Deck 9: The Valuation of Stockprivate
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/36
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 9: The Valuation of Stockprivate
1
The PEG ratio multiplies a stock's earnings, price, and growth rate.
False
2
High P/E stocks should be preferred because they pay larger dividends.
False
3
The efficient market hypothesis suggests that the
current prices of stocks reflect what the investment community believes the stocks are worth.
current prices of stocks reflect what the investment community believes the stocks are worth.
True
4
A higher beta decreases the required rate of return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Value investors tend to prefer stocks with low price to sales and price to book ratios.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
If the anticipated return exceeds the required rate
of return, the investor should buy the stock.
of return, the investor should buy the stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
A P/E ratio depends on
1) the firm's dividends
2) the price of the stock
3) the firm's per share earnings
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above
1) the firm's dividends
2) the price of the stock
3) the firm's per share earnings
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The dividend?growth model requires that dividends grow annually at the same rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A stock's price will tend to fall if
1) the firm's beta declines
2) the firm's beta increases
3) the risk?free rate declines
4) the risk?free rate increases
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
1) the firm's beta declines
2) the firm's beta increases
3) the risk?free rate declines
4) the risk?free rate increases
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
The required return includes the risk?free rate and a risk premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
If the required rate of return is 10 percent and the
Stock pays a fixed $5 dividend, its value is
A) $100
B) $75
C) $50
D) $25
Stock pays a fixed $5 dividend, its value is
A) $100
B) $75
C) $50
D) $25

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
According to the efficient market hypothesis, purchasing high P/E stock should not produce superior
investment results.
investment results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
The risk?adjusted required rate of return includes
1) the firm's earnings
2) the firm's beta coefficient
3) the treasury bill rate (i.e., the risk?free rate)
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above
1) the firm's earnings
2) the firm's beta coefficient
3) the treasury bill rate (i.e., the risk?free rate)
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The dividend?growth model includes both the current
and past years' dividends.
and past years' dividends.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
According to the efficient market hypothesis, purchasing companies with high cash flow should produce superior investment results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
According to the efficient market hypothesis, purchasing low P/S stocks should produce superior investment results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
According to the dividend?growth model, the valuation of common stock depends on
1) the firm's dividends
2) investors' required rate of return
3) the prior year's dividends
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above
1) the firm's dividends
2) investors' required rate of return
3) the prior year's dividends
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
The dividend-growth valuation model employs current dividends, future dividend growth, and the required return.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The expected return depends on future dividends and future price appreciation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
An increase in the risk?free rate will tend to decrease stock prices.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
Your broker recommends that you purchase XYZ Inc. at $60. The stock pays a $2.40 dividend which (like its per share earnings) is expected to grow annually at 8 percent. If you want to earn 12 percent on your funds, is this a good buy?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
As an investor you have a required rate of return of 14 percent for investments in risky stocks. You have analyzed three risky firms and must decide which (if any) to purchase. Your information is
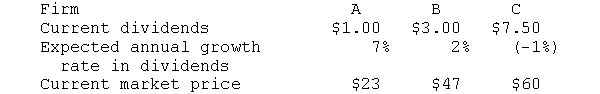
a. What is your valuation of each stock using the dividend-growth model? Which (if any) should you buy?
b. If you bought Stock A, what is your implied rate of return?
c. If your required rate of return were 10 percent, what should be the price necessary to induce you to buy Stock A?
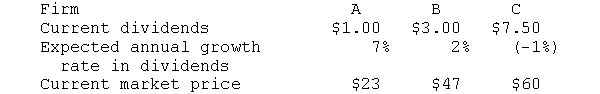
a. What is your valuation of each stock using the dividend-growth model? Which (if any) should you buy?
b. If you bought Stock A, what is your implied rate of return?
c. If your required rate of return were 10 percent, what should be the price necessary to induce you to buy Stock A?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
A low price to sales ratio suggests
A) the firm is generating cash
B) the firm has no earnings
C) the stock valuation is too high
D) the stock may be undervalued
A) the firm is generating cash
B) the firm has no earnings
C) the stock valuation is too high
D) the stock may be undervalued

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Investors may use P/E and price/sales ratios to
Value stocks. If this analysis is used, which of the
Following is desirable?
A) a high P/E and a low price/sales ratio
B) a high P/E and a high price/sales ratio
C) a low P/E and a low price/sales ratio
D) a low P/E and a high price/sales ratio
Value stocks. If this analysis is used, which of the
Following is desirable?
A) a high P/E and a low price/sales ratio
B) a high P/E and a high price/sales ratio
C) a low P/E and a low price/sales ratio
D) a low P/E and a high price/sales ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Use of P/E ratios will not produce superior
Investment results according to the
A) weak form of the efficient market hypothesis
B) semi?strong form of the efficient market hypothesis
C) strong form of the efficient market hypothesis
D) all forms of the efficient market hypothesis
Investment results according to the
A) weak form of the efficient market hypothesis
B) semi?strong form of the efficient market hypothesis
C) strong form of the efficient market hypothesis
D) all forms of the efficient market hypothesis

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Presently, Stock A pays a dividend of $2.00 a share, and you expect the dividend to grow rapidly for the next four years at 20 percent. Thus the dividend payments will be

After this initial period of super growth, the rate of increase in the dividend should decline to 8 percent. If you want to earn 12 percent on investments in common stock, what is the maximum you should pay for this stock?
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS

After this initial period of super growth, the rate of increase in the dividend should decline to 8 percent. If you want to earn 12 percent on investments in common stock, what is the maximum you should pay for this stock?
SOLUTIONS TO PROBLEMS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The risk?free rate of return is 8 percent; the expected rate of return on the market is 12 percent. Stock X has a beta coefficient of 1.3, an earnings and dividend?growth rate of 7 percent, and a current dividend of $2.40. If the stock is selling for $35, what should you do?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
You know the following concerning a common stock:

If you want to earn 10 percent, should you buy this stock? What is the maximum price you should be willing to pay for the stock?

If you want to earn 10 percent, should you buy this stock? What is the maximum price you should be willing to pay for the stock?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
The price to sales ratio may be a preferred
Analytical tool if
A) the firm is not generating cash
B) the firm is not generating earnings
C) the P/E ratio is too high
D) the dividend-growth model suggests the stock is undervalued
Analytical tool if
A) the firm is not generating cash
B) the firm is not generating earnings
C) the P/E ratio is too high
D) the dividend-growth model suggests the stock is undervalued

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
If you purchase TrisCorp stock at $71 a share and the firm pays a $5.20 dividend which is expected to grow at 7.5 percent, what is the implied annual rate of return on the investment?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the financial markets were not efficient,
A) all investors would profit
B) prices indicate the proper valuation of securities
C) prices would adjust rapidly
D) an investor may consistently outperform the market
A) all investors would profit
B) prices indicate the proper valuation of securities
C) prices would adjust rapidly
D) an investor may consistently outperform the market

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The use of P/E ratios to select stocks suggests that
A) high P/E stocks should be purchased
B) low P/E ratio stocks are overvalued
C) a stock should be purchased if it is selling near its historic low P/E
D) a stock should be purchased if it is selling near its historic high P/E
A) high P/E stocks should be purchased
B) low P/E ratio stocks are overvalued
C) a stock should be purchased if it is selling near its historic low P/E
D) a stock should be purchased if it is selling near its historic high P/E

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
The use of price to book ratios to select stocks
Suggests that
A) high price to book stocks are undervalued
B) low price to book stocks are overvalued
C) a stock should be purchased if it is selling near its historic high price to book ratio
D) a stock should be purchased if it is selling near its historic low price to book ratio
Suggests that
A) high price to book stocks are undervalued
B) low price to book stocks are overvalued
C) a stock should be purchased if it is selling near its historic high price to book ratio
D) a stock should be purchased if it is selling near its historic low price to book ratio

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Two stocks each pay a $1 dividend that is growing annually at 8 percent. Stock A has a beta of 1.3; stock B's beta is 0.8.
a. Which stock is more volatile?
b. If treasury bills yield 6 percent and you expect the market to rise by 12 percent, what is your risk?adjusted required rate of return?
c. Using the dividend?growth model, what is the maximum amount you would be willing to pay for each stock?
d. Why are your valuations different?
a. Which stock is more volatile?
b. If treasury bills yield 6 percent and you expect the market to rise by 12 percent, what is your risk?adjusted required rate of return?
c. Using the dividend?growth model, what is the maximum amount you would be willing to pay for each stock?
d. Why are your valuations different?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Higher required returns
A) decrease stock prices
B) are required by the efficient market hypothesis
C) increase dividends
D) are associated with higher dividends
A) decrease stock prices
B) are required by the efficient market hypothesis
C) increase dividends
D) are associated with higher dividends

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
If the ratio of price to book exceeds 1.0,
A) the stock is overvalued
B) the firm's assets are understated
C) the price of the stock is greater than the accounting value of the firm
D) the accounting value of the firm is greater than the market value of the firm
PROBLEMS
A) the stock is overvalued
B) the firm's assets are understated
C) the price of the stock is greater than the accounting value of the firm
D) the accounting value of the firm is greater than the market value of the firm
PROBLEMS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 36 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



