Deck 17: An Introduction to Options
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/84
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 17: An Introduction to Options
1
The intrinsic value of an option to buy stock (i.e., a call option) is the difference between the price of the stock and the per share exercise price of the option.
True
2
The price of an option is generally less than the option's intrinsic value.
False
3
Holders of calls do not receive the cash dividends
paid to the company's stockholders.
paid to the company's stockholders.
True
4
Arbitrage determines the maximum price of an option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
Arbitrage is the act of simultaneously buying and
selling in two markets to take advantage of price differentials.
selling in two markets to take advantage of price differentials.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
An option's intrinsic value exceeds the option's price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
The time period to expiration for call options is usually for less than a year.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
Call options, unlike warrants, may be written by
individuals.
individuals.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
A warrant is an option issued by a corporation to buy
its stock at a specified price within a specified time period.
its stock at a specified price within a specified time period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Investors and speculators rarely, if ever, have an opportunity to establish an arbitrage position.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Because of arbitrage, an option should not sell for
less than its intrinsic value.
less than its intrinsic value.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
Because of the small cash outlay to buy an option, these securities are considered to be conservative investments.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
A covered call is constructed by buying the stock and selling the call.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
Calls are options to sell stock at a specified price
within a specified time period.
within a specified time period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
As the price of a stock rises, the time premium paid for an option to buy stock increases.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
If the price of an option to buy stock were to sell
for less than its strike price, an opportunity for arbitrage exists.
for less than its strike price, an opportunity for arbitrage exists.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
The maximum potential profit on a covered call is the time premium paid for the stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Since options offer potential leverage, they tend to
sell for a time premium.
sell for a time premium.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
The time premium paid for an option reduces the option's potential leverage.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
The strike price of an option is fixed when the option is issued.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
In addition to put and call options on individual stocks, there are also options on the market as a whole (i.e., an index).

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
The value of a put is inversely related to the value of
the underlying stock.
the underlying stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
The intrinsic value of a put is the price of the stock
minus the put's strike price.
minus the put's strike price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Calls tend to sell for a time premium that exceeds the stock's price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
There is no limit to the potential loss from buying a call option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
When a call option is exercised, new stock is issued.
F.23. The intrinsic value of a call option is the strike price minus the stock's price.
F.23. The intrinsic value of a call option is the strike price minus the stock's price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
The intrinsic value of a put establishes the put's
maximum price.
maximum price.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
Writing covered call options is more risky than writing naked call options

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Selling a covered call option is comparable to selling a stock short.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The writer of a call option does not receive any dividends paid by the firm.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
If the price of a stock rises, the writer of a put
option profits.
option profits.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
A put is an option to sell stock at a specified price
within a specified time period.
within a specified time period.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
A writer of a naked call option will lose money if the price of the stock declines.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
The profits (gains) on option trading are exempt from federal income taxation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
The writer of a covered call cannot lose money if the price of the stock rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
The buyer of a call option wants the price of the stock to rise.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
The price of a call option is often more volatile than the price of the underlying stock.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
While individuals can write call options, they can only
buy put options.
buy put options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
An investor may reduce risk by simultaneously purchasing a stock and a put option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
The CBOE is a secondary market for put and call options.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
The intrinsic value of an option sets
A) the minimum price of an option
B) the maximum price of an option
C) neither an option's minimum nor its maximum price
D) both the maximum and the minimum price of an option
A) the minimum price of an option
B) the maximum price of an option
C) neither an option's minimum nor its maximum price
D) both the maximum and the minimum price of an option

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
The time premium paid for an option to buy stock
Is affected by
A) the length of time to expiration
B) the firm's credit rating
C) the existence of a rights offering
D) the firm's financial statements
Is affected by
A) the length of time to expiration
B) the firm's credit rating
C) the existence of a rights offering
D) the firm's financial statements

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Stock index options permit investors to establish a
position in the market without having to select individual stocks.
position in the market without having to select individual stocks.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
In-the-money stock index options are not exercised.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
Warrants are issued by
A) individuals
B) firms
C) governments
D) investor
A) individuals
B) firms
C) governments
D) investor

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
Options sell for a time premium over their intrinsic
Value because
A) they earn dividends
B) they are debt obligations
C) they offer potential leverage
D) they are long-term investments
Value because
A) they earn dividends
B) they are debt obligations
C) they offer potential leverage
D) they are long-term investments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
The intrinsic value of an option to buy stock is
A) its price
B) its strike price
C) the difference between the stock's price and the option's strike price
D) the difference between the option's strike price and the option's price
A) its price
B) its strike price
C) the difference between the stock's price and the option's strike price
D) the difference between the option's strike price and the option's price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The intrinsic value of an option to buy stock rises as
A) the strike price increases and the price of the stock declines
B) the strike price increases and the price of the stock rises
C) the strike price decreases and the price of the stock declines
D) the strike price decreases and the price of the stock rises
A) the strike price increases and the price of the stock declines
B) the strike price increases and the price of the stock rises
C) the strike price decreases and the price of the stock declines
D) the strike price decreases and the price of the stock rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The most the investor who sells a naked stock index
option can lose is the cost of the option.
option can lose is the cost of the option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Warrants and calls do not have
A) an expiration date
B) a specified exercise price
C) the right to receive dividends
D) a strike price
A) an expiration date
B) a specified exercise price
C) the right to receive dividends
D) a strike price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
51
A portfolio manager with a position in many stocks may hedge the portfolio by purchasing a stock index call option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
52
Buying a stock index option reduces systematic risk.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
53
If an investor anticipates that interest rates will increase, that individual should sell an option to buy Treasury bonds

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
54
The most the individual who buys a put option can lose
is the cost of the option.
is the cost of the option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
55
Options to buy stock offer
A) potential leverage
B) potential income
C) safety of principal
D) liquidity
A) potential leverage
B) potential income
C) safety of principal
D) liquidity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
56
If an investor constructs a covered call,
A) there is no limit to the potential profit
B) risk is increased
C) risk is reduced
D) the term of the position is increased
A) there is no limit to the potential profit
B) risk is increased
C) risk is reduced
D) the term of the position is increased

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
57
A call is an option to
A) sell stock at a specified price
B) buy stock at a specified price
C) deliver stock at a specified price
D) deliver bonds at a specified price
A) sell stock at a specified price
B) buy stock at a specified price
C) deliver stock at a specified price
D) deliver bonds at a specified price

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
58
Because of arbitrage, the price of an option
A) exceeds its intrinsic value
B) is less than its intrinsic value
C) cannot be less than its intrinsic value
D) cannot be greater than its intrinsic value
A) exceeds its intrinsic value
B) is less than its intrinsic value
C) cannot be less than its intrinsic value
D) cannot be greater than its intrinsic value

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
59
If an investor is bearish, he or she should not buy
a stock index call option.
a stock index call option.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
60
If the investor buys a stock index put, the individual
will profit if the market rises.
will profit if the market rises.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
61
What are the intrinsic values and time premiums of the following call options if the price of the underlying stock is $35? What are the profits and losses to the buyers and the writers if the stock sells for $31 at the options' expiration?



Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
62
The writer of a naked call option wants
A) the prices of the stock and the call to rise
B) the prices of the stock and the call to fall
C) the prices of the stock to fall and the call to rise
D) the prices of the stock to rise and the call to remain stable
A) the prices of the stock and the call to rise
B) the prices of the stock and the call to fall
C) the prices of the stock to fall and the call to rise
D) the prices of the stock to rise and the call to remain stable

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
63
Which of the following is premised on lower stock prices?
A) buying a stock index call
B) buying a stock index put
C) buying a stock and selling a call
D) buying a stock and selling a put
A) buying a stock index call
B) buying a stock index put
C) buying a stock and selling a call
D) buying a stock and selling a put

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
64
A put is an option to
A) buy stock
B) receive stock
C) sell stock
D) receive dividends
A) buy stock
B) receive stock
C) sell stock
D) receive dividends

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
65
The price of a call depends on
1) the strike price
2) the price of the underlying stock
3) the term (i.e., life) of the call
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above
1) the strike price
2) the price of the underlying stock
3) the term (i.e., life) of the call
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
66
The value of a put rises as the price of
A) stock rises
B) a call falls
C) stock falls
D) a call rises
A) stock rises
B) a call falls
C) stock falls
D) a call rises

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
67
A warrant is the option to buy one share of stock at $40. It expires after one year and currently sells for $10. The price of the stock is $32. What is the maximum possible profit if an investor buys one share of stock and shorts one warrant? What is the range of stock prices that yields a profit on this position?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
68
A writer of a call option closes the position by
A) purchasing the stock
B) selling the stock
C) purchasing the option
D) selling the option
A) purchasing the stock
B) selling the stock
C) purchasing the option
D) selling the option

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
69
The CBOE is
1) a secondary market in put and call options
2) a division of the SEC that regulated option trading
3) the first organized options exchange
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above
1) a secondary market in put and call options
2) a division of the SEC that regulated option trading
3) the first organized options exchange
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
70
Which of the following assumes higher stock prices?
1) buying a stock index call
2) buying a stock index put
3) selling a stock index call
4) selling a stock index put
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
PROBLEMS
1) buying a stock index call
2) buying a stock index put
3) selling a stock index call
4) selling a stock index put
A) 1 and 3
B) 1 and 4
C) 2 and 3
D) 2 and 4
PROBLEMS

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
71
A put and a call have the following terms:
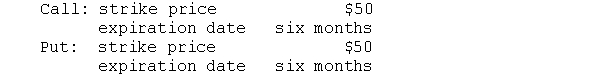
The price of the stock is currently $55. The price of the call and put are, respectively, $9 and $1. What will be the profit from buying the call or buying the put if, after six months, the price of the stock is $40, $50, or $60?
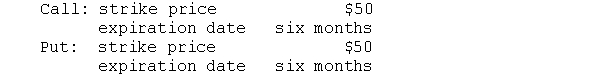
The price of the stock is currently $55. The price of the call and put are, respectively, $9 and $1. What will be the profit from buying the call or buying the put if, after six months, the price of the stock is $40, $50, or $60?

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
72
Given the following information,

a. The intrinsic value of the call is _________.
b. The intrinsic value of the put is _________.
c. The time premium paid for the call is _________.
d. The time premium paid for the put is _________.
At the expiration of the options (i.e., after six months have lapsed), the price of the stock is $45.
e. The profit (loss) from buying the call is _______.

a. The intrinsic value of the call is _________.
b. The intrinsic value of the put is _________.
c. The time premium paid for the call is _________.
d. The time premium paid for the put is _________.
At the expiration of the options (i.e., after six months have lapsed), the price of the stock is $45.
e. The profit (loss) from buying the call is _______.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
73
What are the following call options' intrinsic values and time premiums if the price of the underlying stock is $55?
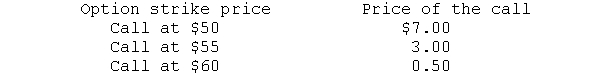
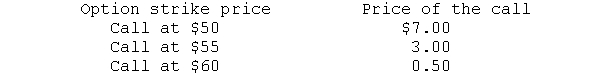

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
74
If the price of a stock rises substantially, the investor who wrote a covered call
1) earns a modest profit
2) sustains a modest loss
3) lost an opportunity for a large profit
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) only 3
1) earns a modest profit
2) sustains a modest loss
3) lost an opportunity for a large profit
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) only 3

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
75
Given the following information,
finish the following sentences:

a. The intrinsic value of the call is _________.
b. The time premium paid for the call is ________.
c. If an investor established a covered call position, the amount invested is _________.
d. The most the buyer of the call can lose is ________.
e. The maximum amount the seller of the call naked can lose is ________.
finish the following sentences:

a. The intrinsic value of the call is _________.
b. The time premium paid for the call is ________.
c. If an investor established a covered call position, the amount invested is _________.
d. The most the buyer of the call can lose is ________.
e. The maximum amount the seller of the call naked can lose is ________.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
76
Stock index options
1) permit the investor to short the market instead
Of individual stocks
2) require delivery of an index of stocks
3) limit the buyer's potential loss to the cost of
The option
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above
1) permit the investor to short the market instead
Of individual stocks
2) require delivery of an index of stocks
3) limit the buyer's potential loss to the cost of
The option
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
77
Call options offer buyers
A) potential leverage
B) liquidity
C) income
D) safety of principal
A) potential leverage
B) liquidity
C) income
D) safety of principal

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
78
One reason for writing and selling a covered call
Option is
A) potential leverage
B) safety of principal
C) income received
D) liquidity
Option is
A) potential leverage
B) safety of principal
C) income received
D) liquidity

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
79
The intrinsic value of a put depends on
1) the strike price
2) the price of the stock
3) the term on the put
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above
1) the strike price
2) the price of the stock
3) the term on the put
A) 1 and 2
B) 1 and 3
C) 2 and 3
D) all of the above

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
80
A call option is similar to a warrant except
A) the strike price is fixed
B) it may be issued by individual investors
C) it is not marketable (saleable)
D) it receives dividend payments
A) the strike price is fixed
B) it may be issued by individual investors
C) it is not marketable (saleable)
D) it receives dividend payments

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 84 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



