Deck 5: Risk and Portfolio Management
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/54
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Risk and Portfolio Management
1
Inflation, which is a general decline in prices, is the source of financial risk.
False
2
In a world of certainty, there would be no risk.
True
3
Investors may reduce risk by constructing diversified portfolios but not eliminate risk.
True
4
Portfolio risk is the summation of business and financial risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A diversified portfolio requires the securities of at least fifty firms.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A portfolio consisting of securities whose returns are highly correlated is not truly diversified.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Unsystematic risk refers to factors that are unique to the specific asset.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Unsystematic risk considers how firms finance their assets and the nature of their operations.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
Investors seek to minimize risk for a given return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The informed investor can expect consistently to outperform the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Diversification reduces reinvestment rate risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Systematic risk is reduced through diversification.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
While diversification decreases risk, it also increases the chance of a large gain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The tendency of individual stock prices to move together is one source of systematic risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The negative relationship between interest rates and securities prices is the source of interest rate risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The dispersion around a stock's return is one measure of risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Investors must bear the systematic risk associated with fluctuating securities prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Exchange rate risk refers to fluctuations in the prices of foreign currencies (i.e., foreign exchange).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
Reinvestment rate risk results from higher stock prices in the future.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
By accepting more risk, the investor will increase the realized return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Exchange rate risk refers to fluctuations ina. the prices of stocks on the New York Stock Exchangeb. the values of bonds and other debt instrumentsc. the price of one currency relative to other currenciesd. a decline in the value of an investor's portfolio when securities are sold

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
During a rising market, stocks with greater beta coefficients may be preferred.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Unsystematic risk is
A) the risk associated with movements in stock prices
B) reduced through diversification
C) higher when interest rates rise
D) the risk of loss of purchasing power
A) the risk associated with movements in stock prices
B) reduced through diversification
C) higher when interest rates rise
D) the risk of loss of purchasing power

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Unsystematic risk
A) is increased through diversification
B) is reduced when markets fluctuate less
C) is affected by the nature of how a firm finances its operations
D) increases during periods of volatile interest rates
A) is increased through diversification
B) is reduced when markets fluctuate less
C) is affected by the nature of how a firm finances its operations
D) increases during periods of volatile interest rates

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
If a beta coefficient is 1.7, that implies the return on the stock tends to be less volatile than the return on the market.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If a stock has a beta of 1.0, it is risk free stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The numerical value of beta for the market equals 1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The expected return on an investment in stock is
A) the expected dividend payments
B) the anticipated capital gains
C) the sum of expected dividends and capital gains
D) less than the realized return
A) the expected dividend payments
B) the anticipated capital gains
C) the sum of expected dividends and capital gains
D) less than the realized return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Diversification reduces
A) systematic risk
B) unsystematic risk
C) market risk
D) purchasing power risk
A) systematic risk
B) unsystematic risk
C) market risk
D) purchasing power risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Sources of risk to an investor include1. loss when funds are reinvested at lower rates2. fluctuations in securities markets3. the financing decisions of the firm
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The "efficient frontier" relates all the combinations of risk and return that represent the same level of satisfaction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Portfolios that offer the highest return for a givenlevel of risk are "efficient."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Low beta stocks tend to generate higher returns in rising markets.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Sources of unsystematic risk include1. the firm's financing decisions2. the firm's operations3. fluctuating market prices
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
If a stock's return has a large standard deviation, that suggests the stock has little risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A portfolio's beta coefficient tends to be stable over time.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If the return on two stocks is highly and positivelycorrelated , combining these stocks will reduce the risk associated with the portfolio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
The beta of a portfolio is a weighted average of each asset's beta coefficient.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
Arbitrage pricing theory is a multi-variable model used to explain securities returns.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Arbitrage is the act of buying a high priced asset in one market and simultaneously selling it in another market at a lower price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The security market line does not
A) indicate the relationship between risk and return
B) relate the market return and beta to a stock's return
C) identify the optimal portfolio for the investor
D) use beta coefficients as a measure of risk
A) indicate the relationship between risk and return
B) relate the market return and beta to a stock's return
C) identify the optimal portfolio for the investor
D) use beta coefficients as a measure of risk

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Portfolio risk encompasses1. a firm's financing decisions2. interest rate risk3. loss of purchasing power
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Beta coefficients1. are a measure of systematic risk2. relate the return on an individual security tothe return on the market3. measure the variability of as asset's return
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Investors who want to bear less risk should acquirestocks whose beta coefficients are
A) greater than 1.5
B) greater than 1.0
C) less than 1.0
D) less than 0.5
A) greater than 1.5
B) greater than 1.0
C) less than 1.0
D) less than 0.5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
An efficient portfolio1. maximizes risk for a given return2. minimizes risk for a given return3. maximizes return for a given level of risk4. minimizes return for a given level of risk
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
What is the expected return on a portfolio consisting of an equal amount invested in each stock  b. What is the expected return on the portfolio if 50 percent of the funds are invested in stock C, 30 percent in stock A, and 20 percent in Stock D
b. What is the expected return on the portfolio if 50 percent of the funds are invested in stock C, 30 percent in stock A, and 20 percent in Stock D
 b. What is the expected return on the portfolio if 50 percent of the funds are invested in stock C, 30 percent in stock A, and 20 percent in Stock D
b. What is the expected return on the portfolio if 50 percent of the funds are invested in stock C, 30 percent in stock A, and 20 percent in Stock D
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
For diversification to reduce risk,
A) the returns on the individual securities should be highly correlated
B) the prices of the stocks should be stable
C) the returns on the individual securities should be negatively correlated
D) one firm should offer dividends and the other should offer capital gains
A) the returns on the individual securities should be highly correlated
B) the prices of the stocks should be stable
C) the returns on the individual securities should be negatively correlated
D) one firm should offer dividends and the other should offer capital gains

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
Beta coefficients of 1.3 indicate
A) the stock has more unsystematic risk
B) the stock has less unsystematic risk
C) the stock is more volatile than the market
D) the stock is less volatile than the market
A) the stock has more unsystematic risk
B) the stock has less unsystematic risk
C) the stock is more volatile than the market
D) the stock is less volatile than the market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The efficient frontier in portfolio theory
A) indicates the highest return for a given risk
B) illustrates the optimal trade-off between long and short-term capital gains
C) quantifies systematic and unsystematic risk
D) identifies the optimal portfolio for the investor
A) indicates the highest return for a given risk
B) illustrates the optimal trade-off between long and short-term capital gains
C) quantifies systematic and unsystematic risk
D) identifies the optimal portfolio for the investor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
What is the expected return on a stock that pays a 4 percent annual dividend and whose price is expected to appreciate annually at 6 percent

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
If the dispersion around a stock's return increases
A) the expected return decreases
B) the standard deviation decreases
C) the stock's price increases
D) the stock's risk increases
A) the expected return decreases
B) the standard deviation decreases
C) the stock's price increases
D) the stock's risk increases

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
(This problem illustrates the computation of beta coefficients may be solved using a statistics program or Excel.) The returns on the market and stock A and stock B are as follows: 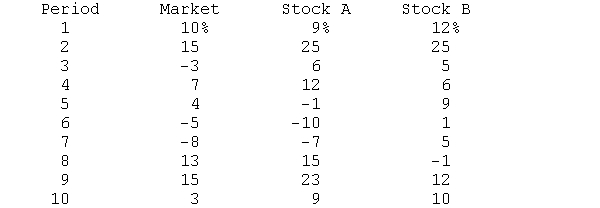 Compute the beta coefficient for each stock and interpret the results of the computations.
Compute the beta coefficient for each stock and interpret the results of the computations.
 Compute the beta coefficient for each stock and interpret the results of the computations.
Compute the beta coefficient for each stock and interpret the results of the computations.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Given the following information:  a. What are the expected returns and standard deviations of the following portfolios:1. 100 percent of funds invested in Stock A 2. 100 percent of funds invested in Stock B 3. 50 percent of funds invested in each stock b. What would be the impact if the correlation coefficient were 0.6 instead of 0.2
a. What are the expected returns and standard deviations of the following portfolios:1. 100 percent of funds invested in Stock A 2. 100 percent of funds invested in Stock B 3. 50 percent of funds invested in each stock b. What would be the impact if the correlation coefficient were 0.6 instead of 0.2
 a. What are the expected returns and standard deviations of the following portfolios:1. 100 percent of funds invested in Stock A 2. 100 percent of funds invested in Stock B 3. 50 percent of funds invested in each stock b. What would be the impact if the correlation coefficient were 0.6 instead of 0.2
a. What are the expected returns and standard deviations of the following portfolios:1. 100 percent of funds invested in Stock A 2. 100 percent of funds invested in Stock B 3. 50 percent of funds invested in each stock b. What would be the impact if the correlation coefficient were 0.6 instead of 0.2
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
According to the arbitrage pricing theory, the returnon a stock
A) is not related to the expected return on the stock
B) depends on the stock's responsiveness to unexpected changes
C) is reduced through the construction of diversified portfolios
D) equals the market return if the expected rate of inflation is realized
A) is not related to the expected return on the stock
B) depends on the stock's responsiveness to unexpected changes
C) is reduced through the construction of diversified portfolios
D) equals the market return if the expected rate of inflation is realized

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 54 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



