Deck 10: Investment Returns and Aggregate Measures of Stock Markets
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/42
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Investment Returns and Aggregate Measures of Stock Markets
1
Aggregate securities prices may be measured by using value weighted or geometric averages.
True
2
Studies of investment returns suggest that investors can expect to earn at least 15 percent annually.
False
3
Movements in stock prices are often illustrated using relative (percentage) price changes instead of absolute price changes.
True
4
With dollar cost averaging, the investor purchases more securities when their prices rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Averaging down will prove to be profitable only if the price of the stock subsequently rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The rate of return on a stock considers the price change but not dividend income.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The Dow Jones industrial and utility averages include a relatively small number of stocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Indices of Nasdaq stocks tend to be less volatile than the S&P 500 index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
The S&P 500 stock index is value-weighted.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Aggregate measures of stock prices include dividendincome.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Comparisons of stock performance should use percentage changes instead of absolute price changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Bond averages that are expressed in percentages are not comparable to the S&P 500.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Stock indices do not consider taxes on capital gains.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
If a stock increased from $25 to $50 in five years, the annual rate of return was 20 percent.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Historical studies of investment returns suggest that the stocks of small companies generate higher returns than the stocks of larger companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Realized returns should include both dividends and price changes.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Studies of investments returns (e.g., the Ibbotson Associates studies of investment returns) determined that large-cap stocks in the S&P earned higher returns than the smaller companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Dollar cost averaging is achieved by periodic, equaldollar investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The Russell 3000 is a broad-based measure of bond prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Averaging down may result in the investor sending good money after bad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
If a stock rose from $10 to $30 over ten years, theannual rate of return
A) was 20 percent
B) was greater than 20 percent
C) was less than 20 percent
D) cannot be determined
A) was 20 percent
B) was greater than 20 percent
C) was less than 20 percent
D) cannot be determined

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Studies of realized rates of return assume thatDividend income is not reinvested.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Which of the following is the least broad-basedmeasure of stock prices
A) Nasdaq market index
B) Dow Jones industrial average
C) S&P 500 stock index
D) Russell 3000
A) Nasdaq market index
B) Dow Jones industrial average
C) S&P 500 stock index
D) Russell 3000

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
The S&P 500 uses
A) a simple average
B) a compound average
C) a geometric average
D) a value-weighted average
A) a simple average
B) a compound average
C) a geometric average
D) a value-weighted average

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
You bought a stock for $20 and sold it for $59.72 after six years. What was the annual rate of return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
The calculation of a rate of return assumes dividendincome is reinvested at the current dividend yield.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
Given the following information concerning three stocks, construct a simple average, a value-weighted average, and a geometric average. 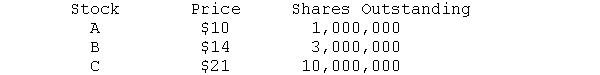 b. What are averages if each price rises to $11, $17, and $35, respectively c. What is the percentage increase in each average
b. What are averages if each price rises to $11, $17, and $35, respectively c. What is the percentage increase in each average
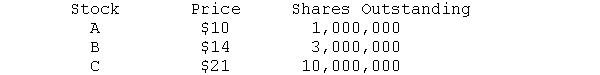 b. What are averages if each price rises to $11, $17, and $35, respectively c. What is the percentage increase in each average
b. What are averages if each price rises to $11, $17, and $35, respectively c. What is the percentage increase in each average
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Holding period returns for greater than a year do not give an accurate measure of the true rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The Wilshire 5000 stock index is more broad based than the S&P 500 stock index.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Movements in individual stock prices tend to be
A) positively correlated
B) positively correlated with inflation
C) negatively correlated
D) positively correlated with changes in interest rates
PROBLEMS
A) positively correlated
B) positively correlated with inflation
C) negatively correlated
D) positively correlated with changes in interest rates
PROBLEMS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
You bought a stock for $28.29 that paid the following dividendsYear 1 2 3Dividend $1.00 $1.50 $1.80After the third year, you sold the stock for $35. What was the annual rate of return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
To determine the realized return on an investment,the investor needs to know1. income received2. the cost of an investment3. the sale price of the investment
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Over time, holding period returns tend to overstatethe true annualized rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Dollar cost averaging is
A) periodically buying a round lot of stock
B) periodically investing a specified dollar amount in a stock
C) a means to increase the average cost basis
D) a means to insure a positive return
A) periodically buying a round lot of stock
B) periodically investing a specified dollar amount in a stock
C) a means to increase the average cost basis
D) a means to insure a positive return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A strategy of averaging down will be profitable if
A) the price of the stock continues to fall
B) the firm pays more dividends
C) the firm retains earnings
D) the price of the stock subsequently rises
A) the price of the stock continues to fall
B) the firm pays more dividends
C) the firm retains earnings
D) the price of the stock subsequently rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The S&P 500 stock index is more sensitive to changesin the prices of small stocks than the stocks of large companies.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
An investment's internal rate of return equates
A) dividend payments and capital gains
B) cash outflows and subsequent cash inflows
C) initial cash outflow and the sale price
D) dividend payments and the investment's cost
A) dividend payments and capital gains
B) cash outflows and subsequent cash inflows
C) initial cash outflow and the sale price
D) dividend payments and the investment's cost

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Historical studies of rates of return on largestocks suggest
A) the average return is about 6.4 percent annually
B) over a period of years, the rate approximates 9-10 percent
C) equity investors rarely sustain losses
D) dividends account for over half the return
A) the average return is about 6.4 percent annually
B) over a period of years, the rate approximates 9-10 percent
C) equity investors rarely sustain losses
D) dividends account for over half the return

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The Standard & Poor's 500 stock index illustrates
A) a value-weighted index
B) a simple average
C) a geometric index
D) an exponential index
A) a value-weighted index
B) a simple average
C) a geometric index
D) an exponential index

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The Russell 1000 index
A) combines 1000 stocks and bonds
B) uses the 1000 largest Nasdaq stocks
C) is a broad measure of listed and over-the-counter (Nasdaq) stocks
D) is a broad-based measure of bonds
A) combines 1000 stocks and bonds
B) uses the 1000 largest Nasdaq stocks
C) is a broad measure of listed and over-the-counter (Nasdaq) stocks
D) is a broad-based measure of bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The market consists of the following stocks. Their prices and number of shares are as follows: 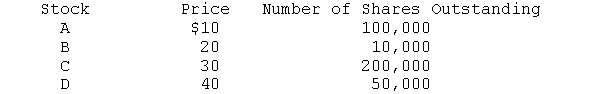
a. The price of Stock C doubles to $60. What is the percentage increase in the market if a S&P 500 type of measure of the market (value-weighted average) is used?
b. Repeat question (a) but use a Value Line type of measure of the market (i.e., a geometric average) to determine the percentage increase.
c. Suppose the price of stock B doubled instead of stock C. How would the market have fared using the aggregate measures employed in (a) and (b)? Why are your answers different?
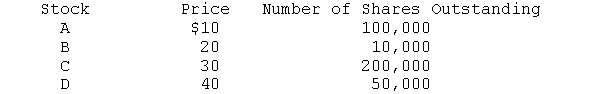
a. The price of Stock C doubles to $60. What is the percentage increase in the market if a S&P 500 type of measure of the market (value-weighted average) is used?
b. Repeat question (a) but use a Value Line type of measure of the market (i.e., a geometric average) to determine the percentage increase.
c. Suppose the price of stock B doubled instead of stock C. How would the market have fared using the aggregate measures employed in (a) and (b)? Why are your answers different?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
You sold 200 shares of DOG short for $24. After three years you closed your position at $17. DOG paid an annual dividend of $1, what was the annualized (compound) return on the trade SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 42 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



