Deck 2: Descriptive Statistics: Tabular and Graphical Displays
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/67
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 2: Descriptive Statistics: Tabular and Graphical Displays
1
The percent frequency of a class is computed by
A) multiplying the frequency by 100.
B) dividing the relative frequency by 100.
C) multiplying the relative frequency by 100.
D) dividing the frequency by 100.
A) multiplying the frequency by 100.
B) dividing the relative frequency by 100.
C) multiplying the relative frequency by 100.
D) dividing the frequency by 100.
multiplying the relative frequency by 100.
2
The most common graphical presentation of quantitative data is a
A) histogram.
B) bar chart.
C) dot plot.
D) pie chart.
A) histogram.
B) bar chart.
C) dot plot.
D) pie chart.
histogram.
3
A frequency distribution is a tabular summary of data showing the _____ of items in several classes.
A) fraction
B) percentage
C) relative percentage
D) number
A) fraction
B) percentage
C) relative percentage
D) number
number
4
In a cumulative frequency distribution, the last class will always have a cumulative frequency equal to
A) one.
B) 100%.
C) the total number of elements in the data set.
D) the class width.
A) one.
B) 100%.
C) the total number of elements in the data set.
D) the class width.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The sum of frequencies for all classes will always equal
A) 1.
B) the number of elements in a data set.
C) the number of classes.
D) a value between 0 and 1.
A) 1.
B) the number of elements in a data set.
C) the number of classes.
D) a value between 0 and 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A cumulative frequency distribution is
A) a tabular summary of a set of data showing the relative frequency.
B) a tabular summary of a set of data showing sums of frequencies.
C) a tabular summary of a set of data showing the frequency of items in each of several nonoverlapping classes.
D) a graphical device for presenting categorical data.
A) a tabular summary of a set of data showing the relative frequency.
B) a tabular summary of a set of data showing sums of frequencies.
C) a tabular summary of a set of data showing the frequency of items in each of several nonoverlapping classes.
D) a graphical device for presenting categorical data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The total number of data items with a value less than the upper limit for the class is given by the _____ distribution.
A) frequency
B) relative frequency
C) cumulative frequency
D) cumulative relative frequency
A) frequency
B) relative frequency
C) cumulative frequency
D) cumulative relative frequency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The relative frequency of a class is computed by
A) dividing the midpoint of the class by the sample size.
B) dividing the frequency of the class by the midpoint.
C) dividing the sample size by the frequency of the class.
D) dividing the frequency of the class by the sample size.
A) dividing the midpoint of the class by the sample size.
B) dividing the frequency of the class by the midpoint.
C) dividing the sample size by the frequency of the class.
D) dividing the frequency of the class by the sample size.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
In a cumulative percent frequency distribution, the last class will have a cumulative percent frequency equal to
A) one.
B) 100.
C) the total number of elements in the data set.
D) None of these alternatives is correct.
A) one.
B) 100.
C) the total number of elements in the data set.
D) None of these alternatives is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A cumulative relative frequency distribution shows
A) the proportion of data items with values less than or equal to the upper limit of each class.
B) the proportion of data items with values less than or equal to the lower limit of each class.
C) the percentage of data items with values less than or equal to the upper limit of each class.
D) the percentage of data items with values less than or equal to the lower limit of each class.
A) the proportion of data items with values less than or equal to the upper limit of each class.
B) the proportion of data items with values less than or equal to the lower limit of each class.
C) the percentage of data items with values less than or equal to the upper limit of each class.
D) the percentage of data items with values less than or equal to the lower limit of each class.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A tabular summary of a set of data showing the fraction of the total number of items in several classes is a _____ distribution.
A) frequency
B) relative frequency
C) cumulative relative frequency
D) cumulative frequency
A) frequency
B) relative frequency
C) cumulative relative frequency
D) cumulative frequency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
In a cumulative relative frequency distribution, the last class will have a cumulative relative frequency equal to
A) one.
B) 100%.
C) the total number of elements in the data set.
D) the total of classes in the data set.
A) one.
B) 100%.
C) the total number of elements in the data set.
D) the total of classes in the data set.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The sum of the relative frequencies for all classes will always equal
A) the sample size.
B) 100%.
C) one.
D) any value larger than one.
A) the sample size.
B) 100%.
C) one.
D) any value larger than one.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The relative frequency of a class is computed by
A) dividing the cumulative frequency of the class by the total number of elements in the data set.
B) dividing n by cumulative frequency of the class.
C) dividing the frequency of the class by the total number of elements in the data set.
D) dividing the frequency of the class by the number of classes.
A) dividing the cumulative frequency of the class by the total number of elements in the data set.
B) dividing n by cumulative frequency of the class.
C) dividing the frequency of the class by the total number of elements in the data set.
D) dividing the frequency of the class by the number of classes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The difference between consecutive lower class or upper class limits of adjacent classes provides the
A) number of classes.
B) class limits.
C) class midpoint.
D) class width.
A) number of classes.
B) class limits.
C) class midpoint.
D) class width.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Data that provide labels or names for categories of like items are known as _____ data.
A) categorical
B) quantitative
C) labeled
D) qualitative
A) categorical
B) quantitative
C) labeled
D) qualitative

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The sum of the percent frequencies for all classes will always equal
A) one.
B) the number of classes.
C) the number of elements in the study.
D) 100.
A) one.
B) the number of classes.
C) the number of elements in the study.
D) 100.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
In a scatter diagram, a line that provides an approximation of the relationship between the variables is known as a _____ line.
A) determination
B) trend
C) control
D) zero-bias
A) determination
B) trend
C) control
D) zero-bias

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A histogram is
A) a graphical presentation of a frequency or relative frequency distribution.
B) a graphical method of presenting a cumulative frequency or a cumulative relative frequency distribution.
C) the history of data elements.
D) the same as a pie chart.
A) a graphical presentation of a frequency or relative frequency distribution.
B) a graphical method of presenting a cumulative frequency or a cumulative relative frequency distribution.
C) the history of data elements.
D) the same as a pie chart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Fifteen percent of the students in a school of Business Administration are majoring in Economics, 20% in Finance, 35% in Management, and 30% in Accounting.The graphical device(s) which can be used to present these data is (are)
A) a line chart.
B) only a bar chart.
C) only a pie chart.
D) both a bar chart and a pie chart.
A) a line chart.
B) only a bar chart.
C) only a pie chart.
D) both a bar chart and a pie chart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The numbers of hours worked (per week) by 400 statistics students are shown below.  The relative frequency of students working 0 - 9 hours per week is
The relative frequency of students working 0 - 9 hours per week is
A) .05
B) .20
C) .25
D) .50
 The relative frequency of students working 0 - 9 hours per week is
The relative frequency of students working 0 - 9 hours per week isA) .05
B) .20
C) .25
D) .50

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The frequency distribution below was constructed from data collected on the quarts of soft drinks consumed per week by 20 students. 
a.
Construct a relative frequency distribution.
b.
Construct a cumulative frequency distribution.
c.
Construct a cumulative relative frequency distribution.

a.
Construct a relative frequency distribution.
b.
Construct a cumulative frequency distribution.
c.
Construct a cumulative relative frequency distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
There are 800 students in the School of Business Administration.There are four majors in the School: Accounting, Finance, Management, and Marketing.The following shows the number of students in each major.  Develop a percent frequency distribution and construct a bar chart and a pie chart.
Develop a percent frequency distribution and construct a bar chart and a pie chart.
 Develop a percent frequency distribution and construct a bar chart and a pie chart.
Develop a percent frequency distribution and construct a bar chart and a pie chart.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The following data set shows the number of hours of sick leave that some of the employees of Bastien's, Inc.have taken during the first quarter of the year (rounded to the nearest hour). 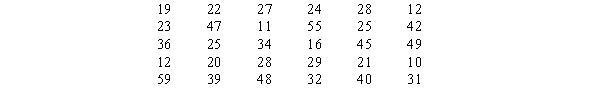
a.
Develop a frequency distribution for the above data.(Let the width of your classes be 10 units and start your first class as 10 - 19.)
b.
Develop a relative frequency distribution and a percent frequency distribution for the data.
c.
Develop a cumulative frequency distribution.
d.
How many employees have taken less than 40 hours of sick leave?

a.
Develop a frequency distribution for the above data.(Let the width of your classes be 10 units and start your first class as 10 - 19.)
b.
Develop a relative frequency distribution and a percent frequency distribution for the data.
c.
Develop a cumulative frequency distribution.
d.
How many employees have taken less than 40 hours of sick leave?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following graphical methods shows the relationship between two variables?
A) Pie chart
B) Histogram
C) Crosstabulation
D) Dot plot
A) Pie chart
B) Histogram
C) Crosstabulation
D) Dot plot

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
You are given the following data on the age of employees at a company.Construct a stem-and-leaf display. 


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The grades of 10 students in their first management test are shown below. 
a.
Construct a frequency distribution.Let the first class be 60 - 69.
b.
Construct a cumulative frequency distribution.
c.
Construct a relative frequency distribution.

a.
Construct a frequency distribution.Let the first class be 60 - 69.
b.
Construct a cumulative frequency distribution.
c.
Construct a relative frequency distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Below you are given the examination scores of 20 students. 
a.
Construct a frequency distribution for this data.Let the first class be 50 - 59.
b.
Construct a cumulative frequency distribution.
c.
Construct a relative frequency distribution.
d.
Construct a cumulative relative frequency distribution.

a.
Construct a frequency distribution for this data.Let the first class be 50 - 59.
b.
Construct a cumulative frequency distribution.
c.
Construct a relative frequency distribution.
d.
Construct a cumulative relative frequency distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The numbers of hours worked (per week) by 400 statistics students are shown below.  The midpoint of the third class is
The midpoint of the third class is
A) 25.5
B) 24.
C) 25.
D) 24.5.
 The midpoint of the third class is
The midpoint of the third class isA) 25.5
B) 24.
C) 25.
D) 24.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A sample of fifteen 7-year old boys shows their favorite superheroes:  Which of the following is the correct relative frequency for Spiderman?
Which of the following is the correct relative frequency for Spiderman?
A) .27
B) .5
C) .4
D) .6
 Which of the following is the correct relative frequency for Spiderman?
Which of the following is the correct relative frequency for Spiderman?A) .27
B) .5
C) .4
D) .6

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A survey of 800 college seniors resulted in the following crosstabulation regarding their undergraduate major and whether or not they plan to go to graduate school.  Of those students who are majoring in engineering, what percentage plans to go to graduate school?
Of those students who are majoring in engineering, what percentage plans to go to graduate school?
A) 28.77
B) 10.5
C) 40.38
D) 71.23
 Of those students who are majoring in engineering, what percentage plans to go to graduate school?
Of those students who are majoring in engineering, what percentage plans to go to graduate school?A) 28.77
B) 10.5
C) 40.38
D) 71.23

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A sample of fifteen 7-year old boys shows their favorite superheroes:  Which of the following is the correct frequency distribution?
Which of the following is the correct frequency distribution?
A) Spiderman 4, Batman 3, Iron Man 1, Aquaman 4, Captain America 3, Superman 1
B) Spiderman 6, Batman 2, Iron Man 2, Aquaman 2, Captain America 2, Superman 1
C) Spiderman 6, Batman 1, Iron Man 3, Aquaman 1, Captain America 2, Superman 2
D) None of these alternatives is correct.
 Which of the following is the correct frequency distribution?
Which of the following is the correct frequency distribution?
A) Spiderman 4, Batman 3, Iron Man 1, Aquaman 4, Captain America 3, Superman 1
B) Spiderman 6, Batman 2, Iron Man 2, Aquaman 2, Captain America 2, Superman 1
C) Spiderman 6, Batman 1, Iron Man 3, Aquaman 1, Captain America 2, Superman 2
D) None of these alternatives is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A sample of fifteen 7-year old boys shows their favorite superheroes:  Which of the following is the correct percent frequency for Spiderman?
Which of the following is the correct percent frequency for Spiderman?
A) 10%
B) 27%
C) 2%
D) 40%
 Which of the following is the correct percent frequency for Spiderman?
Which of the following is the correct percent frequency for Spiderman?A) 10%
B) 27%
C) 2%
D) 40%

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The numbers of hours worked on homework (per week) by 400 statistics students are shown below.  The class width used in this frequency distribution is
The class width used in this frequency distribution is
A) 2.
B) 2.5.
C) 4.
D) 5.
 The class width used in this frequency distribution is
The class width used in this frequency distribution isA) 2.
B) 2.5.
C) 4.
D) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The numbers of hours worked (per week) by 400 statistics students are shown below.  The cumulative percent frequency for students working 10 or more hours per week is
The cumulative percent frequency for students working 10 or more hours per week is
A) 20%.
B) 25%.
C) 80%.
D) 95%.
 The cumulative percent frequency for students working 10 or more hours per week is
The cumulative percent frequency for students working 10 or more hours per week isA) 20%.
B) 25%.
C) 80%.
D) 95%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Thirty students in the School of Business were asked what their majors were.The following represents their responses (M = Management; A = Accounting; E = Economics; O = Others). 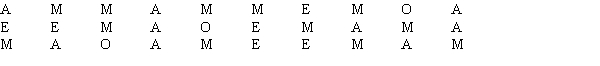
a.
Construct a frequency distribution and a bar chart.
b.
Construct a relative frequency distribution and a pie chart.
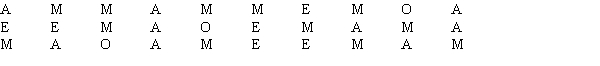
a.
Construct a frequency distribution and a bar chart.
b.
Construct a relative frequency distribution and a pie chart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A sample of the class sizes of 10 statistics classes at a university is shown below. 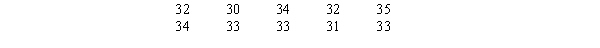
Construct a dot plot for the above data.
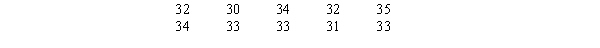
Construct a dot plot for the above data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The frequency distribution below was constructed from data collected from a group of 25 students. 
a.
Construct a relative frequency distribution.
b.
Construct a cumulative frequency distribution.
c.
Construct a cumulative relative frequency distribution.

a.
Construct a relative frequency distribution.
b.
Construct a cumulative frequency distribution.
c.
Construct a cumulative relative frequency distribution.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The numbers of hours worked (per week) by 400 statistics students are shown below.  The percentage of students who work at least 20 hours per week is
The percentage of students who work at least 20 hours per week is
A) 25%.
B) 50%.
C) 75%.
D) 100%.
 The percentage of students who work at least 20 hours per week is
The percentage of students who work at least 20 hours per week isA) 25%.
B) 50%.
C) 75%.
D) 100%.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is a graphical summary of a set of data in which each data value is represented by a dot above the axis?
A) Histogram
B) Pie chart
C) Dot plot
D) Crosstabulation
A) Histogram
B) Pie chart
C) Dot plot
D) Crosstabulation

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The proper way to construct a stem-and-leaf display for the data set {62, 67, 68, 73, 73, 79, 91, 94, 95, 97} is to
A) exclude a stem labeled '8.
B) include a stem labeled '8' and enter no leaves on the stem.
C) include a stem labeled '(8)' and enter no leaves on the stem.
D) include a stem labeled '8' and enter one leaf value of '0' on the stem.
A) exclude a stem labeled '8.
B) include a stem labeled '8' and enter no leaves on the stem.
C) include a stem labeled '(8)' and enter no leaves on the stem.
D) include a stem labeled '8' and enter one leaf value of '0' on the stem.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The test scores of 14 individuals on their first statistics examination are shown below. 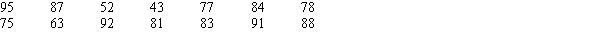
Construct a stem-and-leaf display for these data.
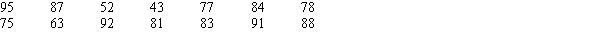
Construct a stem-and-leaf display for these data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A graphical method that can be used to show both the rank order and shape of a distribution of data simultaneously is a
A) relative frequency distribution.
B) pie chart.
C) stem-and-leaf display.
D) dot plot.
A) relative frequency distribution.
B) pie chart.
C) stem-and-leaf display.
D) dot plot.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
When the conclusions based upon the unaggregated data can be completely reversed if we look at the aggregated crosstabulation, the occurrence is known as
A) Reverse correlation.
B) Negative correlation.
C) Simpson's paradox.
D) Pareto's rule.
A) Reverse correlation.
B) Negative correlation.
C) Simpson's paradox.
D) Pareto's rule.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
A graphical presentation of the relationship between two quantitative variables is
A) dot plot.
B) histogram.
C) stem-and-leaf display.
D) scatter diagram.
A) dot plot.
B) histogram.
C) stem-and-leaf display.
D) scatter diagram.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The sales records of a real estate company for the month of May shows the following house prices (rounded to the nearest $1,000).Values are in thousands of dollars. 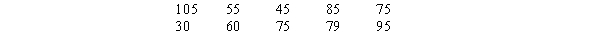
a.
Develop a frequency distribution and a percent frequency distribution for the house prices.(Use 5 classes and have your first class be 20 - 39.)
b.
Develop a cumulative frequency and a cumulative percent frequency distribution for the above data.
c.
What percentage of the houses are sold at a price below $80,000?
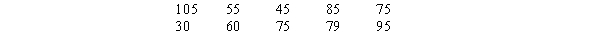
a.
Develop a frequency distribution and a percent frequency distribution for the house prices.(Use 5 classes and have your first class be 20 - 39.)
b.
Develop a cumulative frequency and a cumulative percent frequency distribution for the above data.
c.
What percentage of the houses are sold at a price below $80,000?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
Which of the following is not a recommended guideline for creating an effective graphical display?
A) Give the display a clear and concise title
B) Use three dimensions whenever possible, to give the display depth
C) If colors are used to distinguish categories, use a legend to define them
D) Label each axis and show the units of measure
A) Give the display a clear and concise title
B) Use three dimensions whenever possible, to give the display depth
C) If colors are used to distinguish categories, use a legend to define them
D) Label each axis and show the units of measure

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If several frequency distributions are constructed from the same data set, the distribution with the widest class width will have the
A) fewest classes.
B) most classes.
C) smallest total frequency.
D) largest total frequency.
A) fewest classes.
B) most classes.
C) smallest total frequency.
D) largest total frequency.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
For stem-and-leaf displays where the leaf unit is not stated, the leaf unit is assumed to equal
A) 0.
B) -1.
C) 1.
D) 10.
A) 0.
B) -1.
C) 1.
D) 10.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Before drawing any conclusions about the relationship between two variables shown in a crosstabulation, you should
A) investigate whether any hidden variables could affect the conclusions.
B) construct a scatter diagram and find the trendline.
C) develop a relative frequency distribution.
D) construct a dot plot and look for significant gaps.
A) investigate whether any hidden variables could affect the conclusions.
B) construct a scatter diagram and find the trendline.
C) develop a relative frequency distribution.
D) construct a dot plot and look for significant gaps.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
The approximate class width for a frequency distribution involving quantitative data can be determined using the expression
A) mean frequency/total frequency.
B) total frequency/class midpoint.
C) range/desired number of classes.
D) desired number of classes/class midpoint.
A) mean frequency/total frequency.
B) total frequency/class midpoint.
C) range/desired number of classes.
D) desired number of classes/class midpoint.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Which of the following is least useful in making comparisons or showing the relationships of two variables?
A) Stacked bar chart
B) Stem-and-leaf display
C) Crosstabulation
D) Scatter diagram
A) Stacked bar chart
B) Stem-and-leaf display
C) Crosstabulation
D) Scatter diagram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In quality control applications, bar charts are used to identify the most important causes of problems.When the bars are arranged in descending order of height from left to right with the most frequently occurring cause appearing first, the bar chart is called a
A) Cause-and-effect diagram.
B) Ogive.
C) Pareto diagram.
D) Stacked bar chart.
A) Cause-and-effect diagram.
B) Ogive.
C) Pareto diagram.
D) Stacked bar chart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In a crosstabulation
A) both variables must be categorical.
B) both variables must be quantitative.
C) one variable must be categorical and the other must be quantitative.
D) either or both variables can be categorical or quantitative.
A) both variables must be categorical.
B) both variables must be quantitative.
C) one variable must be categorical and the other must be quantitative.
D) either or both variables can be categorical or quantitative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Which of the following types of data cannot be appropriately displayed by a histogram?
A) Frequency
B) Relative frequency
C) Cumulative frequency
D) Percent frequency
A) Frequency
B) Relative frequency
C) Cumulative frequency
D) Percent frequency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
A researcher is gathering data from four geographical areas designated: South = 1; North = 2; East = 3; West = 4.The designated geographical regions represent?
A) ?categorical data.
B) ?quantitative data.
C) ?crosstabular data.
D) ?either categorical or quantitative data.
A) ?categorical data.
B) ?quantitative data.
C) ?crosstabular data.
D) ?either categorical or quantitative data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A graphical tool typically associated with the display of key performance indicators is a
A) side-by-side bar chart.
B) stem-and-leaf display.
C) stacked bar chart.
D) data dashboard.
A) side-by-side bar chart.
B) stem-and-leaf display.
C) stacked bar chart.
D) data dashboard.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In a stem-and-leaf display,
A) a single digit is used to define each stem, and a single digit is used to define each leaf.
B) a single digit is used to define each stem, and one or more digits are used to define each leaf.
C) one or more digits are used to define each stem, and a single digit is used to define each leaf.
D) one or more digits are used to define each stem, and one or more digits are used to define each leaf.
A) a single digit is used to define each stem, and a single digit is used to define each leaf.
B) a single digit is used to define each stem, and one or more digits are used to define each leaf.
C) one or more digits are used to define each stem, and a single digit is used to define each leaf.
D) one or more digits are used to define each stem, and one or more digits are used to define each leaf.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A graphical device for depicting categorical data that have been summarized in a frequency distribution, relative frequency distribution, or percent frequency distribution is a
A) histogram.
B) stem-and-leaf display.
C) dot plot.
D) bar chart.
A) histogram.
B) stem-and-leaf display.
C) dot plot.
D) bar chart.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
Data that indicate how much or how many are known as
A) categorical data.
B) quantitative data.
C) relative data.
D) cumulative data.
A) categorical data.
B) quantitative data.
C) relative data.
D) cumulative data.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
The numbers of hours worked (per week) by 400 statistics students are shown below.  The cumulative percent frequency for < 29 hours is
The cumulative percent frequency for < 29 hours is
A) 50.
B) 75.
C) 200.
D) 300.
 The cumulative percent frequency for < 29 hours is
The cumulative percent frequency for < 29 hours isA) 50.
B) 75.
C) 200.
D) 300.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A sample of 15 children shows their favorite kind of pet: 
Which of the following displays is most appropriate for this data?
A) Side-by-side bar chart
B) Histogram
C) Stacked bar chart
D) Pie chart

Which of the following displays is most appropriate for this data?
A) Side-by-side bar chart
B) Histogram
C) Stacked bar chart
D) Pie chart

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Histograms based on data on housing prices and salaries typically are
A) skewed to the left.
B) skewed to the right.
C) stacked.
D) symmetric.
A) skewed to the left.
B) skewed to the right.
C) stacked.
D) symmetric.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A sample of 15 children shows their favorite kind of pet: 
Which of the following distributions would be inappropriate for this data?
A) Frequency
B) Relative frequency
C) Cumulative frequency
D) Percent frequency

Which of the following distributions would be inappropriate for this data?
A) Frequency
B) Relative frequency
C) Cumulative frequency
D) Percent frequency

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A survey of 800 college seniors resulted in the following crosstabulation regarding their undergraduate major and whether or not they plan to go to graduate school.  Of those students who are planning on going to graduate school, what percentage are majoring in engineering?
Of those students who are planning on going to graduate school, what percentage are majoring in engineering?
A) 10.5
B) 28.8
C) 30.0
D) 40.4
 Of those students who are planning on going to graduate school, what percentage are majoring in engineering?
Of those students who are planning on going to graduate school, what percentage are majoring in engineering?A) 10.5
B) 28.8
C) 30.0
D) 40.4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A survey of 800 college seniors resulted in the following crosstabulation regarding their undergraduate major and whether or not they plan to go to graduate school.  The above crosstabulation shows
The above crosstabulation shows
A) frequencies.
B) row percentages.
C) column percentages.
D) overall percentages.
 The above crosstabulation shows
The above crosstabulation showsA) frequencies.
B) row percentages.
C) column percentages.
D) overall percentages.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A display used to compare the frequency, relative frequency or percent frequency of two categorical variables is a
A) scatter diagram.
B) stacked bar chart.
C) pie chart.
D) stem-and-leaf display.
A) scatter diagram.
B) stacked bar chart.
C) pie chart.
D) stem-and-leaf display.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 67 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



