Deck 22: Accounting for Influential Investments
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/13
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 22: Accounting for Influential Investments
1
Company P acquired 30% of Company S's common stock on January 1, 20X8, for $100,000. Company P's 30% interest constitutes significant influence. There is no excess of cost over book value. During 20X8, Company S earned $40,000 and paid dividends of $25,000. During 20X9, Company S's $50,000 income was earned evenly, and the company paid dividends of $15,000 on April 1 and $15,000 on October 1. On July 1, 20X9, Company P sold half of its interest in Company S for $66,000 cash; thus, Company P no longer had significant influence The gain on the sale of the investment in Company P's 20X9 income statement should be ____.
A)$16,000
B)$13,700
C)$12,250
D)$10,000
A)$16,000
B)$13,700
C)$12,250
D)$10,000
C
 The gain on the sale is $12,250 (66,000 - 53,750)
The gain on the sale is $12,250 (66,000 - 53,750)
 The gain on the sale is $12,250 (66,000 - 53,750)
The gain on the sale is $12,250 (66,000 - 53,750) 2
If the market value of an equity method investment falls below its book value:
A)it is accounted for at the lower of cost or market so an adjustment is made whenever this occurs.
B)it is written down, but when the value rebounds, it is readjusted to its original value.
C)it is written down if the decline is considered permanent in nature with no subsequent increase in value.
D)it is written down if the decline is considered permanent in nature with no subsequent increase in value other than regular equity method adjustments.
A)it is accounted for at the lower of cost or market so an adjustment is made whenever this occurs.
B)it is written down, but when the value rebounds, it is readjusted to its original value.
C)it is written down if the decline is considered permanent in nature with no subsequent increase in value.
D)it is written down if the decline is considered permanent in nature with no subsequent increase in value other than regular equity method adjustments.
D
If the market value of an equity method investment falls below its book value, it is written down if the decline is considered permanent with no subsequent increase in value other than regular equity method adjustments.
If the market value of an equity method investment falls below its book value, it is written down if the decline is considered permanent with no subsequent increase in value other than regular equity method adjustments.
3
Per the FASB, all but the following are characteristics of an influential investment:
A)Representation on the board of directors.
B)A significant portion of the stock is owned (perhaps 45%), with other ownership interests being widely scattered.
C)Technological dependency.
D)Material intercompany transactions.
A)Representation on the board of directors.
B)A significant portion of the stock is owned (perhaps 45%), with other ownership interests being widely scattered.
C)Technological dependency.
D)Material intercompany transactions.
B
Even if the investor owns less than 50% of the investee's outstanding stock, if a significant portion of stock is owned and the other ownership interests are widely scattered, it is possible that the investor exercises control.
Even if the investor owns less than 50% of the investee's outstanding stock, if a significant portion of stock is owned and the other ownership interests are widely scattered, it is possible that the investor exercises control.
4
Company P Company uses the equity method to account for its January 1, 20X1, purchase of 30% of Company S's common stock. On January 1, 20X1, the market values of Company S's FIFO inventory and land exceed their book values. How do these excesses of market values over book values affect Company P's reported equity in Company S's 20X1 earnings? 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
On January 1, 20X3, Company P purchased a 15% interest in Company S. On July 1, 20X6, Company P purchased an additional 20% interest in Company S. Both purchases were at a cost in excess of underlying book value. Company S paid dividends each December from 20X3 to 20X6.
Required:
a.How would Company P record its investment in Company S in its financial statements originally issued for 20X3 to 20X5?
b.Does a 35% ownership interest absolutely require the use of the equity method?
c.How will Company P account for its investment in Company S in its 20X6 financial statements?
d.How will Company P account for its investment in Company S in the 20X3 to 20X6 comparative statements published in March 20X7?
Required:
a.How would Company P record its investment in Company S in its financial statements originally issued for 20X3 to 20X5?
b.Does a 35% ownership interest absolutely require the use of the equity method?
c.How will Company P account for its investment in Company S in its 20X6 financial statements?
d.How will Company P account for its investment in Company S in the 20X3 to 20X6 comparative statements published in March 20X7?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Under the equity method of accounting, items affecting the investment income account include all but the investor's portion of:
A)the investee's net income.
B)any intercompany profits in inventory.
C)the investee company's dividends.
D)the amortization of the excesses of the price over the book value of the investment.
A)the investee's net income.
B)any intercompany profits in inventory.
C)the investee company's dividends.
D)the amortization of the excesses of the price over the book value of the investment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Company P uses the sophisticated equity method of accounting for its 30% investment in Company S's common stock. During 20X9, Company S reported net earnings of $650,000 and paid dividends of $150,000. Assume that all the undistributed earnings of Company S will be distributed as dividends in future periods. The dividends received from Company S are eligible for the 80% dividends received deduction. Company P's 20X9, tax rate is 30%. In its December 31, 20X9, balance sheet, the increase in the deferred tax liability from these transactions would be ____.
A)$7,500
B)$9,000
C)$150,000
D)$30,000
A)$7,500
B)$9,000
C)$150,000
D)$30,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Assume that Company P purchases a 10% common stock interest in Company S for $12,000 on January 1, 20X2, and an additional 20% interest on January 1, 20X3, for $26,000. There was no excess of cost or book value on either investment. The balance sheets of Company, S which pays no dividends, follow: 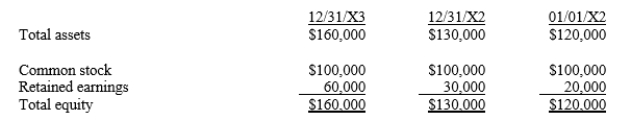 For 20X3, Company P reports investment income of ____.
For 20X3, Company P reports investment income of ____.
A)$18,000
B)$12,000
C)$9,000
D)$6,000
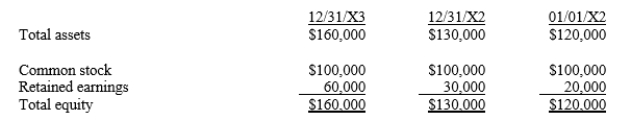 For 20X3, Company P reports investment income of ____.
For 20X3, Company P reports investment income of ____.A)$18,000
B)$12,000
C)$9,000
D)$6,000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Company P owns a 30% interest in Company S and accounts for the investment under the sophisticated equity method. The investment was purchased at underlying book value, and there is no excess of cost or book value. Company S sells merchandise to Company P at cost plus 25%. Intercompany sales during 20X1 were $100,000. There were $20,000 worth of such goods in Company P's beginning inventory and $30,000 worth of such goods in Company P's ending inventory. Company S's reported income for 20X1 is $40,000, and no dividends were paid. What amount will Company P record as investment income in 20X1?
A)$12,000
B)$11,400
C)$9,750
D)$4,500
A)$12,000
B)$11,400
C)$9,750
D)$4,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
All but the following are required disclosures for equity method investors:
A)Percentage of ownership in the investment.
B)Underlying book value of the investment.
C)The market value of the investment, if available.
D)All of these items are required disclosures.
A)Percentage of ownership in the investment.
B)Underlying book value of the investment.
C)The market value of the investment, if available.
D)All of these items are required disclosures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Company P purchased a 30% interest in Company S on January 1, 20X1, for $100,000. The price was equal to the book value of the equity acquired. The reported income (loss) and dividends paid by the Company S are as follows:  Investment income reported in 20X4 under the sophisticated equity method would be ____.
Investment income reported in 20X4 under the sophisticated equity method would be ____.
A)$15,000
B)$13,500
C)$4,000
D)$0
 Investment income reported in 20X4 under the sophisticated equity method would be ____.
Investment income reported in 20X4 under the sophisticated equity method would be ____.A)$15,000
B)$13,500
C)$4,000
D)$0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Company P purchased a 30% interest in Company S for $120,000 on January 1, 20X7, when Company S had the following stockholders' equity: 
Any excess cost was due to equipment that is being depreciated over 5 years using straight-line depreciation.
Since the investment, Company P has consistently sold goods to Company S to realize a 30% gross profit. Such sales totaled $50,000 during 20X9. Company S had $10,000 of such goods in its beginning inventory and $40,000 in its ending inventory.
On January 1, 20X9, Company S sold a machine with a book value of $15,000 to Company P for $30,000. The machine has a 5-year life and is being depreciated on a straight-line basis.
Company S reported income of $75,000 before taxes for 20X9. Both firms are subject to a 30% corporate tax rate. Company S paid no dividends in 20X9. An 80% dividend earned exclusion rate applies.
Required:
Prepare all entries caused by Company P's investment in Company S for 20X9 (including tax ramifications). Assume that Company P has recorded the tax on its internally generated income. Company P has properly recorded the investment in previous periods. Assume that sufficient previously recorded tax liability exists to offset any deferred tax expense.

Any excess cost was due to equipment that is being depreciated over 5 years using straight-line depreciation.
Since the investment, Company P has consistently sold goods to Company S to realize a 30% gross profit. Such sales totaled $50,000 during 20X9. Company S had $10,000 of such goods in its beginning inventory and $40,000 in its ending inventory.
On January 1, 20X9, Company S sold a machine with a book value of $15,000 to Company P for $30,000. The machine has a 5-year life and is being depreciated on a straight-line basis.
Company S reported income of $75,000 before taxes for 20X9. Both firms are subject to a 30% corporate tax rate. Company S paid no dividends in 20X9. An 80% dividend earned exclusion rate applies.
Required:
Prepare all entries caused by Company P's investment in Company S for 20X9 (including tax ramifications). Assume that Company P has recorded the tax on its internally generated income. Company P has properly recorded the investment in previous periods. Assume that sufficient previously recorded tax liability exists to offset any deferred tax expense.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
On January 1, 20X1, Company P purchased a 30% interest in the Company S for $345,000. At that time, Company S had stockholders' equity of $1,000,000. Any excess cost over book value was attributed to a patent with a 15-year life. During 20X1, Company S earned $60,000 and paid dividends of $15,000. What is the balance in the investment account on December 31, 20X1, using the sophisticated equity method?
A)$363,000
B)$360,000
C)$355,500
D)$349,500
A)$363,000
B)$360,000
C)$355,500
D)$349,500

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 13 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



