and III
C) I and III
D) I, II, and III
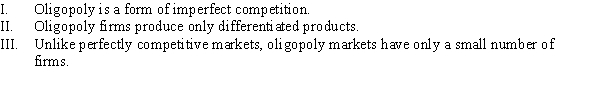
A) I
B) II and III
C) I and III
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Suppose that two firms are competing on price. The firms produce identical goods, and the marginal cost of each firm is constant at $15. If one firm is charging a price of $18, the other firm should:
A) raise its price to $18.01.
B) charge $17.99.
C) also charge $18.
D) cut its output to raise the market price well above $18.
A) raise its price to $18.01.
B) charge $17.99.
C) also charge $18.
D) cut its output to raise the market price well above $18.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In Bertrand competition with identical goods, the market outcome is MOST like:
A) a monopoly.
B) perfect competition.
C) a two-firm cartel.
D) monopolistic competition.
A) a monopoly.
B) perfect competition.
C) a two-firm cartel.
D) monopolistic competition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
In an identical-product Bertrand oligopoly, the market inverse demand curve is P = 100 - 0.5Q. Firm A's average cost and marginal cost are constant at $20; Firm B's average cost and marginal cost are constant at $10. What is the equilibrium price in this market?
A) $10
B) $15
C) $20
D) $19.99
A) $10
B) $15
C) $20
D) $19.99

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Use the following to answer questions 3-4:
Table 11.1
Payoffs: Henry's Monthly Profit, Nancy's Monthly Profit
(Table 11.1) If state law prevented car dealerships from opening on Sunday, Henry's Hyundai would earn _____ and Nancy's Nissan would earn _____.
A) $70K; $70K
B) $100K; $100K
C) $80K; $80K
D) $40K; $40K
Table 11.1
Payoffs: Henry's Monthly Profit, Nancy's Monthly Profit

(Table 11.1) If state law prevented car dealerships from opening on Sunday, Henry's Hyundai would earn _____ and Nancy's Nissan would earn _____.
A) $70K; $70K
B) $100K; $100K
C) $80K; $80K
D) $40K; $40K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The market inverse demand curve is P = 90 - Q, where Q is the total market output consisting of Firm 1's output, q1, and Firm 2's output, q2. Both firms have a constant marginal cost of $10. If Firm 1 selects its output level first, how much output does each firm produce?
A) q1 = 40; q2 = 20
B) q1 = 30; q2 = 15
C) q1 = 18; q2 = 18
D) q1 = 14; q2 = 21
A) q1 = 40; q2 = 20
B) q1 = 30; q2 = 15
C) q1 = 18; q2 = 18
D) q1 = 14; q2 = 21

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Two firms that are engaged in Stackelberg competition face the market inverse demand curve P = 100 - 2Q, where Q is the total market output comprising Firm 1's output, q1, and Firm 2's output, q2. Each firm produces the product at a constant marginal cost of $22. If Firm 2's reaction function is q2 = 22 - 0.5q1, what is Firm 1's (the first-mover's) inverse demand curve?
A) P = 88 - 2q1
B) P = 56 - q1
C) P = 100 - 2(q2 - 22 + 0.05q1)
D) P = 88 - 1.5q1
A) P = 88 - 2q1
B) P = 56 - q1
C) P = 100 - 2(q2 - 22 + 0.05q1)
D) P = 88 - 1.5q1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following statements is TRUE regarding collusion, Bertrand (identical products), and Cournot competition? 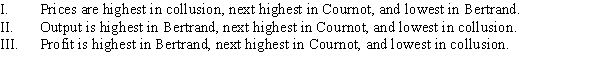
A) I and II
B) III
C) I
D) II
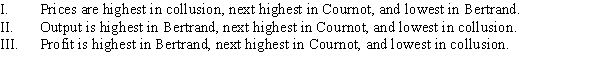
A) I and II
B) III
C) I
D) II

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which of the following is NOT a feature of Cournot competition?
A) Firms sell identical products.
B) Firms compete by choosing a quantity to produce.
C) All goods sell at the same price.
D) One firm sets its quantity to produce before the other firm.
A) Firms sell identical products.
B) Firms compete by choosing a quantity to produce.
C) All goods sell at the same price.
D) One firm sets its quantity to produce before the other firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Consider the following information: Inverse market demand: P = 12 - 0.5(q1 + q2), where q1 and q2 are Firm 1's and Firm 2's output
Firm 1's reaction function: q1 = 9 - 0.5q2
Firm 2's reaction function: q2 = 9 - 0.5q1
The marginal cost of production for both firms is constant at $3. The equilibrium prices in Cournot and Stackelberg competition are _____ and _____, respectively.
A) $8; $7
B) $9; $10
C) $4; $3.50
D) $6; $5.25
Firm 1's reaction function: q1 = 9 - 0.5q2
Firm 2's reaction function: q2 = 9 - 0.5q1
The marginal cost of production for both firms is constant at $3. The equilibrium prices in Cournot and Stackelberg competition are _____ and _____, respectively.
A) $8; $7
B) $9; $10
C) $4; $3.50
D) $6; $5.25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Consider a two-firm oligopoly facing a market inverse demand curve of P = 100 - 2(q1 + q2), where q1 is the output of Firm 1 and q2 is the output of Firm 2. Firm 1's marginal cost is constant at $12, while Firm 2's marginal cost is constant at $20. In Cournot equilibrium, how much output does each firm produce?
A) q1 = 20; q2 = 14
B) q1 = 16; q2 = 12
C) q1 = 18; q2 = 8
D) q1 = 14; q2 = 11
A) q1 = 20; q2 = 14
B) q1 = 16; q2 = 12
C) q1 = 18; q2 = 8
D) q1 = 14; q2 = 11

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A market is served by two firms in Cournot competition, each with a constant marginal cost of $100. The market inverse demand curve is P = 2,000 - 50Q, where Q is the total market output produced by the two firms, q1 + q2. What is Firm 1's reaction function?
A) q1 = 19 - 0.5q2
B) q1 = 210 - q2
C) q1 = 400 - 0.2P
D) q1 = 400 - 100q2
A) q1 = 19 - 0.5q2
B) q1 = 210 - q2
C) q1 = 400 - 0.2P
D) q1 = 400 - 100q2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
CellBat and DuraBat are the only makers of lawn mower batteries. Their batteries are identical, produced at a constant marginal cost of $25. The market inverse demand curve for lawn mower batteries is P = 145 - 0.5Q, where Q is the total output produced by CellBat and DuraBat, qC + qD. How many batteries will each firm produce in Cournot equilibrium?
A) CellBat and DuraBat will each produce 60 batteries.
B) CellBat will produce 40 batteries, and DuraBat will produce 80 batteries.
C) CellBat and DuraBat will each produce 80 batteries.
D) CellBat and DuraBat will each produce 30 batteries.
A) CellBat and DuraBat will each produce 60 batteries.
B) CellBat will produce 40 batteries, and DuraBat will produce 80 batteries.
C) CellBat and DuraBat will each produce 80 batteries.
D) CellBat and DuraBat will each produce 30 batteries.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following characteristics does Bertrand competition with differentiated goods have in common with Bertrand competition with identical goods?
A) Price equals marginal cost.
B) Firms earn zero economic profit.
C) Firms set prices simultaneously.
D) Each firm's product is a perfect substitute for the other firm's product.
A) Price equals marginal cost.
B) Firms earn zero economic profit.
C) Firms set prices simultaneously.
D) Each firm's product is a perfect substitute for the other firm's product.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
In Cournot competition, the market inverse demand curve is P = 240 - 0.5Q, where Q is the total output produced by Firm A and Firm B, qA + qB. The marginal cost for each firm is constant at $30. If Firm B produces 140 units of output, how much output should Firm A produce?
A) 80
B) 140
C) 34
D) 90
A) 80
B) 140
C) 34
D) 90

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Use the following to answer question:
Figure 11.4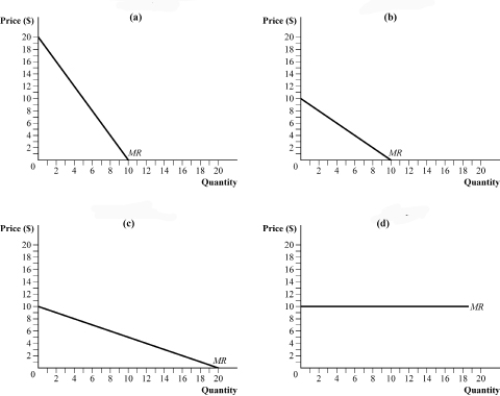
(Figure 11.4) In a Cournot market with two firms, the inverse market demand curve is P = 20 - 0.5Q, where Q = q1 + q2. (Firm 1's output = q1; Firm 2's output = q2.) If Firm 2 produces 20 units of output, Firm 1's residual marginal revenue curve is depicted in:
A) panel a.
B) panel b.
C) panel c.
D) panel d.
Figure 11.4

(Figure 11.4) In a Cournot market with two firms, the inverse market demand curve is P = 20 - 0.5Q, where Q = q1 + q2. (Firm 1's output = q1; Firm 2's output = q2.) If Firm 2 produces 20 units of output, Firm 1's residual marginal revenue curve is depicted in:
A) panel a.
B) panel b.
C) panel c.
D) panel d.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In Bertrand competition with differentiated products and zero marginal costs, Firm A faces the demand curve qA = 80 - 2PA + 0.50PB. If Firm A expects Firm B to charge a price of $20, what price should Firm A charge?
A) $14.25
B) $18.00
C) $22.50
D) $24.75
A) $14.25
B) $18.00
C) $22.50
D) $24.75

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Suppose the outboard motor market is characterized by Stackelberg competition. The market inverse demand curve for outboard motors is P = 10,000 - 50Q, where Q is the total market output produced by Mercury Marine and Yamaha, qM + qY. Suppose that the marginal cost for both firms is constant at $1,000. If Yamaha is the first-mover, what is the equilibrium price?
A) $1,800
B) $2,600
C) $3,250
D) $4,000
A) $1,800
B) $2,600
C) $3,250
D) $4,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Suppose that two manufacturers produce identical fireproof safes at a constant marginal cost of $90. The market inverse demand curve for fireproof safes is P = 450 - 2Q, where Q is the total output of fireproof safes produced by the two manufacturers, q1 + q2. The firms compete by simultaneously choosing their quantity to produce. At Nash equilibrium, what is the market price of a fireproof safe?
A) $340
B) $210
C) $160
D) $130
A) $340
B) $210
C) $160
D) $130

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Which of the following is an example of Stackelberg competition?
A) Firestone offers rebates to keep its tire prices below Goodyear's.
B) A price war between American Airlines and United Airlines leads both airlines to set ticket prices equal to marginal cost.
C) Natura Pet Products introduced the first grain-free dog food; eventually, other dog food companies entered this market but had to limit their production plans, given Natura Pet Products' sizable market share.
D) GlaxoSmithKline and Pfizer compete in the HIV drug market by annually announcing their production quotas during the second week of January.
A) Firestone offers rebates to keep its tire prices below Goodyear's.
B) A price war between American Airlines and United Airlines leads both airlines to set ticket prices equal to marginal cost.
C) Natura Pet Products introduced the first grain-free dog food; eventually, other dog food companies entered this market but had to limit their production plans, given Natura Pet Products' sizable market share.
D) GlaxoSmithKline and Pfizer compete in the HIV drug market by annually announcing their production quotas during the second week of January.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
In Stackelberg competition, the market inverse demand curve is P = 20 - 2(q1 + q2), where q1 and q2 are Firm 1's and Firm 2's output measured in hundreds of units. Firm 1, the first-mover, has a marginal cost of $4, and Firm 2 has a marginal cost of $2. How much output does each firm produce?
A) q1 = 150; q2 = 120
B) q1 = 350; q2 = 275
C) q1 = 80; q2 = 106
D) q1 = 260; q2 = 245
A) q1 = 150; q2 = 120
B) q1 = 350; q2 = 275
C) q1 = 80; q2 = 106
D) q1 = 260; q2 = 245

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
In a Cournot market with two firms, the inverse market demand curve is P = 50 - 2Q, where Q = q1 + q2 (Firm 1's output = q1; Firm 2's output = q2). If Firm 2 produces 10 units of output, what is Firm 1's residual demand curve?
A) P = 30 - 2q1
B) P = 40 - 2q1
C) P = 10 - 2q1
D) P = 40 - q1
A) P = 30 - 2q1
B) P = 40 - 2q1
C) P = 10 - 2q1
D) P = 40 - q1

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Two firms are in Bertrand competition with differentiated goods. Firm A faces the demand curve qA = 40 - PA + 0.50PB.What is Firm A's total revenue?
A) TRA = 40PA -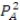 + 0.50PAPB
+ 0.50PAPB
B) TRA = (40 - PA + 0.50PA)PB
C) TRA = (40 - PA + 0.50PA)qA.
D) TRA = (40 - PB + 0.50PB)PA
A) TRA = 40PA -
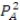 + 0.50PAPB
+ 0.50PAPBB) TRA = (40 - PA + 0.50PA)PB
C) TRA = (40 - PA + 0.50PA)qA.
D) TRA = (40 - PB + 0.50PB)PA

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Use the following to answer question:
Figure 11.5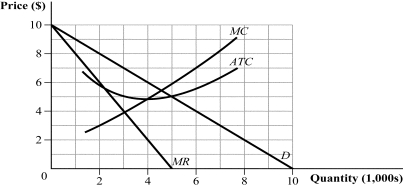
(Figure 11.5) According to the figure, which of the following statements is TRUE?
A) III
B) II
C) I and II
D) I, II, and III
Figure 11.5

(Figure 11.5) According to the figure, which of the following statements is TRUE?

A) III
B) II
C) I and II
D) I, II, and III

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The output of firms is determined simultaneously in _____ competition but sequentially in _____ competition.
A) Cournot; Bertrand with differentiated goods
B) Stackelberg; Cournot
C) collusion; Cournot
D) Cournot; Stackelberg
A) Cournot; Bertrand with differentiated goods
B) Stackelberg; Cournot
C) collusion; Cournot
D) Cournot; Stackelberg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Consider the breakfast cereal market. Post and General Mills must simultaneously decide whether to spend money on advertising their new tuna crunch cereal. If both companies advertise, each company will earn profits of $6 million. If neither company advertises, each company will earn profits of $8 million. However, if one company advertises and the other does not, the company that advertises earns profits of $12 million and the company that does not earns profits of $3 million. Explain why the following outcomes are either a Nash equilibrium or not a Nash equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Gotcha, the only seller of stun guns, faces the inverse market demand curve P = 400 - 12Q, where Q measures the number of stun guns per day and P is the price per stun gun. The marginal cost is constant at $64. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Taggart Express operates in a monopolistically competitive industry. Its inverse demand curve is P = 80 - Q. The total cost curve is TC = 20Q and marginal cost is constant at $20. What is the long-run equilibrium price?
A) $60
B) $75
C) $50
D) $20
A) $60
B) $75
C) $50
D) $20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Using the concept of a Nash equilibrium, explain why cartels are difficult to maintain. What factors make it easier to maintain a cartel?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The market inverse demand curve for thrust bearings is P = 15 - 1.5Q, where Q is measured in hundreds of bearings per day and P is the price per bearing. The marginal cost is $3. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Which of the following statements is TRUE? 
A) I, II, and III
B) I and III
C) II
D) IV
A) I, II, and III
B) I and III
C) II
D) IV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
As firms enter a monopolistically competitive industry, the existing firms' demand curves will:
A) remain unchanged.
B) shift outward and become more inelastic.
C) shift inward and become more elastic.
D) shift outward and become more elastic.
A) remain unchanged.
B) shift outward and become more inelastic.
C) shift inward and become more elastic.
D) shift outward and become more elastic.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Ney Inc. and ARN Parts are the only two producers of bulldozer bucket teeth. The owners of the two firms conspire to charge a monopoly price, with each firm serving half the market. The market inverse demand curve is P = 1,000 - 10Q, where Q measures the daily number of sets of bulldozer bucket teeth and P is the price per set. The marginal cost of production for either firm is constant at $200, and fixed costs are zero. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Answer the following questions. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Chauncey's Burgers sells hamburgers in a monopolistically competitive industry. Chauncey faces an inverse demand curve of P = 9 - 0.4Q, where Q is measured in hamburgers per hour and P is the price per hamburger. The total cost is TC = 20 + Q, and marginal cost is constant at $1. What is Chauncey's hourly profit?
A) $15
B) $20
C) $35
D) $70
A) $15
B) $20
C) $35
D) $70

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
Suppose that Mystic Energy and E-Storm are the only two producers of hydrogen fuel cells. The market inverse demand curve for hydrogen fuel cells is P = 1,300 - 0.08Q, where Q is the number of fuels cells per month and P is the price per fuel cell. The marginal cost is constant at $500. Acting as a cartel, the owners of Mystic Energy and E-Storm agree to evenly split the market output. 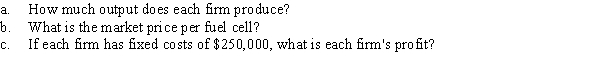

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
(Table) 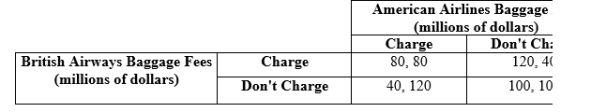 British Airways and American airlines have to decide whether or not to charge baggage fees. The revenue for each company that would result from the four possible outcomes is presented in the table. British Airways will earn _____ and American Airlines will earn _____ in the Nash equilibrium.
British Airways and American airlines have to decide whether or not to charge baggage fees. The revenue for each company that would result from the four possible outcomes is presented in the table. British Airways will earn _____ and American Airlines will earn _____ in the Nash equilibrium.
 British Airways and American airlines have to decide whether or not to charge baggage fees. The revenue for each company that would result from the four possible outcomes is presented in the table. British Airways will earn _____ and American Airlines will earn _____ in the Nash equilibrium.
British Airways and American airlines have to decide whether or not to charge baggage fees. The revenue for each company that would result from the four possible outcomes is presented in the table. British Airways will earn _____ and American Airlines will earn _____ in the Nash equilibrium.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In monopolistic competition, the long-run equilibrium price _____ marginal cost because _____.
A) equals; firms earn zero economic profit
B) exceeds; firms face downward-sloping demand curves
C) exceeds; there are significant barriers to entry
D) less than; firms set their production plans simultaneously
A) equals; firms earn zero economic profit
B) exceeds; firms face downward-sloping demand curves
C) exceeds; there are significant barriers to entry
D) less than; firms set their production plans simultaneously

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In Bertrand competition with differentiated goods, the demand curve for bags of Wilson tennis balls is qW = 80 - 4PW + 2PD , and the demand curve for bags of Dunlop tennis balls is qD = 80 - 2PD + PW. Two firms both have zero marginal costs. How many bags of tennis balls does each firm produce?
A) qW = 44; qD = 44
B) qW = 64; qD = 48
C) qW = 16; qD = 24
D) qW = 38; qD = 32
A) qW = 44; qD = 44
B) qW = 64; qD = 48
C) qW = 16; qD = 24
D) qW = 38; qD = 32

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Use the following to answer question:
Table 11.3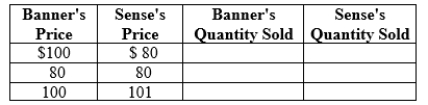
(Table 11.3) Banner and Sense are Bertrand competitors producing identical gascolators. The inverse market demand curve for gascolators is P = 2,000 - 4Q, where Q is the quantity of gascolators and P is the price per gascolator. Banner and Sense produce gascolators at a constant marginal cost of $80. Complete the table:
Table 11.3

(Table 11.3) Banner and Sense are Bertrand competitors producing identical gascolators. The inverse market demand curve for gascolators is P = 2,000 - 4Q, where Q is the quantity of gascolators and P is the price per gascolator. Banner and Sense produce gascolators at a constant marginal cost of $80. Complete the table:

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
(Graph) 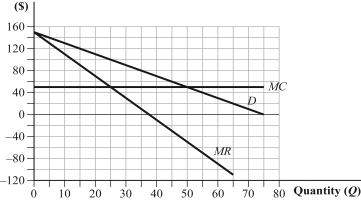 If two firms selling identical products act as a cartel and split the market evenly, each firm will earn profits of _____. Why is quantity collusion not considered a Nash equilibrium?
If two firms selling identical products act as a cartel and split the market evenly, each firm will earn profits of _____. Why is quantity collusion not considered a Nash equilibrium?
 If two firms selling identical products act as a cartel and split the market evenly, each firm will earn profits of _____. Why is quantity collusion not considered a Nash equilibrium?
If two firms selling identical products act as a cartel and split the market evenly, each firm will earn profits of _____. Why is quantity collusion not considered a Nash equilibrium?
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
Pizza Plus operates in a monopolistically competitive industry and faces an inverse demand curve of P = 30 - 2Q, where Q is measured in hundreds of pizzas per week and P is the price per pizza. The marginal cost per pizza is $6. What price should Pizza Plus charge per pizza to maximize profit?
A) $18
B) $16
C) $14
D) $12
A) $18
B) $16
C) $14
D) $12

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Consider two firms engaged in Bertrand competition with differentiated goods and zero marginal costs. Firm A's demand curve: qA = 120 - 3PA + 2PB
Firm B's demand curve: qB = 120 - 3PB + 2PA
In a Nash equilibrium, what is each firm's price?
A) PA = $5; PB = $5
B) PA = $10; PB = $10
C) PA = $30; PB = $30
D) PA = $20; PB = $20
Firm B's demand curve: qB = 120 - 3PB + 2PA
In a Nash equilibrium, what is each firm's price?
A) PA = $5; PB = $5
B) PA = $10; PB = $10
C) PA = $30; PB = $30
D) PA = $20; PB = $20

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Use the following to answer question:
Figure 11.6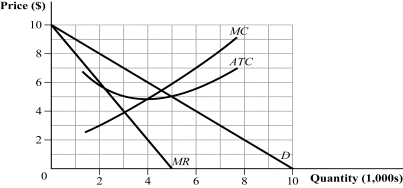
(Figure 11.6) The graph depicts a monopolistically competitive firm. The firm's current economic profit is _____, and its long-run economic profit is _____.
A) $6,000; $0
B) $4,000; $0
C) $2,000; $2,500
D) $4,000; $3,000
Figure 11.6

(Figure 11.6) The graph depicts a monopolistically competitive firm. The firm's current economic profit is _____, and its long-run economic profit is _____.
A) $6,000; $0
B) $4,000; $0
C) $2,000; $2,500
D) $4,000; $3,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Consider two firms engaged in Bertrand competition with differentiated goods and zero marginal costs. Firm A's demand curve is qA = 60 - 0.50PA + 0.40PB.
Firm B's demand curve is qB = 72 - 0.50PB + 0.40PA.
In a Nash equilibrium, approximately how much profit does Firm A earn?
A) $4,800
B) $3,210
C) $6,040
D) $5,588
Firm B's demand curve is qB = 72 - 0.50PB + 0.40PA.
In a Nash equilibrium, approximately how much profit does Firm A earn?
A) $4,800
B) $3,210
C) $6,040
D) $5,588

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The inverse market demand curve for American alligators is P = 4,000 - 2Q, where Q is the quantity of alligators and P is the market price. American alligators can be produced at a constant marginal cost of $1,000, and all American alligators are identical. 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
Answer the following questions. 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A monopolistically competitive firm faces the inverse demand curve P = 100 - Q, and its marginal cost is constant at $20. The firm is in long-run equilibrium. 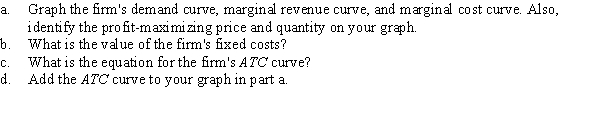
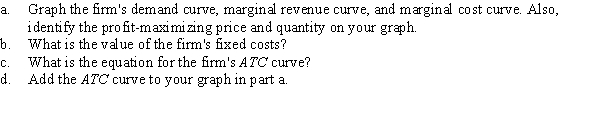

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
Two firms, Aero and Pareto, produce parachutes. Aero faces the demand curve qA = 4,000 - 2PA + PP, and Pareto faces the demand curve qB = 4,000 - 2PP + PA. Aero's output, qA, is sold at a price of PA. Pareto's output, qP, is sold at a price of Pp. The firms' parachutes are differentiated. For simplicity, assume marginal costs are zero. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
Two firms are producing identical goods in a market characterized by the inverse demand curve P = 120 - 4Q, where Q is the sum of Firm 1's and Firm 2's output, q1 + q2. Each firm's marginal cost is constant at $20. Graph the reaction function for each firm and indicate the Nash equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
Suppose two Bertrand firms produce similar but not identical products. Their demand curves follow.
Firm A: qA = 10 - 3PA + PB
Firm B: qB = 10 - 3PB + PA
Assume that marginal cost is zero for both firms.
Firm A: qA = 10 - 3PA + PB
Firm B: qB = 10 - 3PB + PA
Assume that marginal cost is zero for both firms.
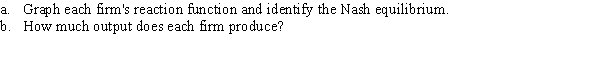

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
Two firms that are Bertrand competitors are producing differentiated goods at a marginal cost of zero. The demand curves facing each firm are as follows:
q1 = 72 - 6P1 + 4P2
q2 = 72 - 6P2 + 4P1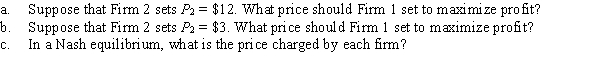
q1 = 72 - 6P1 + 4P2
q2 = 72 - 6P2 + 4P1
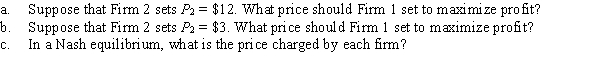

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
The inverse market demand curve is P = 260 - Q, where Q is the output of Firm 1 and Firm 2, q1 + q2. The output of the two firms is identical. 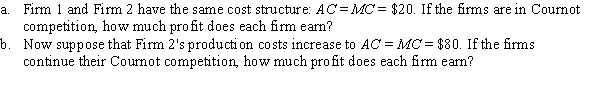
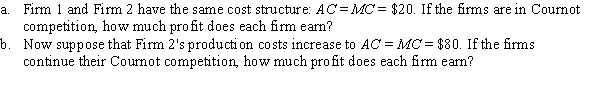

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
Dagger and Jackson offer different types of kayak tours, competing on price. Dagger faces qD = 1,000 - 20pD + 5pJ and constant marginal costs of $30. Jackson faces qJ = 1,000 - 20pJ + 5pD and constant marginal costs of $45. If Jackson charges $50 per kayak tour, then Dagger should charge _____ per kayak tour.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Coca Cola and Polar soda companies are engaged in Stackelberg competition. They face the market inverse demand curve P = 200 - 4Q, where Q is the total market output consisting of Coke's output, q1, and Polar's output, q2. Each firm produces at a constant marginal cost of $10. In a Stackleberg equilibrium, Coca Cola will produce _____ cans of soda while Polar will produce _____ cans of soda.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
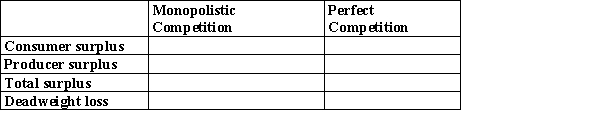
The graph depicts a monopolistically competitive firm in the short run. Complete the following table: 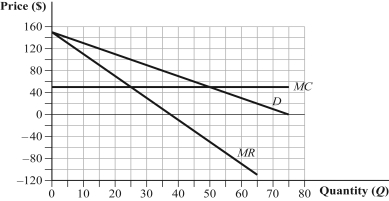



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Two firms are producing identical goods in a market characterized by the inverse demand curve P = 60 - 2Q, where Q is the sum of Firm 1's and Firm 2's output, q1 + q2. Each firm's marginal cost is constant at $12, and fixed costs are zero. Answer the following questions, assuming that the firms are Cournot competitors. 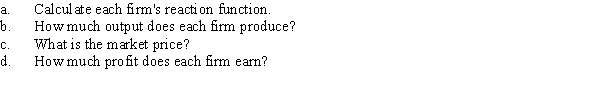

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Majestic Manicures operates in a monopolistically competitive market. Its inverse demand curve is P = 85 - 4Q, where Q is the number of daily manicures and P is the price per manicure. The total cost of providing manicures is TC = 13Q and marginal cost is $13. 

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The Tavern restaurant operates in a monopolistically competitive industry with an inverse demand curve of P = 60 - 10Q, where Q is measured in hundreds of patrons served per week and P is the average price per meal. The marginal cost per meal is $10. What price per meal should the Tavern charge to maximize profit?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Two companies are the only snowplow merchants in a small town. Inverse market demand curve is P = 100 - 10Q, where Q = q1 + q2. (Firm 1's output = q1; Firm 2's output = q2.) Each firm has marginal costs of $25. What is the Nash equilibrium in this market?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
In Stackelberg competition, the market inverse demand curve is P = a - bq1 - bq2, where q1 + q2 is the market output, Q, produced by Firm 1 and Firm 2. Marginal cost is given by MC = c. If Firm 1 chooses its output level before Firm 2, how much output will Firm 1 produce? (Hint: Your answer should have q1 as a function of the parameters a, b, and c.)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Use the following to answer question:
Figure 11.7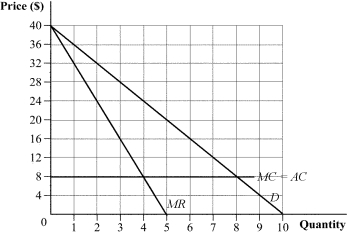
(Figure 11.7) The graph shows the market demand curve. What are the equilibrium price and market output under the following market structures?
a. a two-firm cartel
b. Bertrand competition with identical goods
c. Cournot duopoly with identical goods
Figure 11.7

(Figure 11.7) The graph shows the market demand curve. What are the equilibrium price and market output under the following market structures?
a. a two-firm cartel
b. Bertrand competition with identical goods
c. Cournot duopoly with identical goods

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Consider the market for vegan soup. Two firms, Kibble and Flesh Not, are in Stackelberg competition. Flesh Not observes Kibble's output level before choosing its desired output level. The market inverse demand curve for vegan soup is P = 18 - Q, where Q measures cups of soup produced by Kibble and Flesh Not, qK and qF, and P is the price per cup. Kibble and Flesh Not produce soup at a constant marginal cost of $2. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Dagger and Jackson offer different types of kayak tours, competing on price. Dagger faces qD = 1,000 - 20pD + 5pJ and constant marginal costs of $30. Jackson faces qJ = 1,000 - 20pJ + 5pD and constant marginal costs of $45. Graph the reaction function for each firm and indicate the Nash equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An industry faces the demand curve Q = 400 - 4P, where each firm produces an identical good at a constant marginal cost of $10. What are the Bertrand equilibrium price and quantity?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 99 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



