Deck 17: Electrostatics II: Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/142
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: Electrostatics II: Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential
1
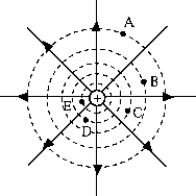 The electrostatic potential energy of a positively charged body is greatest at point _____.
The electrostatic potential energy of a positively charged body is greatest at point _____.A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E
E
2
The voltage between the cathode and the screen of a computer monitor is 12 kV. If we assume a speed of zero for an electron as it leaves the cathode, what is its speed just before it hits the screen?
A) 8.8 × 107 m/s
B) 6.5 × 107 m/s
C) 4.2 × 1015 m/s
D) 7.7 × 1015 m/s
E) 5.3 × 107 m/s
A) 8.8 × 107 m/s
B) 6.5 × 107 m/s
C) 4.2 × 1015 m/s
D) 7.7 × 1015 m/s
E) 5.3 × 107 m/s
6.5 × 107 m/s
3
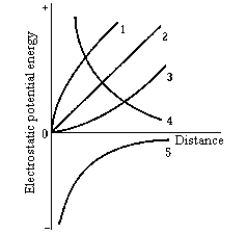 Which of the curves in the graph represents the electrostatic potential energy of a small negative charge plotted as a function of its distance from another positive point charge located at the origin?
Which of the curves in the graph represents the electrostatic potential energy of a small negative charge plotted as a function of its distance from another positive point charge located at the origin?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5
5
4
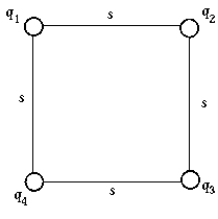 Four point charges q1 = 1 C, q2 = 2 C, q3 = 3 C, and q4 = 4 C are located at the corners of a square whose side s = 1.00 m. The electrostatic potential energy of this system of charges is
Four point charges q1 = 1 C, q2 = 2 C, q3 = 3 C, and q4 = 4 C are located at the corners of a square whose side s = 1.00 m. The electrostatic potential energy of this system of charges isA) 0.167 J
B) 0.176 J
C) 0.286 J
D) 0.337 J
E) 0.492 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
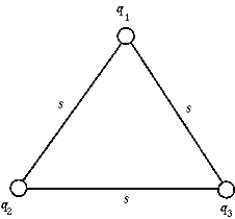 The electrostatic potential energy of the system of point charges q1 = 1 μC, q2 = 2 μC, and q3 = 3 μC at the corners of the equilateral triangle whose side s = 30 cm is
The electrostatic potential energy of the system of point charges q1 = 1 μC, q2 = 2 μC, and q3 = 3 μC at the corners of the equilateral triangle whose side s = 30 cm isA) 1.1 J.
B) 0.99 J.
C) 0.63 J.
D) 0.33 J.
E) 0.11 J.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
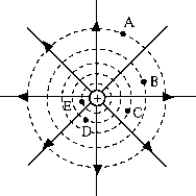 The work required to bring a negatively charged body from very far is greatest for point _____.
The work required to bring a negatively charged body from very far is greatest for point _____.A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
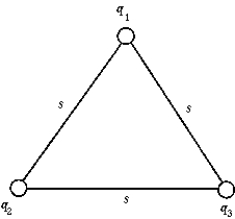 The electrostatic potential energy of the system of point charges q1 = 1 μC, q2 = -2 μC, and q3 = 3 μC at the corners of the equilateral triangle whose side s = 40 cm is
The electrostatic potential energy of the system of point charges q1 = 1 μC, q2 = -2 μC, and q3 = 3 μC at the corners of the equilateral triangle whose side s = 40 cm isA) 1.10 J.
B) 0.990 J..
C) -0.631 J.
D) 0.330 J.
E) -0.113 J.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
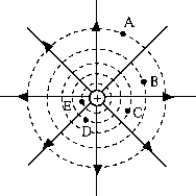 The work required to bring a positively charged body from very far away is greatest for point _____.
The work required to bring a positively charged body from very far away is greatest for point _____.A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
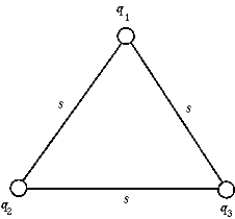 The electrostatic potential energy of the system of point charges q1 = -1 ?C, q2 = -2 ?C, and q3 =-3 ?C at the corners of the equilateral triangle whose side s = 30 cm is
The electrostatic potential energy of the system of point charges q1 = -1 ?C, q2 = -2 ?C, and q3 =-3 ?C at the corners of the equilateral triangle whose side s = 30 cm isA) "-1.1 J."
B) "-0.99 J."
C) "-0.33 J."
D) "0.33 J."
E) "0.11 J."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Two protons in a nucleus of 238U are 6.0 × 10-15 m apart. The electrostatic potential energy of the pair is approximately
A) zero.
B) 4.7 × 10-34 J.
C) 4.3 × 10-24 J.
D) 3.8 × 10-14 J.
E) 2.4 × 104 J.
A) zero.
B) 4.7 × 10-34 J.
C) 4.3 × 10-24 J.
D) 3.8 × 10-14 J.
E) 2.4 × 104 J.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
The voltage between the cathode and the screen of a television set is 22 kV. If we assume a speed of zero for an electron as it leaves the cathode, what is its speed just before it hits the screen?
A) 8.8 × 107 m/s
B) 2.8 × 106 m/s
C) 6.2 × 107 m/s
D) 7.7 × 1015 m/s
E) 5.3 × 107 m/s
A) 8.8 × 107 m/s
B) 2.8 × 106 m/s
C) 6.2 × 107 m/s
D) 7.7 × 1015 m/s
E) 5.3 × 107 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Three charges are brought from infinity and placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle. Which of the following statements is true?
A) The work required to assemble the charges is always positive.
B) The electrostatic potential energy of the system is always positive.
C) The electrostatic potential energy does not depend on the order the charges are placed at the corners.
D) The work required to assemble the charges depends on which charge is placed at which corner.
E) The electrostatic potential energy depends on which charge is placed at which corner.
A) The work required to assemble the charges is always positive.
B) The electrostatic potential energy of the system is always positive.
C) The electrostatic potential energy does not depend on the order the charges are placed at the corners.
D) The work required to assemble the charges depends on which charge is placed at which corner.
E) The electrostatic potential energy depends on which charge is placed at which corner.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
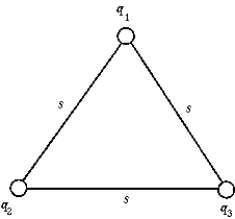 The electrostatic potential energy of the system of point charges q1 = -1 μC, q2 = 2 μC, and q3 = 3 μC at the corners of the equilateral triangle whose side s = 50 cm is
The electrostatic potential energy of the system of point charges q1 = -1 μC, q2 = 2 μC, and q3 = 3 μC at the corners of the equilateral triangle whose side s = 50 cm isA) 18.0 mJ.
B) -18.0 mJ.
C) 21.6 mJ.
D) -24.4 mJ.
E) 1.23 mJ.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Which of the following statements is false?
A) The total work required to assemble a collection of discrete charges is the electrostatic potential energy of the system.
B) The potential energy of a pair of positively charged bodies is positive.
C) The potential energy of a pair of oppositely charged bodies is positive.
D) The potential energy of a pair of oppositely charged bodies is negative.
E) The potential energy of a pair of negatively charged bodies is negative.
A) The total work required to assemble a collection of discrete charges is the electrostatic potential energy of the system.
B) The potential energy of a pair of positively charged bodies is positive.
C) The potential energy of a pair of oppositely charged bodies is positive.
D) The potential energy of a pair of oppositely charged bodies is negative.
E) The potential energy of a pair of negatively charged bodies is negative.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
The electrostatic potential energy of two protons separated by 2.6 × 10-15 m is approximately
A) zero.
B) 4.7 × 10-34 J.
C) 4.3 × 10-24 J.
D) 3.8 × 10-14 J.
E) 8.9 × 10-14 J.
A) zero.
B) 4.7 × 10-34 J.
C) 4.3 × 10-24 J.
D) 3.8 × 10-14 J.
E) 8.9 × 10-14 J.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
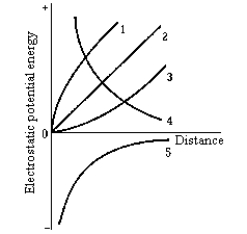 Which of the curves in the graph represents the electrostatic potential energy of a small positive charge plotted as a function of its distance from another positive point charge located at the origin?
Which of the curves in the graph represents the electrostatic potential energy of a small positive charge plotted as a function of its distance from another positive point charge located at the origin?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
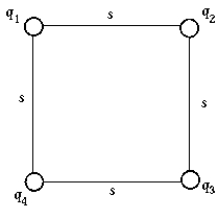 Four point charges q1 = -1 C, q2 = 2 C, q3 = 3 C, and q4 = 4 C are located at the corners of a square whose side s = 1.00 m. The electrostatic potential energy of this system of charges is
Four point charges q1 = -1 C, q2 = 2 C, q3 = 3 C, and q4 = 4 C are located at the corners of a square whose side s = 1.00 m. The electrostatic potential energy of this system of charges isA) 0.140 J.
B) 0.176 J.
C) 0.286 J.
D) 0.337 J.
E) 0.492 J.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A charge of 2.0 mC is located in a uniform electric field of intensity 4.0 × 105 N/C. How much work is required to move this charge 20 cm along a path making an angle of 60° with the electric field?
A) 0.14 J
B) 0.34 J
C) 80 J
D) 14 J
E) 8.0 J
A) 0.14 J
B) 0.34 J
C) 80 J
D) 14 J
E) 8.0 J

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A charge of 5.0 mC is located in a uniform electric field of intensity 3.5 × 105 N/C. How much work is required to move this charge 50 cm along a path making an angle of 33° with the electric field?
A) 0.27 J
B) 0.16 J
C) 0.54 J
D) 0.74 kJ
E) 7.3 mJ
A) 0.27 J
B) 0.16 J
C) 0.54 J
D) 0.74 kJ
E) 7.3 mJ

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
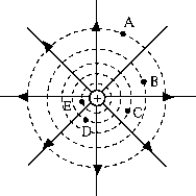 The electrostatic potential energy of a negatively charged body is greatest at point _____.
The electrostatic potential energy of a negatively charged body is greatest at point _____.A) A
B) B
C) C
D) D
E) E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
When 5.0 C of charge moves at constant speed along a path between two points differing in potential by 12 V, the amount of work done by the field is
A) 2.4 J.
B) 0.42 J.
C) 5.0 J.
D) 12 J.
E) 60 J.
A) 2.4 J.
B) 0.42 J.
C) 5.0 J.
D) 12 J.
E) 60 J.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Two parallel metal plates 0.35 cm apart have a potential difference between them of 175 V. The electric force on a positive charge of 6.4 × 10-19 C at a point midway between the plates is approximately
A) 4.8 × 10-18 N.
B) 2.4 × 10-17 N.
C) 1.6 × 10-18 N.
D) 4.8 × 10-16 N.
E) 3.2 × 10-14 N.
A) 4.8 × 10-18 N.
B) 2.4 × 10-17 N.
C) 1.6 × 10-18 N.
D) 4.8 × 10-16 N.
E) 3.2 × 10-14 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
Two parallel horizontal plates are spaced 0.40 cm apart in air. You introduce an oil droplet of mass 4.9 × 10-17 kg between the plates. If the droplet carries two electronic charges and if there were no air buoyancy, you could hold the droplet motionless between the plates if you kept the potential difference between them at
A) 60 V.
B) 12 V.
C) 3.0 V.
D) 0.12 kV.
E) 6.0 V.
A) 60 V.
B) 12 V.
C) 3.0 V.
D) 0.12 kV.
E) 6.0 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
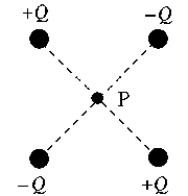 Charges +Q and -Q are arranged at the corners of a square as shown. When the electric field E and the electric potential V are determined at P, the center of the square, we find that
Charges +Q and -Q are arranged at the corners of a square as shown. When the electric field E and the electric potential V are determined at P, the center of the square, we find thatA) E ≠ 0 and V > 0.
B) E = 0 and V = 0.
C) E = 0 and V > 0.
D) E ≠ 0 and V < 0.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
When 2.0 C of charge moves at constant speed along a path between two points differing in potential by 6.0 V, the amount of work done by the field is
A) 2 J.
B) 3 J.
C) 6 J.
D) 12 J.
E) 24 J.
A) 2 J.
B) 3 J.
C) 6 J.
D) 12 J.
E) 24 J.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A uniform electric field exists between two parallel plates separated by 1.2 cm. The intensity of the field is 23 kN/C. What is the potential difference between the plates?
A) 7.5 MV
B) 0.30 kV
C) 3.0 MV
D) 15 kV
E) None of these is correct.
A) 7.5 MV
B) 0.30 kV
C) 3.0 MV
D) 15 kV
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The electrical potential 2.5 cm from a point charge of Q1 = +4.5 × 10-9 C and 2.0 cm from a second charge Q2 is 3.2 kV. Find Q2.
A) 2.7 × 10-9 C
B) 4.4 × 10-9 C
C) 1.1 × 10-8 C
D) 3.5 × 10-9 C
E) 5.5 × 10-9 C
A) 2.7 × 10-9 C
B) 4.4 × 10-9 C
C) 1.1 × 10-8 C
D) 3.5 × 10-9 C
E) 5.5 × 10-9 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A uniform electric field exists between two parallel plates separated by 2.0 cm. The intensity of the field is 15 kN/C. What is the potential difference between the plates?
A) 0.75 MV
B) 30 kV
C) 15 kV
D) 0.30 kV
E) 54 kV
A) 0.75 MV
B) 30 kV
C) 15 kV
D) 0.30 kV
E) 54 kV

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
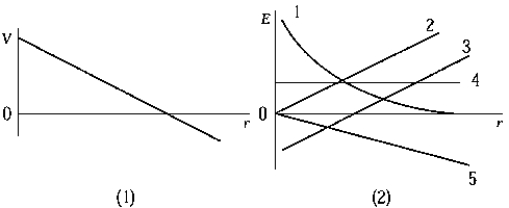 The electrostatic potential as a function of distance along a certain line in space is shown in graph 1). Which of the curves in graph 2) is most likely to represent the electric field as a function of distance along the same line?
The electrostatic potential as a function of distance along a certain line in space is shown in graph 1). Which of the curves in graph 2) is most likely to represent the electric field as a function of distance along the same line?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Two parallel horizontal plates are spaced 0.60 cm apart in air. You introduce an oil droplet of mass 7.4 × 10-17 kg between the plates. If the droplet carries 5 electronic charges and if there were no air buoyancy, you could hold the droplet motionless between the plates if you kept the potential difference between them at
A) 5.4 V.
B) 27 V.
C) 3.0 V.
D) 0.54 V.
E) 0.27 kV.
A) 5.4 V.
B) 27 V.
C) 3.0 V.
D) 0.54 V.
E) 0.27 kV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
The magnitude of the electric field in a region is given by E = kQ / r2 where Q is the charge. What is the potential difference between r = a to r = b?
A)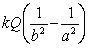
B)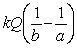
C)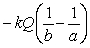
D)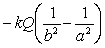
E) None of the above.
A)
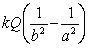
B)
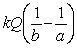
C)
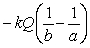
D)
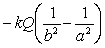
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Two parallel metal plates 5.0 cm apart have a potential difference between them of 75 V. The electric force on a positive charge of 3.2 × 10-19 C at a point midway between the plates is approximately
A) 4.8 × 10-18 N.
B) 4.8 × 10-16 N.
C) 2.4 × 10-17 N..
D) 9.6 × 10-17 N.
E) 1.6 × 10-18 N.
A) 4.8 × 10-18 N.
B) 4.8 × 10-16 N.
C) 2.4 × 10-17 N..
D) 9.6 × 10-17 N.
E) 1.6 × 10-18 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
Electric field in a region is created by a point charge Q located at r = 0. What is the potential difference as one moves from a closer point r = a to a farther location r = b?
A)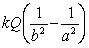
B)
C)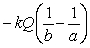
D)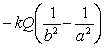
E) None of the above.
A)
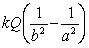
B)

C)
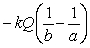
D)
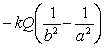
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
A lithium nucleus with a charge of 31.6 × 10-19) C and a mass of 71.67 × 10-27) kg, and an alpha particle with a charge of 21.6 × 10-19) C and a mass of 41.67 × 10-27) kg, are at rest. They could be accelerated to the same kinetic energy by
A) accelerating them through the same electrical potential difference.
B) accelerating the alpha particle through V volts and the lithium nucleus through 2V/3 volts.
C) accelerating the alpha particle through V volts and the lithium nucleus through 7V/4 volts.
D) accelerating the alpha particle through V volts and the lithium nucleus through 7V/6 volts.
E) None of these procedures.
A) accelerating them through the same electrical potential difference.
B) accelerating the alpha particle through V volts and the lithium nucleus through 2V/3 volts.
C) accelerating the alpha particle through V volts and the lithium nucleus through 7V/4 volts.
D) accelerating the alpha particle through V volts and the lithium nucleus through 7V/6 volts.
E) None of these procedures.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An electric dipole that has a positive charge of 4.8 × 10-19 C is separated from a negative charge of the same magnitude by 6.4 × 10-10 m. The electric potential at a point 9.2 × 10-10 m from each of the two charges is
A) 9.4 V.
B) zero.
C) 4.2 V.
D) 5.1 × 109 V.
E) 1.7 V.
A) 9.4 V.
B) zero.
C) 4.2 V.
D) 5.1 × 109 V.
E) 1.7 V.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
Correct units for electric potential are
A) N/C.
B) V/m.
C) N/kg.
D) J/C.
E) C/N.
A) N/C.
B) V/m.
C) N/kg.
D) J/C.
E) C/N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The concept of difference in electric potential is most closely associated with
A) the mechanical force on an electron.
B) the number of atoms in one gram-atom.
C) the charge on one electron.
D) the resistance of a certain specified column of mercury.
E) the work per unit quantity of electricity.
A) the mechanical force on an electron.
B) the number of atoms in one gram-atom.
C) the charge on one electron.
D) the resistance of a certain specified column of mercury.
E) the work per unit quantity of electricity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
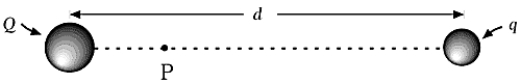 Charges Q and q Q ≠ q), separated by a distance d, produce a potential VP = 0 at point P. This means that
Charges Q and q Q ≠ q), separated by a distance d, produce a potential VP = 0 at point P. This means thatA) no force is acting on a test charge placed at point P.
B) Q and q must have the same sign.
C) the electric field must be zero at point P.
D) the net work in bringing Q to distance d from q is zero.
E) the net work needed to bring a charge from infinity to point P is zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The potential at a point due to a unit positive charge is found to be V. If the distance between the charge and the point is tripled, the potential becomes
A) V/3.
B) 3V.
C) V/9.
D) 9V.
E) 1/V2.
A) V/3.
B) 3V.
C) V/9.
D) 9V.
E) 1/V2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The electron volt is a unit of
A) capacitance.
B) charge.
C) energy.
D) momentum.
E) potential.
A) capacitance.
B) charge.
C) energy.
D) momentum.
E) potential.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
A metal sphere with a radius of 10 cm is used to accumulate charges until the electric field at the surface is 3.0 MV/m. How much charge can be accumulated on this sphere?
A) 67 μC
B) 33 μC
C) 13 μC
D) 6.7 μC
E) 3.3 μC
A) 67 μC
B) 33 μC
C) 13 μC
D) 6.7 μC
E) 3.3 μC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
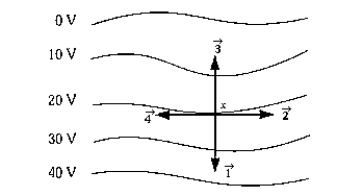 The vector that best represents the direction of the electric field intensity at point x on the 20-V equipotential line is
The vector that best represents the direction of the electric field intensity at point x on the 20-V equipotential line isA) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
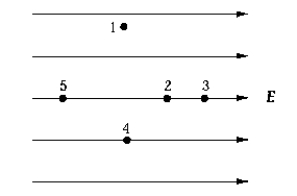 Which point in the electric field in the diagram is at the highest potential?
Which point in the electric field in the diagram is at the highest potential?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Which of the following statements regarding electric potential is true?
A) The units of electric potential are N/C.
B) Electric potential is a vector quantity.
C) Equipotential surfaces are at right angles to lines of force.
D) Potential differences can be measured directly with a ballistic galvanometer.
E) Equipotential surfaces for an isolated point charge are cubes concentric with the charge.
A) The units of electric potential are N/C.
B) Electric potential is a vector quantity.
C) Equipotential surfaces are at right angles to lines of force.
D) Potential differences can be measured directly with a ballistic galvanometer.
E) Equipotential surfaces for an isolated point charge are cubes concentric with the charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
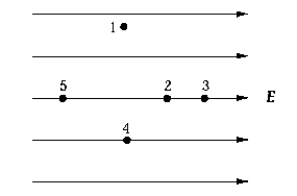 Which point in the electric field in the diagram is at the lowest potential?
Which point in the electric field in the diagram is at the lowest potential?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A metal sphere with a radius of 8.0 cm is used to accumulate charges until the electric field at the surface is 3.0 MV/m. How much charge can be accumulated on this sphere?
A) 2.1 μC
B) 3.3 μC
C) 1.3 nC
D) 6.7 μC
E) 4.2 μC
A) 2.1 μC
B) 3.3 μC
C) 1.3 nC
D) 6.7 μC
E) 4.2 μC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
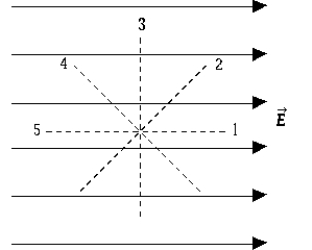 The figure depicts a uniform electric field. The direction in which the increase in the electric potential is a maximum is
The figure depicts a uniform electric field. The direction in which the increase in the electric potential is a maximum isA) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
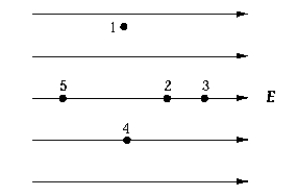 Which of the points shown in the diagram are at the same potential?
Which of the points shown in the diagram are at the same potential?A) 2 and 5
B) 2, 3, and 5
C) 1 and 4
D) 1 and 5
E) 2 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
Two charges Q1 = +6 C) and Q2 = -2 C) are brought from infinity to positions on the x-axis of x = -4 cm and x = +4 cm, respectively. Is it possible to bring a third charge
Q3 = +3 C) from infinity to a point on the x-axis between the charges where the potential is zero, and if so, where would this position be?
A) It is not possible.
B) x = 0 cm
C) x = +2 cm
D) x = +6 cm
E) x = +1.5 cm
Q3 = +3 C) from infinity to a point on the x-axis between the charges where the potential is zero, and if so, where would this position be?
A) It is not possible.
B) x = 0 cm
C) x = +2 cm
D) x = +6 cm
E) x = +1.5 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
The potential on the surface of a solid conducting sphere of radius r = 20 cm is 100 V. The potential at r = 10 cm is
A) 100 V.
B) 50 V.
C) 25 V.
D) zero.
E) cannot be determined.
A) 100 V.
B) 50 V.
C) 25 V.
D) zero.
E) cannot be determined.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
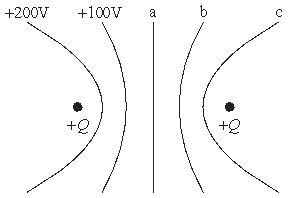 Two equal positive charges are placed x m apart. The equipotential lines are at 100 V interval.The potential for line c is
Two equal positive charges are placed x m apart. The equipotential lines are at 100 V interval.The potential for line c isA) "-100 V."
B) "+0 V."
C) "-200 V."
D) "+200 V."
E) "zero."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
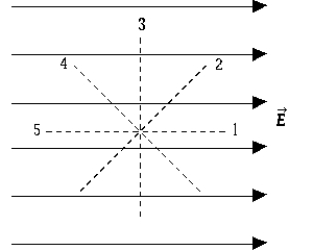 The figure depicts a uniform electric field. The direction in which there is no change in the electric potential is
The figure depicts a uniform electric field. The direction in which there is no change in the electric potential isA) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
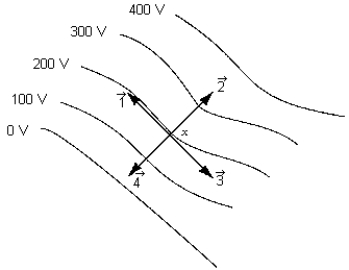 The vector that best represents the direction of the electric field intensity at point x on the 200-V equipotential line is
The vector that best represents the direction of the electric field intensity at point x on the 200-V equipotential line isA) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
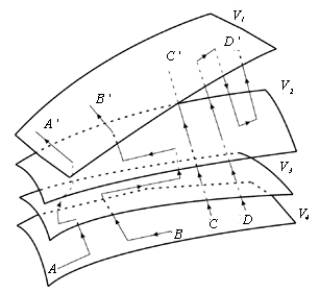 The figure shows portions of four equipotential surfaces whose potentials are related as follows: V1 > V2 > V3 > V4. The lines represent four paths A → A', B → B', C → C', D → D'), along which equal test charges are moved. The work involved can be said to be
The figure shows portions of four equipotential surfaces whose potentials are related as follows: V1 > V2 > V3 > V4. The lines represent four paths A → A', B → B', C → C', D → D'), along which equal test charges are moved. The work involved can be said to beA) the greatest for path A → A'.
B) the greatest for path B → B'.
C) the greatest for path C → C'.
D) the greatest for path D → D'.
E) the same for all paths.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
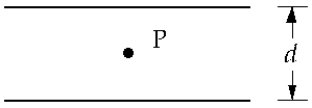 Two flat parallel plates are d = 0.40 cm apart. The potential difference between the plates is 360 V. The electric field at the point P at the center is approximately
Two flat parallel plates are d = 0.40 cm apart. The potential difference between the plates is 360 V. The electric field at the point P at the center is approximatelyA) 90 kN/C.
B) 3.6 kN/C.
C) 0.9 kN/C.
D) zero.
E) 3.6 × 105 N/C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
From a very large distance, a proton charge = e, mass = 1.67 × 10-27 kg) with initial kinetic energy 3 MeV is fired head-on toward a fixed stationary uranium nucleus charge 92e, mass = 3.95 × 10-25 kg). Calculate how close to the uranium the proton gets before it comes to rest. Assume the uranium nucleus does not move.)
A) 2.75 × 105 m
B) 4.40 × 10-8 m
C) 4.40 × 10-14 m
D) 2.10 × 10-7 m
E) None of the above.
A) 2.75 × 105 m
B) 4.40 × 10-8 m
C) 4.40 × 10-14 m
D) 2.10 × 10-7 m
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
The electrical potential 2.0 cm from a point charge of Q1 = +6.5 × 10-9 C and 3.5 cm from a second charge Q2 is 1.2 kV. Find Q2.
A) -6.7 × 10-9 C
B) -3.8 × 10-9 C
C) -1.0 × 10-9 C
D) 3.8 × 10-9 C
E) 1.0 × 10-9 C
A) -6.7 × 10-9 C
B) -3.8 × 10-9 C
C) -1.0 × 10-9 C
D) 3.8 × 10-9 C
E) 1.0 × 10-9 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Two large metallic plates are parallel to each other and charged. The distance between the plates is d. The potential difference between the plates is V. The magnitude of the electric field in the region between the plates and away from the edges is given by
A) d/V.
B) V2/d.
C) dV.
D) V/d2.
E) None of these is correct.
A) d/V.
B) V2/d.
C) dV.
D) V/d2.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Two charges Q1 = +6 C) and Q2 = -2 C) are brought from infinity to positions on the x-axis of x = -4 cm and x = +4 cm, respectively. How much work was done in bringing the charges together?
A) -1.80 × 106 J
B) -9.00 × 105 J
C) -16.9 J
D) -1.35 J
E) None of the above.
A) -1.80 × 106 J
B) -9.00 × 105 J
C) -16.9 J
D) -1.35 J
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
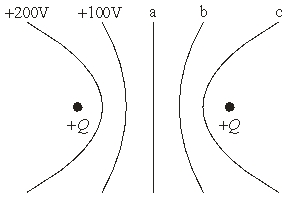 Two equal positive charges are placed x m apart. The equipotential lines are at 100 V interval.The work required to move a third charge, q = -e, from the+0 V line to b is
Two equal positive charges are placed x m apart. The equipotential lines are at 100 V interval.The work required to move a third charge, q = -e, from the+0 V line to b isA) "-0 eV."
B) "-100 eV."
C) "-200 eV."
D) "-200 eV.".
E) "zero."

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
An 80-nF capacitor is charged to a potential of 500 V. How much charge accumulates on each plate of the capacitor?
A) 4.0 × 10-4 C
B) 4.0 × 10-5 C
C) 4.0 × 10-10 C
D) 1.6 × 10-10 C
E) 1.6 × 10-7 C
A) 4.0 × 10-4 C
B) 4.0 × 10-5 C
C) 4.0 × 10-10 C
D) 1.6 × 10-10 C
E) 1.6 × 10-7 C

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
When a small, positively charged metal ball comes in contact with the interior of a positively charged metal shell,
A) the charge on the ball becomes negative.
B) the amount of positive charge on the ball increases.
C) the positive charge on the shell decreases.
D) the charge on the shell and the ball reach the same value.
E) the ball loses all of its excess charge.
A) the charge on the ball becomes negative.
B) the amount of positive charge on the ball increases.
C) the positive charge on the shell decreases.
D) the charge on the shell and the ball reach the same value.
E) the ball loses all of its excess charge.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A capacitor of capacitance C holds a charge Q when the potential difference across the plates is V. If the charge Q on the plates is doubled to 2Q,
A) the capacitance becomes 1/2)V.
B) the capacitance becomes 2C.
C) the potential changes to 1/2)V.
D) the potential changes to 2V.
E) the potential does not change.
A) the capacitance becomes 1/2)V.
B) the capacitance becomes 2C.
C) the potential changes to 1/2)V.
D) the potential changes to 2V.
E) the potential does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
What is the approximate radius of an equipotential spherical surface of 30 V about a point charge of +15 nC if the potential at an infinite distance from the surface is zero?
A) 1.0 m
B) 2.1 m
C) 3.0 m
D) 4.5 m
E) 6.8 m
A) 1.0 m
B) 2.1 m
C) 3.0 m
D) 4.5 m
E) 6.8 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A solid spherical conductor of radius 15 cm has a charge Q = 6.5 nC on it. A second, initially uncharged, spherical conductor of radius 10 cm is moved toward the first until they touch and is then moved far away from it. How much charge is there on the second sphere after the two spheres have been separated?
A) 2.6 nC
B) 2.2 nC
C) 3.2 nC
D) 3.9 nC
E) 4.3 nC
A) 2.6 nC
B) 2.2 nC
C) 3.2 nC
D) 3.9 nC
E) 4.3 nC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A solid spherical conductor of radius 15 cm has a charge Q = 6.5 nC on it. A second, initially uncharged, spherical conductor of radius 10 cm is moved toward the first until they touch and is then moved far away from it. How much charge is there on the first sphere after the two spheres have been separated?
A) 2.6 nC
B) 2.2 nC
C) 3.2 nC
D) 3.9 nC
E) 4.3 nC
A) 2.6 nC
B) 2.2 nC
C) 3.2 nC
D) 3.9 nC
E) 4.3 nC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A solid conducting sphere of radius ra is placed concentrically inside a conducting spherical shell of inner radius rb1 and outer radius rb2. The inner sphere carries a charge Q while the outer sphere does not carry any net charge. The potential for r < ra is
A)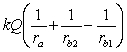 .
.
B)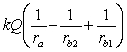 .
.
C)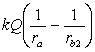 .
.
D)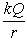 .
.
E) zero.
A)
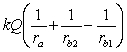 .
.B)
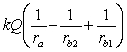 .
.C)
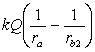 .
.D)
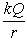 .
.E) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
Dielectric breakdown occurs in the air at an electric field strength of Emax = 3.0 × 106 V/m. If the maximum charge that can be placed on a spherical conductor is 2.0 × 10-3 C before breakdown, calculate the diameter of the sphere.
A) 6.0 m
B) 4.9 m
C) 1.2 m
D) 2.5 m
E) 3.0 m
A) 6.0 m
B) 4.9 m
C) 1.2 m
D) 2.5 m
E) 3.0 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
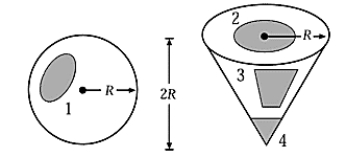 We give the same charge to a metal sphere of radius R and a metal cone of radius R and height 2R. The shaded regions in the figure are of equal area. Which region has the greatest surface charge density?
We give the same charge to a metal sphere of radius R and a metal cone of radius R and height 2R. The shaded regions in the figure are of equal area. Which region has the greatest surface charge density?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) All have equal charge densities.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The dielectric strength of the atmosphere is of the order of
A) 1 V/m.
B) 102 V/m.
C) 104 V/m.
D) 106 V/m.
E) 108 V/m.
A) 1 V/m.
B) 102 V/m.
C) 104 V/m.
D) 106 V/m.
E) 108 V/m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A solid spherical conductor of radius 20 cm has a charge Q = 25 nC on it. A second, initially uncharged, spherical conductor of radius 12 cm is moved toward the first until they touch and is then moved far away from it. How much charge is there on the second sphere after the two spheres have been separated?
A) 15 nC
B) 9.4 nC
C) 25 nC
D) 3.9 nC
E) 2.1 nC
A) 15 nC
B) 9.4 nC
C) 25 nC
D) 3.9 nC
E) 2.1 nC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
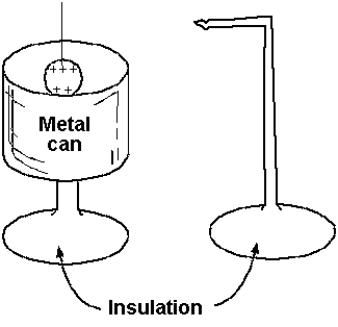 A charged metal ball is lowered into an insulated metal can and permitted to touch the inside of the can. The ball is then withdrawn and hung on a stand. A second uncharged ball will be attracted to
A charged metal ball is lowered into an insulated metal can and permitted to touch the inside of the can. The ball is then withdrawn and hung on a stand. A second uncharged ball will be attracted toA) the outside of the can.
B) the inside of the can.
C) the outside and the inside of the can.
D) the metal ball and the inside of the can.
E) the metal ball, the inside of the can, and the outside of the can.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A solid conducting sphere of radius ra is placed concentrically inside a conducting spherical shell of inner radius rb1 and outer radius rb2. The inner sphere carries a charge Q while the outer sphere does not carry any net charge. The potential for rb1 < r < rb2 is
A)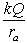 .
.
B)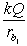 .
.
C)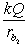 .
.
D)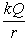 .
.
E) zero.
A)
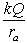 .
.B)
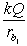 .
.C)
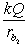 .
.D)
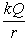 .
.E) zero.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
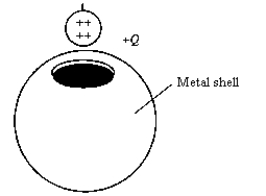 A metal ball of charge +Q is lowered into an insulated, uncharged metal shell and allowed to rest on the bottom of the shell. When the charges reach equilibrium,
A metal ball of charge +Q is lowered into an insulated, uncharged metal shell and allowed to rest on the bottom of the shell. When the charges reach equilibrium,A) the outside of the shell has a charge of -Q and the ball has a charge of +Q.
B) the outside of the shell has a charge of +Q and the ball has a charge of +Q.
C) the outside of the shell has a charge of zero and the ball has a charge of +Q.
D) the outside of the shell has a charge of +Q and the ball has zero charge.
E) the outside of the shell has a charge of +Q and the ball has a charge of -Q.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Dielectric breakdown occurs in the air at an electric field strength of Emax = 3.0 × 106 V/m. If the maximum potential at the surface of a spherical conductor is 5.0 × 106 V, then calculate the radius of the sphere.
A) 0.60 m
B) 1.3 m
C) 1.7 m
D) 0.77 m
E) 15 m
A) 0.60 m
B) 1.3 m
C) 1.7 m
D) 0.77 m
E) 15 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
If the area of the plates of a parallel-plate capacitor is doubled, the capacitance is
A) not changed.
B) doubled.
C) halved.
D) increased by a factor of 4.
E) decreased by a factor of 1/4.
A) not changed.
B) doubled.
C) halved.
D) increased by a factor of 4.
E) decreased by a factor of 1/4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If a capacitor of capacitance 2.0 μF is given a charge of 1.0 mC, the potential difference across the capacitor is
A) 0.50 kV.
B) 2.0 V.
C) 2.0 μV.
D) 0.50 V.
E) None of these is correct.
A) 0.50 kV.
B) 2.0 V.
C) 2.0 μV.
D) 0.50 V.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
Dielectric breakdown occurs in the air at an electric field strength of Emax = 3.0 × 106 V/m. What is the maximum surface charge density that can be placed on a spherical conductor of radius 1.5 m before breakdown?
A) 2.7 × 10-5 C/m2
B) 1.2 × 10-5 C/m2
C) 8.1 × 10-5 C/m2
D) 8.6 × 10-6 C/m2
E) 1.8 × 10-5 C/m2
A) 2.7 × 10-5 C/m2
B) 1.2 × 10-5 C/m2
C) 8.1 × 10-5 C/m2
D) 8.6 × 10-6 C/m2
E) 1.8 × 10-5 C/m2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
What is the approximate radius of an equipotential spherical surface of 100 V about a point charge of +45 nC if the potential at an infinite distance from the surface is zero?
A) 1.0 m
B) 2.1 m
C) 3.0 m
D) 4.5 m
E) 4.0 m
A) 1.0 m
B) 2.1 m
C) 3.0 m
D) 4.5 m
E) 4.0 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
An electric charge q is placed on an isolated metal sphere of radius r1. If an uncharged sphere of radius r2 with r2 > r1) is then connected to the first sphere, the spheres will have equal
A) and like charges on their surfaces.
B) electric fields.
C) potentials.
D) capacitances.
E) but opposite charges on their surfaces.
A) and like charges on their surfaces.
B) electric fields.
C) potentials.
D) capacitances.
E) but opposite charges on their surfaces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 142 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



