Deck 14: Thermodynamics I
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/146
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 14: Thermodynamics I
1
The highest and lowest temperatures ever recorded in the United States are 134oF California, 1913) and -80oF Alaska, 1971). What are these temperatures in kelvins?
A) 407 K and 193 K
B) 330 K and 211 K
C) 347 K and 228 K
D) 340 K and 211 K
E) 330 K and 246 K
A) 407 K and 193 K
B) 330 K and 211 K
C) 347 K and 228 K
D) 340 K and 211 K
E) 330 K and 246 K
330 K and 211 K
2
A temperature of 14oF is equivalent to
A) -10oC.
B) 7.77oC.
C) 25.5oC.
D) 26.7oC.
E) 47.7oC.
A) -10oC.
B) 7.77oC.
C) 25.5oC.
D) 26.7oC.
E) 47.7oC.
-10oC.
3
Which of the following statements about absolute zero temperature is true?
A) At absolute zero all translational motion of the particles ceases.
B) At absolute zero all rotational motion of the particles ceases.
C) Absolute zero is defined at 273.15°C.
D) At absolute zero all particles are at rest, except for quantum motion.
E) All the above.
A) At absolute zero all translational motion of the particles ceases.
B) At absolute zero all rotational motion of the particles ceases.
C) Absolute zero is defined at 273.15°C.
D) At absolute zero all particles are at rest, except for quantum motion.
E) All the above.
All the above.
4
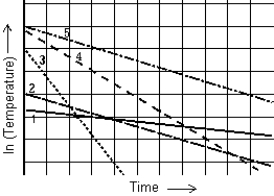 The graph shows the natural logarithm of the temperature of various thermometers as a function of time. The thermometer that cools at the quickest rate is
The graph shows the natural logarithm of the temperature of various thermometers as a function of time. The thermometer that cools at the quickest rate isA) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The temperature in January in Winnipeg, Manitoba, has been known to go down to -40oC. What is this temperature on the Fahrenheit scale?
A) -40oF
B) -104oF
C) +9.8oF
D) -72oF
E) -32oF
A) -40oF
B) -104oF
C) +9.8oF
D) -72oF
E) -32oF

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
The temperature at which the Celsius and Fahrenheit scales read the same is
A) 40oC.
B) -40oC.
C) 20oF.
D) 68oF.
E) 100oC.
A) 40oC.
B) -40oC.
C) 20oF.
D) 68oF.
E) 100oC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Normal human body temperature is 98.6ºF. What is the corresponding Celsius temperature?
A) 54.8oC
B) 72.6oC
C) 40.0oC
D) 37.0oC
E) 35.5oC
A) 54.8oC
B) 72.6oC
C) 40.0oC
D) 37.0oC
E) 35.5oC

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Calculate the point on the Fahrenheit scale when numerically it is 100 degrees larger than that of the Celsius scale for the same temperature.
A) 85
B) 265
C) 185
D) 165
E) No such point exists.
A) 85
B) 265
C) 185
D) 165
E) No such point exists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
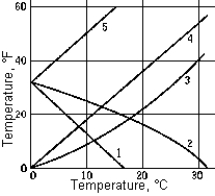 Which curve correctly represents the relation of the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit to the temperature in degrees Celsius?
Which curve correctly represents the relation of the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit to the temperature in degrees Celsius?A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) 5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
If it is known that two bodies are in thermal equilibrium, one can conclude that
A) they must be in thermal equilibrium with a third body.
B) there must be a net heat flow between them.
C) the bodies must be at different temperatures.
D) some shared physical property must be changing.
E) they must be at the same temperature.
A) they must be in thermal equilibrium with a third body.
B) there must be a net heat flow between them.
C) the bodies must be at different temperatures.
D) some shared physical property must be changing.
E) they must be at the same temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
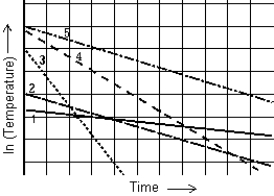 The graph shows the natural logarithm of the temperature of various thermometers as a function of time. The thermometer that cools at the slowest rate is
The graph shows the natural logarithm of the temperature of various thermometers as a function of time. The thermometer that cools at the slowest rate isA) 1.
B) 2.
C) 3.
D) 4.
E) 5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
An example of a thermometric property is
A) the volume of a gas.
B) the pressure of a confined gas.
C) the electrical resistance of an electrical conductor.
D) the length of a column of mercury.
E) All of these are correct.
A) the volume of a gas.
B) the pressure of a confined gas.
C) the electrical resistance of an electrical conductor.
D) the length of a column of mercury.
E) All of these are correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
 A thermometer is constructed by filling a small glass tube with a liquid that expands linearly with temperature. The thermometer is then calibrated at 0°C and 100°C, and the scale evenly divided between the two values. Unfortunately, a manufacturing defect results in the middle one-third of the tube being narrower, otherwise the tube has uniform diameter. For what range of temperatures is the reading accurate?
A thermometer is constructed by filling a small glass tube with a liquid that expands linearly with temperature. The thermometer is then calibrated at 0°C and 100°C, and the scale evenly divided between the two values. Unfortunately, a manufacturing defect results in the middle one-third of the tube being narrower, otherwise the tube has uniform diameter. For what range of temperatures is the reading accurate?A) 0°C to 33°C
B) 0°C and 67°C
C) 0°C to 33°C and 67°C to 100°C
D) 67°C to 100°C
E) At no point does this thermometer gives the right reading except at 0°C and 100°C.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A temperature difference of 9oF is the same as a difference of
A) 5oC.
B) 9oC.
C) 20oC.
D) 68oC.
E) 100oC.
A) 5oC.
B) 9oC.
C) 20oC.
D) 68oC.
E) 100oC.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A temperature difference of 5 Co is the same as a difference of
A) 41 Fo.
B) 14 Fo.
C) 9 Fo.
D) 5 Fo.
E) -15 Fo.
A) 41 Fo.
B) 14 Fo.
C) 9 Fo.
D) 5 Fo.
E) -15 Fo.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Which of the following statements about thermal contact and thermal equilibrium is NOT true?
A) Two objects can be in thermal equilibrium even if they are not in thermal contact with each other.
B) Heat may be transferred between two objects when they are in thermal contact.
C) For energy to be transferred between two objects they have to be in thermal contact.
D) Thermal contact between two objects allows energy to be transferred without the use of macroscopic work.
E) Two objects, one that feels cold and the other does not feel as cold, does not imply that they are not in thermal equilibrium.
A) Two objects can be in thermal equilibrium even if they are not in thermal contact with each other.
B) Heat may be transferred between two objects when they are in thermal contact.
C) For energy to be transferred between two objects they have to be in thermal contact.
D) Thermal contact between two objects allows energy to be transferred without the use of macroscopic work.
E) Two objects, one that feels cold and the other does not feel as cold, does not imply that they are not in thermal equilibrium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
An interval of 30 kelvins is equivalent to an interval of
A) 30 Fahrenheit degrees.
B) 76 Fahrenheit degrees.
C) 577 Fahrenheit degrees.
D) 303 Fahrenheit degrees.
E) None of these is correct.
A) 30 Fahrenheit degrees.
B) 76 Fahrenheit degrees.
C) 577 Fahrenheit degrees.
D) 303 Fahrenheit degrees.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
If it is known that two bodies are in thermal equilibrium, one can conclude that
A) they must be in thermal equilibrium with a third body.
B) there must be a net heat flow between them.
C) the bodies must be at different temperatures.
D) some shared physical property must be changing.
E) None of these is correct.
A) they must be in thermal equilibrium with a third body.
B) there must be a net heat flow between them.
C) the bodies must be at different temperatures.
D) some shared physical property must be changing.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The air on a hot day is 108oF. What is it in degrees Celsius?
A) 10oC
B) 110oC
C) 32 K
D) 315 K
E) 420 K
A) 10oC
B) 110oC
C) 32 K
D) 315 K
E) 420 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
If you plot a graph with Fahrenheit temperatures along the horizontal axis and the corresponding Celsius temperatures along the vertical axis, the slope of the equal-temperature line will be
A) -40 Fo/Co.
B) 32 Fo/Co.
C) 1.8 Fo/Co.
D) 0.56 Fo/Co.
E) 0 Fo/Co.
A) -40 Fo/Co.
B) 32 Fo/Co.
C) 1.8 Fo/Co.
D) 0.56 Fo/Co.
E) 0 Fo/Co.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Assume that helium is a perfect gas and that the volume of a cylinder containing helium is independent of temperature. A cylinder of helium at +85oC has a pressure of 208 atm. The pressure of the helium when it is cooled to -55oC is
A) -132 atm.
B) 127 atm.
C) 335 atm.
D) 132 atm.
E) 204 atm.
A) -132 atm.
B) 127 atm.
C) 335 atm.
D) 132 atm.
E) 204 atm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
Which of the following statements about the ideal gas law, PV = nRT, is NOT true?
A) When the temperature of two low density gases, which are initially at the same temperature, pressure, and volume, is increased by the same amount, the volume increases by the same amount.
B) When the volume of two low density gases, which are initially at the same temperature, pressure, and volume, is compressed by the same amount, the temperature increases by the same amount.
C) A P-T plot of any gas at low density intercept the T-axis at the same point.
D) The intercept at the ordinate for PV/nT vs P plot of any gas is the gas constant.
E) The ideal gas law is valid for high density of all gases.
A) When the temperature of two low density gases, which are initially at the same temperature, pressure, and volume, is increased by the same amount, the volume increases by the same amount.
B) When the volume of two low density gases, which are initially at the same temperature, pressure, and volume, is compressed by the same amount, the temperature increases by the same amount.
C) A P-T plot of any gas at low density intercept the T-axis at the same point.
D) The intercept at the ordinate for PV/nT vs P plot of any gas is the gas constant.
E) The ideal gas law is valid for high density of all gases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If the pressure and volume of an ideal gas are both reduced to half their original value, the absolute temperature of the gas is
A) unchanged.
B) doubled.
C) halved.
D) increased by a factor of 4.
E) decreased by a factor of 4.
A) unchanged.
B) doubled.
C) halved.
D) increased by a factor of 4.
E) decreased by a factor of 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A large balloon is being filled with helium He) from gas cylinders. The temperature is 25°C and the pressure is 1 atmosphere. The volume of the inflated balloon is 2500 m3. What was the volume of He in the cylinders if the gas was under a pressure of 110 atmospheres and at a temperature of 12°C when in the gas cylinders?
A) 11 m3
B) 22 m3
C) 24 m3
D) 15 m3
E) 23 m3
A) 11 m3
B) 22 m3
C) 24 m3
D) 15 m3
E) 23 m3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Inside a sphere of radius 12 cm are 8.0 × 1023 gas molecules at a temperature of 50°C. What pressure do the gas molecules exert on the inside of the sphere?
A) 650 × 103 Pa
B) 370 × 103 Pa
C) 76.0 × 103 Pa
D) 160 × 103 Pa
E) 490 × 103 Pa
A) 650 × 103 Pa
B) 370 × 103 Pa
C) 76.0 × 103 Pa
D) 160 × 103 Pa
E) 490 × 103 Pa

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Boltzmann's constant, k, has a value of 1.381 × 10-23 J/K. What is the significance of the constant?
A) It defines a characteristic energy at the microscopic level, given the temperature in kelvins.
B) It allows the pressure of the gas to be calculated, given the volume and temperature.
C) It measures the average kinetic energy of a molecule at a given temperature for each degree of freedom.
D) A) and B)
E) A) and C)
A) It defines a characteristic energy at the microscopic level, given the temperature in kelvins.
B) It allows the pressure of the gas to be calculated, given the volume and temperature.
C) It measures the average kinetic energy of a molecule at a given temperature for each degree of freedom.
D) A) and B)
E) A) and C)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A rigid container of air is at atmospheric pressure and 27oC. To double the pressure in the container, heat it to
A) 54oC.
B) 300oC.
C) 327oC.
D) 600oC.
E) 327 K.
A) 54oC.
B) 300oC.
C) 327oC.
D) 600oC.
E) 327 K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
What mass of He gas occupies 8.5 liters at 0°C and 1 atmosphere? The molar mass of He = 4.00 g/mol.)
A) 10.5 g
B) 0.66 g
C) 2.6 g
D) 0.38 g
E) 1.52 g
A) 10.5 g
B) 0.66 g
C) 2.6 g
D) 0.38 g
E) 1.52 g

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
A mass of He gas occupies a volume V at standard temperature and pressure. What volume is occupied if the mass is halved, the absolute temperature doubled, and the pressure increased by a third?
A) 3/16)V
B) 4/3)V
C) 3/4)V
D) 3/8)V
E) 1/3)V
A) 3/16)V
B) 4/3)V
C) 3/4)V
D) 3/8)V
E) 1/3)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If both the temperature and the volume of an ideal gas are doubled, the pressure is
A) increased by a factor of 4.
B) doubled also.
C) unchanged.
D) diminished by a factor of ¼.
E) None of these is correct.
A) increased by a factor of 4.
B) doubled also.
C) unchanged.
D) diminished by a factor of ¼.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A gas thermometer could measure temperature change by measuring the change in
A) density at constant volume.
B) specific heat at constant volume.
C) pressure at constant volume.
D) volume at constant temperature.
E) mass at constant volume.
A) density at constant volume.
B) specific heat at constant volume.
C) pressure at constant volume.
D) volume at constant temperature.
E) mass at constant volume.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
In a vacuum system, a container is pumped down to a pressure of 1.33 × 10-6 Pa at 20oC. How many molecules of gas are there in 1 cm3 of this container? Boltzmann's constant k = 1.38 × 10-23 J/K)
A) 3.3 × 108
B) 4.8 × 109
C) 3.3 × 1014
D) 7.9 × 1012
E) 4.8 × 1012
A) 3.3 × 108
B) 4.8 × 109
C) 3.3 × 1014
D) 7.9 × 1012
E) 4.8 × 1012

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A collection of oxygen molecules occupies a volume V at standard temperature and pressure. What is the new volume if the amount of oxygen is doubled and the pressure is tripled?
A) V
B) 2/3)V
C) 3/2)V
D) 6V
E) 5/9)V
A) V
B) 2/3)V
C) 3/2)V
D) 6V
E) 5/9)V

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
You can double both the pressure and the volume of an ideal gas if you change the temperature of the gas by
A) reducing it to one-quarter of its original value.
B) doubling it.
C) reducing it to one-half of its original value.
D) quadrupling it.
E) doing none of these.
A) reducing it to one-quarter of its original value.
B) doubling it.
C) reducing it to one-half of its original value.
D) quadrupling it.
E) doing none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A gas has a density X at standard temperature and pressure. What is the new density when the absolute temperature is doubled and the pressure increased by a factor of 3?
A) 2/3)X
B) 4/3)X
C) 3/4)X
D) 6)X
E) 3/2)X
A) 2/3)X
B) 4/3)X
C) 3/4)X
D) 6)X
E) 3/2)X

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The relationship between the pressure and the volume of a gas expressed by Boyle's law holds true
A) for some gases under any conditions.
B) if the density is constant.
C) if the container of the gas can expand with increasing pressure.
D) if the temperature is constant.
E) for all gases under any conditions.
A) for some gases under any conditions.
B) if the density is constant.
C) if the container of the gas can expand with increasing pressure.
D) if the temperature is constant.
E) for all gases under any conditions.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
If a mass of oxygen gas occupies a volume of 8 L at standard temperature and pressure, what is the change in the volume if the temperature is reduced by one half and the pressure is doubled?
A) It increases to 12 L.
B) It decreases to 6 L.
C) It increases to 24 L.
D) It decreases to 2 L.
E) It does not change.
A) It increases to 12 L.
B) It decreases to 6 L.
C) It increases to 24 L.
D) It decreases to 2 L.
E) It does not change.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
If a mass of oxygen gas occupies a volume of 8 L at standard temperature and pressure, what is the change in the volume if the temperature is decreased to 136 K and the pressure remains constant?
A) It increases to 16 L.
B) It decreases to 12 L.
C) It increases to 24 L.
D) It decreases to 4 L.
E) It increases to 12 L.
A) It increases to 16 L.
B) It decreases to 12 L.
C) It increases to 24 L.
D) It decreases to 4 L.
E) It increases to 12 L.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The air in a balloon occupies a volume of 0.10 m3 when at a temperature of 27oC and a pressure of 1.2 atm. What is the balloon's volume at 7oC and 1.0 atm? The amount of gas remains constant.)
A) 0.022 m3
B) 0.078 m3
C) 0.089 m3
D) 0.11 m3
E) 0.13 m3
A) 0.022 m3
B) 0.078 m3
C) 0.089 m3
D) 0.11 m3
E) 0.13 m3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The air around us has 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. If the pressure is 1 atm, the pressure due to oxygen is
A) 0.21 atm.
B) 0.78 atm.
C) 1 atm.
D) 0.5 atm.
E) 0.67 atm.
A) 0.21 atm.
B) 0.78 atm.
C) 1 atm.
D) 0.5 atm.
E) 0.67 atm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
Ethyl chloride C2H5Cl) is used as a refrigerant under certain circumstances. One mole of this substance contains Avogadro's number of
A) carbon atoms.
B) hydrogen atoms.
C) chlorine atoms.
D) All of these are correct.
E) None of these is correct.
A) carbon atoms.
B) hydrogen atoms.
C) chlorine atoms.
D) All of these are correct.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A mass of air is at pressure P and volume V at 1°C. When it is made to occupy half this volume at 3 times this pressure, its temperature becomes approximately
A) 411°C.
B) 0.67°C.
C) 1.5°C.
D) 6°C.
E) 411 K.
A) 411°C.
B) 0.67°C.
C) 1.5°C.
D) 6°C.
E) 411 K.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Which of the following is an assumption that is made in the kinetic theory of gases?
A) Molecules are not described by Newton's laws.
B) Molecules make up only a small fraction of the volume occupied by a gas.
C) Molecules collide inelastically.
D) The total number of molecules is actually very small.
E) There are forces acting on the molecules at all times.
A) Molecules are not described by Newton's laws.
B) Molecules make up only a small fraction of the volume occupied by a gas.
C) Molecules collide inelastically.
D) The total number of molecules is actually very small.
E) There are forces acting on the molecules at all times.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Doubling the Kelvin temperature of a gas increases which of the following measures of its molecular velocity by a factor of 1.4?
A) the rms speed
B) the average speed
C) the most probable speed
D) All three of these speeds are correct.
E) None of these is correct.
A) the rms speed
B) the average speed
C) the most probable speed
D) All three of these speeds are correct.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
The oxygen molar mass = 32 g/mol) and nitrogen molar mass = 28 g/mol) molecules in this room have equal average
A) kinetic energies, but the oxygen molecules are faster.
B) kinetic energies, but the oxygen molecules are slower.
C) kinetic energies and speeds.
D) speeds, but the oxygen molecules have a higher average kinetic energy.
E) speeds, but the oxygen molecules have a lower average kinetic energy.
A) kinetic energies, but the oxygen molecules are faster.
B) kinetic energies, but the oxygen molecules are slower.
C) kinetic energies and speeds.
D) speeds, but the oxygen molecules have a higher average kinetic energy.
E) speeds, but the oxygen molecules have a lower average kinetic energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
A room measures 3 m × 4 m × 2 m and is at 15°C and 1 atm. When the temperature is increased to 25°C, the number of molecules that escape from the room, assuming that the pressure stays at 1 atm, is
A) 6.1 × 1026.
B) 2.1 × 1025.
C) 2.9 × 1026.
D) 1.2 × 1028.
E) 7.04 × 1027.
A) 6.1 × 1026.
B) 2.1 × 1025.
C) 2.9 × 1026.
D) 1.2 × 1028.
E) 7.04 × 1027.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
At room temperature, which of the following diatomic molecules has the greater average kinetic energy: carbon monoxide molar mass = 28 g/mol), nitrogen molar mass = 28 g/mol), or oxygen molar mass = 32 g/mol)?
A) carbon monoxide
B) nitrogen
C) oxygen
D) Both a and b are correct.
E) All three have the same average kinetic energy.
A) carbon monoxide
B) nitrogen
C) oxygen
D) Both a and b are correct.
E) All three have the same average kinetic energy.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
At what common Celsius temperature is the rms velocity of oxygen molecules molar mass = 32 g/mol) double that of hydrogen molecules molar mass = 2.0 g/mol)?
A) −50
B) zero
C) No such temperature exists.
D) 2.0
E) 16
A) −50
B) zero
C) No such temperature exists.
D) 2.0
E) 16

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
If the absolute temperature of a gas is doubled, what is the change in the average kinetic energy of its molecules?
A) no change
B) increases by a factor of 2
C) decreases by a factor of 2
D) increases by a factor of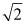
E) decreases by a factor of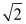
A) no change
B) increases by a factor of 2
C) decreases by a factor of 2
D) increases by a factor of
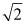
E) decreases by a factor of
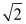

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Two monoatomic gases, helium and neon, are mixed in the ratio of 2 to 1 and are in thermal equilibrium at temperature T the molar mass of helium = 4.0 g/mol and the molar mass of neon = 20.2 g/mol). If the average kinetic energy of each helium atom is 6.3 × 10−21 J, calculate the temperature T.
A) 304 K
B) 456 K
C) 31 K
D) 31°C
E) 101 K
A) 304 K
B) 456 K
C) 31 K
D) 31°C
E) 101 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
One mole of hydrogen gas molar mass = 2.0 g/mol) has an rms velocity of 2.0 × 103 m/s. To what temperature on the Celsius scale does this correspond?
A) 4.8 × 104
B) 3.2 × 102
C) 3.2 × 105
D) 48
E) 69
A) 4.8 × 104
B) 3.2 × 102
C) 3.2 × 105
D) 48
E) 69

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
If the absolute temperature of a gas is doubled, what is the change in the rms speed of its molecules?
A) no change
B) increases by a factor of 2
C) decreases by a factor of 2
D) increases by a factor of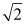
E) decreases by a factor of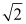
A) no change
B) increases by a factor of 2
C) decreases by a factor of 2
D) increases by a factor of
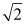
E) decreases by a factor of
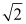

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A cylinder of volume 50 L contains oxygen gas at a pressure of 2 atm. If nitrogen gas of volume 25 L and at pressure 1 atm is added to the oxygen cylinder, the new pressure is
A) 2 atm.
B) 3 atm.
C) 2.5 atm.
D) 3.5 atm.
E) 4 atm.
A) 2 atm.
B) 3 atm.
C) 2.5 atm.
D) 3.5 atm.
E) 4 atm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
Two monoatomic gases, helium and neon, are mixed in the ratio of 2 to 1 and are in thermal equilibrium at temperature T the molar mass of neon = 5 × the molar mass of helium). If the average kinetic energy of each helium atom is U, calculate the average energy of each neon atom.
A) U
B) 0.5U
C) 2U
D) 5U
E) U/5
A) U
B) 0.5U
C) 2U
D) 5U
E) U/5

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A cylinder contains oxygen gas at a temperature of 7°C and a pressure of 15 atm in a volume of 100 L. A fitted piston is lowered into the cylinder, decreasing the volume occupied by the gas to 80 L and raising the temperature to 40°C. The gas pressure is now approximately
A) 3040 atm.
B) 595 atm.
C) 108 atm.
D) 21 atm.
E) 17 atm.
A) 3040 atm.
B) 595 atm.
C) 108 atm.
D) 21 atm.
E) 17 atm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If you carry a sealed cylinder of oxygen to the Moon, you should expect no change in the oxygen's
A) mass.
B) weight.
C) temperature.
D) pressure.
E) rms molecular velocity.
A) mass.
B) weight.
C) temperature.
D) pressure.
E) rms molecular velocity.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
An ideal gas whose original temperature and volume are 27°C and 0.283 m3 undergoes an isobaric expansion. If the final temperature is 87°C, then the final volume is approximately
A) 0.0340 m3.
B) 0.0552 m3.
C) 0.170 m3.
D) 0.340 m3.
E) 1.45 m3.
A) 0.0340 m3.
B) 0.0552 m3.
C) 0.170 m3.
D) 0.340 m3.
E) 1.45 m3.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
At what Kelvin temperature does the rms speed of the oxygen O2) molecules in the air near the surface of Earth become equal to the escape speed from Earth? R = 8.31 J/mol · K; molar mass of O2 gas is 32 g/mol; radius of Earth RE = 6.37 × 106 m; the escape speed from Earth is 11.2 km/s.)
A) 4.8 × 105 K
B) 8.0 × 104 K
C) 1.6 × 105 K
D) 1.1 × 104 K
E) 3.6 × 105 K
A) 4.8 × 105 K
B) 8.0 × 104 K
C) 1.6 × 105 K
D) 1.1 × 104 K
E) 3.6 × 105 K

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
Which of the following is NOT an assumption made in the kinetic theory model of a gas?
A) A gas consists of particles called molecules.
B) The molecules are in random motion and their behavior is described by Newton's laws.
C) The range of molecular forces is much greater than the molecular size.
D) Between collisions, molecules travel with constant speed and in a straight line.
E) Collisions are perfectly elastic and are of negligible duration.
A) A gas consists of particles called molecules.
B) The molecules are in random motion and their behavior is described by Newton's laws.
C) The range of molecular forces is much greater than the molecular size.
D) Between collisions, molecules travel with constant speed and in a straight line.
E) Collisions are perfectly elastic and are of negligible duration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A hailstorm causes an average pressure of 1.4 N/m2 on the 200-m2 flat roof of a house. The hailstones, each of mass 7.0 × 10-3 kg, have an average velocity of 10 m/s perpendicular to the roof and rebound after hitting the roof with the same speed. How many hailstones hit the roof each second?
A) 4000
B) 2000
C) 1000
D) 10
E) 800
A) 4000
B) 2000
C) 1000
D) 10
E) 800

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
You have cut a hole in the middle of a large sheet of metal. When the sheet is heated, the area of the hole
A) does not change.
B) always increases.
C) always decreases.
D) increases if the hole is not in the exact center of the sheet.
E) decreases only if the hole is in the exact center of the sheet.
A) does not change.
B) always increases.
C) always decreases.
D) increases if the hole is not in the exact center of the sheet.
E) decreases only if the hole is in the exact center of the sheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The amount of linear expansion of a rod does not depend on
A) the original length of the rod.
B) the specific heat of the rod.
C) the change in the absolute temperature of the rod.
D) the coefficient of linear expansion.
E) the material from which the rod is made.
A) the original length of the rod.
B) the specific heat of the rod.
C) the change in the absolute temperature of the rod.
D) the coefficient of linear expansion.
E) the material from which the rod is made.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A clock pendulum made of aluminum, which has a coefficient of linear expansion of 24 × 10-6/K, has a period of exactly 1 s at 20oC. Before a homeowner leaves town for one week, he turns the thermostat down to 10oC. When he returns, the clock is
A) fast by about 73 s.
B) fast by about 7.6 min.
C) exactly on time.
D) slow by about 7.6 min.
E) slow by about 73 s.
A) fast by about 73 s.
B) fast by about 7.6 min.
C) exactly on time.
D) slow by about 7.6 min.
E) slow by about 73 s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A common trick to open the lid of a jar that is stuck is to put the lid under hot running water. Suppose the diameter of the lid of a jar of strawberry jam is 6 cm. By how much does the circumference change if the temperature is increased by 30°C? Assume the lid is made of steel.
A) 2.0 × 10-3 cm
B) 3.1 × 10-3 cm
C) 4.1 × 10-3 cm
D) 6.2 × 10-3 cm
E) 5.2 × 10-3 cm
A) 2.0 × 10-3 cm
B) 3.1 × 10-3 cm
C) 4.1 × 10-3 cm
D) 6.2 × 10-3 cm
E) 5.2 × 10-3 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
In a Maxwell-Boltzmann distribution function of molecular speeds, the rms speed is
A) always greater than the mean speed.
B) always less than the mean speed.
C) equal to the mean speed.
D) equal to the most probable speed.
E) independent of the temperature.
A) always greater than the mean speed.
B) always less than the mean speed.
C) equal to the mean speed.
D) equal to the most probable speed.
E) independent of the temperature.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
75 × 10-10 m, the mean free path of the O2 molecule is
A) 5.96 × 10-8 m.
B) 6.53 × 10-8 m.
C) 4.57 × 10-8 m.
D) 6.89 × 10-8 m.
E) 7.67 × 10-8 m.
A) 5.96 × 10-8 m.
B) 6.53 × 10-8 m.
C) 4.57 × 10-8 m.
D) 6.89 × 10-8 m.
E) 7.67 × 10-8 m.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
If α is the coefficient of linear expansion of a material at 0oC, the volume thermal-expansion coefficient of this material at 0oC is
A) ∼α
B) 3α
C) ∼
D) ∼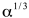
E) None of these is correct.
A) ∼α
B) 3α
C) ∼

D) ∼
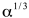
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A room measures 3 m × 4 m × 2 m and is at 20°C and 1 atm. Assuming that it only has the two diatomic gases N2 and O2, the amount of kinetic energy in the gases is
A) 3.6 MJ.
B) 6.1 MJ.
C) 0.25 MJ.
D) 0.41 MJ.
E) none of the above.
A) 3.6 MJ.
B) 6.1 MJ.
C) 0.25 MJ.
D) 0.41 MJ.
E) none of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
If the rms speed of oxygen molecules is 460 m/s at 0oC, the rms speed of oxygen molecules at 273oC is approximately
A) 230 m/s.
B) 325 m/s.
C) 650 m/s.
D) 920 m/s.
E) 1.84 km/s.
A) 230 m/s.
B) 325 m/s.
C) 650 m/s.
D) 920 m/s.
E) 1.84 km/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
The coefficient of linear expansion for most materials
A) is much less than 1 K-1.
B) is much greater than 1 K-1.
C) is approximately 1 K-1.
D) can be less than, greater than, or about equal to 1 K-1.
E) is described by none of these.
A) is much less than 1 K-1.
B) is much greater than 1 K-1.
C) is approximately 1 K-1.
D) can be less than, greater than, or about equal to 1 K-1.
E) is described by none of these.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
When the temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 300 K to 400 K, the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules increases by a factor of
A) 1.15.
B) 1.33.
C) 1.54.
D) 1.78.
E) 2.47.
A) 1.15.
B) 1.33.
C) 1.54.
D) 1.78.
E) 2.47.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
On the basis of the kinetic theory of gases, when the absolute temperature is doubled, the average kinetic energy of the gas molecules changes by a factor of
A) 16.
B) 2.
C)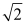 .
.
D) 4.
E) 0.5.
A) 16.
B) 2.
C)
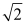 .
.D) 4.
E) 0.5.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
Five molecules of a gas have the following speeds: 200 m/s, 300 m/s, 400 m/s, 500 m/s, and 600 m/s.The rms speed for these molecules is
A) 300 m/s.
B) 344 m/s.
C) 400 m/s.
D) 424 m/s.
E) 534 m/s.
A) 300 m/s.
B) 344 m/s.
C) 400 m/s.
D) 424 m/s.
E) 534 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
The coefficient of thermal expansion of water at 20°C is 0.207 × 10-3 K-1. A thin glass tube contains a 75.0 cm column of water at 20°C. If the thermal expansion of the glass tube is negligible, by how much does the length of the column of water expand when it is heated to 80°C?
A) 3.1 mm
B) 9.3 mm
C) 12.4 mm
D) 4.1 mm
E) 28 mm
A) 3.1 mm
B) 9.3 mm
C) 12.4 mm
D) 4.1 mm
E) 28 mm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
The coefficient of linear expansion for a certain metal is α. The coefficient of area expansion for a square plate made of the same metal is approximately
A) α.
B) α/2.
C) α2.
D)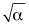 .
.
E) 2α.
A) α.
B) α/2.
C) α2.
D)
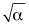 .
.E) 2α.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
A volume of an ideal gas goes through a temperature change from 20oC to 60oC. The relation between the average molecular kinetic energy at 20oC K1) and that at 60oC K2) is
A) K1 = K2.
B) K1 = 0.33 K2.
C) K1 = 3 K2.
D) K1 = 0.88 K2.
E) K1 = 1.14 K2.
A) K1 = K2.
B) K1 = 0.33 K2.
C) K1 = 3 K2.
D) K1 = 0.88 K2.
E) K1 = 1.14 K2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
If the rms speed of nitrogen molecules molecular weight of N2 is 28 g/mol) at 273 K is 492 m/s, the rms speed of oxygen molecules molecular weight of O2 is 32 g/mol) at the same temperature is approximately
A) 430 m/s.
B) 461 m/s.
C) 492 m/s.
D) 526 m/s.
E) 562 m/s.
A) 430 m/s.
B) 461 m/s.
C) 492 m/s.
D) 526 m/s.
E) 562 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
The rms speed of oxygen molecules is 460 m/s at 0oC. The molecular weight of oxygen is 8 times the molecular weight of helium. The rms speed of helium at 40oC is approximately
A) 3.68 km/s.
B) 1.84 km/s.
C) 1.40 km/s.
D) 880 m/s.
E) 440 m/s.
A) 3.68 km/s.
B) 1.84 km/s.
C) 1.40 km/s.
D) 880 m/s.
E) 440 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
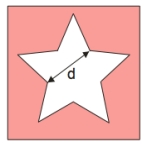 A sheet of metal has a star-shaped hole. What happens to the distance, d, when the temperature of the sheet is increased?
A sheet of metal has a star-shaped hole. What happens to the distance, d, when the temperature of the sheet is increased?A) does not change
B) always increases
C) always decreases
D) unable to tell
E) depends on the thickness of the metal sheet.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
Modern railway tracks consist of continuous welded-steel rails of 1.0-km lengths. If the coefficient of linear expansion of steel is 11 × 10-6 K-1, by how much would such a rail change in length between the highest summer temperature 40oC) and the lowest winter temperature -40oC)?
A) 44 cm
B) 88 cm
C) 0.88 mm
D) 1.8 mm
E) 4.4 cm
A) 44 cm
B) 88 cm
C) 0.88 mm
D) 1.8 mm
E) 4.4 cm

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 146 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



