Deck 10: Audit Sampling
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question
Question

Unlock Deck
Sign up to unlock the cards in this deck!
Unlock Deck
Unlock Deck
1/50
Play
Full screen (f)
Deck 10: Audit Sampling
1
In making a decision about the extent of misstatement in a population, the known misstatement in the sample must be projected to the population.
True
2
Using the audit risk model: If audit risk is 0.05, inherent risk is 1.0, control risk is 0.20, and analytical procedures risk is 1.0, the risk of incorrect acceptance is 0.25.
True
3
An advantage of statistical sampling over non-statistical sampling is that statistical sampling helps an auditor to
A)Minimize the failure to detect errors and irregularities.
B)Eliminate the risk of non-sampling errors.
C)Reduce the level of audit risk and materiality to a relatively low amount.
D)Make a preliminary estimate of the appropriate sample size.
A)Minimize the failure to detect errors and irregularities.
B)Eliminate the risk of non-sampling errors.
C)Reduce the level of audit risk and materiality to a relatively low amount.
D)Make a preliminary estimate of the appropriate sample size.
D
4
An example of non-sampling risk is the selection of a random sample that is not representative of the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
5
The sample deviation rate is the best single-point estimate of the actual, but unknown, deviation rate in the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
6
In specifying the objectives for substantive testing of accounts receivable, an auditor hypothesizes that the company does not have a right to collect the money, and looks for evidence that they do.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
7
Assessing control risk too low threatens the efficiency of the audit but not the effectiveness.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
8
The risk of incorrect rejection exists both in statistical and nonstatistical sampling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
9
If statistical calculations were not applied then a sampling method would be considered non-statistical even though a random sample was selected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
10
Attribute sampling is audit sampling in which auditors look for the presence or absence of a control condition.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
11
Non-statistical sampling is audit sampling in which auditors do not use the probability calculations to express the results.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
12
When the projected likely misstatement is greater than the tolerable misstatement in a sample-based audit of an account balance, the auditor can decide that the account balance is materially misstated and therefore run the risk of incorrect acceptance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
13
Analytical procedures, such as vertical analysis, ratio calculations, and time series analysis, are usually done on a sample basis.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
14
The determination of an appropriate sample on a representative basis must be made using statistical methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
15
Sampling risk is the risk that the sample does not represent the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
16
The set of all of the elements that comprise an account balance or a class of transactions is referred to as a
A)Sampling unit.
B)Sample.
C)Population unit.
D)Population.
A)Sampling unit.
B)Sample.
C)Population unit.
D)Population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
17
Non-sampling risk exists in both statistical and non-statistical sampling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
18
Which of the following audit procedures is not typically used in audit sampling applications?
A)Observation of personnel and procedures.
B)Physical count of tangible assets.
C)Recalculation.
D)Confirmation.
A)Observation of personnel and procedures.
B)Physical count of tangible assets.
C)Recalculation.
D)Confirmation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
19
When auditors perform procedures using statistical sampling and obtain sufficient evidence, a conclusion about the population characteristics will not be wrong.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
20
Auditing a larger sample reduces the probability of determining that the control is working well when in fact it is not.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
21
The risk of assessing control risk too high is the risk that the evidence of compliance with control procedures in the sample indicates
A)Low control risk when the actual degree of compliance does not justify a low control risk assessment.
B)Low control risk when the actual degree of compliance justifies a low control risk assessment.
C)High control risk when the actual degree of compliance would justify a lower control risk assessment.
D)High control risk when the actual degree of compliance would justify a higher control risk assessment.
A)Low control risk when the actual degree of compliance does not justify a low control risk assessment.
B)Low control risk when the actual degree of compliance justifies a low control risk assessment.
C)High control risk when the actual degree of compliance would justify a lower control risk assessment.
D)High control risk when the actual degree of compliance would justify a higher control risk assessment.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
22
When performing the substantive tests on an account balance, the auditor is concerned about two aspects of sampling-based decision errors: 1) the risk of incorrect rejection (RIR) and 2) the risk of incorrect acceptance (RIA).Which of the following is true about RIR and RIA?
A)RIR is of greater concern to the auditor than the RIA.
B)RIA is of greater concern to the auditor than the RIR.
C)RIA and the RIR are of equal importance to the auditor.
D)Neither the RIR nor the RIA need be considered by the auditor.
A)RIR is of greater concern to the auditor than the RIA.
B)RIA is of greater concern to the auditor than the RIR.
C)RIA and the RIR are of equal importance to the auditor.
D)Neither the RIR nor the RIA need be considered by the auditor.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
23
If the association of population items with random numbers is difficult and expensive, but the auditor does not have sufficient knowledge about the population the auditor should:
A)Use non statistical sampling.
B)Use statistical sampling.
C)Use a computer to analyze and the population and then decide which method to use.
D)First determine the possible impacts of an error in the population on the financial statements to decide if sampling is reasonable.
A)Use non statistical sampling.
B)Use statistical sampling.
C)Use a computer to analyze and the population and then decide which method to use.
D)First determine the possible impacts of an error in the population on the financial statements to decide if sampling is reasonable.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
24
Which description best illustrates sampling risk?
A)Applying audit procedures that are inappropriate for the audit objectives.
B)Failing to recognize errors or deviations in the documents examined.
C)Arriving at incorrect statistical conclusions because of computational errors.
D)Choosing a sample that does not represent the population.
A)Applying audit procedures that are inappropriate for the audit objectives.
B)Failing to recognize errors or deviations in the documents examined.
C)Arriving at incorrect statistical conclusions because of computational errors.
D)Choosing a sample that does not represent the population.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
25
Which of the following is used in attribute sampling to determine the sample size?
A)Sampling risk, sample deviation rate, tolerable deviation rate.
B)Sampling risk, sample deviation rate, expected population deviation rate.
C)Sampling risk, tolerable deviation rate, expected population deviation rate.
D)Sample deviation rate, tolerable deviation rate, expected population deviation rate.
A)Sampling risk, sample deviation rate, tolerable deviation rate.
B)Sampling risk, sample deviation rate, expected population deviation rate.
C)Sampling risk, tolerable deviation rate, expected population deviation rate.
D)Sample deviation rate, tolerable deviation rate, expected population deviation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
26
Detection risk is the risk that the auditor will not detect material misstatements in the accounts.To limit detection risk to an acceptable level, the auditor
A)Performs substantive tests.
B)Tests controls.
C)Gains an understanding of the internal control system.
D)Applies statistical methods.
A)Performs substantive tests.
B)Tests controls.
C)Gains an understanding of the internal control system.
D)Applies statistical methods.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
27
As a result of tests of controls, an auditor assessed control risk too low and decreased substantive testing.This assessment resulted because the true deviation rate in the population was
A)More than the risk of assessing control risk too low based on the auditor's sample.
B)Less than the risk of assessing control risk too low based on the auditor's sample.
C)More than the deviation rate in the auditor's sample.
D)Less than the deviation rate in the auditor's sample.
A)More than the risk of assessing control risk too low based on the auditor's sample.
B)Less than the risk of assessing control risk too low based on the auditor's sample.
C)More than the deviation rate in the auditor's sample.
D)Less than the deviation rate in the auditor's sample.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
28
The probability that an auditor's conclusion based on a sample might differ from the auditor's conclusion based on the entire population identifies the concept of
A)Sampling risk.
B)Confidence levels.
C)Statistical sampling.
D)Tolerable rate and the expected deviation rate.
A)Sampling risk.
B)Confidence levels.
C)Statistical sampling.
D)Tolerable rate and the expected deviation rate.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
29
Which of the following is an advantage of statistical sampling?
A)It permits a less rigid approach to unique audit problems.
B)It uses an evaluation method that allows evaluation of the sample on factors other than the sample evidence.
C)It permits auditors to use a computer to select a random sample.
D)It requires auditors to be exact in their judgements on risk and materiality.
A)It permits a less rigid approach to unique audit problems.
B)It uses an evaluation method that allows evaluation of the sample on factors other than the sample evidence.
C)It permits auditors to use a computer to select a random sample.
D)It requires auditors to be exact in their judgements on risk and materiality.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
30
The purpose of tests of controls is to determine whether
A)Internal control policies and procedures are working as prescribed.
B)Substantive testing can be kept to a minimum.
C)Errors and irregularities are prevented or detected in a timely manner.
D)The auditor has an understanding of the control system.
A)Internal control policies and procedures are working as prescribed.
B)Substantive testing can be kept to a minimum.
C)Errors and irregularities are prevented or detected in a timely manner.
D)The auditor has an understanding of the control system.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
31
In a sample-based audit of an account balance, which of the following combinations properly expresses the relationship between changes in the factors indicated and changes in sample size? 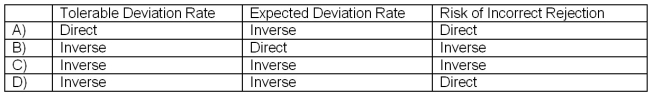
A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

A)A
B)B
C)C
D)D

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
32
The risk model is defined as AR = IR x CR x DR.The risk of assessing control risk too low can lead to:
A)The auditor performing more work than needed, thus wasting resources.
B)The auditor failing to do additional work that should be done.
C)Poor choice of procedures.
D)Expanding sample sizes required for statistical sampling of account balances.
A)The auditor performing more work than needed, thus wasting resources.
B)The auditor failing to do additional work that should be done.
C)Poor choice of procedures.
D)Expanding sample sizes required for statistical sampling of account balances.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
33
In testing controls over invoices an auditor discovers that in 10% of her statistical sample invoices were sent for full shipments, even if shipping documents suggested partial shipments.In this case, she would likely:
A)Increase her sample size to determine the extent of the control weakness.
B)Recalculate control risk to determine if there is any effect on the nature, timing or extent of her yearend procedures.
C)Conclude that controls are working at 90% effectiveness and classify control risk as low.
D)Consult with her partner to consider launching a fraud investigation.
A)Increase her sample size to determine the extent of the control weakness.
B)Recalculate control risk to determine if there is any effect on the nature, timing or extent of her yearend procedures.
C)Conclude that controls are working at 90% effectiveness and classify control risk as low.
D)Consult with her partner to consider launching a fraud investigation.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
34
Which of the following courses of action is an auditor most likely to follow in designing a sampling plan for cash disbursements if the auditor is aware of several unusually large cash disbursements?
A)Increase the sample size to reduce the effect of the unusually large disbursements.
B)Continue to draw new samples until all the unusually large disbursements are included in the sample.
C)Set the tolerable deviation rate at a lower level than originally planned.
D)Stratify the cash disbursements population so that all of the unusually large disbursements are selected.
A)Increase the sample size to reduce the effect of the unusually large disbursements.
B)Continue to draw new samples until all the unusually large disbursements are included in the sample.
C)Set the tolerable deviation rate at a lower level than originally planned.
D)Stratify the cash disbursements population so that all of the unusually large disbursements are selected.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
35
Non-statistical sampling may be better to use than statistical sampling when:
A)The auditor has insufficient knowledge about the population to take a statistical sample.
B)The inherent risk of error in the population is low.
C)The population is known to be diverse, with a high inherent risk of error.
D)Auditors are not technically proficient in sampling.
A)The auditor has insufficient knowledge about the population to take a statistical sample.
B)The inherent risk of error in the population is low.
C)The population is known to be diverse, with a high inherent risk of error.
D)Auditors are not technically proficient in sampling.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
36
For which of the following audit tests is an auditor most likely to use attribute sampling?
A)Making an independent estimate of the amount of a FIFO inventory.
B)Examining invoices in support of the valuation of fixed asset additions.
C)Selecting accounts receivable for confirmation of account balances.
D)Inspecting employee time cards for proper approval by supervisors.
A)Making an independent estimate of the amount of a FIFO inventory.
B)Examining invoices in support of the valuation of fixed asset additions.
C)Selecting accounts receivable for confirmation of account balances.
D)Inspecting employee time cards for proper approval by supervisors.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
37
After extrapolating the results of performing substantive tests on a sample of accounts from the accounts receivable subsidiary ledger, Allen CA concluded that the accounts receivable balance was materially misstated.In fact, the balance was materially correct.This situation illustrates the risk of
A)Incorrect rejection.
B)Incorrect acceptance.
C)Assessing control risk too low.
D)Assessing control risk too high.
A)Incorrect rejection.
B)Incorrect acceptance.
C)Assessing control risk too low.
D)Assessing control risk too high.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
38
Which of the following is a term used to describe a departure from a prescribed internal control procedure?
A)Exception.
B)Event.
C)Misstatement.
D)Known error.
A)Exception.
B)Event.
C)Misstatement.
D)Known error.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
39
The standard deviation of a population of data is a statistical measure of
A)How much data are skewed.
B)How much data are correlated.
C)The dispersion of data.
D)The average value of data items.
A)How much data are skewed.
B)How much data are correlated.
C)The dispersion of data.
D)The average value of data items.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
40
A number of factors can affect the size of a sample for a substantive audit of the details of an account balance.All other factors being equal, which of the following would lead to a larger sample size?
A)A lower assessed level of control risk.
B)Using a larger number of effective analytical procedures to obtain evidence about particular assertions.
C)Smaller expected frequency of account item errors.
D)Smaller measure of tolerable misstatement.
A)A lower assessed level of control risk.
B)Using a larger number of effective analytical procedures to obtain evidence about particular assertions.
C)Smaller expected frequency of account item errors.
D)Smaller measure of tolerable misstatement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
41
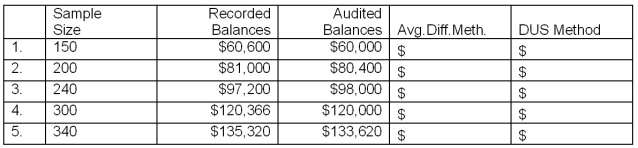
Assume several auditors selected various unrestricted, unstratified random samples from a population of 1,200 customers' accounts receivable with a recorded value of $480,000.The results of their tests are shown in the table below.
Required:
For each of the sample sizes, calculate the projected likely misstatement (PLM) using (1) average difference method, and (2) the Dollar Unit Sample method.Treat each case independently.Round the PLM solutions to the nearest dollar.
Projected Likely Misstatement
Overstatement (Understatement)
Required:
For each of the sample sizes, calculate the projected likely misstatement (PLM) using (1) average difference method, and (2) the Dollar Unit Sample method.Treat each case independently.Round the PLM solutions to the nearest dollar.
Projected Likely Misstatement
Overstatement (Understatement)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
42
Jack and Jill, two auditors who have separate accounting practices, have independently assessed the risks associated with the accounts receivable of their respective clients.The appropriate audit risk for both is determined to be .02.Both agree that inherent risk should be set at the maximum (1.0) and that no analytical procedures will be performed.Jack evaluates control risk as moderate (.40) while Jill assesses it as relatively low (.20).Using the audit risk model, answer the following questions.
Required:
A) What is the risk of incorrect acceptance for Jack and for Jill?
B) Based on your answer in part a, which auditor will have to collect the most evidence? Explain your reasoning.
C) What effect does differing assessments of control risk have on the sample size of accounts receivable? Explain.
Required:
A) What is the risk of incorrect acceptance for Jack and for Jill?
B) Based on your answer in part a, which auditor will have to collect the most evidence? Explain your reasoning.
C) What effect does differing assessments of control risk have on the sample size of accounts receivable? Explain.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
43
Green CA audited the inventory of ABC Company on a sample basis.Green audited a sample of 120 items and found a net overstatement of $600.The audited sample had a recorded value of $12,000.The entire inventory contained 2,400 items with a total book value of $280,000.The projected likely overstatement using the average difference method is
A)$12,000.
B)$14,000.
C)$48,000.
D)$56,000.
A)$12,000.
B)$14,000.
C)$48,000.
D)$56,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
44
Green CA audited the inventory of ABC Company on a sample basis.Green audited a sample of 120 items and found a net overstatement of $600.The audited sample had a recorded value of $12,000.The entire inventory contained 2,400 items with a total book value of $280,000.The projected likely overstatement using the dollar unit sampling method is
A)$12,000.
B)$14,000.
C)$48,000.
D)$56,000.
A)$12,000.
B)$14,000.
C)$48,000.
D)$56,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
45
When evaluating the results of substantive audit procedures, auditors run the sampling risk(s) of
A)Assessing control risk too high or too low.
B)Incorrect acceptance and incorrect rejection of the population.
C)Assessing control risk too low only.
D)Incorrect acceptance of the population only.
A)Assessing control risk too high or too low.
B)Incorrect acceptance and incorrect rejection of the population.
C)Assessing control risk too low only.
D)Incorrect acceptance of the population only.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
46
In the audit of account balances, the sample size will tend to be smaller when the
A)Risk of incorrect acceptance is lower.
B)Risk of incorrect rejection is lower.
C)Tolerable misstatement is smaller.
D)Population variability is smaller.
A)Risk of incorrect acceptance is lower.
B)Risk of incorrect rejection is lower.
C)Tolerable misstatement is smaller.
D)Population variability is smaller.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
47
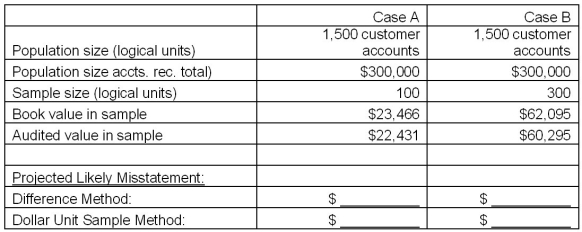
Calculate the projected likely misstatement (PLM) for the data given below using the average difference method and the ratio method.(Round to the nearest dollar.)


Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
48
The total amount of monetary error that is found in a sample is referred to as the
A)Projected likely misstatement.
B)Tolerable misstatement.
C)Known misstatement.
D)Possible misstatement.
A)Projected likely misstatement.
B)Tolerable misstatement.
C)Known misstatement.
D)Possible misstatement.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
49
The amount by which a projected, likely misstatement differs from an actual misstatement is usually the result of
A)A misunderstanding of accounting principles.
B)Sampling error.
C)Management override of an internal control procedure.
D)Risk of incorrect acceptance.
A)A misunderstanding of accounting principles.
B)Sampling error.
C)Management override of an internal control procedure.
D)Risk of incorrect acceptance.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck
50
Left and Right PAs audited the accounts receivable of Investo Limited on a sample basis.There were 2,000 customer accounts in the subsidiary ledger with a total recorded value of
$375,000.As part of the audit program, Left and Right selected a sample of 100 accounts having a recorded value of $20,000.They performed the audit procedures and determined that the audited amount of the sample totalled $19,000.
Required:
A) Calculate the projected likely misstatement (PLM) using (1) the average difference method and (2) the ratio method.
B) Evaluate the results of the calculation in part a.- assume that Left and Right set the tolerable misstatement for accounts receivable at $25,000.
$375,000.As part of the audit program, Left and Right selected a sample of 100 accounts having a recorded value of $20,000.They performed the audit procedures and determined that the audited amount of the sample totalled $19,000.
Required:
A) Calculate the projected likely misstatement (PLM) using (1) the average difference method and (2) the ratio method.
B) Evaluate the results of the calculation in part a.- assume that Left and Right set the tolerable misstatement for accounts receivable at $25,000.

Unlock Deck
Unlock for access to all 50 flashcards in this deck.
Unlock Deck
k this deck



