Deck 19: Magnetism
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/105
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 19: Magnetism
1
An electron is traveling horizontally east in the magnetic field of Earth near the equator. The direction of the force on the electron is
A) zero.
B) north.
C) south.
D) upward.
E) downward.
A) zero.
B) north.
C) south.
D) upward.
E) downward.
downward.
2
An electron q = -1.6 × 10-19 C) is traveling east with an instantaneous velocity of 2.5 × 105 m/s when it enters a uniform magnetic field B of 0.45 T that points 35º north of east. What are the magnitude and direction of the force on the electron?
A) 1.8 × 10-14 N up
B) 1.5 × 10-14 N down
C) 1.5 × 10-14 N up
D) 1.0 × 10-14 N down
E) 1.0 × 10-14 N up
A) 1.8 × 10-14 N up
B) 1.5 × 10-14 N down
C) 1.5 × 10-14 N up
D) 1.0 × 10-14 N down
E) 1.0 × 10-14 N up
1.0 × 10-14 N down
3
If the magnetic field vector is directed toward the north and a negatively charged particle is moving toward the west, what is the direction of the magnetic force on the particle?
A) up
B) west
C) south
D) down
E) east
A) up
B) west
C) south
D) down
E) east
up
4
The phenomenon of magnetism is best understood in terms of
A) the existence of magnetic poles.
B) the magnetic fields associated with the motion of charged particles.
C) gravitational forces between nuclei and orbital electrons.
D) electrical fluids.
E) None of these is correct.
A) the existence of magnetic poles.
B) the magnetic fields associated with the motion of charged particles.
C) gravitational forces between nuclei and orbital electrons.
D) electrical fluids.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A positively charged particle is moving northward in a magnetic field. The magnetic force on the particle is toward the northeast. What is the direction of the magnetic field?
A) up
B) west
C) south
D) down
E) This situation cannot exist.
A) up
B) west
C) south
D) down
E) This situation cannot exist.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
Isolated magnetic poles
A) are readily available in nature.
B) cannot be found in nature.
C) are due to motion of isolated electric charges.
D) can be created by breaking a bar magnet in half.
E) are created by current carrying coils.
A) are readily available in nature.
B) cannot be found in nature.
C) are due to motion of isolated electric charges.
D) can be created by breaking a bar magnet in half.
E) are created by current carrying coils.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A charged particle is moving horizontally westward with a velocity of 3.5 × 106 m/s in a region where there is a magnetic field of magnitude 5.6 × 10-5 T directed vertically downward. The particle experiences a force of 7.8 × 10-16 N northward. What is the charge on the particle?
A) +4.0 × 10-18 C
B) -4.0 × 10-18 C
C) +4.9 × 10-5 C
D) -1.2 × 10-14 C
E) +1.4 × 10-11 C
A) +4.0 × 10-18 C
B) -4.0 × 10-18 C
C) +4.9 × 10-5 C
D) -1.2 × 10-14 C
E) +1.4 × 10-11 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The SI unit of magnetic field is the tesla T). This is equivalent to
A) N · s/C · m)
B) N · C/s · m)
C) N · m/s2
D) C/A · s)
E) None of these is correct.
A) N · s/C · m)
B) N · C/s · m)
C) N · m/s2
D) C/A · s)
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
An electron is traveling east with an instantaneous velocity of 3.3 × 105 m/s when it enters a uniform magnetic field of 0.25 T that points X degrees north of east. Take east as to the right of the paper and north as toward the top of the paper, i.e., both in the plane of the paper.) If the magnitude of the force on the electron is 5.5 × 10-15 N, then calculate the angle X and whether the electron moves up out of or down into the plane of the page, or otherwise.
A) 25° and up out of the page
B) 65° and down into the page
C) 25° and down into the page
D) 65° and up out of the page
E) 65° and south in the plane of the paper
A) 25° and up out of the page
B) 65° and down into the page
C) 25° and down into the page
D) 65° and up out of the page
E) 65° and south in the plane of the paper

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The region of space around a moving proton contains
A) a gravitational field only.
B) a magnetic field only.
C) an electric field only.
D) both an electric and a magnetic field.
E) neither an electric nor a magnetic field.
A) a gravitational field only.
B) a magnetic field only.
C) an electric field only.
D) both an electric and a magnetic field.
E) neither an electric nor a magnetic field.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A proton q = +1.6 × 10-19 C) is traveling east with an instantaneous velocity of 2.5 × 105 m/s when it enters a uniform magnetic field B of 0.45 T that points 35º north of east. What are the magnitude and direction of the force on the proton?
A) 1.8 × 10-14 N up
B) 1.5 × 10-14 N down
C) 1.5 × 10-14 N up
D) 1.0 × 10-14 N down
E) 1.0 × 10-14 N up
A) 1.8 × 10-14 N up
B) 1.5 × 10-14 N down
C) 1.5 × 10-14 N up
D) 1.0 × 10-14 N down
E) 1.0 × 10-14 N up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A proton is traveling horizontally east in the magnetic field of Earth near the equator. The direction of the force on the proton is
A) zero.
B) north.
C) south.
D) upward.
E) downward.
A) zero.
B) north.
C) south.
D) upward.
E) downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
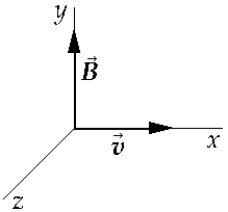 A neutron moving along the +x-axis with velocity v enters a region where there is a uniform magnetic field B along the +y-axis. As the neutron moves through this region, it is
A neutron moving along the +x-axis with velocity v enters a region where there is a uniform magnetic field B along the +y-axis. As the neutron moves through this region, it isA) deflected in the positive y direction.
B) deflected in the positive z direction.
C) deflected in the negative y direction.
D) deflected in the negative z direction.
E) undeviated in its motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements is false?
A) Electric field lines due to an electric dipole and magnetic field lines due a magnetic dipole have similar configuration.
B) Electric field lines starts from a positive charge and ends at a negative charge.
C) Magnetic field lines starts at the south pole and ends at the north pole.
D) Magnetic poles always occur in pairs.
E) Magnetic fields result from the motion of electric charges.
A) Electric field lines due to an electric dipole and magnetic field lines due a magnetic dipole have similar configuration.
B) Electric field lines starts from a positive charge and ends at a negative charge.
C) Magnetic field lines starts at the south pole and ends at the north pole.
D) Magnetic poles always occur in pairs.
E) Magnetic fields result from the motion of electric charges.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A uniform magnetic field of 200 T is directed vertically upward. The force on an electron q = -1.6 × 10-19 C) moving horizontally northward at 2.0 × 106 m/s is approximately
A) 4.0 × 108 N, east.
B) 24 × 108 N, west.
C) 6.4 × 10-11 N, west.
D) 6.4 × 10-11 N, east.
E) zero.
A) 4.0 × 108 N, east.
B) 24 × 108 N, west.
C) 6.4 × 10-11 N, west.
D) 6.4 × 10-11 N, east.
E) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
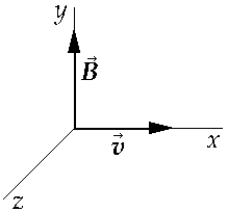 An electron moving along the +x-axis with velocity v enters a region where there is a uniform magnetic field B along the +y-axis. As the electron moves through this region, it is
An electron moving along the +x-axis with velocity v enters a region where there is a uniform magnetic field B along the +y-axis. As the electron moves through this region, it isA) deflected in the positive y direction.
B) deflected in the positive z direction.
C) deflected in the negative y direction.
D) deflected in the negative z direction.
E) undeviated in its motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
If the magnetic field vector is directed toward the north and a positively charged particle is moving toward the east, what is the direction of the magnetic force on the particle?
A) up
B) west
C) south
D) down
E) east
A) up
B) west
C) south
D) down
E) east

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
An alpha particle has a charge of +2e e = 1.6 × 10-19 C) and is moving at right angles to a magnetic field B = 0.27 T with a speed v = 6.15 × 105 m/s. The force acting on this charged particle is
A) zero.
B) 5.3 × 10-14 N.
C) 3.3 × 105 N.
D) 2.7 × 10-14 N.
E) 4.8 × 105 N.
A) zero.
B) 5.3 × 10-14 N.
C) 3.3 × 105 N.
D) 2.7 × 10-14 N.
E) 4.8 × 105 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A particle with charge q and mass m moving with speed v in the +x direction enters a magnetic field of strength B pointing in the +y direction. The magnitude of the acceleration of the particle as it travels one semicircle is
A) qvB/m.
B) mv2/2B.
C) qvB.
D) mqvB.
E) mv/qB.
A) qvB/m.
B) mv2/2B.
C) qvB.
D) mqvB.
E) mv/qB.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The magnetic force on a charged particle
A) depends on the sign of the charge on the particle.
B) depends on the velocity of the particle.
C) depends on the magnetic field at the particle's instantaneous position.
D) is at right angles to both the velocity of the particle and the direction of the magnetic field.
E) is described by all of these.
A) depends on the sign of the charge on the particle.
B) depends on the velocity of the particle.
C) depends on the magnetic field at the particle's instantaneous position.
D) is at right angles to both the velocity of the particle and the direction of the magnetic field.
E) is described by all of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
An alpha particle of charge +2e and mass 41.66 × 10-27) kg, and an 16O nucleus of charge +8e and mass 161.66 × 10-27) kg have been accelerated from rest through the same electric potential. They are then injected into a uniform magnetic field B, where both move at right angles to the field. The ratio of the radius of the path of the alpha particle to the radius of the path of the nucleus 16O is
A) r /rO = 1/1.
B) r /rO = 1/4.
C) r /rO = 1/8.
D) r /rO = 1/2.
E) None of these is correct.
A) r /rO = 1/1.
B) r /rO = 1/4.
C) r /rO = 1/8.
D) r /rO = 1/2.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A small positively charged body is moving horizontally and westward. If it enters a uniform horizontal magnetic field that is directed from north to south, the body is deflected
A) upward.
B) downward.
C) toward the north.
D) toward the south.
E) not at all.
A) upward.
B) downward.
C) toward the north.
D) toward the south.
E) not at all.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
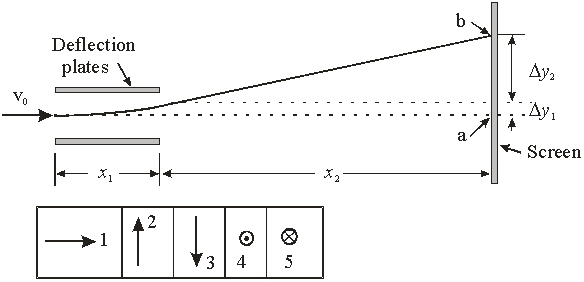 Electrons traveling at a speed of v0 = 3 × 107 m/s pass through the deflection plates. The electric field between the plates is E = 5000 V/m and spans a distance of x1 = 5 cm. The electrons then travel a further distance of x2 = 40 cm along the x-axis. What should the strength of the magnetic field be for the electrons to land at a?
Electrons traveling at a speed of v0 = 3 × 107 m/s pass through the deflection plates. The electric field between the plates is E = 5000 V/m and spans a distance of x1 = 5 cm. The electrons then travel a further distance of x2 = 40 cm along the x-axis. What should the strength of the magnetic field be for the electrons to land at a?A) 1.67 G
B) 3.33 G
C) 6000 G
D) 3000 G
E) 12000 G

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
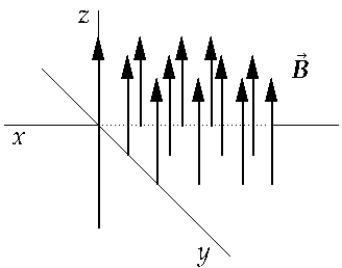 A uniform magnetic field is parallel to and in the direction of the positive z axis. For an electron to enter this field and not be deflected by the field, the electron must be traveling in which direction?
A uniform magnetic field is parallel to and in the direction of the positive z axis. For an electron to enter this field and not be deflected by the field, the electron must be traveling in which direction?A) Any direction as long as it is in the xy plane.
B) Any direction as long as it is in the xz plane.
C) Along the positive x-axis.
D) Along the positive y-axis.
E) Along the positive z-axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
A beam of electrons is undeflected when it passes simultaneously through an electric field of 10 N/C perpendicular to its path and a magnetic field of 2 × 10-4 T perpendicular both to its path and to the electric field. The speed of the electrons is approximately
A) 2 × 10-4 m/s.
B) 1 × 104 m/s.
C) 5 × 10-4 m/s.
D) 2 × 104 m/s.
E) 5 × 104 m/s.
A) 2 × 10-4 m/s.
B) 1 × 104 m/s.
C) 5 × 10-4 m/s.
D) 2 × 104 m/s.
E) 5 × 104 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
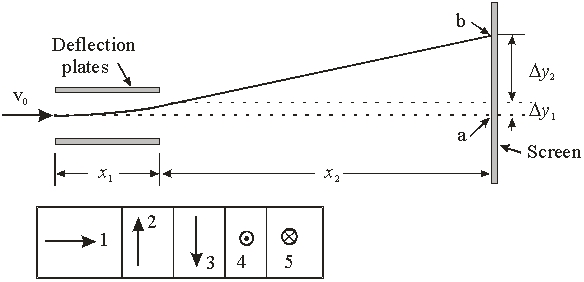 Electrons traveling at a speed of v0 = 3 × 107 m/s pass through the deflection plates. The electric field between the plates is E = 5000 V/m and spans a distance of x1 = 5 cm. The electrons then travel a further distance of x2 = 40 cm along the x-axis. In which direction should the magnetic field be applied so that the electron lands undeflected at a?
Electrons traveling at a speed of v0 = 3 × 107 m/s pass through the deflection plates. The electric field between the plates is E = 5000 V/m and spans a distance of x1 = 5 cm. The electrons then travel a further distance of x2 = 40 cm along the x-axis. In which direction should the magnetic field be applied so that the electron lands undeflected at a?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
All of the charged particles that pass through crossed electric and magnetic fields without deflection have the same
A) mass.
B) speed.
C) momentum.
D) energy.
E) charge-to-mass ratio.
A) mass.
B) speed.
C) momentum.
D) energy.
E) charge-to-mass ratio.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
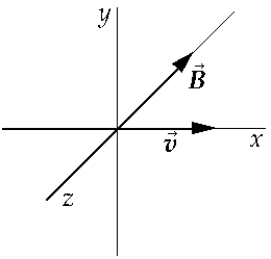 A positively charged particle moves with velocity v along the +x-axis. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the negative z direction. You want to balance the magnetic force with an electric field so that the particle will continue along a straight line. The electric field should be in the
A positively charged particle moves with velocity v along the +x-axis. A uniform magnetic field B exists in the negative z direction. You want to balance the magnetic force with an electric field so that the particle will continue along a straight line. The electric field should be in theA) positive x direction.
B) positive z direction.
C) negative y direction.
D) negative x direction.
E) negative z direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
 When a cathode-ray tube with its axis horizontal is placed in a magnetic field that is directed vertically upward, the electrons emitted from the cathode follow one of the dashed paths to the face of the tube. The correct path is
When a cathode-ray tube with its axis horizontal is placed in a magnetic field that is directed vertically upward, the electrons emitted from the cathode follow one of the dashed paths to the face of the tube. The correct path isA) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
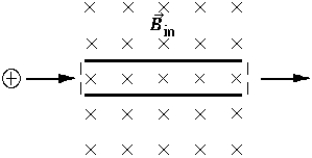 The apparatus in the figure consists of two parallel plates shown on edge) and a large magnet not shown). The field of the magnet is uniform, perpendicular to the electric field between the plates, and directed into the plane of the paper. The magnitude of B is 0.40 T. Charged particles with speeds of 5.0 × 105 m/s enter this region through the slit at the left and emerge through the exit slit at the right. What magnitude and direction must the E field have so that positively charged particles entering from the left will traverse to the exit slit undeviated?
The apparatus in the figure consists of two parallel plates shown on edge) and a large magnet not shown). The field of the magnet is uniform, perpendicular to the electric field between the plates, and directed into the plane of the paper. The magnitude of B is 0.40 T. Charged particles with speeds of 5.0 × 105 m/s enter this region through the slit at the left and emerge through the exit slit at the right. What magnitude and direction must the E field have so that positively charged particles entering from the left will traverse to the exit slit undeviated?A) 2.0 × 105 V/m up
B) 2.0 × 105 V/m down
C) 1.2 × 106 V/m down
D) 1.2 × 106 V/m up
E) 2.4 × 106 V/m down

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The radius of curvature of the path of a charged particle in a uniform magnetic field is directly proportional to
A) the particle's charge.
B) the particle's momentum.
C) the particle's energy.
D) the flux density of the field.
E) All of these are correct.
A) the particle's charge.
B) the particle's momentum.
C) the particle's energy.
D) the flux density of the field.
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A beam of electrons q = 1.6 × 10-19 C) is moving through a region of space in which there is an electric field of intensity 3.4 × 104 V/m and a magnetic field of 2.0 × 10-3 T. The electric and magnetic fields are so oriented that the beam of electrons is not deflected. The velocity of the electrons is approximately
A) 6.8 × 106 m/s.
B) 3.0 × 108 m/s.
C) 6.0 × 10-9 m/s.
D) 0.68 km/s.
E) 1.7 × 107 m/s.
A) 6.8 × 106 m/s.
B) 3.0 × 108 m/s.
C) 6.0 × 10-9 m/s.
D) 0.68 km/s.
E) 1.7 × 107 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
An alpha particle with a charge of 2e e = 1.6 × 10-19 C) is moving at right angles to a uniform magnetic field of 1.20 T. The radius of curvature of the track of the particle is 0.20 m. What is the momentum of the alpha particle?
A) The question cannot be answered because the speed of the particle is not given.
B) 7.7 × 10-20 kg m/s
C) 3.1 × 10-19 kg m/s
D) 0.77 kg m/s
E) 4.6 × 10-21 kg m/s
A) The question cannot be answered because the speed of the particle is not given.
B) 7.7 × 10-20 kg m/s
C) 3.1 × 10-19 kg m/s
D) 0.77 kg m/s
E) 4.6 × 10-21 kg m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
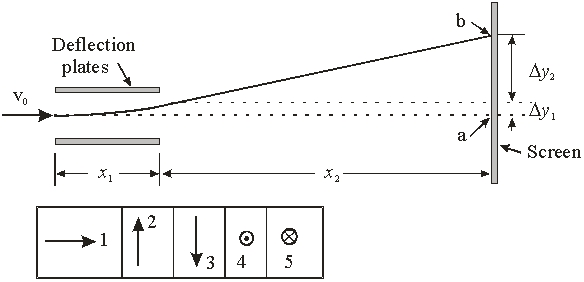 Electrons traveling at a speed of v0 = 3 × 107 m/s pass through the deflection plates. The electric field between the plates is E = 5000 V/m and spans a distance of x1 = 5 cm. The electrons then travel a further distance of x2 = 40 cm along the x-axis. With the magnetic field turned off, what is the deflection y1 as the electron exits the region between the plates?
Electrons traveling at a speed of v0 = 3 × 107 m/s pass through the deflection plates. The electric field between the plates is E = 5000 V/m and spans a distance of x1 = 5 cm. The electrons then travel a further distance of x2 = 40 cm along the x-axis. With the magnetic field turned off, what is the deflection y1 as the electron exits the region between the plates?A) 1.22 × 10-3 m
B) 1.95 × 10-2 m
C) 2.07 × 10-2 m
D) 9.50 × 10-3 m
E) 1.38 × 10-2 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An electron is accelerated from rest by an electric field. After the acceleration, the electron is injected into a uniform magnetic field of 1.27 × 10-3 T. The velocity of the electron and the magnetic field lines are perpendicular to one another. The electron remains in the magnetic field for 5.00 × 10-9 s. The angle between the electron velocity on entry and the electron velocity at exit from the magnetic field is
A) 1.1 rad.
B) 5.8 × 10-2 rad.
C) 8.68 × 10-2 rad.
D) 6.5 × 10-2 rad.
E) 2.3 rad.
A) 1.1 rad.
B) 5.8 × 10-2 rad.
C) 8.68 × 10-2 rad.
D) 6.5 × 10-2 rad.
E) 2.3 rad.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
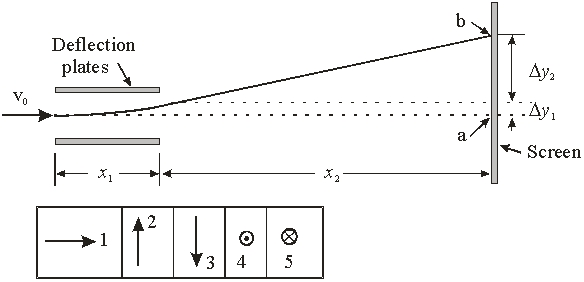 Electrons traveling at a speed of v0 = 3 × 107 m/s pass through the deflection plates. The electric field between the plates is E = 5000 V/m and spans a distance of x1 = 5 cm. The electrons then travel a further distance of x2 = 40 cm along the x-axis. With the magnetic field turned off, the total deflection in the y direction is
Electrons traveling at a speed of v0 = 3 × 107 m/s pass through the deflection plates. The electric field between the plates is E = 5000 V/m and spans a distance of x1 = 5 cm. The electrons then travel a further distance of x2 = 40 cm along the x-axis. With the magnetic field turned off, the total deflection in the y direction isA) 1.22 × 10-3 m.
B) 1.95 × 10-2 m.
C) 2.07 × 10-2 m.
D) 9.50 × 10-3 m.
E) 1.38 × 10-2 m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A deuteron is moving with a speed of 2.0 × 106 m/s at right angles to a magnetic field. The field is uniform, with magnitude B = 0.40 T. The mass and charge of a deuteron are 3.3 × 10-27 kg and 1.6 × 10-19 C, respectively. The radius of the deuteron orbit is approximately
A) 0.21 m.
B) 1.8 m.
C) 6.3 m.
D) 10 cm.
E) 27 cm.
A) 0.21 m.
B) 1.8 m.
C) 6.3 m.
D) 10 cm.
E) 27 cm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
An electric field and a magnetic field are at right angles to each other and to the direction of a beam of electrons. There is no deflection of the beam when the magnitudes of the fields are 30 × 104 V/m and 2.0 × 10-3 T, respectively. The velocity of the electrons must be approximately
A) 0.60 km/s.
B) 6.7 × 10-8 m/s.
C) 2.3 × 1016 m/s.
D) 1.5 × 108 m/s.
E) 1.5 × 10-8 m/s.
A) 0.60 km/s.
B) 6.7 × 10-8 m/s.
C) 2.3 × 1016 m/s.
D) 1.5 × 108 m/s.
E) 1.5 × 10-8 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An electron passes through a region where there is an electric field E = 4.0 × 105 V/m and a magnetic field B = 0.090 T. The directions of the electric field, the magnetic field, and the electron velocity are mutually perpendicular. If the electron is not deflected from its straight-line path through these fields, its speed must be
A) 3.6 × 104 m/s.
B) 5.0 × 105 m/s.
C) 2.2 × 10-7 m/s.
D) 1.2 × 104 m/s.
E) 4.4 × 106 m/s.
A) 3.6 × 104 m/s.
B) 5.0 × 105 m/s.
C) 2.2 × 10-7 m/s.
D) 1.2 × 104 m/s.
E) 4.4 × 106 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The radius of curvature of the path of a charged particle moving perpendicular to a magnetic field is given by
A) qE/m.
B) Bm/qv.
C) Bv/qm.
D) mv/qB.
E) Bq/mv.
A) qE/m.
B) Bm/qv.
C) Bv/qm.
D) mv/qB.
E) Bq/mv.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
In a mass spectrometer, chlorine ions of mass 35u and 37u, each with charge +5e, are emitted from a source and accelerated through a potential difference of 300 kV. They then enter at the same point) a region with a magnetic field of 0.20 T that is perpendicular to their original direction of motion. Calculate the separation between the two chlorine ions after they have made a half circle path in the magnetic field region. u = 1.66 × 10-27 kg, e = 1.6 × 10-19 C)
A) 1.0 m
B) 24 cm
C) 5.9 cm
D) 2.9 cm
E) 12 cm
A) 1.0 m
B) 24 cm
C) 5.9 cm
D) 2.9 cm
E) 12 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The radius of the orbit of an electron moving with a speed of 108 m/s perpendicular to a magnetic field of 5.0 × 10-3 T is approximately
A) 1.1 m.
B) 0.11 m.
C) 0.34 m.
D) 0.011 m.
E) 8.9 m.
A) 1.1 m.
B) 0.11 m.
C) 0.34 m.
D) 0.011 m.
E) 8.9 m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A wire of length L carries a current I, going from west to east, in the presence of a magnetic field B that is pointing vertically up. The wire moves a distance d to the south. The work done by the magnetic force on the moving charges is
A) "+ILlBd."
B) "-ILBd."
C) "+IL2B/d."
D) "-IL2B/d."
E) "zero."
A) "+ILlBd."
B) "-ILBd."
C) "+IL2B/d."
D) "-IL2B/d."
E) "zero."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
An alpha particle with a charge 2e and mass 4m is moving with velocity v when it enters a magnetic field B at right angles to its direction of motion. A deuteron of charge e and mass 2m also enters the field in the same direction and the same speed. Calculate the difference in radius of motion between the alpha particle and the deuteron in the magnetic field region.
A) mv/eB
B) 0
C) 2mv/eB
D) mv/2eB
E) mv/4eB
A) mv/eB
B) 0
C) 2mv/eB
D) mv/2eB
E) mv/4eB

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
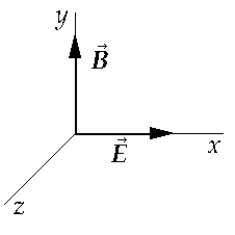 A negatively charged particle is moving through uniform fields E and B, which are directed in the positive x and positive y directions, respectively. If there is no resultant force on the particle, then its velocity is in the
A negatively charged particle is moving through uniform fields E and B, which are directed in the positive x and positive y directions, respectively. If there is no resultant force on the particle, then its velocity is in theA) positive x direction.
B) positive y direction.
C) negative x direction.
D) positive z direction.
E) negative z direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
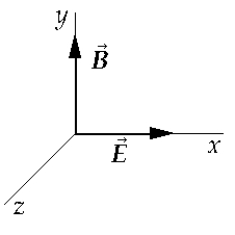 A positively charged particle is moving through uniform fields E and B, which are directed in the positive x and positive y directions, respectively. If there is no resultant force on the particle, then its velocity is in the
A positively charged particle is moving through uniform fields E and B, which are directed in the positive x and positive y directions, respectively. If there is no resultant force on the particle, then its velocity is in theA) positive x direction.
B) positive y direction.
C) negative x direction.
D) positive z direction.
E) negative z direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
5 T when a current of 1.3 A passes through the wire in a perpendicular direction to the magnetic field. Find the mass per unit length of the wire. The wire is connected to a battery by ultra light flexible leads.)
A) 0.40 kg/m
B) 0.20 kg/m
C) 20 g/m
D) 40 g/m
E) None of the above.
A) 0.40 kg/m
B) 0.20 kg/m
C) 20 g/m
D) 40 g/m
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
A beam of charged particles moving with a speed of 106 m/s enters a uniform magnetic field of 0.1 T at right angles to the direction of motion. If the particles move in a radius of 0.2 m, then calculate their period of motion.
A) 6.3 × 10-7 s
B) 1.3 × 10-7 s
C) 1.3 × 10-6 s
D) 4.1 × 10-7 s
E) None of the above.
A) 6.3 × 10-7 s
B) 1.3 × 10-7 s
C) 1.3 × 10-6 s
D) 4.1 × 10-7 s
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
In a mass spectrometer, ions of nickel with mass 9.62 × 10-26 kg and charge +2e are accelerated through a potential difference of X volts and then deflected in a magnetic field of 0.15 T. If the radius of curvature of the ions is 0.55 m, then calculate the value of the potential difference X.
A) 5.7 kV
B) 274 kV
C) 137 kV
D) 11.3 kV
E) None of the above.
A) 5.7 kV
B) 274 kV
C) 137 kV
D) 11.3 kV
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An electric field of 3.0 kV/m is perpendicular to a magnetic field of 0.20 T. An electron moving in a direction perpendicular to both E and B is not deflected if it has a velocity of
A) 6 km/s.
B) 9 km/s.
C) 12 km/s.
D) 15 km/s.
E) 6.7 m/s.
A) 6 km/s.
B) 9 km/s.
C) 12 km/s.
D) 15 km/s.
E) 6.7 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A small permanent magnet is placed in a uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.35 T. If the maximum torque experienced by the magnet is 0.50 N · m, what is the magnitude of the magnetic moment 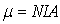 ) of the magnet
) of the magnet 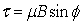 )?
)?
A) 1.4 A · m2
B) 0.70 A · m2
C) 0.18 A · m2
D) 2.8 A · m2
E) 0.35 A · m2
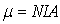 ) of the magnet
) of the magnet 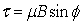 )?
)?A) 1.4 A · m2
B) 0.70 A · m2
C) 0.18 A · m2
D) 2.8 A · m2
E) 0.35 A · m2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A 30 cm long wire with an east-west orientation carries a current of 3.0 A westward. There is a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to this wire. If the force on the wire is 0.18 N upward, what are the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field?
A) 0.20 T up
B) 0.20 T north
C) 0.20 T south
D) 2.0 × 10-3 T north
E) 2.0 × 10-3 T up
A) 0.20 T up
B) 0.20 T north
C) 0.20 T south
D) 2.0 × 10-3 T north
E) 2.0 × 10-3 T up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
In a mass spectrometer, chlorine ions of mass 35u and charge +5e are emitted from a source and accelerated through a potential difference of 250 kV. They then enter a region with a magnetic field that is perpendicular to their original direction of motion. The chlorine ions exit the spectrometer after being bent along a path with a radius of curvature 3.5 m. What is the speed of the chlorine ions as they enter the magnetic field region u = 1.66 × 10-27 kg, e = 1.6 × 10-19 C)?
A) 2.6 × 106 m/s
B) 1.9 × 106 m/s
C) 1.2 × 106 m/s
D) 1.5 × 107 m/s
E) None of the above.
A) 2.6 × 106 m/s
B) 1.9 × 106 m/s
C) 1.2 × 106 m/s
D) 1.5 × 107 m/s
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
A beam of electrons moving at a speed of 8 × 104 m/s is undeflected when it passes through an electric field of 5 N/C perpendicular to its path and a magnetic field that is perpendicular to its path and also to that of the electric field. Calculate the strength of the magnetic field.
A) 1.60 × 104 T
B) 6.25 × 10-5 T
C) 7.81 × 10-10 T
D) 3.13 × 10-5 T
E) 1.25 × 10-4 T
A) 1.60 × 104 T
B) 6.25 × 10-5 T
C) 7.81 × 10-10 T
D) 3.13 × 10-5 T
E) 1.25 × 10-4 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A 3.0-m long straight wire segment makes an angle of 28º with a uniform magnetic field of 1.0 T. The magnitude of the force on the wire if it carries a current of 1.5 A is approximately
A) 2.1 N.
B) 4.0 N.
C) 1.4 N.
D) 0.70 N.
E) 4.7 N.
A) 2.1 N.
B) 4.0 N.
C) 1.4 N.
D) 0.70 N.
E) 4.7 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
In a mass spectrometer, chlorine ions of mass 35u and charge +5e are emitted from a source and accelerated through a potential difference of 250 kV. They then enter a region with a magnetic field, which is perpendicular to their original direction of motion. The chlorine ions exit the spectrometer after being bent along a path with a radius of curvature 3.5 m. What is the value of the magnetic field u = 1.66 × 10-27 kg, e = 1.6 × 10-19 C)?
A) 3.9 × 10-2 T
B) 2.5 × 10-2 T
C) 3.1 × 10-2 T
D) 5.4 × 10-2 T
E) None of the above.
A) 3.9 × 10-2 T
B) 2.5 × 10-2 T
C) 3.1 × 10-2 T
D) 5.4 × 10-2 T
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
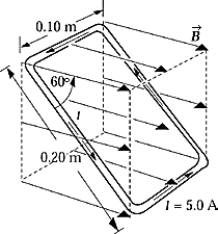 A rectangular loop of wire 0.10 m by 0.20 m) carries a current of 5.0 A in a counterclockwise direction. The loop is oriented as shown in a uniform magnetic field of 1.5 T. The force acting on the upper 0.10-m side of the loop is
A rectangular loop of wire 0.10 m by 0.20 m) carries a current of 5.0 A in a counterclockwise direction. The loop is oriented as shown in a uniform magnetic field of 1.5 T. The force acting on the upper 0.10-m side of the loop isA) 1.5 N.
B) 0.75 N.
C) 0.50 N.
D) 0.15 N.
E) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
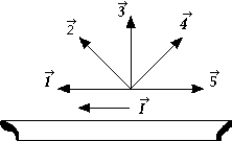 A current I flows in a wire that is oriented as shown. The vector representing the magnetic field that results in a maximum force on the wire is
A current I flows in a wire that is oriented as shown. The vector representing the magnetic field that results in a maximum force on the wire isA) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A long straight wire parallel to the y-axis carries a current of 6.3 A in the positive y direction. There is a uniform magnetic field B = 1.5 T along the positive x direction. The magnitude of the force per unit length on the wire is approximately
A) 6.3 N/m.
B) 9.5 N/m.
C) 4.2 N/m.
D) 0.29 N/m.
E) 1.5 N/m.
A) 6.3 N/m.
B) 9.5 N/m.
C) 4.2 N/m.
D) 0.29 N/m.
E) 1.5 N/m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A 30-cm long wire with an east-west orientation carries a current of 3.0 A eastward. There is a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to this wire. If the force on the wire is 0.18 N upward, what are the direction and magnitude of the magnetic field?
A) 0.20 T up
B) 0.20 T north
C) 0.20 T south
D) 2.0 × 10-3 T north
E) 2.0 × 10-3 T up
A) 0.20 T up
B) 0.20 T north
C) 0.20 T south
D) 2.0 × 10-3 T north
E) 2.0 × 10-3 T up

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
In a circular loop of wire lying on a horizontal floor, the current is constant and, to a person looking downward, has a clockwise direction. The accompanying magnetic field at the center of the circle is directed
A) horizontally and to the east.
B) horizontally and to the north.
C) vertically upward.
D) parallel to the floor.
E) vertically downward.
A) horizontally and to the east.
B) horizontally and to the north.
C) vertically upward.
D) parallel to the floor.
E) vertically downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
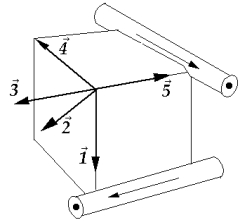 Current-carrying wires are located along two edges of a cube with the directions of the currents as indicated. The vector that indicates the resultant magnetic field at the corner of the cube is
Current-carrying wires are located along two edges of a cube with the directions of the currents as indicated. The vector that indicates the resultant magnetic field at the corner of the cube isA) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
At great axial distances x from a current-carrying loop, the magnetic field varies as
A) x2.
B) x-3.
C) x-2.
D) x3.
E) x-1.
A) x2.
B) x-3.
C) x-2.
D) x3.
E) x-1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
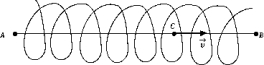 A solenoid carries a current I. An electron is injected with velocity v along the axis AB of the solenoid. When the electron is at C, it experiences a force that is
A solenoid carries a current I. An electron is injected with velocity v along the axis AB of the solenoid. When the electron is at C, it experiences a force that isA) zero.
B) not zero and along AB.
C) not zero and along BA.
D) not zero and perpendicular to the page.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A circular, 20-turn coil of radius 5.0 cm is oriented in such a way that its axis makes a 30º angle with a uniform magnetic field of 0.15 T. What is the torque on the coil when it carries a current of 2.5 A?
A) 1.5 × 10-3 N · m
B) 9.4 × 10-3 N · m
C) 2.9 × 10-2 N · m
D) 5.1 × 10-2 N · m
E) 0.59 N · m
A) 1.5 × 10-3 N · m
B) 9.4 × 10-3 N · m
C) 2.9 × 10-2 N · m
D) 5.1 × 10-2 N · m
E) 0.59 N · m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
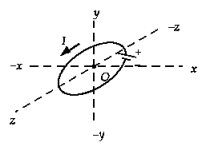 The sketch shows a circular coil in the xz plane carrying a current I. A uniform magnetic field exists along the y-axis. The coil will
The sketch shows a circular coil in the xz plane carrying a current I. A uniform magnetic field exists along the y-axis. The coil willA) rotate around the x-axis.
B) rotate around the y-axis.
C) rotate around the z-axis.
D) not rotate at all.
E) will experience a force along the y-axis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
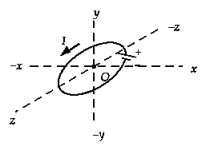 The sketch shows a circular coil in the xz plane carrying a current I. The direction of the magnetic field at point O is
The sketch shows a circular coil in the xz plane carrying a current I. The direction of the magnetic field at point O isA) +x.
B) -x.
C) +y.
D) -y.
E) -z.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
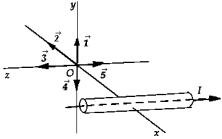 A long conductor carrying current I lies in the xz plane parallel to the z-axis. The current travels in the negative z direction, as shown in the figure. The vector that represents the magnetic field at the origin O is
A long conductor carrying current I lies in the xz plane parallel to the z-axis. The current travels in the negative z direction, as shown in the figure. The vector that represents the magnetic field at the origin O isA) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
What is the magnetic field at the center of a circular loop with a diameter of 15.0 cm that carries a current of 1.50 A?
A) zero
B) 6.28 × 10-6 T
C) 1.26 × 10-5 T
D) 2.51 × 10-5 T
E) 1.68 × 10-4 T
A) zero
B) 6.28 × 10-6 T
C) 1.26 × 10-5 T
D) 2.51 × 10-5 T
E) 1.68 × 10-4 T

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The magnetic field at a distance of 50 cm from a long, straight wire carrying a current of 5.0 A is approximately
A) 10 µT.
B) 50 µT.
C) 5.0 µT.
D) 32 µT.
E) 2.0 µT.
A) 10 µT.
B) 50 µT.
C) 5.0 µT.
D) 32 µT.
E) 2.0 µT.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
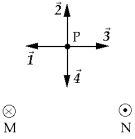 Two straight wires perpendicular to the plane of this page are shown in the figure. The currents in the wires are the same. The current in M is into the page and the current in N is out of the page. The vector that represents the resultant magnetic field at point P is
Two straight wires perpendicular to the plane of this page are shown in the figure. The currents in the wires are the same. The current in M is into the page and the current in N is out of the page. The vector that represents the resultant magnetic field at point P isA) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A circular loop of wire of radius 6.0 cm has 30 turns and lies in the yz plane with its center at the origin. It carries a counterclockwise current of 5 A when viewed along the +x-axis. The magnetic field on the x-axis at x = 6.0 cm is approximately
A) 19 µT.
B) 0.56 mT.
C) 0.11 mT.
D) 47 µT.
E) 0.88 mT.
A) 19 µT.
B) 0.56 mT.
C) 0.11 mT.
D) 47 µT.
E) 0.88 mT.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
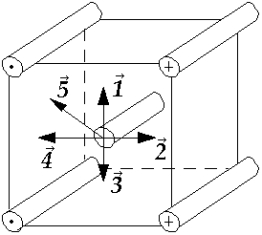 Four wires carry equal currents along the four parallel edges of a cube. A parallel current-carrying wire through the center of the cube is free to move. The vector that might represent the direction in which the center wire will move is
Four wires carry equal currents along the four parallel edges of a cube. A parallel current-carrying wire through the center of the cube is free to move. The vector that might represent the direction in which the center wire will move isA) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A wire carries an electric current straight upward. At a point directly north of the wire, what is the direction of the magnetic field due to the current?
A) north
B) east
C) west
D) south
E) upward
A) north
B) east
C) west
D) south
E) upward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
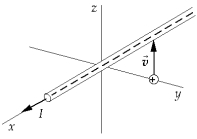 The current in a wire along the x-axis flows in the positive x direction. If a proton, located as shown in the figure, has an initial velocity in the positive z direction, it experiences
The current in a wire along the x-axis flows in the positive x direction. If a proton, located as shown in the figure, has an initial velocity in the positive z direction, it experiencesA) a force in the direction of positive x.
B) a force in the direction of negative x.
C) a force in the direction of positive z.
D) a force in the direction of positive y.
E) no force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
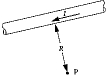 The magnetic field at point P, due to the current in the very long wire, varies with distance R according to
The magnetic field at point P, due to the current in the very long wire, varies with distance R according toA) R2.
B) R-3.
C) R-2.
D) R3.
E) R-1.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
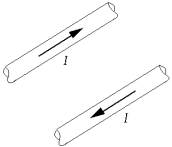 Two wires lying in the plane of this page carry equal currents in opposite directions, as shown. At a point midway between the wires, the magnetic field is
Two wires lying in the plane of this page carry equal currents in opposite directions, as shown. At a point midway between the wires, the magnetic field isA) zero.
B) into the page.
C) out of the page.
D) toward the top or bottom of the page.
E) toward one of the two wires.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
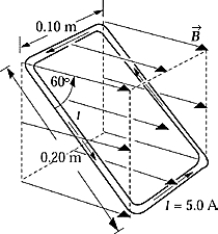 A rectangular loop of wire 0.10 m by 0.20 m) carries a current of 5.0 A in a counterclockwise direction. The loop is oriented as shown in a uniform magnetic field of 1.5 T. The magnitude of the torque acting on the loop is
A rectangular loop of wire 0.10 m by 0.20 m) carries a current of 5.0 A in a counterclockwise direction. The loop is oriented as shown in a uniform magnetic field of 1.5 T. The magnitude of the torque acting on the loop isA) 15 x 10-2 N . m.
B) 75 x 10-2 N . m.
C) 50 x 10-2 N . m.
D) 13 x 10-2 N.
E) 7.5 x 10-2 N . m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
A circular, 20-turn coil has a radius of 5.0 cm. What is the magnitude of the magnetic moment 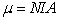 ) of the coil when it carries a current of 2.5 A?
) of the coil when it carries a current of 2.5 A?
A) 1.5 A · m2
B) 0.16 A · m2
C) 2.0 × 10-2 A · m2
D) 0.39 A · m2
E) 3.9 kA · m2
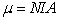 ) of the coil when it carries a current of 2.5 A?
) of the coil when it carries a current of 2.5 A?A) 1.5 A · m2
B) 0.16 A · m2
C) 2.0 × 10-2 A · m2
D) 0.39 A · m2
E) 3.9 kA · m2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
What is the direction of the magnetic field around a wire carrying a current that is perpendicularly into this page?
A) The field is parallel to and in the same direction as the current flow.
B) It is parallel to but directed opposite to the current flow.
C) It is counterclockwise around the wire in the plane of the page.
D) It is clockwise around the wire in the plane of the page.
E) None of these is correct.
A) The field is parallel to and in the same direction as the current flow.
B) It is parallel to but directed opposite to the current flow.
C) It is counterclockwise around the wire in the plane of the page.
D) It is clockwise around the wire in the plane of the page.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 105 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



