Deck 4: Forces and Motion I: Newtons Laws
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/93
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 4: Forces and Motion I: Newtons Laws
1
A force accelerates a body of mass M. A second body requires half as much force to produce twice the acceleration. What is the mass of the second body?
A) M
B) 2M
C) M/2
D) 4M
E) M/4
A) M
B) 2M
C) M/2
D) 4M
E) M/4
4M
2
A net force is exerted toward the east on an object that is initially at rest. In which direction does the object start to move?
A) north
B) east
C) west
D) south
E) It may start to move in any of these directions.
A) north
B) east
C) west
D) south
E) It may start to move in any of these directions.
east
3
A force F produces an acceleration a on an object of mass m. A force 3F is exerted on a second object, and an acceleration 8a results. What is the mass of the second object?
A) 3m
B) 9m
C) 24m
D) 3/8)m
E) 8/3)m
A) 3m
B) 9m
C) 24m
D) 3/8)m
E) 8/3)m
3/8)m
4
A force accelerates a body of mass M. A second body requires twice as much force to produce the same acceleration. What is the mass of the second body?
A) M
B) 2M
C) M/2
D) 4M
E) M/4
A) M
B) 2M
C) M/2
D) 4M
E) M/4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A net force of 64 N acts on a mass of 16 kg. The resulting acceleration is
A) 16 m/s2.
B) 0.51 m/s2.
C) 64 m/s2.
D) 9.0 m/s2.
E) 4.0 m/s2.
A) 16 m/s2.
B) 0.51 m/s2.
C) 64 m/s2.
D) 9.0 m/s2.
E) 4.0 m/s2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A 10-N force is applied to mass M. The same force is applied to mass 4M. The ratio of the acceleration of the smaller mass to the acceleration of the larger mass is
A) 4 to 1.
B) 20 to 1.
C) 1 to 1.
D) 1 to 2.
E) 1 to 4.
A) 4 to 1.
B) 20 to 1.
C) 1 to 1.
D) 1 to 2.
E) 1 to 4.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A mass m is traveling at an initial speed of 25.0 m/s. It is brought to rest in a distance of 62.5 m by a net force of 15.0 N. The mass is
A) 37.5 kg.
B) 3.00 kg.
C) 1.50 kg.
D) 6.00 kg.
E) 3.75 kg.
A) 37.5 kg.
B) 3.00 kg.
C) 1.50 kg.
D) 6.00 kg.
E) 3.75 kg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
If you apply the same net force to objects with masses M and 4M, the acceleration of the mass M is
A) the same as for the mass 4M.
B) four times the acceleration of the mass 4M.
C) one-fourth the acceleration of the mass 4M.
D) twice the acceleration of the mass 4M.
E) one-half the acceleration of the mass 4M.
A) the same as for the mass 4M.
B) four times the acceleration of the mass 4M.
C) one-fourth the acceleration of the mass 4M.
D) twice the acceleration of the mass 4M.
E) one-half the acceleration of the mass 4M.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A net force is exerted on an object toward the north. The object
A) is moving toward the north.
B) is moving toward the east.
C) is moving toward the west.
D) is moving toward the south.
E) may be moving in any direction.
A) is moving toward the north.
B) is moving toward the east.
C) is moving toward the west.
D) is moving toward the south.
E) may be moving in any direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
A 3.00 kg mass is traveling at an initial speed of 25.0 m/s. What is the magnitude of the force required to bring the mass to rest in a distance of 62.5 m?
A) 7.50 N
B) 3.00 N
C) 15.0 N
D) 62.5 N
E) 37.5 N
A) 7.50 N
B) 3.00 N
C) 15.0 N
D) 62.5 N
E) 37.5 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A force accelerates a body of mass M. The same force applied to a second body produces three times the acceleration. What is the mass of the second body?
A) M
B) 3M
C) M/3
D) 9M
E) M/9
A) M
B) 3M
C) M/3
D) 9M
E) M/9

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A mass of 25 kg is acted on by two forces, one of which is 10 N due east while the second one is 15 N due north. The acceleration of the mass is
A) 0.72 m/ s2, 56.3o north of east.
B) 0.20 m/ s2, due east.
C) 0.72 m/ s2, 33.7 o north of east.
D) 1.0 m/ s2, 33.7 o north of east.
E) 0.20 m/ s2, 56.3 o north of east.
A) 0.72 m/ s2, 56.3o north of east.
B) 0.20 m/ s2, due east.
C) 0.72 m/ s2, 33.7 o north of east.
D) 1.0 m/ s2, 33.7 o north of east.
E) 0.20 m/ s2, 56.3 o north of east.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
If you want the same acceleration with masses M and 4M, the force applied on the mass M is
A) the same as for the mass 4M.
B) four times the force applied on the mass 4M.
C) one-fourth the force applied on the mass 4M.
D) twice the force applied on the mass 4M.
E) one-half the force applied on the mass 4M.
A) the same as for the mass 4M.
B) four times the force applied on the mass 4M.
C) one-fourth the force applied on the mass 4M.
D) twice the force applied on the mass 4M.
E) one-half the force applied on the mass 4M.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A ball of mass 2.0 kg is acted on by two forces, 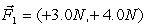 and
and 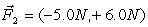 . The magnitude of the acceleration is
. The magnitude of the acceleration is
A) 2.5 m/s2.
B) 3.9 m/s2.
C) 4.6 m/s2.
D) 5.1 m/s2.
E) 5.8 m/s2.
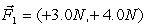 and
and 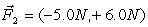 . The magnitude of the acceleration is
. The magnitude of the acceleration isA) 2.5 m/s2.
B) 3.9 m/s2.
C) 4.6 m/s2.
D) 5.1 m/s2.
E) 5.8 m/s2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A particle with a mass of 200 g is acted on by a net force of 4.5 N. The acceleration of the particle is
A) 90 cm/s2.
B) 2.3 cm/s2.
C) 0.90 km/s2.
D) 23 m/s2.
E) 9.0 m/s2.
A) 90 cm/s2.
B) 2.3 cm/s2.
C) 0.90 km/s2.
D) 23 m/s2.
E) 9.0 m/s2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
A mass of 25 kg is acted on by two forces, one of which is 15 N due east while the second one is 10 N due north. The acceleration of the mass is
A) 0.72 m/ s2, 56.3o north of east.
B) 0.20 m/ s2, due east.
C) 0.72 m/ s2, 33.7 o north of east.
D) 1.0 m/ s2, 33.7 o north of east.
E) 0.20 m/ s2, 56.3 o north of east.
A) 0.72 m/ s2, 56.3o north of east.
B) 0.20 m/ s2, due east.
C) 0.72 m/ s2, 33.7 o north of east.
D) 1.0 m/ s2, 33.7 o north of east.
E) 0.20 m/ s2, 56.3 o north of east.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
A ball of mass 2.0 kg is acted on by two forces 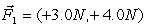 , and
, and 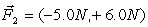 . The acceleration vector,
. The acceleration vector, 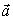 , of the mass is in m/s2)
, of the mass is in m/s2)
A)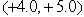 .
.
B)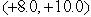 .
.
C) .
.
D)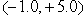 .
.
E)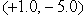 .
.
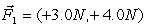 , and
, and 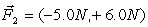 . The acceleration vector,
. The acceleration vector, 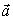 , of the mass is in m/s2)
, of the mass is in m/s2)A)
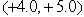 .
.B)
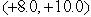 .
.C)
 .
.D)
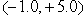 .
.E)
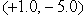 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A third force is applied on the object so that the net force on the object is zero. Which force vector best represents the third force?
A) 1)
B) 2)
C) 3)
D) 4)
E) none of the vectors
A) 1)
B) 2)
C) 3)
D) 4)
E) none of the vectors

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A ball of mass 2.0 kg is acted on by two forces, 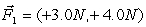 , and
, and 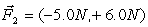 . The direction of the acceleration vector
. The direction of the acceleration vector 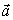 ) w.r.t to the +x-axis is
) w.r.t to the +x-axis is
A)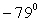 .
.
B)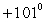 .
.
C)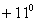 .
.
D)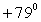 .
.
E)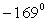 .
.
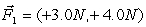 , and
, and 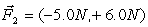 . The direction of the acceleration vector
. The direction of the acceleration vector 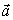 ) w.r.t to the +x-axis is
) w.r.t to the +x-axis isA)
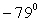 .
.B)
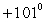 .
.C)
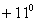 .
.D)
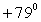 .
.E)
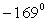 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An object is moving to the right at a constant speed. Which one of the following statements must be correct?
A) No forces are acting on the object.
B) A larger number of forces are acting on the object to the right than to the left.
C) The net force acting on the object is to the right.
D) No net force is acting on the object.
E) Just one force is acting on the object, and it is acting downward.
A) No forces are acting on the object.
B) A larger number of forces are acting on the object to the right than to the left.
C) The net force acting on the object is to the right.
D) No net force is acting on the object.
E) Just one force is acting on the object, and it is acting downward.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The force needed to accelerate the rover Opportunity on Mars at 1 m/s2 in the horizontal direction is ____ the force needed to accelerate the rover while it was undergoing testing on Earth.
A) less than
B) equal to
C) greater than
D) Unable to tell
E) dependent on what g is on Mars
A) less than
B) equal to
C) greater than
D) Unable to tell
E) dependent on what g is on Mars

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The SI unit of force is the
A) newton.
B) gram.
C) pound.
D) kilogram.
E) None of these is correct.
A) newton.
B) gram.
C) pound.
D) kilogram.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
An unknown force  is applied to two unknown masses MA and MB. Their accelerations
is applied to two unknown masses MA and MB. Their accelerations 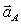 and
and 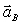 are measured. From these data we can determine
are measured. From these data we can determine
A) the magnitude of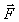 only.
only.
B) MA and MB only.
C) the magnitudes of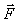 , MA, and MB only.
, MA, and MB only.
D) the ratio of MA to MB only.
E) MA, MB, and the weights of MA and MB.
 is applied to two unknown masses MA and MB. Their accelerations
is applied to two unknown masses MA and MB. Their accelerations 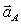 and
and 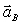 are measured. From these data we can determine
are measured. From these data we can determineA) the magnitude of
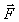 only.
only.B) MA and MB only.
C) the magnitudes of
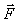 , MA, and MB only.
, MA, and MB only.D) the ratio of MA to MB only.
E) MA, MB, and the weights of MA and MB.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
According to Newton's law of inertia,
A) objects moving with an initial speed relative to a given frame of reference eventually come to rest relative to the reference frame.
B) whether an object is at rest or is moving with constant velocity depends on the inertial reference frame in which the object is observed.
C) rest is the most natural state of motion.
D) an object at rest in a given frame of reference eventually finds itself in motion relative to the frame of reference.
E) forces always exist in pairs.
A) objects moving with an initial speed relative to a given frame of reference eventually come to rest relative to the reference frame.
B) whether an object is at rest or is moving with constant velocity depends on the inertial reference frame in which the object is observed.
C) rest is the most natural state of motion.
D) an object at rest in a given frame of reference eventually finds itself in motion relative to the frame of reference.
E) forces always exist in pairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
The diagrams below show the application of a net force F on a block of mass m. 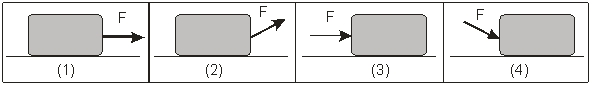 Which diagrams) produces the largest acceleration on the block in the horizontal direction?
Which diagrams) produces the largest acceleration on the block in the horizontal direction?
A) 1) and 3)
B) 2)
C) 3)
D) 2) and 4)
E) The acceleration is the same for all four.
 Which diagrams) produces the largest acceleration on the block in the horizontal direction?
Which diagrams) produces the largest acceleration on the block in the horizontal direction?A) 1) and 3)
B) 2)
C) 3)
D) 2) and 4)
E) The acceleration is the same for all four.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
If force in N), length in m), and time in s) were considered to be the fundamental quantities, the units of mass would be
A) s2/N · m).
B) m · s.
C) N2 · m/s2.
D) N · s2/m.
E) m/N.
A) s2/N · m).
B) m · s.
C) N2 · m/s2.
D) N · s2/m.
E) m/N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A body is sent out in space. Which of the following statements is true of this body as it moves away from Earth?
A) The body's mass and weight remain equal.
B) The body's mass remains constant, and its weight decreases.
C) The body's mass decreases, and its weight remains constant.
D) The body's mass and weight decrease.
E) The body's mass decreases, and its weight increases.
A) The body's mass and weight remain equal.
B) The body's mass remains constant, and its weight decreases.
C) The body's mass decreases, and its weight remains constant.
D) The body's mass and weight decrease.
E) The body's mass decreases, and its weight increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
An inertial reference frame is one in which
A) Newton's first law describes the behavior of matter.
B) the law of inertia is not applicable.
C) there is a great deal of matter.
D) the object of interest is traveling in a circular path.
E) forces do not necessarily exist in pairs.
A) Newton's first law describes the behavior of matter.
B) the law of inertia is not applicable.
C) there is a great deal of matter.
D) the object of interest is traveling in a circular path.
E) forces do not necessarily exist in pairs.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The mass of a body that weighs 2.00 N at sea level is
A) 0.204 kg.
B) 2.00 kg,
C) 19.6 kg,
D) 9.80 kg.
E) 0.451 kg.
A) 0.204 kg.
B) 2.00 kg,
C) 19.6 kg,
D) 9.80 kg.
E) 0.451 kg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
A physical quantity that is sometimes described as the measure of the resistance of a body to a change in its motion is
A) force.
B) mass.
C) acceleration.
D) weight.
E) friction.
A) force.
B) mass.
C) acceleration.
D) weight.
E) friction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
Which of the following statements includes all the essential elements of Newton's first law?
A) A body at rest persists in its state of rest unless acted on by a nonzero net external force.
B) A body persists in its state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line as long as the net external force remains constant.
C) For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
D) A body persists in its state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless acted on by a nonzero net external force.
E) The acceleration of a body is proportional to the net external force acting on it and to the mass of the body.
A) A body at rest persists in its state of rest unless acted on by a nonzero net external force.
B) A body persists in its state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line as long as the net external force remains constant.
C) For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
D) A body persists in its state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless acted on by a nonzero net external force.
E) The acceleration of a body is proportional to the net external force acting on it and to the mass of the body.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
Newton's law of inertia does not describe the behavior of objects that are
A) in inertial frames of reference.
B) moving with constant velocity relative to a given frame of reference.
C) at rest relative to a given frame of reference.
D) moving in accelerated frames of reference.
E) moving in a straight line at constant speed relative to a given reference frame.
A) in inertial frames of reference.
B) moving with constant velocity relative to a given frame of reference.
C) at rest relative to a given frame of reference.
D) moving in accelerated frames of reference.
E) moving in a straight line at constant speed relative to a given reference frame.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A body moves with constant speed in a straight line. Which of the following statements must be true?
A) No force acts on the body.
B) A single constant force acts on the body in the direction of motion.
C) A single constant force acts on the body in the direction opposite to the motion.
D) A net force of zero acts on the body.
E) A constant net force acts on the body in the direction of motion.
A) No force acts on the body.
B) A single constant force acts on the body in the direction of motion.
C) A single constant force acts on the body in the direction opposite to the motion.
D) A net force of zero acts on the body.
E) A constant net force acts on the body in the direction of motion.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following is a unit of force?
A) m2/s2
B) kg · s2/m
C) kg · m/s2
D) N · s
E) N/kg
A) m2/s2
B) kg · s2/m
C) kg · m/s2
D) N · s
E) N/kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
An astronaut lands on an Earthlike planet and drops a small lead ball with a mass of 76.5 g from the top of her spaceship. The point of release is 18 m above the surface of the planet and the ball takes 2.5 s to reach the ground. The astronaut's mass on Earth is 68.5 kg. Her weight on the planet is
A) 69.0 N.
B) 395 N.
C) 670 N.
D) 990 N.
E) 1.02 kN.
A) 69.0 N.
B) 395 N.
C) 670 N.
D) 990 N.
E) 1.02 kN.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
An object moves with constant speed in a straight line. Which of the following statements can be true according to Newton's laws of motion? I. No force is acting. II. Only one nonzero force is acting.III. Two nonzero forces are acting. IV. Three nonzero forces are acting.
A) Only I.
B) Only I and II.
C) Only II and III.
D) Only I, III, and IV.
E) Only II, III, and IV.
A) Only I.
B) Only I and II.
C) Only II and III.
D) Only I, III, and IV.
E) Only II, III, and IV.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
When Newton's first law of motion is mentioned, you should immediately think of
A) .
.
B) action-and-reaction forces.
C) inertia.
D) gravitational forces.
E) centripetal acceleration.
A)
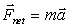 .
.B) action-and-reaction forces.
C) inertia.
D) gravitational forces.
E) centripetal acceleration.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following statements is true?
A) The mass of a body is a quantitative measure of its inertia.
B) Mass is a vector quantity.
C) The mass of a body is directly proportional to the acceleration it is experiencing.
D) The unit of mass in the U.S. customary system is the newton.
E) The mass of a body is inversely proportional to the resultant force acting on it.
A) The mass of a body is a quantitative measure of its inertia.
B) Mass is a vector quantity.
C) The mass of a body is directly proportional to the acceleration it is experiencing.
D) The unit of mass in the U.S. customary system is the newton.
E) The mass of a body is inversely proportional to the resultant force acting on it.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The weight of an object is
A) the same as the mass of the object.
B) the quantity of matter in the object.
C) the mass of the object multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity at sea level, regardless of where the object is located.
D) the result of the gravitational force acting on the object.
E) the reading on a spring scale attached to the object.
A) the same as the mass of the object.
B) the quantity of matter in the object.
C) the mass of the object multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity at sea level, regardless of where the object is located.
D) the result of the gravitational force acting on the object.
E) the reading on a spring scale attached to the object.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
Which of the following is not a unit of force?
A) newton
B) pound
C) slug
D) dyne
E) kg · m/s2
A) newton
B) pound
C) slug
D) dyne
E) kg · m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
An astronaut lands on an Earthlike planet and drops a small lead ball with a mass of 76.5 g from the top of her spaceship. The point of release is 18 m above the surface of the planet and the ball takes 2.5 s to reach the ground. The astronaut's mass on Earth is 68.5 kg. Her mass on the planet is
A) 68.5 kg.
B) 395 kg.
C) 670 kg,
D) 99.0 kg.
E) 40.2 kg.
A) 68.5 kg.
B) 395 kg.
C) 670 kg,
D) 99.0 kg.
E) 40.2 kg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
You want to elope by sliding down a nylon rope made by tying stockings together. The rope will withstand a maximum tension of 300 N without breaking. Your mass is 61.2 kg. The magnitude of the smallest acceleration a with which you can slide down the rope is
A) 9.81 m/s2.
B) 4.91 m/s2.
C) zero.
D) 2.40 m/s2.
E) 19.6 m/s2.
A) 9.81 m/s2.
B) 4.91 m/s2.
C) zero.
D) 2.40 m/s2.
E) 19.6 m/s2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
The diagrams below show the application of an external force F on a block of mass m resting on a horizontal surface. 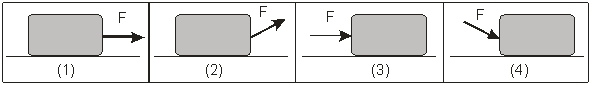 In which diagrams) does the block experience the largest normal force?
In which diagrams) does the block experience the largest normal force?
A) Both 1) and 3)
B) Only 1)
C) Only 2)
D) Only 3)
E) Only 4)
 In which diagrams) does the block experience the largest normal force?
In which diagrams) does the block experience the largest normal force?A) Both 1) and 3)
B) Only 1)
C) Only 2)
D) Only 3)
E) Only 4)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A particle of mass 1.3 kg is sliding down a frictionless slope inclined at 30o to the horizontal. The acceleration of the particle down the slope is
A) 1.3 m/s2.
B) 9.8 m/s2.
C) 0.5 m/s2.
D) 8.5 m/s2.
E) 4.9 m/s2.
A) 1.3 m/s2.
B) 9.8 m/s2.
C) 0.5 m/s2.
D) 8.5 m/s2.
E) 4.9 m/s2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
What is the weight of a 50-kg boy on the Moon, where the acceleration due to gravity is 1.6 m/s2?
A) 80 N
B) 100 N
C) 490 N
D) 50 N
E) 80 lbs
A) 80 N
B) 100 N
C) 490 N
D) 50 N
E) 80 lbs

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
The diagrams below show the application of an external force F on a block of mass m resting on a horizontal surface. 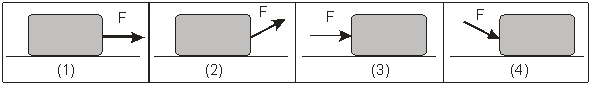 In which diagrams) does the block experience the smallest normal force?
In which diagrams) does the block experience the smallest normal force?
A) Both 1) and 3)
B) Only 1)
C) Only 2)
D) Only 3)
E) Only 4)
 In which diagrams) does the block experience the smallest normal force?
In which diagrams) does the block experience the smallest normal force?A) Both 1) and 3)
B) Only 1)
C) Only 2)
D) Only 3)
E) Only 4)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
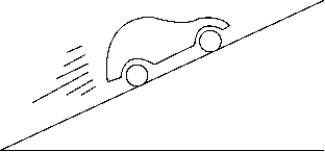 Which of the following free-body diagrams represents the car going uphill at a constant speed?
Which of the following free-body diagrams represents the car going uphill at a constant speed? 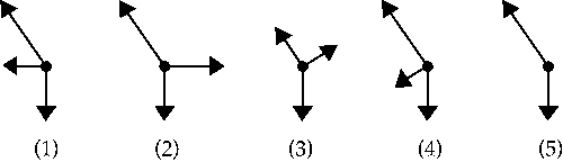
A) 1)
B) 2)
C) 3)
D) 4)
E) 5)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
In a crash test, the strapped-in 75-kg dummy moves a distance of 0.80 m when the test car is slammed straight into a wall at 11.2 m/s ~25 mph). The average force acting on the dummy during the collision is how many times his own weight?
A) 0.13
B) 78
C) 0.71
D) 8.0
E) 4.0
A) 0.13
B) 78
C) 0.71
D) 8.0
E) 4.0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
A boy sits in a tire that is attached to a rope that passes over a pulley fastened to the ceiling and then passes back down to the boy's hands. The weight of the boy plus the tire is W. The force with which the boy must pull on the free end of the rope to support his weight in the tire is
A) 1/2)W.
B) W.
C) 2W.
D) 2/3)W.
E) 3/2)W.
A) 1/2)W.
B) W.
C) 2W.
D) 2/3)W.
E) 3/2)W.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
A vertical rope is attached to an object that has a mass of 40.0 kg and is at rest. The tension in the rope needed to give the object an upward speed of 3.50 m/s in 0.700 s is
A) 592 N.
B) 390 N.
C) 200 N.
D) 980 N.
E) 720 N.
A) 592 N.
B) 390 N.
C) 200 N.
D) 980 N.
E) 720 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A car is accelerating horizontally at a rate of 2.5 m/s2. A mass of 250 g is hanging from the ceiling on a string 1.2 m long. The angle that the string makes with the vertical is
A) 14.3o toward the back of the car.
B) 76o toward the back of the car.
C) 7o toward the front of the car.
D) 14.3o toward the front of the car.
E) 0o, or straight down.
A) 14.3o toward the back of the car.
B) 76o toward the back of the car.
C) 7o toward the front of the car.
D) 14.3o toward the front of the car.
E) 0o, or straight down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
A 44.5-N weight is hung on a spring scale, and the scale is hung on a string. The string is lowered at a rate such that the entire assembly has a downward acceleration of 4.90 m/s2. The scale reads 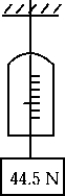
A) 0 N.
B) 22.2 N.
C) 44.5 N.
D) 66.7 N.
E) 71.2 N.

A) 0 N.
B) 22.2 N.
C) 44.5 N.
D) 66.7 N.
E) 71.2 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
Of the following values, which is most nearly equal to the weight of a 1-kg body?
A) 1 N
B) 103 dynes
C) 2.2 lbs
D) 0.454 lbs
E) 2.2 N
A) 1 N
B) 103 dynes
C) 2.2 lbs
D) 0.454 lbs
E) 2.2 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
We all know it makes sense to bend one's knees when dropping from a height.Suppose a very silly 70-kg person were instead to drop down from a height of 1.4 m onto the ground and stop stiffly within a distance of only 0.60 cm. Calculate how many times his own weight is the average force his body feels.
A) 15
B) 24
C) 2.3 * 103
D) 6.1 *102
E) 2.3 *102
A) 15
B) 24
C) 2.3 * 103
D) 6.1 *102
E) 2.3 *102

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
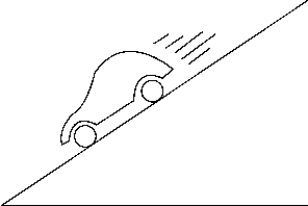 Which of the following free-body diagrams represents the car going downhill without acceleration?
Which of the following free-body diagrams represents the car going downhill without acceleration? 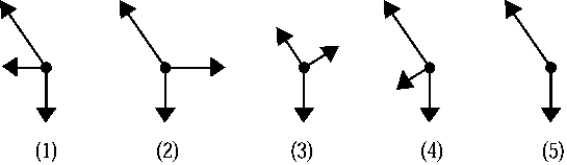
A) 1)
B) 2)
C) 3)
D) 4)
E) 5)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
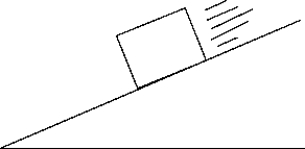 Which of the following free-body diagrams represents the block sliding down a frictionless inclined plane?
Which of the following free-body diagrams represents the block sliding down a frictionless inclined plane? 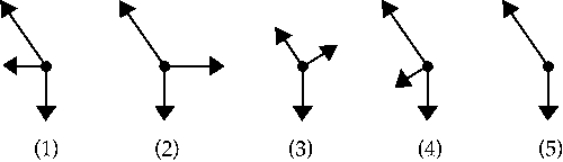
A) 1)
B) 2)
C) 3)
D) 4)
E) 5)

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A horse-drawn coach is decelerating at 3.0 m/s2 while moving in a straight line horizontally. A 350-g mass is hanging on a string 1.6 m long from the ceiling of the coach. The angle that the string makes with the vertical is
A) 9.3o toward the front of the coach.
B) 17o toward the front of the coach.
C) 9.3o toward the back of the coach.
D) 2.5o toward the front of the coach.
E) 0o, or straight down.
A) 9.3o toward the front of the coach.
B) 17o toward the front of the coach.
C) 9.3o toward the back of the coach.
D) 2.5o toward the front of the coach.
E) 0o, or straight down.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Which of the following is not a unit of mass?
A) pound
B) kilogram
C) gram
D) slug
E) milligram
A) pound
B) kilogram
C) gram
D) slug
E) milligram

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
A shopper steps on an escalator moving downward at a constant speed toward the bargain basement in a large department store. On his way down, the normal force exerted on him by the step of the escalator is
A) greater than his weight when he is off the escalator.
B) equal to his weight when he is off the escalator.
C) less than his weight when he is off the escalator.
D) dependent on how fast the escalator is moving.
E) unknown; insufficient information is given to answer correctly.
A) greater than his weight when he is off the escalator.
B) equal to his weight when he is off the escalator.
C) less than his weight when he is off the escalator.
D) dependent on how fast the escalator is moving.
E) unknown; insufficient information is given to answer correctly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
The acceleration due to gravity on the Moon is only about 1/6 of that on Earth. An astronaut whose weight on Earth is 600 N travels to the lunar surface. His mass as measured on the Moon is
A) 600 kg.
B) 100 kg.
C) 61.2 kg.
D) 10.0 kg.
E) 360 kg.
A) 600 kg.
B) 100 kg.
C) 61.2 kg.
D) 10.0 kg.
E) 360 kg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
An 80-kg man on ice skates pushes a 40-kg boy, also on skates, with a force of 100 N. The force exerted by the boy on the man is
A) 200 N.
B) 100 N.
C) 50 N.
D) 40 N.
E) zero unless the boy pushes back.
A) 200 N.
B) 100 N.
C) 50 N.
D) 40 N.
E) zero unless the boy pushes back.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A fat cat, ever conscious of its weight, walks into an elevator and steps on a scale. The elevator begins to accelerate downward. While the elevator is accelerating, the scale reads
A) more than when the elevator is stationary.
B) more than if the elevator were accelerating upward.
C) less than when the elevator is stationary.
D) a negative value.
E) Insufficient information is given to answer correctly.
A) more than when the elevator is stationary.
B) more than if the elevator were accelerating upward.
C) less than when the elevator is stationary.
D) a negative value.
E) Insufficient information is given to answer correctly.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
An object with a mass m = 250 g is on a plane inclined at 30o above the horizontal and is attached by a string to a mass m = 150 g. There is no friction and mass m hangs freely and is initially at rest. When mass m has descended a distance h = 10 cm, its speed will be
A) 35.0 cm/s.
B) 7.00 cm/s.
C) 140 cm/s.
D) 110 cm/s.
E) 70.0 cm/s.
A) 35.0 cm/s.
B) 7.00 cm/s.
C) 140 cm/s.
D) 110 cm/s.
E) 70.0 cm/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A horse exerts a force F on a cart, causing the cart to move with increasing speed. What force does the cart exert on the horse?
A) zero
B) F
C) greater than F
D) less than F
E) The force cannot be determined unless the acceleration is given.
A) zero
B) F
C) greater than F
D) less than F
E) The force cannot be determined unless the acceleration is given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A body of weight w rests on the surface of Earth. What force does the body exert on Earth? Ignore Earth's rotation.)
A) w
B) greater than w
C) less than w
D) 9.81w
E) zero
A) w
B) greater than w
C) less than w
D) 9.81w
E) zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A body of weight w is in free fall near the surface of Earth. What force does the body exert on the Earth?
A) w
B) greater than w
C) less than w
D) 9.81w
E) zero
A) w
B) greater than w
C) less than w
D) 9.81w
E) zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A horse harnessed to a wagon refuses to pull, citing Newton's third law, which states that for every force there is an equal but opposite reaction force. The horse, incorrect in its reasoning, can pull the wagon because
A) after it gives a jerk and the wagon is moving, its pulling force will be greater than the reaction to this force.
B) the law applies only to static cases.
C) the wagon cannot possibly pull back with a force equal in magnitude to the pulling force.
D) the action and reaction forces are acting on different bodies.
E) after friction is overcome, the reaction force is less than the pulling force.
A) after it gives a jerk and the wagon is moving, its pulling force will be greater than the reaction to this force.
B) the law applies only to static cases.
C) the wagon cannot possibly pull back with a force equal in magnitude to the pulling force.
D) the action and reaction forces are acting on different bodies.
E) after friction is overcome, the reaction force is less than the pulling force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A 100-kg man on ice skates pushes a 25-kg boy, also on skates, with a force of 250 N. As a result,
A) both the man and the boy will have an acceleration of magnitude 2 m/s2.
B) only the boy will have an acceleration of magnitude 2 m/s2.
C) only the man will have an acceleration of magnitude 10 m/s2.
D) the man will have an acceleration of magnitude 2.5 m/s2.
E) the heavier man will be stationary.
A) both the man and the boy will have an acceleration of magnitude 2 m/s2.
B) only the boy will have an acceleration of magnitude 2 m/s2.
C) only the man will have an acceleration of magnitude 10 m/s2.
D) the man will have an acceleration of magnitude 2.5 m/s2.
E) the heavier man will be stationary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
A 100-kg man on ice skates pushes a 25-kg boy, also on skates, with a force of 250 N. As a result,
A) both the man and the boy will have an acceleration of magnitude 2 m/s2.
B) only the boy will have an acceleration of magnitude 2 m/s2.
C) only the man will have an acceleration of magnitude 2 m/s2.
D) the boy will have an acceleration of magnitude 10 m/s2.
E) the heavier man will be stationary.
A) both the man and the boy will have an acceleration of magnitude 2 m/s2.
B) only the boy will have an acceleration of magnitude 2 m/s2.
C) only the man will have an acceleration of magnitude 2 m/s2.
D) the boy will have an acceleration of magnitude 10 m/s2.
E) the heavier man will be stationary.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A boy holds a bird in his hand. The reaction force to the weight of the bird is the force of the
A) Earth on the bird.
B) bird on the Earth.
C) hand on the bird.
D) bird on the hand.
E) Earth on the hand.
A) Earth on the bird.
B) bird on the Earth.
C) hand on the bird.
D) bird on the hand.
E) Earth on the hand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
You are riding an elevator that is accelerating upward at 2.20 m/s2. You have a spring balance that is accurately calibrated in newtons. When you hang a mass of 10.0 kg on the balance, the reading of the balance is
A) 120 N.
B) 981 N.
C) 76.0 N.
D) 10.0 N.
E) 9.81 N.
A) 120 N.
B) 981 N.
C) 76.0 N.
D) 10.0 N.
E) 9.81 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
A cricket batsman hits a ball with a bat. If the force with which the bat hits the ball is considered the action force, what is the reaction force?
A) The force the bat exerts on the batsman's hands
B) The force on the ball exerted by the hand of the person who catches it
C) The force the ball exerts on the bat
D) The force the bowler exerts on the ball in throwing it
E) Friction as the ball rolls to a stop
A) The force the bat exerts on the batsman's hands
B) The force on the ball exerted by the hand of the person who catches it
C) The force the ball exerts on the bat
D) The force the bowler exerts on the ball in throwing it
E) Friction as the ball rolls to a stop

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
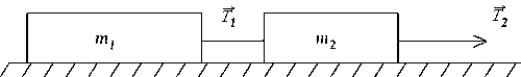 Two masses, m1 and m2, connected by a massless string, are accelerated uniformly on a frictionless surface as shown. The ratio of the magnitude of tensions
Two masses, m1 and m2, connected by a massless string, are accelerated uniformly on a frictionless surface as shown. The ratio of the magnitude of tensions 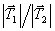 is given by
is given byA) m1/m2 .
B) m2/m1.
C) m1 + m2)/m2 .
D) m1/m1 + m2).
E) m2/m1 + m2).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A person of weight w is in an upward-moving elevator when the cable suddenly breaks. What is the person's apparent weight immediately after the elevator starts to fall?
A) w
B) greater than w
C) less than w
D) 9.81w
E) zero
A) w
B) greater than w
C) less than w
D) 9.81w
E) zero

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
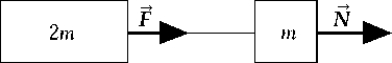 A mass 2m is attached by a string to another mass m as illustrated. A force of
A mass 2m is attached by a string to another mass m as illustrated. A force of 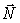 newtons acts on mass m to accelerate the system. The force
newtons acts on mass m to accelerate the system. The force 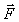 in the string, which acts on mass 2m, is
in the string, which acts on mass 2m, isA) 2/3)N.
B) N.
C) 2N.
D) 3N.
E) 3/2)N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
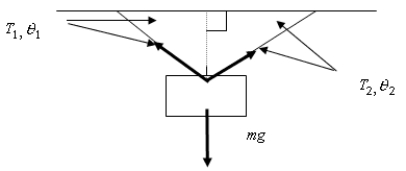 A block of mass m is suspended by two strings and is in equilibrium as suggested in the figure above. The tension of the right-hand string divided by the tension of the left-hand string is given by
A block of mass m is suspended by two strings and is in equilibrium as suggested in the figure above. The tension of the right-hand string divided by the tension of the left-hand string is given byA) sin 2 / sin 1.
B) cos 1 / cos 2.
C) cos 2 / cos 1.
D) sin 1 / sin 2.
E) mg T1 sin 1) / T1 sin 2).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
A boy holds a bird in his hand. The reaction force to the normal force exerted on the bird by the boy's hand is the force of
A) the Earth on the bird.
B) the bird on the Earth.
C) the hand on the bird.
D) the bird on the hand.
E) the Earth on the hand.
A) the Earth on the bird.
B) the bird on the Earth.
C) the hand on the bird.
D) the bird on the hand.
E) the Earth on the hand.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
You are riding an elevator that is accelerating downward at 2.20 m/s2. You have a spring balance that is accurately calibrated in newtons. When you hang a mass of 10.0 kg on the balance, the reading of the balance is
A) 120 N.
B) 981 N.
C) 76.0 N.
D) 10.0 N.
E) 9.81 N.
A) 120 N.
B) 981 N.
C) 76.0 N.
D) 10.0 N.
E) 9.81 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
Rachel has been reading her physics book. She takes her weighing scales into an elevator and stands on them. If her normal weight is 690 N 155 lbs) and the elevator moves upward at 0.25 g and then down at 0.25 g, what is the difference between the up and down scale readings?
A) 690 N
B) 520 N
C) 170 N
D) 345 N
E) 1.04 * 103 N
A) 690 N
B) 520 N
C) 170 N
D) 345 N
E) 1.04 * 103 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
You are riding an elevator that is in motion. Using a spring balance calibrated in newtons, you notice that a 10.0 kg hanging mass reads 120 N on the scale. What is the acceleration of the elevator?
A) 9.8 m/s2 downward
B) 4.9 m/s2 upward
C) 2.2 m/s2 downward
D) 2.2 m/s2 upward
E) 1.1 m/s2 downward
A) 9.8 m/s2 downward
B) 4.9 m/s2 upward
C) 2.2 m/s2 downward
D) 2.2 m/s2 upward
E) 1.1 m/s2 downward

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 93 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



