Deck 5: Forces and Motion II: Applications
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/75
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 5: Forces and Motion II: Applications
1
A 2.0 kg-book is on the floor of an elevator. If the elevator is accelerating downward at a rate of , the normal force acting on the book by the floor is
A) 0 N.
B) 2.0 N.
C) 10 N.
D) 20 N.
E) 30 N.
A) 0 N.
B) 2.0 N.
C) 10 N.
D) 20 N.
E) 30 N.
10 N.
2
A 2.0 kg-book is on the floor of an elevator. If the elevator is accelerating upward at a rate of , the normal force acting on the book by the floor is
A) 2.0 N.
B) 10 N.
C) 20 N.
D) 30 N.
E) 40 N.
A) 2.0 N.
B) 10 N.
C) 20 N.
D) 30 N.
E) 40 N.
30 N.
3
A 2.0-kg book is at rest on the horizontal desk. The normal force exerted on the book by the desk is
A) 2.0 kg.
B) 2.0 N.
C) 20 N.
D) 200 N.
E) 20 kg.
A) 2.0 kg.
B) 2.0 N.
C) 20 N.
D) 200 N.
E) 20 kg.
20 N.
4
A 2.0 kg-book is at rest on the horizontal floor. You are applying a 10 N downward force, on the book, at an angle of 60 o from the horizontal. The normal force on the book exerted by the floor is
A) 5.0 N.
B) 10 N.
C) 25 N.
D) 28 N.
E) 30 N.
A) 5.0 N.
B) 10 N.
C) 25 N.
D) 28 N.
E) 30 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
A 2.0 kg-book is at rest on a 30 o inclined plane. The normal force acting on the book by the inclined plane is
A) 2.0 N.
B) 5.0 N.
C) 10 N.
D) 17 N.
E) 20 N.
A) 2.0 N.
B) 5.0 N.
C) 10 N.
D) 17 N.
E) 20 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
A 2.0-kg book is on the floor of an elevator. If the elevator is moving upward at a constant speed of 5.0 m/s, the normal force acting on the book is
A) 0 N.
B) 2.0 N.
C) 5.0 N.
D) 10 N.
E) 20 N.
A) 0 N.
B) 2.0 N.
C) 5.0 N.
D) 10 N.
E) 20 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The net force acting on an object is zero. You can therefore definitely conclude that the object is
A) at rest.
B) moving in a straight line at constant speed.
C) moving in a circle at constant speed.
D) undergoing acceleration.
E) either at rest or moving in a straight line at constant speed.
A) at rest.
B) moving in a straight line at constant speed.
C) moving in a circle at constant speed.
D) undergoing acceleration.
E) either at rest or moving in a straight line at constant speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
A horizontal force 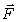 acts on a mass m that lies on a horizontal surface. The acceleration of m is
acts on a mass m that lies on a horizontal surface. The acceleration of m is 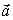 . The coefficient of kinetic friction µk between mass m and the surface can be calculated from
. The coefficient of kinetic friction µk between mass m and the surface can be calculated from
A) µk = a/g.
B) µk = F/mg) - a/g).
C) µk = F/mg) + a/g).
D) µk = 0.
E) None of these is correct.
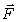 acts on a mass m that lies on a horizontal surface. The acceleration of m is
acts on a mass m that lies on a horizontal surface. The acceleration of m is 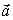 . The coefficient of kinetic friction µk between mass m and the surface can be calculated from
. The coefficient of kinetic friction µk between mass m and the surface can be calculated fromA) µk = a/g.
B) µk = F/mg) - a/g).
C) µk = F/mg) + a/g).
D) µk = 0.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A block of mass mb rests on a horizontal surface and is accelerated by means of a horizontal cord that passes over a frictionless peg to a hanging weight of mass mw. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is µ and the tension in the cord is T. The acceleration of the block is given by
A) T - mwg)/mw + mb).
B) T/µmbg + mb).
C) T - µmb)/mb.
D) mwg - T)/mw.
E) T/mb - µmbg.
A) T - mwg)/mw + mb).
B) T/µmbg + mb).
C) T - µmb)/mb.
D) mwg - T)/mw.
E) T/mb - µmbg.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
An atomic force microscope consists of a cantilever with a very fine tip on one end. The lever is driven by a piezoelectric motor allowing the tip to scan a surface on an atomic scale. As it scans the surface, what is the main frictional force between the tip and the surface?
A) static
B) kinetic
C) rolling
D) all three
E) There is no frictional force.
A) static
B) kinetic
C) rolling
D) all three
E) There is no frictional force.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
A block of wood is pulled by a horizontal string across a rough surface at a constant velocity with a force of 20 N. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the surfaces is 0.2, what is the weight of the wooden block?
A) 20 N
B) 40 N
C) 75 N
D) 100 N
E) 10 N
A) 20 N
B) 40 N
C) 75 N
D) 100 N
E) 10 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
A heavy truck and a light car are traveling at the same speed on the same roadway. If the coefficients of static friction between their tires and the road are the same, which vehicle will be able to stop in the shortest distance? Assume both have the same braking force.
A) the car
B) the truck
C) Both will be able to stop in the same distance.
D) One cannot tell without knowing their coefficients of kinetic friction.
E) One cannot tell without knowing their masses.
A) the car
B) the truck
C) Both will be able to stop in the same distance.
D) One cannot tell without knowing their coefficients of kinetic friction.
E) One cannot tell without knowing their masses.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The SI units for the coefficient of friction are
A) newtons per meter.
B) meters.
C) newtons.
D) newtons times meters.
E) None of these is correct; the coefficient of friction has no units.
A) newtons per meter.
B) meters.
C) newtons.
D) newtons times meters.
E) None of these is correct; the coefficient of friction has no units.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
A 2.0 kg-book is at rest on the horizontal floor. You are applying a 10 N downward force, on the book, at an angle of 30 o from the vertical. The normal force on the book exerted by the floor is
A) 5.0 N.
B) 10 N.
C) 25 N.
D) 28 N.
E) 30 N.
A) 5.0 N.
B) 10 N.
C) 25 N.
D) 28 N.
E) 30 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
A block of mass m is at rest on an inclined plane that makes an angle of 30 o with the horizontal. Which of the following statements about the force of static friction is true?
A) fs > mg
B) fs > mg cos 30o
C) fs = mg cos 30o
D) fs = mg sin 30o
E) None of these statements is true.
A) fs > mg
B) fs > mg cos 30o
C) fs = mg cos 30o
D) fs = mg sin 30o
E) None of these statements is true.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
Two objects are sliding at the same speed across a wooden surface. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the first object and the surface is twice that between the second object and the surface. The distance traveled by the first object before it stops is S. The distance traveled by the second object is
A) impossible to determine without knowing the masses involved.
B) 2S
C) S/2
D) S
E) 4S
A) impossible to determine without knowing the masses involved.
B) 2S
C) S/2
D) S
E) 4S

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Four identical blocks are moving on a surface for which the coefficient of kinetic friction between each block and the surface is µk. The velocity of each block is indicated by the vector on the block. For which block is the force of friction between the surface and the block greatest? 
A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) The force of friction is the same for all blocks.

A) 1
B) 2
C) 3
D) 4
E) The force of friction is the same for all blocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
A block of mass mb rests on a horizontal surface and is accelerated by means of a horizontal cord that passes over a frictionless peg to a hanging weight of mass mw. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the horizontal surface is µk and the tension in the cord is T. The acceleration of the block is given by
A) g.
B)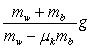 .
.
C) .
.
D)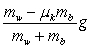 .
.
E)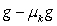 .
.
A) g.
B)
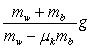 .
.C)
 .
.D)
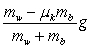 .
.E)
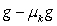 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
A block of wood is pulled by a horizontal string across a rough surface at a constant velocity with a force of 20 N. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the surfaces is 0.3. The force of friction is
A) impossible to determine without knowing the mass of the block.
B) impossible to determine without knowing the speed of the block.
C) 0.3 N.
D) 6 N.
E) 20 N.
A) impossible to determine without knowing the mass of the block.
B) impossible to determine without knowing the speed of the block.
C) 0.3 N.
D) 6 N.
E) 20 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
A 2.0 kg-book is at rest on a frictionless horizontal floor. You are applying a 10 N downward force, on the book, at an angle of 30 o from the vertical. The acceleration of the book is
A) 5.0 m/s2.
B) 2.5 m/s2.
C) 1.0 m/s2.
D) 9.8 m/s2.
E) 0 m/s2.
A) 5.0 m/s2.
B) 2.5 m/s2.
C) 1.0 m/s2.
D) 9.8 m/s2.
E) 0 m/s2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
A mass M = 5.6 kg on a horizontal table is pulled by a horizontal string that passes over a frictionless pulley to a free-hanging mass m = 3.4 kg. The coefficient of friction between M and the table is 0.28. The acceleration of M is
A) 3.7 m/s2.
B) 2.0 m/s2.
C) 2.2 m/s2.
D) 0.20 m/s2.
E) 0.49 m/s2.
A) 3.7 m/s2.
B) 2.0 m/s2.
C) 2.2 m/s2.
D) 0.20 m/s2.
E) 0.49 m/s2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
A tired worker pushes a heavy 100-kg) crate that is resting on a thick pile carpet. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction are 0.6 and 0.4, respectively. The worker pushes with a horizontal force of 490 N. The frictional force exerted by the surface is
A) 980 N.
B) 588 N.
C) 490 N.
D) 392 N.
E) 100 N.
A) 980 N.
B) 588 N.
C) 490 N.
D) 392 N.
E) 100 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A worker pushes a heavy 100-kg) crate that is resting on a thick pile carpet. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction are 0.6 and 0.4, respectively. The worker pushes with a horizontal force of 600 N. Use g = 9.8 m/s2. The frictional force exerted by the surface is
A) 980 N.
B) 588 N.
C) 490 N.
D) 392 N.
E) 98 N.
A) 980 N.
B) 588 N.
C) 490 N.
D) 392 N.
E) 98 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
A worker pushes a heavy 100-kg) crate that is resting on a thick pile carpet. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction are 0.6 and 0.4, respectively. The worker pushes with a horizontal force of 600 N. Use g = 9.8 m/s2. The acceleration of the crate will be
A) 9.8 m/s2.
B) 4.9 m/s2.
C) 3.5 m/s2.
D) 2.1 m/s2.
E) 0 m/s2.
A) 9.8 m/s2.
B) 4.9 m/s2.
C) 3.5 m/s2.
D) 2.1 m/s2.
E) 0 m/s2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
An object with a mass of 5.5 kg is allowed to slide from rest down an inclined plane. The plane makes an angle of 30 o with the horizontal. The coefficient of friction between the plane and the object is 0.35. The acceleration of the object is
A) 5.3 m/s2.
B) 2.8 m/s2.
C) 3.4 m/s2.
D) 9.8 m/s2.
E) 1.9 m/s2.
A) 5.3 m/s2.
B) 2.8 m/s2.
C) 3.4 m/s2.
D) 9.8 m/s2.
E) 1.9 m/s2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
A block is placed on an inclined plane with an angle of inclination in degrees) with respect to horizontal. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the inclined plane is 0.7. For what maximum value of will the block remain stationary on the inclined surface?
A) 35o
B) 82o
C) 44o
D) 30o
E) 18o
A) 35o
B) 82o
C) 44o
D) 30o
E) 18o

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
A block is placed on a plane whose angle of inclination is 30 o . The coefficients of static and kinetic friction for the block on the inclined plane are 0.5 and 0.4, respectively. The block
A) remains stationary on the inclined plane.
B) accelerates down the inclined plane.
C) travels down the inclined plane at constant velocity.
D) travels up the inclined plane at constant velocity.
E) accelerates up the inclined plane.
A) remains stationary on the inclined plane.
B) accelerates down the inclined plane.
C) travels down the inclined plane at constant velocity.
D) travels up the inclined plane at constant velocity.
E) accelerates up the inclined plane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
A 100-kg block is pushed up a 30 o incline at constant velocity. If the coefficient of friction between the block and the incline is 0.1, what constant force parallel to the incline is required to move the block?
A) 0.49 kN
B) 0.085 kN
C) 0.22 kN
D) 0.80 kN
E) 0.58 kN
A) 0.49 kN
B) 0.085 kN
C) 0.22 kN
D) 0.80 kN
E) 0.58 kN

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
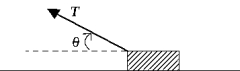 A block of mass m is pulled in the direction shown in the figure across a rough surface at a constant velocity. The magnitude of the frictional force is
A block of mass m is pulled in the direction shown in the figure across a rough surface at a constant velocity. The magnitude of the frictional force isA) µkmg.
B) µkT cos
C) µkT - mg).
D) µkT sin
E) µkmg - T sin ).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
Which of the following statements is NOT true about friction?
A) µk is less than µs.
B) µk is independent of the relative speed of the surfaces in the range of about 1 cm/s to several meters per second.
C) µk depends on the relative speed of the surfaces at speeds over several meters per second.
D) The coefficients of friction depend on the nature of the surfaces.
E) The force of static friction depends on the area of contact between the two surfaces.
A) µk is less than µs.
B) µk is independent of the relative speed of the surfaces in the range of about 1 cm/s to several meters per second.
C) µk depends on the relative speed of the surfaces at speeds over several meters per second.
D) The coefficients of friction depend on the nature of the surfaces.
E) The force of static friction depends on the area of contact between the two surfaces.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
A worker pulls horizontally on a rope that is attached to a 10-kg crate resting on a rough floor. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction are 0.5 and 0.3, respectively. The worker pulls with a force of 40 N. The frictional force exerted by the surface is
A) 30 N.
B) 50 N.
C) 10 N.
D) 100 N.
E) 40 N.
A) 30 N.
B) 50 N.
C) 10 N.
D) 100 N.
E) 40 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
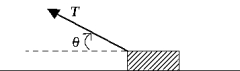 A block of mass m is pulled in the direction shown in the figure across a rough surface at a constant velocity. The magnitude of the frictional force is
A block of mass m is pulled in the direction shown in the figure across a rough surface at a constant velocity. The magnitude of the frictional force isA) µkmg.
B) T cos
C) T - µkmg).
D) µkT sin
E) µkmg - T sin ).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A mass m is placed on a rough incline at an angle to the horizon. A force F is applied up the incline so that the mass slides up the incline. Using the compass rose, the direction of the frictional force is along 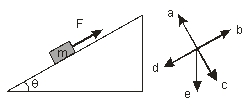
A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) d.
E) e.

A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) d.
E) e.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
An object with a mass of 5.5 kg is allowed to slide from rest down an inclined plane. The plane makes an angle of 30 o with the horizontal and is 72 m long. The coefficient of friction between the plane and the object is 0.35. The speed of the object at the bottom of the plane is
A) 5.3 m/s.
B) 15 m/s.
C) 24 m/s.
D) 17 m/s.
E) 11 m/s.
A) 5.3 m/s.
B) 15 m/s.
C) 24 m/s.
D) 17 m/s.
E) 11 m/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
A block is placed on a plane whose angle of inclination is 30 o . The coefficients of static and kinetic friction for the block on the inclined plane are 0.7 and 0.5, respectively. The block
A) remains stationary on the inclined plane.
B) accelerates down the inclined plane.
C) travels down the inclined plane at constant velocity.
D) travels up the inclined plane at constant velocity.
E) accelerates up the inclined plane.
A) remains stationary on the inclined plane.
B) accelerates down the inclined plane.
C) travels down the inclined plane at constant velocity.
D) travels up the inclined plane at constant velocity.
E) accelerates up the inclined plane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
A block is placed on a plane whose angle of inclination is 30 o . The coefficients of static and kinetic friction for the block on the inclined plane are both 0.2. The block
A) remains stationary on the inclined plane.
B) accelerates down the inclined plane.
C) travels down the inclined plane at constant velocity.
D) travels up the inclined plane at constant velocity.
E) accelerates up the inclined plane.
A) remains stationary on the inclined plane.
B) accelerates down the inclined plane.
C) travels down the inclined plane at constant velocity.
D) travels up the inclined plane at constant velocity.
E) accelerates up the inclined plane.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
A 50-kg block rests on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction s = 0.50. The coefficient of kinetic friction k = 0.35. A force 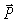 of 250 N is applied as shown. Which of the following statemen best describes the subsequent motion?
of 250 N is applied as shown. Which of the following statemen best describes the subsequent motion? 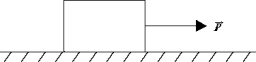
A) The block remains at rest.
B) The block moves and continues to move at constant velocity.
C) The block accelerates to the right.
D) The block does not move until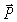 is increased to greater than 490 N.
is increased to greater than 490 N.
E) No conclusions can be drawn concerning the movement of the block from the information given.
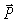 of 250 N is applied as shown. Which of the following statemen best describes the subsequent motion?
of 250 N is applied as shown. Which of the following statemen best describes the subsequent motion? 
A) The block remains at rest.
B) The block moves and continues to move at constant velocity.
C) The block accelerates to the right.
D) The block does not move until
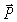 is increased to greater than 490 N.
is increased to greater than 490 N.E) No conclusions can be drawn concerning the movement of the block from the information given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
 An object with a mass M = 250 g is at rest on a plane that makes an angle = 30 o above the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between M and the plane is µk = 0.100. Mass M is attached by a string to another mass, m = 200 g, which hangs freely. When mass m has fallen 30.0 cm, its speed is
An object with a mass M = 250 g is at rest on a plane that makes an angle = 30 o above the horizontal. The coefficient of kinetic friction between M and the plane is µk = 0.100. Mass M is attached by a string to another mass, m = 200 g, which hangs freely. When mass m has fallen 30.0 cm, its speed isA) 83 cm/s.
B) 48 cm/s.
C) 160 cm/s.
D) 59 cm/s.
E) 72 cm/s.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
A mass m is placed on a rough incline at an angle to the horizon. A force F is applied up the incline, to prevent the mass from sliding down the incline, and it is just enough to prevent the mass from sliding down the incline. Using the compass rose, the direction of the frictional force is along 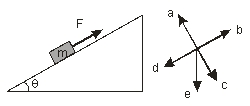
A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) d.
E) e.

A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) d.
E) e.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A 100-kg block is pushed up a 30 o incline that is 10 m long. If the coefficient of friction between the block and the incline is 0.1, the constant force parallel to the incline that is required to move the block from rest at the bottom of the incline to the top in 3 s is approximately
A) 0.49 kN.
B) 0.085 kN.
C) 0.22 kN.
D) 0.80 kN.
E) 0.58 kN.
A) 0.49 kN.
B) 0.085 kN.
C) 0.22 kN.
D) 0.80 kN.
E) 0.58 kN.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
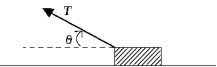 A block of mass m is pulled in the direction shown in the figure across a rough surface with a constant acceleration. The coefficient of kinetic friction is k. The acceleration of the object is given by
A block of mass m is pulled in the direction shown in the figure across a rough surface with a constant acceleration. The coefficient of kinetic friction is k. The acceleration of the object is given byA)
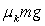 .
.B)
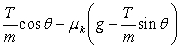 .
.C)
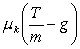 .
.D)
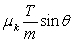 .
.E)
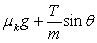 .
.
Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
A 6000-kg truck is accelerating at 0.5 m/s2 up a slope of 5 degrees. If the opposing forces due to road friction and air resistance are 80 N per 1000 kg of truck mass, calculate the driving force needed for the truck to accelerate up the incline.
A) 8100 N
B) 8600 N
C) 8200 N
D) 7700 N
E) 1700 N
A) 8100 N
B) 8600 N
C) 8200 N
D) 7700 N
E) 1700 N

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
A block of mass M is sliding down a rough inclined surface that makes an angle with respect to the horizontal. If the coefficient of static friction is s and kinetic friction k, then the acceleration of the block down the incline is equal to:
A) "g sin - s g cos ."
B) " g cos - k g cos "
C) " s g cos -g sin "
D) "g sin - k g cos "
E) "g sin - s g cos - k g cos "
A) "g sin - s g cos ."
B) " g cos - k g cos "
C) " s g cos -g sin "
D) "g sin - k g cos "
E) "g sin - s g cos - k g cos "

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
A box M = 20 kg) is sitting on a horizontal surface. It is connected to a massless hook by a light string passing over a massless pulley wheel. The coefficients of friction between the box and the surface are 0.80 static) and 0.30 kinetic). If 15 kg in total) are placed on the hook, calculate the acceleration of the box.
A) 9.8 m/s2
B) 4.4 m/s2
C) 2.5 m/s2
D) 12 m/s2
E) 0
A) 9.8 m/s2
B) 4.4 m/s2
C) 2.5 m/s2
D) 12 m/s2
E) 0

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
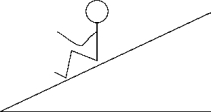 The free-body diagram that best represents the forces acting on the student sliding down a rough incline is
The free-body diagram that best represents the forces acting on the student sliding down a rough incline is 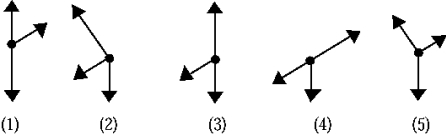
A) 1).
B) 2).
C) 3).
D) 4).
E) 5).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
 A 2-kg block sits on an incline where the top part of the incline has a coefficient of kinetic friction k) of 0.70. The bottom section of the plane has k = 0.95. The angle of inclination is 40 degrees. The block is released and travels 10 m along the initial part of the incline and then enters the lower section. Calculate how far the block travels along the second section before it is brought to a stop.
A 2-kg block sits on an incline where the top part of the incline has a coefficient of kinetic friction k) of 0.70. The bottom section of the plane has k = 0.95. The angle of inclination is 40 degrees. The block is released and travels 10 m along the initial part of the incline and then enters the lower section. Calculate how far the block travels along the second section before it is brought to a stop.A) 2.7 m
B) 21 m
C) 23 m
D) 13 m
E) 260 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
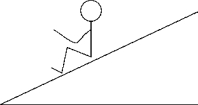 The free-body diagram that best represents the forces acting on the student at rest on the incline is
The free-body diagram that best represents the forces acting on the student at rest on the incline is 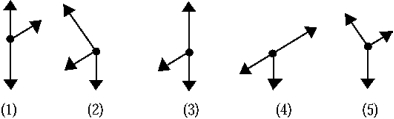
A) 1).
B) 2).
C) 3).
D) 4).
E) 5).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
If a jet plane doubles the speed, the drag force on the jet plane
A) decreases by half.
B) is unchanged.
C) is doubled.
D) is quadrupled.
E) depends how many passengers the plane is carrying.
A) decreases by half.
B) is unchanged.
C) is doubled.
D) is quadrupled.
E) depends how many passengers the plane is carrying.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
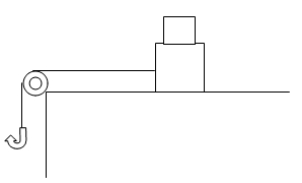 A box m = 20 kg) is sitting on a horizontal surface. It is connected to a massless hook by a light string passing over a massless pulley wheel. The coefficients of friction between the box and the surface are 0.50 static) and 0.30 kinetic). On top of m is a second box M of mass 20 kg. The coefficients of friction between the boxes m and M are 0.80 static) and 0.60 kinetic). How much weight needs to be added to the hook until the box just begins to move?
A box m = 20 kg) is sitting on a horizontal surface. It is connected to a massless hook by a light string passing over a massless pulley wheel. The coefficients of friction between the box and the surface are 0.50 static) and 0.30 kinetic). On top of m is a second box M of mass 20 kg. The coefficients of friction between the boxes m and M are 0.80 static) and 0.60 kinetic). How much weight needs to be added to the hook until the box just begins to move?A) 10 kg
B) 98 kg
C) 20 kg
D) 16 kg
E) 200 kg

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
An object with a mass of m = 12.0 g is falling through a resistive fluid in which g is constant. The drag force due to the fluid is F = bv, where F is the force in newtons, b is a constant, and v is the speed in meters per second. If F = 3.2 * 10-2 N when v = 16.0 m/s, the terminal speed of the object falling through the fluid is
A) 0.12 m/s.
B) 59 m/s.
C) 0.19 km/s.
D) 16.0 m/s.
E) None of these is correct.
A) 0.12 m/s.
B) 59 m/s.
C) 0.19 km/s.
D) 16.0 m/s.
E) None of these is correct.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
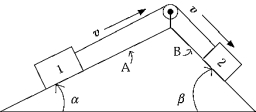 The system in the figure is moving with constant speed v to the right on a stationary ramp. The system will accelerate to the right if
The system in the figure is moving with constant speed v to the right on a stationary ramp. The system will accelerate to the right ifA) angle is increased.
B) angle is increased.
C) coefficient of friction µk for surface A is increased.
D) coefficient of friction µk for surface B is increased.
E) normal force on block 2 is increased.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
As a skydiver falls through the air, her terminal speed
A) depends on her mass.
B) depends on her body's orientation.
C) depends on the local value of the acceleration due to gravity.
D) depends on the density of the air.
E) is described by all of the above.
A) depends on her mass.
B) depends on her body's orientation.
C) depends on the local value of the acceleration due to gravity.
D) depends on the density of the air.
E) is described by all of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
A horizontal force 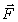 is used to push an object of mass m up an inclined plane. The angle between the plane and the horizontal is . The normal reaction force of the plane acting on the mass m is
is used to push an object of mass m up an inclined plane. The angle between the plane and the horizontal is . The normal reaction force of the plane acting on the mass m is
A) mg cos + F cos
B) mg cos
C) mg cos + F sin
D) mg cos - F cos
E) impossible to determine because the coefficient of friction is not given.
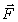 is used to push an object of mass m up an inclined plane. The angle between the plane and the horizontal is . The normal reaction force of the plane acting on the mass m is
is used to push an object of mass m up an inclined plane. The angle between the plane and the horizontal is . The normal reaction force of the plane acting on the mass m isA) mg cos + F cos
B) mg cos
C) mg cos + F sin
D) mg cos - F cos
E) impossible to determine because the coefficient of friction is not given.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
In the equation F = bv, F is the force on an object that is moving in a viscous medium, b is a constant, and v is the speed of the falling object. The SI units of the constant b are
A) m/s.
B) kg · s.
C) kg/s.
D) kg · m.
E) m/s2.
A) m/s.
B) kg · s.
C) kg/s.
D) kg · m.
E) m/s2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
A 50-kg box is placed in the bed of a truck. The coefficient of friction between the box and the truck bed is 0.54. If the truck is traveling at 87 km/h ~54 mph) then calculate the minimum distance the truck can stop in without the box sliding into the cab.
A) 99 m
B) 1.4 *103 m
C) 55 m
D) 1.2 * 102 m
E) 2.8 * 102 m
A) 99 m
B) 1.4 *103 m
C) 55 m
D) 1.2 * 102 m
E) 2.8 * 102 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
When a particle moves in a circle with constant speed, its acceleration is
A) constantly increasing.
B) constant in direction.
C) zero.
D) constant in magnitude.
E) constant in magnitude and direction.
A) constantly increasing.
B) constant in direction.
C) zero.
D) constant in magnitude.
E) constant in magnitude and direction.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
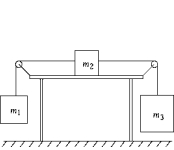 A mass m2 = 1.5 kg rests on a horizontal table. The coefficients of friction between m2 and the table are µs = 0.3 and µk = 0.25. The mass m2 is attached by strings to masses m1 = 2.5 kg and m3 = 4.5 kg as shown. Masses m1 and m3 hang freely. The system is initially held at rest. After it is released, the acceleration of m2 is approximately
A mass m2 = 1.5 kg rests on a horizontal table. The coefficients of friction between m2 and the table are µs = 0.3 and µk = 0.25. The mass m2 is attached by strings to masses m1 = 2.5 kg and m3 = 4.5 kg as shown. Masses m1 and m3 hang freely. The system is initially held at rest. After it is released, the acceleration of m2 is approximatelyA) 1.9 m/s2.
B) 2.4 m/s2.
C) 3.0 m/s2.
D) zero.
E) 13 m/s2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
In drag racing, the driver deploys a parachute at the end of the mile run. The parachute works well because
A) the dragster does not have any brakes to reduce weight.
B) the drag force due to the parachute is large at high speeds.
C) there is no rolling friction at high speeds.
D) the driver has no time to apply the brakes.
E) the deployment of the parachute is part of the show.
A) the dragster does not have any brakes to reduce weight.
B) the drag force due to the parachute is large at high speeds.
C) there is no rolling friction at high speeds.
D) the driver has no time to apply the brakes.
E) the deployment of the parachute is part of the show.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
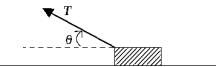 A block of mass m is pulled in the direction shown in the figure across a rough surface with a constant acceleration
A block of mass m is pulled in the direction shown in the figure across a rough surface with a constant acceleration 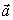 . The magnitude of the frictional force is
. The magnitude of the frictional force isA) µkmg.
B) T cos - ma.
C) µkT - mg).
D) µkT sin
E) µkmg + sin ).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
A block with a mass of 10 kg is at rest on a horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is 0.30, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25. A force of 20 N acts on the block toward the left. The magnitude of the frictional force on the block is
A) 10 N.
B) 20 N.
C) 0.10 kN.
D) 30 N.
E) 3.0 N.
A) 10 N.
B) 20 N.
C) 0.10 kN.
D) 30 N.
E) 3.0 N.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
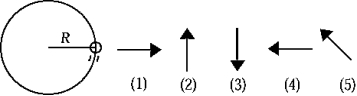 The figure shows a top view of a ball on the end of a string traveling counterclockwise in a circular path. Assume that air resistance is negligible. The free-body diagram that best represents the net force acting on the ball is
The figure shows a top view of a ball on the end of a string traveling counterclockwise in a circular path. Assume that air resistance is negligible. The free-body diagram that best represents the net force acting on the ball isA) 1).
B) 2).
C) 3).
D) 4).
E) 5).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
A professor likes to demonstrate centripetal force by swinging a bucket of water in the vertical direction. What is the minimum speed he must swing the bucket at the top of the circle if he is not to get drenched? Assume that his arm is 1 m long.)
A) 1.1 m/s
B) 2.1 m/s
C) 3.1 m/s
D) 4.1 m/s
E) 5.1 m/s
A) 1.1 m/s
B) 2.1 m/s
C) 3.1 m/s
D) 4.1 m/s
E) 5.1 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
A car going around a curve of radius R at a speed V experiences a centripetal acceleration ac. What is its acceleration if it goes around a curve of radius 3R at a speed of 2V?
A) 2/3)ac
B) 4/3)ac
C) 2/9)ac
D) 9/2)ac
E) 3/2)ac
A) 2/3)ac
B) 4/3)ac
C) 2/9)ac
D) 9/2)ac
E) 3/2)ac

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
An object traveling in a circle at constant speed
A) is moving with constant velocity.
B) may be slowing down or picking up speed.
C) experiences no acceleration.
D) experiences an acceleration toward the center of the circle.
E) is described by none of the above statements.
A) is moving with constant velocity.
B) may be slowing down or picking up speed.
C) experiences no acceleration.
D) experiences an acceleration toward the center of the circle.
E) is described by none of the above statements.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
A car experiences both a centripetal and a tangential acceleration. For which of the following would this be true?
A) It is going around a curve at a constant speed.
B) It is going around a curve and slowing down.
C) It is going along a straight road at a constant speed.
D) It is going along a straight road and increasing its speed.
E) It is going along a straight road and decreasing its speed.
A) It is going around a curve at a constant speed.
B) It is going around a curve and slowing down.
C) It is going along a straight road at a constant speed.
D) It is going along a straight road and increasing its speed.
E) It is going along a straight road and decreasing its speed.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
A particle moving uniformly along a curved path has a period of 0.24 s and a speed of 4.2 m/s. The radius of the path of the particle is
A) 16 cm.
B) 2.6 cm.
C) 1.0 m.
D) 0.062 cm.
E) 1.4 cm.
A) 16 cm.
B) 2.6 cm.
C) 1.0 m.
D) 0.062 cm.
E) 1.4 cm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A proud new Jaguar owner drives her car at a speed of 25 m/s into a corner. The coefficients of friction between the road and the tires are 0.70 static) and 0.40 kinetic). What is the minimum radius of curvature for the corner in order for the car not to skid?
A) 3.5 * 102 m
B) 64 m
C) 2.1 * 102 m
D) 1.6 * 102 m
E) 91 m
A) 3.5 * 102 m
B) 64 m
C) 2.1 * 102 m
D) 1.6 * 102 m
E) 91 m

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A proud new Jaguar owner drives her car into a circular section of the width radius 30 m. The coefficients of friction between the road and the tires are 0.70 static) and 0.40 kinetic). What is the maximum speed she could drive around the corner without skidding?
A) 21 m/s
B) 14 m/s
C) 9.8 m/s
D) 6.9 m/s
E) 25 m/s
A) 21 m/s
B) 14 m/s
C) 9.8 m/s
D) 6.9 m/s
E) 25 m/s

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The figure shows a top view of a ball on the end of a string traveling counterclockwise in a circular path. The speed of the ball is constant. If the string should break at the instant shown, the path that the ball would follow is 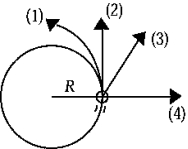
A) 1).
B) 2).
C) 3).
D) 4).
E) impossible to tell from the given information.

A) 1).
B) 2).
C) 3).
D) 4).
E) impossible to tell from the given information.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
A proud new Jaguar owner drives her car at a speed of 25 m/s into a corner. The coefficients of friction between the road and the tires are 0.70 static) and 0.40 kinetic). Assuming the car is not skidding while traveling along a path with minimum radius, what is the magnitude of the centripetal acceleration of the car?
A) 21 m/s2
B) 14 m/s2
C) 9.8 m/s2
D) 6.9 m/s2
E) 25 m/s2
A) 21 m/s2
B) 14 m/s2
C) 9.8 m/s2
D) 6.9 m/s2
E) 25 m/s2

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
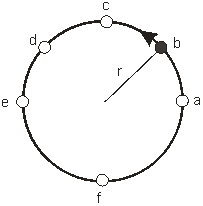 A ball of mass m is attached to a thin string and whirled in a vertical circle or radius r. The tension in the string at point e where the ball is moving with speed v is
A ball of mass m is attached to a thin string and whirled in a vertical circle or radius r. The tension in the string at point e where the ball is moving with speed v isA) mg.
B) mg - mv2/r.
C) mg + mv2/r.
D) mv2/r.
E) None of the above.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
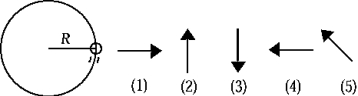 The figure shows a top view of a ball on the end of a string traveling counterclockwise in a circular path. Assume that air resistance is negligible. The free-body diagram that best represents the acceleration of the ball is
The figure shows a top view of a ball on the end of a string traveling counterclockwise in a circular path. Assume that air resistance is negligible. The free-body diagram that best represents the acceleration of the ball isA) 1).
B) 2).
C) 3).
D) 4).
E) 5).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
A particle is moving uniformly in a circle with radius 50 cm. The linear speed of the particle is 60 cm/s. The acceleration of the particle has a magnitude of
A) zero.
B) 36 m/s2.
C) 1.8 *0 105 cm/s2.
D) 72 cm/s2.
E) 3.6 m/s2.
A) zero.
B) 36 m/s2.
C) 1.8 *0 105 cm/s2.
D) 72 cm/s2.
E) 3.6 m/s2.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
A car going around a curve of radius R at a speed V experiences a centripetal acceleration ac. What is its acceleration if it goes around a curve of radius 2R at a speed of 3V?
A) 2/3)ac
B) 4/3)ac
C) 2/9)ac
D) 9/2)ac
E) 3/2)ac
A) 2/3)ac
B) 4/3)ac
C) 2/9)ac
D) 9/2)ac
E) 3/2)ac

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
A block slides down a frictionless incline. The path at the bottom of the incline is an arc of a circle. Using the compass rose, the direction of the net force on the block at the bottom of the arc point P) is along 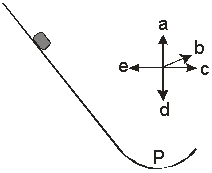
A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) d.
E) e.

A) a.
B) b.
C) c.
D) d.
E) e.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 75 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



